Photo: UGC Many women are aware that during pregnancy the placenta protects the baby in the womb. However, not many people know about its functions in detail. The term “degree of maturity of the placenta” also causes confusion. Let's try to consider the questions in detail and answer them in layman's language.
Attention! The material is for informational purposes only. You should not resort to the treatment methods described herein without first consulting your doctor.
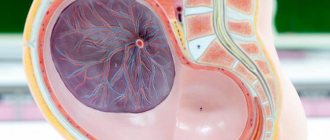
Placenta - what is it?
In Latin, the word “placenta” means “pie, flatbread.” It's all about how the placenta looks: the organ received this name due to its flattened shape, because in appearance it resembles a flat disk.
When does the placenta form during pregnancy?
Its formation begins only when conception occurs, and when the child is born, it is excreted along with the membranes.
The placenta performs the following functions:
- respiratory - through it oxygen enters the fetus and carbon dioxide comes out;
- barrier – protects the fetus from those harmful substances that are in the mother’s blood;
- nutritious - nutrients come from mother to fetus;
- hormonal - produces a number of hormones that determine the normal development of pregnancy;
- excretory - waste products of the fetus are excreted through it.
Changes in the structure of the placenta
The normal placenta has a lobular structure; it is divided into approximately 15-20 lobules of equal size and volume. Each of the lobules is formed from villi and a special tissue that is located between them, and the lobules themselves are separated from each other by partitions, however, not complete ones. If changes occur in the formation of the placenta, new variants of the structure of the lobules may arise. Thus, the placenta can be bilobed, consisting of two equal parts that are connected to each other by special placental tissue; a double or triple placenta can also be formed, the umbilical cord will be attached to one of the parts. Also, a small additional lobule may be formed in a normal placenta. Even less commonly, a so-called “fenestrated” placenta may occur, which has areas covered with a membrane and resembling windows. There can be many reasons for such deviations in the structure of the placenta. Most often this is a genetically determined structure, or a consequence of problems with the uterine mucosa. Prevention of such problems with the placenta can be the active treatment of inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity even before pregnancy, during the planning period. Although deviations in the structure of the placenta do not have such a strong effect on the child during pregnancy, and almost never affect its development. But during childbirth, such a placenta can cause a lot of trouble for doctors - such a placenta can be very difficult to separate from the wall of the uterus after the baby is born. In some cases, separation of the placenta requires manual control of the uterus under anesthesia. Treatment for the abnormal structure of the placenta during pregnancy is not required, but during childbirth you must remind the doctor about this so that all parts of the placenta are born and no pieces of the placenta remain in the uterus. This is dangerous due to bleeding and infection.
Development of the placenta
The development of this organ does not occur immediately after conception. In the fourth week of pregnancy, the fertilized egg is surrounded by the chorion - this is a special villous tissue. The formation of the early placenta occurs around the ninth week. It is formed by chorionic villi that penetrate the upper layer of the uterus and connect with the blood vessels there.
By the end of gestation, the placenta already weighs about half a kilogram, and its diameter is 15-20 cm. The permeability of the placenta membrane increases until the 32nd week of pregnancy. After all, every week the size of the fetus increases, and it requires more and more oxygen and nutrients.
Accordingly, in order to provide such nutrition, the number of vessels in the child's place increases, and the membrane becomes thinner. After the thirty-second week, the development of the placenta stops and it begins to age. If this happens earlier, then early aging of the placenta .
How does maturation occur?
The formation of the organ begins 6-8 days after conception, when the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus and the chorionic villi grow into the endometrial tissue. Normally, the placentation process takes about 12-14 weeks. The baby's place takes its final form closer to the 20th week of gestation and from that moment on it completely ensures the metabolism between mother and child.
Active growth of placental tissue is observed throughout the first half of pregnancy. During this period, many blood vessels are formed in them, and the organ itself thickens. Starting from the middle of the second trimester, the development of the baby's place stops, its structure becomes more dense due to the appearance of salt deposits. Normally, the organ reaches maturity by the 36th week of gestation, after which its functions gradually fade away.
Degrees of placenta maturity
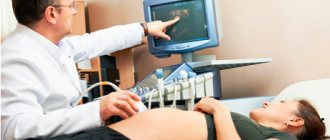
During the development of pregnancy, the doctor looks for all internal changes during an ultrasound examination. And the degree of maturity is also determined during the ultrasound process, taking into account certain parameters.
Based on the duration of pregnancy, the degrees of maturity are determined as follows:
- degree of maturity 0 – up to 30 weeks;
- degree of maturity of the placenta 1 – 27-36 weeks;
- degree of maturity of the placenta 2 – 34-39 weeks;
- degree of maturity of the placenta 3 – after 36 weeks.
