Premature maturation of the placenta is a condition in which its functions fade ahead of schedule. This leads to a deterioration in fetoplacental blood flow, as well as metabolic disorders between mother and fetus. As a result, the child does not receive enough nutrients necessary for growth, which entails intrauterine hypoxia and delayed development of the embryo. We will discuss below what are the causes and consequences of placental aging during pregnancy, and whether there are ways to prevent pathology.
Causes
The process of early aging of a child’s place can be triggered by any factor that affects the blood supply to the fetoplacental system. The risk of developing pathology is increased by complications during pregnancy, unfavorable social factors, and chronic diseases of the mother. Doctors identify several main reasons that lead to premature aging of the organ:
- Infections. Sexually transmitted infections and various viral diseases pose a serious danger during pregnancy. The threat of infection of the fetus with infectious agents leads to increased growth of placental tissue. To prevent infection of the embryo, the placenta activates its protective functions, which is why it experiences increased stress and wears out ahead of time.
- Extragenital pathologies. Exacerbation of chronic diseases and functional failure of internal organs in the expectant mother can also provoke accelerated development of the child's place. Premature ripening is often observed in patients with diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and endocrine disorders.
- Gynecological complications. Pathologies of the endometrium of the uterus and a history of abortion lead to structural changes in the uterine mucosa, which causes problems with placentation and the functionality of the baby's place during pregnancy. Premature aging of the organ can also occur against the background of ovarian dysfunction.
- Rhesus conflict between mother and fetus. Immunological incompatibility increases the risk of developing hemolytic disease in the embryo, which is why the child needs increased nutrition. There is an increased load on the placental tissues and the organ ages prematurely.
- Preeclampsia. The development of complications is often accompanied by disruption of uteroplacental blood flow, which increases the load on the placenta. And if in the early stages the compensatory capabilities of the body allow maintaining normal blood supply to the embryo, then as the pathology progresses, increased growth and premature maturation of the child’s place is observed.
Also, the disorder can develop due to such unfavorable factors as poor ecology, harmful working conditions, and the presence of pathological addictions in the expectant mother. The likelihood of premature aging of the placenta increases if a pregnant woman leads a sedentary lifestyle, eats poorly, or takes potent medications.
Hospital or...
Regime and diet
If premature aging of the placenta is detected, comprehensive treatment is carried out in a hospital setting. Treatment is aimed at eliminating risk factors, normalizing blood flow and preventing fetal hypoxia. Treatment in a hospital allows you to provide full assistance to mother and child.
A woman is recommended physical and emotional rest, nutritious nutrition rich in vitamins and minerals. The expectant mother is advised to avoid fried, smoked and salty foods, limit flour products and sugar consumption in general. It is necessary to increase the amount of vegetables and fruits in the diet.
Main groups of drugs
The basis is drug treatment.
To improve uterine-placental blood flow, pentoxifylline is indicated for a course of 10-14 days. This drug has vasodilating, angioprotective and antiaggregation properties.
In order to prevent oxygen starvation of the fetus, drugs such as Actovegin or Curantil are used. The main effects of these antihypoxants are metabolic, microcirculatory and neuroprotective. The absorption and utilization of oxygen increases, capillary blood flow improves, and the condition of the central and peripheral nervous system improves.
Correction of the rheological properties of blood occurs with the help of Acetylsalicylic acid, Dextran.
Metabolic therapy is carried out with the help of vitamin E, methionine, folic acid. Ascorbic acid and dry (aqueous) extract of artichoke leaves also improve placental function.
If necessary, sedative therapy is indicated. The drugs of choice are valerian tincture, peony tincture, motherwort tincture, herbal teas (sedative mixtures).
Pathogenesis
With premature aging of the placenta, the formation of a large number of calcifications is often observed. These pathological inclusions damage the integrity of the organ, causing it to no longer function normally. The accumulation of calcium salts increases the likelihood of blood clots, as well as damage and necrosis of placental tissue. The functions of the organ fade ahead of time, which leads to fetoplacental insufficiency.
