Skin and hair problems, irregular menstruation, infertility, decreased libido are just some of the alarming symptoms of elevated prolactin levels.
Prolactin is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland (its anterior lobe). It directly stimulates the growth and development of the mammary glands during the development of a girl and during pregnancy, and during lactation it controls milk production. Prolactin is produced in large quantities during sleep, stress, pregnancy, and certain diseases (for example, lungs, liver).
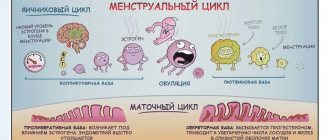
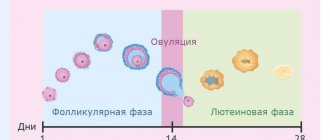
In addition to its direct effect on lactation, prolactin is also involved in other vital processes. For example, it prolongs the corpus luteum phase, participates in the regulation of water-salt metabolism, and during lactation it suppresses hormones that cause ovulation.
Normal prolactin levels are up to 30 ng/ml (600 mU/L). But under certain conditions it can increase, causing hyperprolactinemia. Signs of increased prolactin in women manifest themselves as symptoms in the form of dysfunction of the thyroid gland, bone fragility and other pathologies.
Increased prolactin in women. Causes
There are a number of reasons why the hormone prolactin in women is elevated:
- Physiological. The increased content of prolactin in women in this case is determined by the daily rhythms of hormone secretion, pregnancy, lactation, increased physical activity, and intimacy. Some surgical interventions can also cause signs of increased prolactin in women (for example, frequent uterine curettage).
- Iatrogenic. Some medications can cause hyperprolactemia. These include: antidepressants, antipsychotics, estrogens in high dosages, antihypertensive drugs, oral contraceptives and some others.
- Pathological reasons. Elevated prolactin levels in women occur in pathological conditions such as pituitary tumors, renal and liver failure, liver cirrhosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, thyroid diseases, pulmonary tuberculosis, tumor diseases of the hypothalamus, vitamin B6 deficiency, radiation exposure, compression of the pituitary gland. Of particular note It should be noted that the cause of increased prolactin levels may be chronic stress conditions and persistent sleep disturbances (for example, insomnia).
Causes of hyperprolactinemia
Causes of hyperprolactinemia
Hyperprolactinemia is 3 times more common in women than in men. This pathology is usually diagnosed between the ages of 25 and 34 years, but can rarely develop in children and adolescents.
Because prolactin is produced by lactotropic cells of the pituitary gland, increases in blood levels usually occur due to factors that cause hyperplasia or hyperfunction of these cells, damage to the pituitary gland, or slowing of hormone metabolism. These factors may be physiological, pathological or pharmacological (Table 1).
| Physiological factors | Pathological factors | Pharmacological factors |
| Pregnancy, lactation period | Systemic diseases breast pathology, chronic kidney disease, cirrhosis, polycystic ovary syndrome | Neuroleptics and antipsychotics, anticonvulsants, antidepressants |
| Breast stimulation | Damage to the hypothalamus and pituitary infundibulum due to:
| Anesthetics, opioid analgesics |
| Dream | Hypersecretion of the pituitary gland as a result of:
| Oral contraceptives (estrogens) |
| Stress (physical and emotional) | Lymphocytic pituitary gland | Antihistamines |
| Sexual intercourse | Epilepsy (with seizures) | Antihypertensive drugs |
| Exercise stress | Dopamine receptor blockers. Dopamine synthesis inhibitors |
Elevated prolactin in women - symptoms
Elevated prolactin levels in women can manifest as the following symptoms:
- Increased prolactin in women may manifest symptoms in the form of impaired reproductive function, repeated miscarriages that occur in the earliest stages, infertility (usually due to anovulatory cycles);
- menstrual irregularities up to amenorrhea;
- decreased libido up to frigidity;
- galactorrhea. Depending on the duration of the disease and its degree of development, milk can be released from a few single drops to copious amounts with gentle pressure;
- hirsutism. More often, hair begins to grow in the area around the nipple, on the face and along the white line of the abdomen (from the navel and below to the pubis);
- acne (acne);
- secondary osteoporosis due to decreased bone density;
- obesity due to increased appetite and a tendency to excessive deposits;
- Even before elevated prolactin in women is determined, symptoms manifest themselves in the form of psycho-emotional disorders. Usually manifested by sleep disturbances, depression, increased fatigue, weakened attention and memory;
- visual disturbances are also signs of increased prolactin in women. Hormonal imbalance is characterized by numerous other symptoms - sweating, fever, nausea, constant buzzing in the head and dizziness, chest pain, the face looks flushed, and the patient is drowsy. Symptoms of this disorder sometimes indicate life-threatening diseases, signs of tumor damage to the pituitary gland appear - if increased prolactin in women arises as a result of this pathology, then there may be compression of the optic chiasm, in some cases paralysis of the cranial nerves (oculomotor, trochlear, abducens ).