To determine what degree of aging - first, second or third - the doctor determines its thickness, looks for calcium deposits and cysts.
Not so long ago, the maturity of a child's place was viewed differently than it is now. Thus, it was believed that with premature aging, miscarriages , there is a high risk of antenatal fetal death, and low-weight children are born. However, after scientists conducted a series of studies, such interdependence was refuted.
If a woman has a third degree of maturity before 35 weeks (for example, at 32 weeks), she is considered to be at increased risk.
A gynecologist will explain in more detail about the characteristics of maturity, for example, the degree of placenta maturity 2, what this means.
In the table below you can clearly see the degrees of ripeness by week.
Table of degrees of placenta maturity by week of pregnancy
| Chorionic part (the one that is adjacent to the fetus) | Structure | Are there calcium deposits? | |
| 0 tbsp. (up to 30 weeks) | Completely smooth | Homogeneous | Virtually none |
| I Art. (27-36 weeks) | Wavy | A little seal | Microscopic |
| II stage (34-39 weeks) | There are indentations | There are seals | Visible |
| III Art. (after 36 weeks) | Recesses to the basement membrane | Cysts | A large number of |
Deviations from the norm
It is important to understand that aging of the placental barrier is an absolutely natural process. However, you should worry when the stage of maturity of the embryonic organ does not correspond to the period of pregnancy. In most cases, this indicates that there is a threat to the fetus. That is why this condition requires close monitoring and examination in a hospital setting.
Most gynecologists agree that the aging process is premature when, at the time of 32 weeks of gestation, the degree of maturity exceeds the second, and before the onset of the 36th week - the third.
What can cause deviations in the development of the placental barrier:
- The presence of Rh conflict between the female body and the fetus.
- Endocrine system disorders, especially diagnosed diabetes mellitus and thyroid problems.
- Chronic organ diseases in pregnant women.
- The woman has a history of abortion or difficult childbirth. These conditions often lead to disturbances in the structure of the uterus.
- Infectious diseases affecting the organs of the genitourinary system.
- Severe toxicosis or late gestosis.
- Placenta previa, or placenta abruption.
- The presence of more than one fetus in the uterine cavity.
Placenta thickness
This parameter is a very important point in the diagnosis, since deviations from the norm can be evidence of pathologies. There is a special table of placental thickness by week, which indicates the normal limits.
The thickness of the placenta by week is determined by ultrasound, which is performed after 20 weeks. If the process of bearing a baby proceeds normally, then the greatest thickness of the placental tissue is observed at 34 weeks, and at 36 weeks. its growth stops, and its thickness may even decrease slightly.
If the placenta is too thin, placental hypoplasia . However, as a rule, this is not a very threatening phenomenon, unless a significant decrease in size is noted. Very often, such deviations are associated with genetic disposition, the influence of unfavorable factors, and diseases of the woman. If this is due to illness, treatment is carried out; in all other cases, supportive therapy is practiced.
This indicator is also influenced by the physique of the expectant mother. Short, thin women have smaller baby seats than tall, curvy women. If thickening of the placental tissue is diagnosed, this condition can threaten the termination of pregnancy. But with the right approach to treatment, pregnancy can be saved.
Thickening can occur due to Rh conflict , diabetes mellitus , gestosis , iron deficiency anemia , or previous infections . In case of serious deviations, careful monitoring of the expectant mother is important. The fact is that with the rapid growth of a child's place, its active aging occurs. When thickened, hormonal function is disrupted, which can negatively affect pregnancy.
However, if after a series of additional examinations the doctor concludes that the fetus is developing normally, only careful observation will be needed.
Should I worry if an ultrasound reveals abnormalities of the placenta?
The placenta develops from the cells of the fetal egg, and not from the maternal cells, so the organ cannot be ideal. Violations are mild, moderate and significant. If abnormalities are detected, a diagnosis of placental insufficiency is made.
Gynecologists believe that only significant changes are dangerous for the fetus, since thanks to the extensive vascular network, the organ can perform all functions even with partial damage or detachment.
To understand how dangerous the changes are, it is not enough to assess the degree of problems in the placenta; it is important to take into account the quality of fetal development. If there is a discrepancy between the parameters of growth and development and the norms for the period, you need to sound the alarm and take action. If the baby develops normally, you can limit yourself to observation. For this purpose, non-screening (unscheduled) ultrasounds are performed.
Why does the placenta age too early?
If an old placenta is diagnosed during pregnancy, this may be due to various factors.