Normally, calcification of the baby's place begins after the 37th week of pregnancy. The appearance of premature structural changes and the detection of stage 3 aging of the placenta at earlier stages of gestation is dangerous for the health of the fetus. Due to deteriorating blood supply, the child does not receive enough oxygen and other nutrients, which leads to intrauterine hypoxia and developmental delay.
What is the placenta and why is it needed?
The content of the article
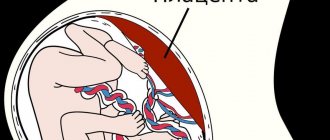
The placenta is a network of tubes that includes 2 circulatory systems - the woman and the fetus. The organ completely ensures the life of the baby in the uterus, performing vital functions:
- Nutritious
. Thanks to the placenta, the embryo receives all nutrients, vitamins, and electrolytes from the mother. - Excretory.
With the blood flow, waste products of the fetus are removed from the placenta: (urea, creatine). - Respiratory
. The baby receives oxygen from the mother and releases carbon dioxide. - Protective or immune
. Mother's antibodies that cross the placenta protect the unborn child from various immune diseases. - Endocrine
. Estrogens, progesterones, serotonin and other hormones are formed in the placenta, promoting the development of the organ and bearing a child.
Without the placenta, the fetus will die because it will not be able to breathe or eat.
Classification
Depending on the gestational age, there are 4 degrees of placental aging:
- Grade 0 – active growth of placental tissue occurs before the 30th week of pregnancy. During this period, the organ has an integral structure without foreign inclusions, all functions work without disturbances.
- Grade 1 – persists until 32-34 weeks of gestation. It is characterized by slight compaction of the walls of the placenta, as well as the appearance of a small number of pathological inclusions in the tissues, which does not have a strong effect on blood flow. The fetus continues to receive sufficient nutrients necessary for development.
- 2nd degree - by the 34th week of pregnancy, the baby's place reaches its maximum size. The walls of the organ become thinner, and the amount of salt deposits increases.
- 3rd degree - from the 37th week, the final stage of maturity of the baby's place begins, during which its functions gradually fade away. Extensive calcification leads to deterioration of blood supply and irreversible changes in tissues and blood vessels.
Premature maturation of the organ is diagnosed if signs of 1st degree of maturity are detected before the 27th week of pregnancy, 2nd degree of placental aging - before the 32nd week, and 3rd degree - before the 36th week of gestation. This dynamics indicates an increased risk of developing fetoplacental insufficiency and decompensation of the adaptive reactions of the mother and fetus.
What functions does the placenta perform during pregnancy?
The placenta (baby place) is an important organ that forms in the uterus of a pregnant woman and ensures a reliable connection between the fetus and the mother’s body.
The placenta has many functions. Of course, all of them are aimed at ensuring that the growing baby develops normally, provided with everything necessary. Through it, nutrition and gas exchange (respiration) of the fetus are carried out, the release of metabolic products, and the formation of the hormonal and immune status of the fetus. The placenta protects the fetus from viruses, bacteria and harmful substances, being a unique barrier.
Complete formation of the placenta is completed by the end of the first trimester of pregnancy. Subsequently, the “fetal site” increases in size (grows with the fetus and differentiates) up to the 36th week of gestation. At this point, it reaches full functional maturity. Then only the baby grows, but the placenta ages. Towards the end of pregnancy, the so-called physiological aging of the placenta occurs.
Symptoms
In most cases, premature aging of the placenta during pregnancy is asymptomatic for the patient and is detected only through diagnostics. You can independently recognize the pathology only by changes in the nature of fetal movements. Due to a deficiency of nutrients, a child may exhibit erratic motor activity, and, with severe hypoxia, on the contrary, subside for a long time. Another symptom is a rapid heartbeat of the embryo, which slows down as the disorder progresses.