However, all these symptoms are also inherent in other disorders in the functioning of systems and organs; additional examination should be performed to make an accurate diagnosis.
Prolactinoma and pregnancy
If, while taking drugs that reduce prolactin levels in the blood, reproductive function is restored and pregnancy occurs, dopamine agonists should be discontinued. In the first trimester of pregnancy, when the risk of spontaneous abortion in patients with prolactinoma is very high, natural progesterone is prescribed. Monitoring of a pregnant woman with prolactinoma by an ophthalmologist and neurologist throughout pregnancy is mandatory. Dopamine agonists are prescribed only when progressive tumor growth is noted. It is not advisable to perform magnetic resonance imaging during pregnancy, however, if there is no positive dynamics from the use of conservative treatment, it is necessary to decide on neurosurgical intervention.
A control magnetic resonance examination is recommended a couple of months after birth. There are no contraindications for breastfeeding, but in cases of tumor enlargement, suppression of milk production may be necessary.
Elevated prolactin levels in women and its diagnosis
Before answering the question “Why is prolactin elevated in women?”, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination. First of all, you need to find out your life history and family history. In particular, you need to know about diseases of the thyroid gland, previous operations on the pituitary gland, ovaries, and chest. The patient is asked whether there are any attacks of depression or insomnia, whether there have ever been pathological fractures, how pronounced the hirsutism is and other questions that help determine the degree of hyperprolactinemia and clarify its cause.
To determine the true cause of hyperprolactinemia, studies such as:
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys, liver, thyroid gland, ovaries, mammary glands to identify pathologies.
- X-ray or magnetic resonance imaging of the skull to identify pathology of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. If necessary, the study is performed with contrast.
- X-ray of skeletal bones to determine the presence or absence of bone loss as a result of secondary osteoporosis developing with an increase in prolactin.
- Biochemical blood test to detect pathology of the kidneys (increased creatinine and urea), liver (ALAT, AST).
- The main diagnostic method to determine whether hyperprolactinemia is present and to determine its degree is a blood test for prolactin. Donate blood in the morning on an empty stomach. Before conducting this analysis, you must refrain from intense physical activity, stress, and sexual intercourse. If there are doubts about the correctness of the results obtained, it is recommended to conduct a blood test for prolactin again.
Doctors and laboratory assistants at our center will not only select an individual examination program suitable for a particular patient, taking into account all the characteristics of the disease, but will also help to correctly interpret the results of the study.
If prolactin is elevated, treatment in women should be prescribed depending on the degree of its increase. With a slight increase in the level of the hormone (up to 50 ng/ml) with lifestyle adjustments and withdrawal of provoking drugs, it can decrease to normal values on its own. If prolactin levels above normal are associated with pregnancy or lactation, treatment is not required.
If prolactin levels are significantly elevated, specialized treatment should be performed. If the cause of hyperprolactinemia is a tumor disease of the pituitary gland, drug or surgical treatment is carried out depending on the malignancy of the process and the degree of its maturity.
Doctors at our clinic will select the optimal treatment based on the diagnosis of each patient.
Drug treatment
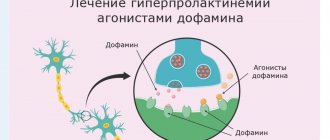
Symptomatic hyperprolactinemia due to any cause is treated with oral dopamine agonists, cabergoline, bromocriptine, quinagolide, and pergolide. Treatment begins with low doses of the drug, which are gradually increased to therapeutic doses.
Consistent adherence to the treatment plan allows a very rapid reduction in clinical symptoms to be observed, with regression of vision-related symptoms in the first days and restoration of sexual function within 2-3 weeks.
If hyperprolactinemia is caused by an adenoma, a repeat MRI scan may show improvement as early as 6 weeks after starting treatment.
Currently, the first-line dopamine agonist is cabergoline due to its greater efficacy and lower likelihood of side effects compared with bromocriptine. This difference in effectiveness may be explained by the fact that cabergoline is more specific for dopamine receptors in lactotrope cells.
