Dysgraphia is a written language disorder. Signs and symptoms of deviation, treatment and methods of prevention - what parents of schoolchildren should know.
Children who have just started learning to write try to write neatly. However, the handwriting of most primary school children is clumsy and illegible. Many people write with errors because they do not yet know the basic rules of the Russian language. A child's written speech improves over time, but some children continue to write sloppily, changing letters in places, missing spaces and in the right places. There are a number of signs that should cause parents to become concerned and take their child to see a speech therapist, as they may be symptoms of dysgraphia.
Timely treatment of this disorder is the key to the fact that the child will have competent written speech in the future. That is why it is important to know what dysgraphia is, what its causes and main symptoms are, as well as how this deviation is treated.
Dysgraphia: general information
Dysgraphia is a writing disorder that involves crooked letter writing with multiple misspellings of words. The handwriting of a child with this disorder is illegible, and words may be written in reverse with a large number of grammatical errors. This defect is a consequence of disruption of certain parts of the brain.
Writing impairment, the causes of which lie in the improper functioning of certain parts of the brain, occurs in many children who are beginning to learn the basics of writing. Thus, among second grade students, on average, such a violation occurs in more than half of the class. In the absence of timely treatment, such a deviation entails a decrease in the child’s self-esteem, affects his academic performance, and affects relationships with peers.
Dysgraphia is often accompanied by minor problems with the speech apparatus. This violation has several types and is classified according to severity.
Reasons for the imperfection of written speech
The reasons for the development of dysgraphia can be both previous injuries or diseases of the brain, as well as socio-psychological factors. Many experts note a hereditary predisposition to this disease. Underdevelopment of some individual areas of the brain is genetically transmitted to the child from the parents. Mental illnesses in relatives can also become a prerequisite for dysgraphia in a child.
Researchers studying the etiology (translated from Greek as the study of the causes) of this disorder note the presence of pathological factors affecting the child in the prenatal and postnatal periods, as well as at the time of birth. This includes infections and other diseases suffered during pregnancy by a woman, bad habits of the mother, early and prolonged toxicosis, birth injuries of the newborn, rapid or prolonged labor, asphyxia (oxygen starvation), meningitis, head injuries, a short period between pregnancies (less than one and a half years ) and so on.
The causes of dysgraphia can be both organic and functional. Functional reasons, in turn, are divided into internal, for example, long-term somatic diseases, and external - incorrect tongue-tied speech of others, frequent lisping with the baby, lack of verbal communication with him, inattention to the child’s speech development, bilingualism in the family, etc. Experts consider children at risk to be children whose parents began to teach them to read and write very early when the children were completely psychologically unprepared.
Dysgraphia is often observed in children suffering from delayed mental and speech development, with a diagnosis of minimal brain dysfunction, general speech underdevelopment and attention deficit disorder.
In addition, this disorder can also occur in adults. The causes of dysgraphia in this case are head injuries, brain tumors, and strokes.
Mechanism of occurrence, causes
Writing is a process that requires the coordinated work of the visual, auditory, speech and motor systems. By the time the child masters the basics of writing, he should have mastered oral speech well. If the lateralization of brain functions is not carried out as needed, then a disorder such as dysgraphia develops. Usually these processes are normalized by the time the child begins school.
If the delay in lateralization causes disturbances in a part of the brain, the child develops dysgraphia, which requires correction. Otherwise, the deviation may affect the child’s thinking, memory, and perception.
Causes of occurrence in children
Dysgraphia can be caused by birth trauma. The development of such deviations is provoked by various infectious diseases and improper upbringing. Also, experts do not exclude such a factor as genetic predisposition.
Dysgraphia in children may be accompanied by other concomitant diseases that were previously diagnosed.
Causes of occurrence in adults
In adults, imperfections in written speech can be caused by both internal and external factors. Main reasons for deviation:
- presence of a tumor in the brain;
- low saturation;
- stroke;
- previous brain surgery;
- poor social conditions.
Social factors include insufficient upbringing in childhood, incorrect speech of people around, and lack of communication with others.
With dysgraphia, errors in the process of writing are persistent, despite the fact that the person knows well all the rules of writing words.
Etiology of defects
Difficulties in mastering reading and writing skills are due to a number of organic or social reasons:
- Organic damage and underdevelopment of the cortical areas of the brain involved in the process of reading and writing.
- Immaturity of the cortical areas involved in the formation of written speech.
- Somatic weakness of the child.
- Incorrect speech environment in which the child grows up.
- Speech disorders.
- Bilingualism.
- Unfavorable social situation in the family.
Depending on the etiology of the violation, a corrective work plan is drawn up. By eliminating the cause of the reading and writing disorder, you can correct the defect itself. Each form of these violations has its own specific causes, on the basis of which correctional work is based.
Types of dysgraphia
Dysgraphia can be the result of various reasons. Signs and symptoms of the disorder may vary. The method of rehabilitation and duration of treatment also depend on the type of deviation.
Optical
It is difficult for a child to write letters correctly; he may skip them when writing words, or add unnecessary elements in the form of strokes and sticks. Due to incompletely formed visual-spatial connections, the child often misses letters, writes them incorrectly, and confuses them with others.
Acoustic
Characterized by a lack of ability to correctly recognize sounds. The patient confuses similar-sounding letters and may make mistakes in the degree of softness of the pronounced sounds.
Articulatory-acoustic
The child writes and pronounces letters incorrectly and replaces them with similar sounds. Requests from parents and teachers to pay attention to the correct pronunciation and spelling do not bring results. With this form of disorder, work aimed at auditory differentiation of the child is required. Only by carrying out such corrective work is it possible to completely get rid of the problem.
Ungrammatical
This type of violation is characterized by the fact that the child, when pronouncing and writing, confuses case endings, misses or replaces prepositions with others. This deviation is a consequence of speech disorders.
Disorder caused by defective processes of analysis and synthesis
The main symptoms of this disorder are omitting or replacing letters with others, adding extra syllables, and spelling several words in a row. Such a deviation is preceded by social, psychological, and educational factors, which become the main cause of disturbances in the analysis and synthesis of speech.
Signs of the disease
Dysgraphia is a diagnosis that should be made by a specialist. The deviation can easily be confused with a common misunderstanding of grammar that occurs in most children. With dysgraphia, the mistakes that a child makes while writing are in no way related to the level of knowledge of the Russian language. The teacher at school, as well as the student’s parents, should be wary if the child repeatedly makes the same mistakes: misses letters, confuses the combined and separate spelling of words. In addition, such a child’s handwriting is illegible, and the size of the letters constantly changes from small to large, not only in one sentence, but also in one word. The writing speed is very slow. Often, children with dysgraphia are given poor grades due to mistakes and poor handwriting, which greatly affects the child’s academic performance and self-esteem. That is why it is very important to promptly identify a violation of written speech in a child, find out the cause of the deviation in order to undergo a course of correction.
Classification of dyslexia
In modern speech therapy there are a large number of classifications of reading disorders. One of the most frequently used is the one proposed by R.I. Lalaeva. She created it taking into account reading disorders:
- With insufficient development of phonemic and phonetic-phonemic processes, a phonemic form of dyslexia appears. The student does not have a clear sound image of the letter. This manifests itself in the replacement and mixing of letters during reading. There may also be a violation of the syllabic structure of the word.
- Optical dyslexia is caused by insufficient development of the visual analytical system and optical-spatial representations. While reading, the student makes mistakes in letters that have similar optical characteristics. He has difficulty mastering the visual image of a letter and the arrangement of elements.
- The mnestic form is associated with the complexities of speech memory processes, manifested in the correlation of phoneme and letter images. A child cannot remember a letter and its components for a long time.
- When a child reads but does not understand the meaning of what he read, this is a manifestation of semantic dyslexia, also known as rote reading. A student may have an ideal reading technique, but he cannot establish semantic connections between words. Or if he reads syllable by syllable, he cannot understand what word he is talking about and cannot correlate it with a suitable picture.
- When the grammatical structure of speech, morphological and syntactic categories is insufficiently formed, an agrammatic form appears. Its characteristic features are incorrect endings, violation of word agreement norms, difficulties in word formation; incorrect accent placement.
- The tactile form is caused by a malfunction of the spatial analyzing system. This dyslexia can only occur in blind children who use Braille.
The described forms are rarely found in their pure form. Usually it is a combination of several types. And you need to select exercises to eliminate all errors that arise during reading.
Diagnosis of dysgraphia
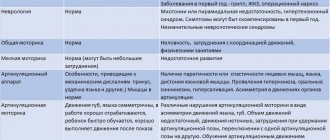
Only a specialist who has previously diagnosed the disorder using special studies can prescribe an appropriate course for dysgraphia correction. In addition, consultation with specialists such as a neurologist and speech therapist is necessary to make a diagnosis.
The examination of the patient includes several stages, the first of which is to assess the condition of the central nervous system, vision, and hearing of the patient. Then specialists analyze the child’s articulation and motor skills. Important stages include assessing sound pronunciation, vocabulary, and literacy level. A writing assessment is then required, with experts taking into account whether the patient is right-handed or left-handed.
For the purpose of research, the child will be asked to write down words under dictation, rewrite capital and printed letters, and perform special exercises. After analyzing the information obtained during the study, the speech therapist makes a diagnosis and gives the necessary recommendations on how to correct written speech disorders, if any.
Speech therapy help for dyslexia
Tasks are selected in accordance with the form of reading impairment. Correction is carried out in the following areas:
- correction of sound pronunciation;
- working with the syllabic structure of a word;
- work on the development of phonetic-phonemic processes;
- overcoming agrammatisms.
They offer tasks for recognizing the image of a letter in “noisy” images. The speech therapist together with the child draws up sentence diagrams. Asks to identify the sound in a word while showing an image. Then he pronounces the sounds with a pause and asks to name the spoken word.
In addition, they offer to add the missing syllable or letter. Or perform the action you read and point to the appropriate picture. During lessons, students are asked to work with various fonts to form a visual image of a letter.
In modern speech therapy, dysgraphia and dyslexia continue to be studied and effective ways to correct them are selected. Some experts believe that this is a gift, people just need to learn how to use it. But this does not mean that there is no need to correct writing disorders. If the correction was started on time, the parents and the child follow all the recommendations of specialists, the student will be able to master writing and reading without much difficulty.
Methods for correcting dysgraphia
The method of correction depends on the severity of the child’s written language impairment. In addition, the method of treating the deviation is influenced by the degree of neglect, as well as the characteristics of the patient. Correction is a long and complex process that requires persistence on the part of teachers and parents, patience, endurance and a positive attitude of the patient. If you follow all the necessary recommendations, dysgraphia can be completely cured. It is better if the disorder is diagnosed at an earlier age, since the course of correction for older schoolchildren is longer due to the presence in most cases of additional speech and writing disorders. In this case, the time required for rehabilitation will take more. There is also a high risk that the violation cannot be eliminated completely.
It is impossible to get rid of dysgraphia on your own. This process requires the participation of many highly specialized specialists, for example, a psychologist, a neuropsychologist. However, the main work falls on the speech therapist, who will have to select a rehabilitation program appropriate to the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient. The specialist individually selects the necessary sound pronunciation exercises. Classes are aimed at improving motor skills, developing the patient’s lexical and grammatical structure, as well as improving phonemic speech recognition.
Methods for correcting dysgraphia, which are among the most effective:
- Exercises through which the patient learns to correctly understand sounds, words, and letters.
- Tasks aimed at training memory, improving thinking, and developing perception.
- Exercises necessary for the patient to learn to correctly recognize letters that are similar in appearance.
- Proper production of sounds, work on speech automation.
- Educational games to improve sound analysis.
In some cases, specialists include drug treatment, physiotherapy, massage, and exercise therapy in the rehabilitation course. This often applies to patients whose dysgraphia was caused by organic causes. It is important to know that drug treatment should be prescribed exclusively by a qualified specialist.
Speech therapy correction
Auditory differentiation of sounds is what needs to be achieved initially when treating dysgraphia. If a child cannot distinguish sounds, then further exercises will not be effective. The rehabilitation period is determined individually and depends on many factors. Classes with a speech therapist are possible both in a group with other children and individually. It depends on the wishes of the child and his parents.
During classes, the speech therapist gives the child verbal and visual exercises, as well as practical lessons, during which correctional work takes place.
Exercises you can do at home
Since it is impossible to get rid of dysgraphia on your own, experts, in addition to basic classes, recommend doing additional exercises at home to consolidate the results obtained with a speech therapist.
Exercises that can be done at home should also be agreed upon with a speech therapist. It is important that parents supervise the technique and regularity of classes. The simplest but most effective exercises that you can do at home with your parents include:
- Labyrinth. The child draws a line on a piece of paper, moving only his hand. You cannot make breaks or change the position of the sheet.
- Search for objects or pictures. The child searches for and paints the objects found.
- Exercises aimed at developing attention. The child must read the text and look for missing letters or words, writing them in the right places.
- Improved articulation. The child learns songs, rhymes, and tongue twisters.
- Logorhythmics.
To get a positive result as quickly as possible, home exercises should be performed regularly. This will significantly shorten the rehabilitation period.
Forecast, preventive measures
The prognosis for the treatment of dysgraphia depends on a number of factors: the timeliness of the measures taken, the severity of the deviation, its form, the reasons that provoked the formation of the written speech disorder, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient. Only through the well-coordinated work of specialists, the patience and perseverance of parents, as well as the positive attitude of the child, can a positive result be obtained in the end. The problem associated with impaired written speech can be completely corrected in more than 80% of cases.
Parents of a child who has been diagnosed with dysgraphia should be aware that the lack of a timely response can lead in the future to:
- Poor academic performance, which is fraught with intellectual retardation in the development of the child.
- The appearance of suspiciousness and anxiety.
- The emergence of problems with peers.
In addition, an advanced form of dysgraphia is the cause of a child’s deviant behavior and low self-esteem.
For a child with an advanced form of dysgraphia, the need to write something will always cause discomfort. This leads not only to poor academic performance, but also to a complete lack of desire to learn and master new material.
Prevention of dysgraphia
Experts cannot name the exact causes of dysgraphia. In addition, it is believed that such a violation of written speech cannot be prevented. However, there are known risk groups whose representatives more often suffer from the presence of such a deviation. This:
- Bilingual children;
- Patients with mental retardation
- Children who were retrained to write with their right hand
- Hyperactive children
- Children who started learning too early
Prevention measures include training memory and attentiveness, increasing vocabulary. It is important to know that if a child constantly makes the same mistakes when writing words, there is no need to postpone visiting a speech therapist until later. If a child has a written speech disorder, the sooner correctional work is started, the faster and easier it will be to get rid of the problem, which is fraught with serious consequences for the child in the future.
Prevention of writing disorders in children
Experts are confident that it is impossible to prevent dysgraphia, since its exact causes have not been fully studied. However, risk groups have been identified whose representatives suffer from it more often than others:
- delayed psychological development;
- left-handers retrained to be right-handed;
- children with articulation problems;
- bilingual children;
- learning from rude or insufficiently competent teachers;
- hyperactive children;
- children who started school early.
Prevention consists of certain skills - attentiveness, perception of the surrounding space, memory, insufficient vocabulary. If parents or a teacher notice that the child is making the same mistakes, it is necessary to seek help from a speech therapist or neurologist in order to begin corrective work on time.