First degree of placenta maturity
Normally, the first degree of placental maturity on ultrasound is observed from the 30th week of pregnancy. What does the placenta look like at the first stage of maturity? During this period, the structure of the organ becomes uneven, compactions appear in it, which are determined by ultrasound, and the surface of the placenta becomes wavy. The thickness of the placenta at this moment can be between 24 and 40 mm.
The transition from zero to first degree of placental maturity does not occur instantly. The first signs of aging of the placenta, the first degree of maturity, can be detected by ultrasound examination as early as the 27th week of pregnancy; this period is the lower limit of the norm. When it is impossible to clearly assess the structure of the organ (whether it is zero or the first degree), in conclusion, the maturity of the placenta is determined as degree 0 - 1.
What is dangerous about premature ripening of the placenta?
With early maturation, the functionality of the child's place decreases, therefore, in frequent cases, the pathology is accompanied by the development of fetoplacental insufficiency. Salt deposits that appear during the aging process of the organ cause necrosis of placental tissues and affect blood vessels. This leads to deterioration of fetoplacental blood flow, intrauterine hypoxia of the embryo and serious perinatal disorders.
If aging of placental tissues occurs at 22-26 weeks of pregnancy, then by the beginning of the third trimester the fetus often exhibits signs of severe hypoxia and developmental defects. In especially severe cases, the pathology entails intrauterine death of the embryo. Also, early aging of the baby place increases the risk of placental abruption, premature rupture of amniotic fluid and the onset of labor before the due date.
Diagnostics
If, during routine ultrasound screening, structural changes in the placental tissue are detected that are not typical for the current stage of pregnancy, the woman is referred for a comprehensive diagnosis. Additional examination allows you to determine the degree of maturity of the organ and evaluate its functionality. The most informative methods are:
- Ultrasound examination of the placenta. The method helps to measure the thickness of the baby's place, as well as identify compactions, calcifications, cysts and other pathological inclusions in the placental tissue.
- Doppler. Diagnosis is based on studying the state of the uteroplacental and fetal-placental circulation. The procedure allows you to evaluate the speed and direction of blood flow, the patency of the main blood vessels and their location.
Premature ripening of the placenta at 31 weeks or earlier increases the risk of fetoplacental insufficiency, so the pregnant woman requires special medical supervision. Unscheduled CTG procedures and fetometry of the embryo help to assess the condition of the fetus. To establish the etiology of the disorder, laboratory tests are prescribed - PCR, bacteriological studies, ELISA, analysis for intrauterine infections.
How does the placenta develop?
The placenta is formed in the early stages from the embryonic membranes; the development of the placenta occurs parallel to the development of fetal growth. During pregnancy, the structure of the placenta constantly changes, as the organ must adapt to the needs of the growing baby. From the fifth month of pregnancy, the weight of the placenta increases, and a month before birth it reaches full maturity. The maturity of the placenta is one of the main indicators of its condition. Visible changes that occur in the placenta as pregnancy progresses are assessed as the degree of placental maturity.
What to do when a pathology is detected?
The organ is formed from the tissues of the fetus, and not from the mother’s cells, so the ideal structure of the child’s place is found in rare cases. When studying structural changes, experts distinguish three forms of deviations: mild, moderate or significant. Only significant changes in the integrity of placental tissues pose a particular danger to the child. When mild and moderate forms of disorders are detected, the organ continues to function normally thanks to a developed system of blood vessels.
For an objective assessment, the doctor also analyzes the general condition of the fetus. Important attention is paid to the fetometric parameters of the embryo. If the baby’s parameters do not correspond to the established gestational age, this is a sign of growth retardation and requires comprehensive treatment. In the case when the embryo develops without abnormalities, the patient is prescribed unscheduled diagnostics to monitor the condition of the fetus.
Treatment
When identifying pathology, medical tactics are based on eliminating the causes of premature aging of the child's place, normalizing blood flow in the fetoplacental complex, as well as determining the appropriate method of delivery. The treatment regimen depends on the gestational age at which the disorder was detected.
If early aging of the placenta is diagnosed in the second trimester of pregnancy, the woman is hospitalized in a hospital for a comprehensive examination and observation. To monitor the condition of the fetus, Doppler measurements are performed once a week and the child’s motor activity is monitored daily. If the diagnosis reveals critical disturbances in blood flow in the umbilical artery, severe intrauterine hypoxia or a sharp deterioration in the vital signs of the fetus, this is a direct indication for emergency delivery.
If premature aging of the placenta is detected at 32 weeks of pregnancy or later, the risk of serious perinatal disorders is reduced. If, according to the diagnostic results, the child’s condition is normal, the woman is allowed to give birth naturally. Caesarean section is indicated in cases where the fetus is severely delayed in development or the pathology is accompanied by severe complications of pregnancy.
Regardless of the timing of detection of premature aging of the child's place, the pregnant woman is prescribed drug therapy to eliminate the causes that provoked the disorder, as well as to improve the blood supply to the embryo. The treatment regimen also includes recommendations on a balanced diet, physical activity, normalization of sleep patterns and other measures that affect the condition of the mother and fetus.
All vital organs are formed in a person long before birth. And it seems that it does not happen that any organ suddenly appears in a person during his life. However, it is possible. A similar organ is the placenta, which is formed in women during pregnancy.
Sometimes placental maturity occurs earlier than the corresponding perinatal period. This phenomenon is called premature aging of the placenta. The pathology negatively affects the development of pregnancy and the condition of the fetus. Why does the placenta age? What factors provoke this process? How to diagnose and properly treat pathology?
What is premature aging of the placenta?
Placenta is a medical term. People call it a children's place. So, the placenta is an organ that forms during pregnancy. It is through it that the baby receives oxygen and all the necessary nutrients. The placenta allows you to remove waste products from the baby and carbon dioxide. It is endowed with the most important function - it protects the baby from reactions of the mother’s immune system and various infections.
If we consider the placenta from a scientific point of view, then it is a small disk (20 cm in diameter) weighing about 5 kg and approximately 3 cm thick. One side of it is directed towards the fetus (it is from this side that the umbilical cord departs), and the second, consisting of villi, attached to the uterus.
In gynecology, “aging of the placenta” refers to a condition in which the growth of the placenta slows down or completely stops.
This condition is extremely dangerous, because The following functions of the placenta are blocked:
- ensuring gas exchange for the child;
- removal of the child's waste products;
- transport of essential nutrients;
- fetal protection;
- synthesis of some hormones that are necessary for the proper development of the child.
Premature aging of the placenta requires treatment and constant monitoring by doctors.
Aging of the placenta
Aging of the placenta during pregnancy is a fairly common diagnosis that doctors make to expectant mothers. This diagnosis is made on the basis of an ultrasound scan and is important for the normal development of the fetus.
The placenta goes through 4 stages of maturation:
- zero, which is typical for pregnancy up to 30 weeks;
- the first, which lasts from the 30th to the 34th week of pregnancy;
- the second, which corresponds to pregnancy from the 34th to the 37th week;
- the third, characteristic of the last weeks of pregnancy, that is, from the 37th week until the moment of birth.
Depending on the stage, the placenta changes and has characteristic features.
Aging of the placenta during pregnancy is a decrease in the functionality of this organ. This does not mean at all that the placenta, which, for example, has a second degree of maturity, ceases to perform its functions. This body simply gradually reduces the scope of its capabilities.
In this regard, the detection of such pathology in late pregnancy should not cause serious concern. It is much worse when aging of the placenta during pregnancy is detected in the first or second trimester.
Stages of placenta aging
The age of the placenta is the most important indicator that informs about intrauterine development and fetal formation. It happens that the outcome of pregnancy depends on this indicator.
As already mentioned, there are 4 stages of placental maturation.