Dopamine agonists cause side effects such as nausea, postural hypotension, and impulsive behavior. Long-term use of high doses of cabergoline has been shown to be associated with valvular fibrosis, so periodic cardiac ultrasound examination is recommended.
Pathogenesis
Excessive levels of prolactin in the blood through a negative feedback mechanism suppresses the secretion of GnRH in the hypothalamus, which leads to a decrease in the production of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones. As a result, deficiency of sex hormones develops, hypoplasia of the external genitalia (hypogonadism), active proliferation of the secretory apparatus of the mammary gland, increased lactogenesis and lactation (galactorrhea), especially in women.
Long-lasting hyperprolactinemia stimulates bone resorption processes, which reduces its mineral density (osteoporosis). Leptin resistance, adiponectin deficiency and hypogonadism contribute to the deposition of fat in subcutaneous fat and an increase in the content of cholesterol fractions in the serum. There is moderate hyperproduction of androgens in the reticular zone of the adrenal cortex.
Prevention
There are no special preventive measures for this disease. The risk of developing hyperprolactinemia can only be reduced by avoiding serious physical activity and psycho-emotional stress.
Women who have been diagnosed with hyperprolactinemia should consider other methods of contraception. If desired, you can continue to use oral contraceptives, but estrogen-containing drugs should be replaced with agents whose action is based on pure gestagens or prolonged gestagens. Also, in case of hyperprolactinemia, the advisability of surgical sterilization should be considered. It is not recommended to use intrauterine devices: they provoke irritation of endometrial receptors, which can cause increased secretion of prolactin.
Diagnosis of the disease
Patients with suspected pituitary adenoma complain to various doctors: a neurologist, ophthalmologist or endocrinologist.
At the initial appointment, the doctor will conduct a general examination, collect an anamnesis of life and illness, prescribe laboratory and instrumental tests: general blood and urine tests, blood biochemistry, ECG. A doctor of appropriate specialization will conduct an ophthalmoscopy, test visual acuity, neurological examination, and evaluate the existing symptoms.
In addition, the following studies are indicated for patients with pituitary adenoma:
- radiography of the skull;
- CT, MRI of the brain;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland, heart, liver, spleen;
- analysis of hormone levels in blood and saliva.
If surgical intervention is indicated, the patient must consult a neurosurgeon.
Treatment of patients with high prolactin
There is no need to treat elevated levels if:
- hormone concentration up to 1000 U/l;
- the structure of the pituitary gland is not changed;
- the functioning of the organs of the reproductive system occurs without changes;
- the person is of normal weight.
The main assistant in the fight against increased prolactin is dopamine. They “compete” with each other, creating balance. To normalize the condition, it is recommended to do what brings pleasure and give the body time to rest. The following have a positive effect on hormonal levels:
- bananas,
- apples,
- watermelons,
- strawberry,
- prunes.
A good relaxing effect is massage, which allows you to normalize your emotional state.
Regular physical activity can reduce stress hormone levels. They should not be debilitating, as this may become a prerequisite for its increase. The best option is to perform gymnastics in a well-ventilated area or outdoors.
Before bed, you can make and take soothing infusions that contain mint, lemon balm and hops. Tablets with valerian extract also reduce anxiety levels. When using twigs, give preference to a tincture made from seeds. For this purpose 40 gr. raw materials are poured with alcohol or vodka in an amount of 230 grams, infused for two weeks in a dark place. The tincture is taken in a large spoon, diluted in 60 ml. water 30 minutes before meals.
During drug treatment, different therapeutic techniques are used for women and men. They are contacted only if other methods cannot reduce the hormone level.
Is it possible to prevent hormonal imbalance during stress?
The main rule is to listen to your body. With hormonal changes due to stress, unreasonable palpitations and anxiety appear. Sleep ceases to give a feeling of rest. In the morning there is fatigue, fog in the head, muscle pain. There is a decrease in sexual desire and a disruption in eating behavior.
You need to give time for rest and relaxation. Try to spend more time outdoors. Don’t forget about communication, which helps reduce anxiety and switch to positive experiences.
Thus, prolactin is more of a female stress hormone, since its increase is more often observed in the fairer sex. An increase in certain substances in the body is a protective effect. But if the condition is not corrected, physiological problems appear. Therefore, it is important to monitor your emotional state.