Hypertension
Gestational hypertension , that is, increased blood pressure during pregnancy, is very often associated with the function of the placenta. Due to various reasons, defective blood vessels are formed in the child's place, and this affects both the condition of the fetus and the health of the woman. As a result, the expectant mother develops edema , high blood pressure, and sometimes, in severe cases, preeclampsia . A child, developing in the womb, does not receive enough oxygen due to defective blood vessels. As a result, the placenta has to “work” at full capacity, which is why it ages prematurely.
Infections
If the expectant mother falls ill with any infectious disease, then the placental tissue works more actively. It filters the mother's blood from viruses, allows more oxygen and antibodies to pass through to the baby in order to intensify the fight against the disease. As a result, its maturation and, accordingly, aging accelerates.
Eating Excessive Calcium
Calcium deposits are one of the main signs of aging in a child's place. The closer to the end of pregnancy, the more calcifications are detected in the placenta. And if a woman’s body constantly receives a large amount of this microelement, then gradually calcium replaces the placental tissue, which provokes its active premature aging. This often happens if a pregnant woman takes vitamin supplements uncontrollably.
What does early maturation of the placenta lead to?
For every expectant mother who is interested in the dangers of early maturation of the placenta during pregnancy, it is important to realize that this phenomenon in itself is not a threat to the health of the mother and baby. Only if other signs of fetal aging are observed during aging can a health threat be noted. Such signs are the following manifestations:
- Severe intrauterine developmental delay.
- Violation of the fetal-placental and uteroplacental blood supply.
- Presence of signs of Rh conflict in the fetus.
- Severe hypertension in the mother.
- Diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman (decompensated).
It is important to understand that even if there is no premature maturation of the placenta at 32 weeks of pregnancy or at another period, the conditions listed above are dangerous in themselves. In such conditions, special therapy is required, and in some cases, urgent delivery is necessary.
What is an immature placenta and why is it dangerous?
If the placenta does not reach 2-3 degrees of maturity by the end of pregnancy, it is considered immature. This is a fairly rare occurrence; as a rule, it is associated with errors in the diagnostic process.
For example, if there is a Rh conflict between mother and fetus, then the baby’s place may “swell.” When an ultrasound examination is performed, due to the edematous smoothness, the placenta looks like it is at 0 degree of maturity. Therefore, an immature placenta is not a dangerous phenomenon, but such signs can often mask dangerous complications for the mother and child.
Umbilical cord
The placenta on the fetal side is connected to the baby by a special strong cord - the umbilical cord, inside which there are two arteries and one vein. The umbilical cord can attach to the placenta in several ways. The first and most common is the central umbilical cord attachment, but lateral or marginal umbilical cord attachment may also occur. The umbilical cord functions are not affected in any way by the method of attachment. A very rare option for attaching the umbilical cord may be attachment not to the placenta itself, but to its fetal membranes, and this type of attachment is called membrane.
What additional research methods are practiced?
To determine the degree of maturity of the fetus and placenta and to diagnose or exclude dangerous conditions, additional research methods are practiced.
Ultrasound with Doppler
It is impossible to assess the child’s condition based on information about the degree of maturity of the placenta. Therefore, it is the data obtained from Doppler ultrasound that is considered to be indicators of a normal pregnancy.
Data is obtained due to the reflection of ultrasonic waves from a variety of biological media. They make it possible to assess blood circulation through the placenta. Provided that everything goes well, after 20 weeks the blood resistance in the vessels that connect the uterus, fetus and baby's place decreases. Thanks to stable resistance, oxygen and nutrients are constantly supplied to the fetus. If a good result was obtained during an ultrasound with Doppler, then there is no need to be afraid, even if during an ultrasound examination the placental tissue looks older than it should be at this moment.
It is also important to take into account that the opposite situation is possible: placental tissue may be of normal maturity, but it may not perform its functions as needed. Accordingly, this will negatively affect the child’s condition. Therefore, it is important to carry out regular examinations.
Cardiotocography CTG
This method is good because it makes it possible to assess the baby’s current condition. With the help of special sensors, it is possible to detect the fetal heartbeat, count the number of its movements, and register how the uterus contracts. The totality of the data obtained allows us to determine even the most minor disturbances in the functions of the placenta.
If an ultrasound examination reveals premature aging of the placental tissue, then it is necessary to perform CTG and Dopplerography to determine the condition of the child.
Consequences
The danger of early aging of the placental barrier is that this condition, for the most part, develops completely asymptomatically . Thus, if a woman does not attend scheduled ultrasound examinations, then it is impossible to avoid negative consequences. If the embryonic organ matures prematurely in the early stages of pregnancy, a miscarriage is possible; in later stages, severe hypoxia occurs, which can lead to serious pathologies in the fetus, including its death.
Did you know? To clarify the diagnosis, Doppler measurements and CTG are often used. Doppler allows you to identify disturbances in the blood flow and determine how critically this affects the fetus. With the help of CTG, you can find out how much the child suffers from oxygen starvation and whether this problem can be corrected with medication.