Starting from the 12th week of pregnancy, an organ such as the placenta begins to form and actively grow. Every week it gets denser. In the period from the 12th to the 30th week of pregnancy, the degree of maturation of this organ is normally zero. During this period, the structure of the child's place is smooth and uniform. In the zero stage, the placenta fully performs all the functions assigned to it: it actively saturates the fetus with oxygen and nutrients, removes carbon dioxide and waste products of the unborn baby.
Stage one
The normal course of pregnancy in the period from the 30th to the 34th week corresponds to the first stage of maturation of the child's place. It is characterized by the fact that it is during this period that the first signs of aging begin to appear on the placenta. They are expressed by the appearance of small irregularities and inclusions. At the same time, this organ does not lose its functions: the placenta continues to actively help the baby develop, grow and eat. Sometimes this period is called the period of placental development, since it is during this period that the fetus is actively growing and developing.
Second stage
The second stage of maturation (aging) is characteristic of the pregnancy period from the 34th to the 37th week of pregnancy. Ultrasound examination of the placenta during this period shows the appearance of a large number of inclusions and changes in the relief of this organ. The thickness of the placenta gradually begins to decrease, which leads to a decrease in its functional tasks. However, for the period from the 34th to the 37th weeks of pregnancy, the placenta performs all the necessary functions: the baby receives the amount of nutrients that it needs for proper development and growth.
Final stage
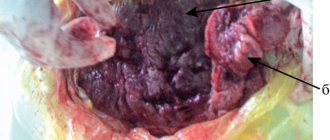
The third (final) stage of maturation is observed at 36 weeks of pregnancy. The aging of the placenta is reaching the “finish line”. The functioning of the child's seat is significantly reduced, and natural aging occurs. This stage is typical for full-term pregnancy and indicates that the fetus is ripe and the mother’s body is ready for childbirth. Externally, the placenta at this stage has many inclusions and deposits of salts. Its structure is very heterogeneous; large waves are visible on the placenta, the depth of which in some places reaches the basal layer.
Any deviation from these norms is considered a pathology and requires systematic monitoring and treatment. However, premature aging of the placenta is not a death sentence. Timely detection of this deviation will help stabilize the condition of the fetus and bring the expectant mother to a successful birth.
Why does the placenta age too early?
There are many factors that cause aging of the placenta during pregnancy.
Reasons that provoke premature aging of the placenta during pregnancy:
- late toxicosis is a pathology that occurs in the second half of the perinatal period;
- toxic poisoning of the mother's body;
- negative Rh factor in a woman, the presence of Rh conflict with the fetus;
- surgical intervention performed on the uterus - the presence of scars;
- abuse of nicotine and alcoholic beverages;
- pathologies of the excretory system and kidneys;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels in women;
- liver diseases;
- several fetuses in the uterus;
- past abortions;
- hormonal imbalance and improper functioning of the endocrine system;
- placenta previa;
- placental abruption;
- the presence of infectious and inflammatory processes in the uterus.
As you can see, there are a huge number of reasons why premature aging of the placenta occurs during pregnancy. These include chronic diseases, acquired viral and infectious diseases, as well as improper behavior of the mother during pregnancy. The presence in a woman’s history of one or more factors from the above list places the woman at risk for the likelihood of early aging of the placenta. It is worth remembering that a diagnosis such as premature aging of the placenta is made in cases where the second degree of maturity is diagnosed at up to 32 weeks or the third at up to 36 weeks.
Symptoms of premature aging of the placenta
As a rule, this pathology does not have pronounced symptoms. Premature aging of the placenta can only be diagnosed using ultrasound.
During this procedure, the following signs of pathology are noted:
- decrease in the thickness of the walls of the placenta;
- the appearance of calcifications;
- fetal pathologies.
In the first half of pregnancy, the placenta has a thick wall, which is densely penetrated with blood vessels.
As the gestational age increases, this figure decreases and the placenta becomes thinner.