Classification
By nature, pathological and physiological hyperprolactinemia are distinguished. Separately, macroprolactinemia is distinguished, in which an increased level of a biologically inactive high-molecular fraction of the hormone (big-big prolactin) is observed in the blood. In the latter version of the condition, there are no clinical symptoms. According to the mechanism of occurrence, hyperprolactinemia is divided into:
- Primary.
Caused by damage to the hypothalamic-pituitary system (tumors, surgical interventions). - Secondary.
Develops as a result of granulomatous processes, diseases of the endocrine system, kidneys, liver, taking medications,
Based on size, the following types of prolactinoma are distinguished:
- Microprolactinomas.
The size of the tumor does not exceed 10 mm. Occurs in the vast majority of cases (up to 90%). - Macroprolactinomas.
The diameter of the formation is more than 10 mm. It accounts for 10% of all prolactinomas and is more often detected in men.
Gonadotropinomas
Most often hormonally inactive, they can rarely produce active forms of follicle-stimulating or luteinizing hormones, causing ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome in women.
Neuro-ophthalmological signs
With endosuprasellar adenoma, partial loss of visual fields is observed while maintaining visual acuity. An increase in tumor size leads to gradual atrophy of the optic nerves and blindness.
A tumor growing to the sides causes impaired oculomotor function (ophthalmoplegia) and double vision (diplopia), and decreased visual acuity.
When an adenoma grows into the bottom of the sella turcica, patients note nasal congestion, simulating the clinical picture of sinusitis or nasal tumors.
If the tumor grows towards the hypothalamus, patients complain of sleep disturbances, uncontrolled appetite, unstable thermoregulation (fever, chills), emotional disturbances: unstable mood, tearfulness, irritability.
With a large adenoma and its multidirectional growth, the symptoms will overlap each other and be masked. The following neurological manifestations are possible:
- headache, dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- speech and facial expression disorders;
- dysphagia is a swallowing disorder.
Preparing for analysis
Testing can be done at any phase of the menstrual cycle, but results will vary due to normal fluctuations in prolactin concentrations throughout the month. Usually the attending physician himself chooses the required period if he suggests some kind of diagnosis. When searching for the causes of infertility, the patient is sent to donate blood on days 2-5 of the cycle, if necessary, including other hormones in the list of tests³.
Men don't need to worry about calendar intricacies. It is enough just to follow the recommended rules before performing the analysis.
Patients (both men and women) should begin preparing for the study in advance - the informativeness of the data obtained depends on this. For 2-3 days before analysis, it is necessary to exclude the influence of such factors:
- sex;
- severe psycho-emotional overload;
- alcohol;
- exhausting physical activity;
- bath, sauna;
- solarium;
- binge eating;
- unbalanced consumption of sweet, fatty, protein foods;
- additional stimulation of the mammary glands and nipples - during self-examination, sexual stimulation, wearing tight bras;
- lack of sleep;
- calorie deficit diet;
- psychoactive substances.
Blood is drawn from a vein in the usual way in the morning from 8 to 11-12 hours. The patient comes on an empty stomach - the last meal can be taken the night before, and dinner should be light. A few hours before submitting the material, give up cigarettes and other types of smoking (vaping, hookah).
A test for prolactin will be uninformative if you donate blood in the acute period of inflammatory diseases - colds (ARVI), sinusitis, pneumonia. There is also no point in conducting analysis in the first weeks after surgery and trauma, especially in the chest area. Some pharmaceutical drugs (antidepressants, hormones) affect the level of prolactin in the blood serum. Usually 3-5 days before testing, their use is suspended. However, you cannot stop the prescribed therapy yourself - consult your doctor.
Diagnosis and treatment of hyperprolactinemia in Moscow
Any form of hyperprolactinemia, regardless of the cause, requires medical supervision. Modern methods of therapy are based primarily on drug treatment and lifestyle correction. It is also important that normalizing prolactin secretion during hyperprolactinemia often requires the participation of several specialized specialists: they select a method that not only reduces the clinical manifestations of the disease, but in most cases leads to complete recovery. The success of therapy depends on both the causes of the disorder and the timeliness of the patient’s treatment.
At the Alfa Health Center clinic in Moscow you can get a personal consultation with a gynecologist-endocrinologist.
Our specialist will prepare personal recommendations on organizing your daily routine, level of physical activity, sleep patterns and nutrition. Registration is made by phone or through an automated form on the website. We work seven days a week. Share: