Vitamin D or calceferol is synthesized by the body under the influence of sunlight, and its deficiency is dangerous for the development of rickets. The fact is that calceferol tends to accumulate in the fatty tissues of the body, and most often infants are at risk of an overabundance of this vitamin, less often - school-age children and adults However, in an attempt to avoid this disease, children are often prescribed additional medicinal doses of vitamin D, which in turn can have negative consequences if medical recommendations are not followed.
Hypovitaminosis in infants
Babies receive vitamin D through their mother's milk, but sometimes it is not enough, so doctors often recommend supplementing the baby's diet with vitamin supplements. This is especially true for those babies born in October and later, when solar activity is not enough to ensure the synthesis of this vitamin. However, with regular intake of an artificial drug into the body, infants may develop hypervitaminosis. This is due to the fact that they have rather little adipose tissue in which vitamin D can be stored as a reserve, so it accumulates in excess in the blood.
Causes and types of hypervitaminosis
Hypervitaminosis in children is a consequence of the accumulation of vitamins in the body and has the following causes:
- intolerance to certain vitamins;
- increased sensitivity to certain substances;
- taking vitamin preparations, organic substances and foods rich in specific vitamins in amounts exceeding the permissible limit.
All vitamins have their own dose and duration of administration. Various deviations from recommended intakes manifest themselves in different ways, so there are two types of vitamin overdose:
- Chronic. A type of hypervitaminosis caused by the systematic intake of vitamins, the amount of which exceeds the norm.
- Spicy. Intoxication occurs after a one-time consumption of a megadose of one or more vitamins.
In what doses is the vitamin harmful?
To diagnose and monitor the dosage of vitamin D, it is recommended to give the child’s urine a Sulkovich test. In infants, this analysis is one of the main ones in pediatrics. It is based on the visual cloudiness of urine when combined with a solution containing oxalic acid and indicates the calcium content in the urine. The test is usually performed using morning urine collected on an empty stomach. Based on the results of the study, the doctor determines the need for additional vitamin D in the baby’s diet and its dosage.
It should be taken into account that the body produces it on its own, so if you take vitamin D in a prophylactic dose during the sunny season, an overdose may occur. Symptoms in children occur both with constant excess and with one-time poisoning. Even one extra drop for a baby can negatively affect his health.
#PROMO_BLOCK#
How does hypervitaminosis manifest itself?
The effect of each vitamin known to mankind on the human body is so individual that satiety with different vitamins manifests itself in different ways. All hypervitaminosis is united by symptoms similar to poisoning, especially when the mechanism of acute hypervitaminosis is triggered.
A difference is also observed between hypervitaminosis of water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins. The latter (namely vitamins A, E and D), due to their ability to accumulate in the body, cause more severe intoxication. Hypervitaminosis with water-soluble vitamins is recorded much less frequently and has less dangerous consequences for the body, and the reason is that vitamins of this category can be excreted from the body along with urine.
Since each vitamin in the human body determines a different set of functions, hypervitaminosis with each of them must be analyzed in particular and move downwards - from more dangerous types of hypervitaminosis to less dangerous ones.
Hypervitaminosis A
Vitamin A saturation occurs either due to excessive consumption in tablet form, or due to frequent consumption of sea fish, seafood, and liver. Hypervitaminosis A develops both in childhood and in adults. The symptoms are similar, and in adults they are supplemented by several clinical manifestations.
Hypervitaminosis A should be suspected when several of the following symptoms are combined, taking into account that the person has consumed tablets or vitamin-rich foods; the possibility of individual intolerance should not be excluded. Signs of hypervitaminosis A:
- lethargy, weakness, reluctance to move;
- development of hydrocephalus (fluid accumulation in the head);
- sleep disturbances, irritability, tearfulness and other symptoms of an irritated nervous system;
- lack of appetite, upset stool, nausea and vomiting, and similar disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- hair loss, inflammation of the mucous membranes, cracks and dry skin, dehydration, low-grade fever and other symptoms of intoxication and poisoning;
- skin rashes similar to scarlet fever rashes;
- brittle nails and hair.
Among the symptoms that can be observed in people of any age, in adulthood and old age, hypervitaminosis A manifests itself:
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- joint pain;
- decreased vision;
- increased cholesterol levels in the blood;
- bradycardia and related disorders;
- disruption of the liver, spleen and kidneys.
Hypervitaminosis A in pregnant women is fraught with miscarriage or premature development of labor. Chronic hypervitaminosis A in pregnant women can lead to deformities and various malformations of the fetus.
Hypervitaminosis D
Hypervitaminosis D extremely rarely develops only due to satiety with products containing it. More often, excessive sun exposure is involved in the process, that is, uncontrolled intake of vitamin D and fish oil. Calcium supplements also affect the absorption of vitamin D, so it is necessary to combine them as prescribed by a professional physician. An overdose of vitamin D in childhood is especially dangerous for the development of severe defects, and in general, the clinical manifestations of hypervitaminosis D are similar to the symptoms of hypercalcemia, and these are:
- lethargy, inactivity, whims and other deviations from adequate behavior;
- feeling of thirst and the need for increased water consumption;
- against the background of constant thirst, polyuria develops;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea and vomiting;
- unreasonable weight loss;
- increased body temperature to subfebrile, sometimes fever;
- the occurrence of seizures.
To such universal symptoms we can add several signs specific to hypervitaminosis D in adulthood:
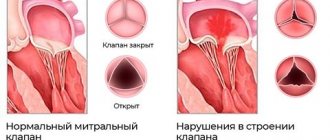
- bradycardia, cardiopathy and cardioneurosis;
- atherosclerosis;
- hypercalcinosis due to a long-term excess of calcium, the retention of which is facilitated by hypervitaminosis D;
- yellowness of the skin;
- muscle weakness, tremors of limbs;
- joint pain, pain in the heart area.
Chronic hypervitaminosis D is the basis for the development of osteoporosis. For pregnant women, hypervitaminosis D is fraught with abnormal development of the fetus and defects in the musculoskeletal system.
Hypervitaminosis E
Vitamin E is one of those vitamins, a sufficient amount of which can be obtained from naturally consumed foods, provided that a person eats a varied and at the same time balanced diet. In this case, it is difficult to provoke hypervitaminosis E; this happens more often with uncontrolled consumption of pharmaceuticals, at the same time the vitamin is absorbed both from them and from food.
The clinical picture of hypervitaminosis E is as follows:
- headaches, fatigue, weakness, constant tiredness (including in the morning);
- muscle and joint pain;
- disorder in the functioning of the stomach and intestines;
- changes in the structure of bone tissue and an increase in fractures against this background;
- visual impairment, double vision.
Medical research practice shows that an excess of vitamin E interferes with the normal absorption of vitamins A, D and K.
Hypervitaminosis of B vitamins
An excess of B vitamins does not lead to severe intoxication, but can cause some discomfort. Common symptoms, each of which can be explained by hypervitaminosis of any vitamin from a given group, include:
- redness of the skin;
- hypersensitivity of the skin;
- dizziness and headaches of unknown origin;
- upset stool, abdominal pain, nausea, and sometimes vomiting
- sleep disturbance, most often insomnia;
- cramps, mainly in the calf muscles.
An excess of a certain B vitamin can affect the function of a certain organ, namely:
- hypervitaminosis B2 determines liver and heart dysfunction, explains the appearance of cracks and sticking in the corners of the mouth, photophobia and conjunctivitis;
- hypervitaminosis B5 provokes water retention in the body, which can manifest itself as prolonged diarrhea;
- hypervitaminosis B6 can cause coordination problems, numbness of the limbs and the inability to hold small objects in the hands;
- hypervitaminosis B9 provokes cramps of any muscle in the absence of any other reason;
- hypervitaminosis B12 is manifested by allergic reactions and urticaria, obvious rash, cardiac dysfunction, thrombosis of small vessels, and in advanced cases (with large dosages) anaphylactic shock may occur.
Hypervitaminosis C
Hypervitaminosis C occurs, or rather manifests itself, extremely rarely. This is explained by the ability of this substance to be excreted in the urine in case of excess. However, prolonged and apparently high intake of vitamin C may result in the following unpleasant symptoms:
- itching and hyperemia (redness) of the skin;
- irritation of the urinary tract and resulting discomfort;
- dizziness and headache.
Excessive consumption of vitamin C can cause a decrease in blood clotting, increased blood pressure, impaired carbohydrate metabolism, and an increased risk of kidney stones.
Symptoms of hypervitaminosis D in infants
Symptoms common to all ages are indigestion, difficulty breathing, increased blood pressure, headaches, joint and muscle pain and cramps. It is difficult to identify most of these signs in a small child who cannot say what hurts. Symptoms hinting at excess vitamin D in children:
- taking a long time to fall asleep, restless sleep, crying at night;
- frequent regurgitation or even vomiting;
- loss of appetite, sudden weight loss;
- slower hair growth;
- severe thirst, increased urine output;
- constipation or diarrhea.
When the first signs appear, be sure to consult a doctor and tell them what medications and vitamins your baby is receiving.
Vitamin A hypervitaminosis
Intoxication occurs from prolonged daily use of medications containing vitamin A, or food (beef liver, seafood, eggs) in large quantities.
Signals of excess vitamin A:
- hair loss;
- brittle nails;
- dryness and flaking of the skin;
- the appearance of pigment spots on the skin;
- pain in the legs and arms;
- headache;
- vomiting, nausea, constipation;
- drowsiness.
Hypervitaminosis A contributes to the accumulation of fluid in the skull (hydrocephalus). In newborns, excess vitamin A is manifested by swelling of the fontanel, increased body temperature, vomiting and slow growth. The disease is fraught for an unborn child if a pregnant woman takes more than 10 mg of vitamin A per day for a long time. Newborn babies may have facial defects, heart defects, nervous system disorders and other developmental problems.
What does this mean?
Too much vitamin D in children can cause harm that will last the rest of their lives. The main problem is that when there is an excess of vitamin, bones grow too quickly - faster than joints and muscles can strengthen. In the long term, this leads to various curvatures of the spine, frequent fractures and dislocations. There are a number of other risks:
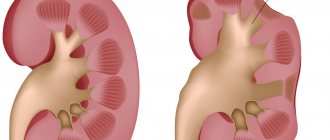
- Osteoporosis is a deficiency of calcium in bone tissue. As a result, bones become brittle, joint covers may become ossified, and the spine may become deformed.
- Resorption of bone marrow connective tissue. Our bones have a spongy structure. White and red blood cells mature in the cells of this sponge. If the connective tissue is not strong enough, hematopoiesis and immunity suffer.
- Atherosclerosis is deposits on the walls of blood vessels. Leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the arteries, deterioration of blood supply to organs. In the most severe cases, it can lead to blockage of blood vessels with blood clots and necrosis.
- Increased calcium deposition in internal organs - organs lose elasticity, increasing the risk of internal injuries and a number of diseases.
Classification of hypervitaminosis D
By severity:
- light
- average
- heavy
By periods of development:
- elementary
- the height of
- convalescence (residual effects)
With the flow:
- acute – up to 6 months
- chronic – over 6 months
- Calcinosis and sclerosis of organs, development of coarctation of the aorta, urolithiasis, pulmonary stenosis, chronic renal failure
How to avoid overdose
It should be remembered that not a single vitamin preparation is useful on its own. All of them only make up for the deficiency and can be harmful if there is no deficiency. A healthy child whose mother receives normal nutrition should not have a lack of vitamin D in the sunny season. In cold weather, when there is little light, preventive vitamin intake is justified, but only as prescribed by a doctor.
The most common cause of excess vitamin D is self-medication. Parents noticed some symptoms, interpreted them based on information from popular literature or the Internet, and independently decided that the child needs more vitamin D. Don’t be overly arrogant, consult a pediatrician - and you will avoid this and many other problems.
Hypervitaminosis: the terrible power of excess vitamins
A frightening reaction from parents is caused by symptoms that indicate malfunctions in the functioning of various internal systems of the child. Fatigue, hair loss or peeling skin usually resembles a lack of vitamins. And since the child’s body needs vitamins to normalize biological processes, mothers stuff their babies mainly with fruits and vegetables. But such manifestations may indicate the opposite situation - excess vitamins.
Hypervitaminosis is a disease caused by an overdose of vitamins. In other words, this is vitamin poisoning, so its symptoms are similar to ordinary food poisoning. Due to the increasing popularity of vitamin supplements, children are increasingly encountering this disease. Various supplements based on nutrients and minerals are used for treatment, prevention and support of good health. Their reasonable consumption has a positive effect on the development of children. But some substances that exceed the norm even slightly are toxic and quite dangerous.
The effect of an overdose of some vitamins has not been fully studied. Scientists' opinions are divided on two fronts. Some say that megadoses of vitamins save you from cancer. Opponents of this theory admit that the development of cancer is provoked by taking huge doses of vitamins.
TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
Remember that treatment of hypervitaminosis must be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor! The specialist determines the cause of the disease based on the patient’s test data. Therapy consists of three main points that promote a speedy recovery.
First, the intake of excess vitamin is reduced to the required daily dose. This is achieved by adjusting a person’s diet and following a diet.
Next, symptomatic treatment begins. Painful or allergic reactions of the body to hypervitaminosis are eliminated. If you carry out only symptomatic therapy without reducing the supply of vitamins from outside, the disease will progress!
The last stage is detoxification. The body is cleansed of excess of certain substances, since a surplus of vitamins is similar to poisoning.
It is much easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. Carefully monitor the dosage of vitamins you take, having previously agreed on prevention with a specialist. Hypervitaminosis threatens all people, depending on age groups, so take it seriously!