As the thickness decreases, inclusions of special calcium salts appear, which interfere with normal blood flow. Consequently, the child does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients.
As a rule, with premature aging of the placenta, the fetus lags behind in development. Its size does not correspond to the perinatal period.
- The fetus's heart rate increases. This occurs as a result of oxygen starvation and lack of nutrients. This symptom indicates that the placenta is not coping with its functions;
- due to oxygen starvation, the expectant mother may feel sharp tremors in the abdomen (starting from the second trimester): the baby begins to actively move, kick and push with arms and legs;
- due to a lack of nutrients, the fetus may completely stop moving and moving.
Diagnosis of premature aging of the placenta
The assumption that the placenta is aging prematurely can be made by a specialist during a routine ultrasound examination.
Detection of morphological changes in the structure of a child's place is a reason for undergoing an additional comprehensive examination.
The pregnant woman receives referrals for the following procedures:
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs (in particular the uterus and placenta);
- Dopplerometry of uteroplacental blood flow.
Ultrasound examination allows you to determine such signs as:
- structural changes in the placenta;
- tissue compaction;
- the appearance of salt inclusions;
- change in shell thickness;
- formation of lobules.
Doppler testing is aimed at examining the blood vessels of the placenta. Using this procedure, you can determine the speed of placental blood flow and the quality of blood supply to the fetus.
In addition, the woman is recommended to undergo additional procedures to diagnose the cause of placental aging.
Treatment for premature aging of the placenta
So, the expectant mother was diagnosed with “premature aging of the placenta during pregnancy.” Treatment in this case will be carried out in a hospital setting. In most cases, doctors will use medications to eliminate the resulting pathology. It is worth knowing that it is impossible to cure this pathology. In this regard, treatment will be aimed at helping the unborn baby.
Therapy includes:
- maintaining a balanced diet;
- reducing anxiety and stress, maintaining psycho-emotional calm;
- walks in the open air;
- taking medications to improve placental blood flow.
Treatment includes closer monitoring of the intrauterine condition of the fetus.
If the indicators suddenly deteriorate, the woman undergoes an emergency caesarean section. In this case, it is possible to leave the child in a special box and save his life.
It is worth knowing that in most cases, when diagnosed with “premature aging of the placenta,” doctors manage to stabilize the condition of the fetus and expectant mothers give birth to absolutely healthy and full-fledged children.
What is the danger of premature aging of the placenta?
Rapid aging of the placenta negatively affects the intrauterine development of the child. Pathologies that may occur due to premature aging:
- intrauterine developmental delay of the child;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- intrauterine death of a child.
There are no negative consequences for a woman’s body with this pathology. It does not affect general well-being and does not cause discomfort.
If premature aging of the placenta was detected at 32 weeks, the consequences will not be so strong. As a rule, the woman is not even prescribed special treatment.
The expectant mother is recommended to regularly undergo ultrasound and CTG procedures to monitor the child’s condition.
Prognosis and prevention
The earlier the problem is diagnosed, the more favorable the prognosis for the course of pregnancy.
If all medical recommendations are followed, pregnancy with premature aging of the placenta ends with natural delivery at the expected time.
If earlier aging of the placenta corresponds to stage 3 maturity before the 37th week of the perinatal period, it is recommended to perform an emergency cesarean section.
Prevention recommendations:
- pregnancy must be planned;
- at the planning stage, future parents are advised to get tested and treat existing diseases;
- complete cessation of bad habits;
- maintaining an active lifestyle (walking, exercise);
- attending scheduled consultations with a doctor;
- timely completion of all recommended tests and examinations;
- taking vitamin and mineral complexes for pregnant women;
- complete nutrition.
Any pregnancy is accompanied by aging of the placenta. If this process occurs within the prescribed time frame, it does not pose any danger.
If the process occurs faster than the corresponding gestational age, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination and follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Proper therapy can minimize the risk of developing pathologies in a child.
Text: ChelMami