With a lack of nutrients, the child begins to lag behind in development . On ultrasound, this is characterized by a smaller size that does not correspond to the gestational age. If the delay exceeds two weeks, then observation in a pregnancy pathology hospital is recommended. In severe forms of underdevelopment, surgical methods of delivery are recommended.
Depending on the reasons that caused the maturity of the placenta to be inappropriate for the period, therapeutic treatment may be different. Most often recommended:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- undergo correction of treatment of chronic diseases;
- take antibacterial drugs in the presence of infectious diseases;
- use special mineral and vitamin complexes;
- take medications to improve blood circulation in the placental barrier.
In the issue of treating premature aging of the placental barrier, we are talking primarily about maintaining pregnancy until the period when the fetus is already fully formed . The effectiveness of drugs for improving blood circulation during pregnancy has not been fully established. Rejuvenation of a child's place is virtually impossible, and therefore treatment is aimed only at slowing down the aging process.
How to stop the aging process?
If the doctor, based on research results, has concluded that the placental tissue is aging prematurely, then pregnant women, of course, worry about this and try to find out how to “rejuvenate” it. If it is diagnosed that aging of the placenta is stage 3 during pregnancy, or aging of a lesser degree, any attempts at “rejuvenation” are pointless.
Every expectant mother needs to be aware of the following:
- Immediately early maturation of the child's place is not a threatening condition for either the mother or the baby.
- If ultrasound reveals aging of the placental tissue, additional studies must be performed - CTG and Dopplerography. However, this fact is not a reason to worry.
- In the process of determining the maturity of a child's place, diagnostic errors occur quite often.
- If, in the course of additional studies, normal indicators of the fetal heartbeat and placental blood flow are determined, then the expectant mother has no reason to worry about the aging of the placenta.
- Provided that severe fetal hypoxia , then the condition of the pregnant woman and child must be monitored. The doctor makes a decision on treatment or emergency delivery.
- There are no drugs or methods to slow down the aging process of placental tissue.
- Currently, there is no evidence base regarding the use of Curantil , Actovegin , Pentoxifylline , multivitamin complexes, etc. for this purpose.
Ultrasound standards for first screening
The very first screening should be done from the 11th week of pregnancy to the 13th. It is during this period that the doctor prescribes an examination. Some expectant mothers can’t wait to go for an ultrasound before the 11th week. But there is no urgent need for this. After all, many indicators simply cannot be determined before this date. Therefore, the information content of the study will be small.
At the first screening, the doctor:
- reveals the exact duration of pregnancy;
- calculates the size of the fetus;
- looks at the uterus.
There are standards for each value. Let's look at them.
- The CTE or, more simply put, the length of the fetus is assessed. The norm is from 43 to 65 mm. When the deviation increases, it is believed that the baby will be born large. If it is to a lesser extent, then this indicates a slowdown in development, illness, or even the death of the fetus.
- The next indicator they look at is called BPR. The distance from one temple to another temple is measured. Normally it should be from 17 to 24 mm. Low scores may indicate developmental delays. High - about a large fetus (if other criteria also indicate this), or about hydrocephalus.
- Thickness of the collar space. The norm is 1.6-1.7 mm. If other numbers are revealed, then this is a bad sign, and we may be talking about Down syndrome.
- The length of the nasal bone should be from 2 to 4.2 mm.
- Heart rate. The norm is from 140 to 160 beats.
- Amnion. The norm of amniotic fluid is 50-100 ml.
- Cervical length. The norm is 35-40 mm.
How to prevent early aging of the placenta?
To prevent such manifestations, a woman must be very careful in planning her pregnancy and in her lifestyle while carrying a baby. It is important to practice the following preventive measures:
- plan pregnancy;
- do not drink alcohol or smoke;
- practice moderate physical activity;
- to walk outside;
- carry out screenings, CTG, Doppler ultrasound in a timely manner;
- take Folic acid ;
- for anemia, take iron supplements;
- try to avoid crowds of people to prevent infection with infectious diseases.
If a woman is worried about certain indicators obtained during the examination, she should definitely seek additional advice from a doctor. Perhaps he will order additional examinations.
Video about the placental barrier
From the presented video you can get detailed information about what a baby's place is and what its importance is in the process of bearing a child. What to do if its maturity does not correspond to the week of pregnancy.
During pregnancy, a woman begins to monitor her health even more carefully than usual . But the success of pregnancy does not always depend on this. Did you have any problems while expecting your baby? Did the degree of maturity of the placental barrier correspond to the duration of pregnancy? What methods did doctors use in case of violations? Share your experience with our readers and give practical advice that can help other pregnant women.