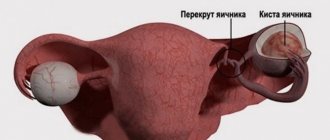
An ovarian cyst is a benign cavity formation that tends to grow and contains fluid inside.
Very often, ovarian cysts are asymptomatic, but can manifest as pain, discomfort in the lower abdomen, irregular menstrual cycle, and urinary disorders. Cyst is a widespread disease that is more often diagnosed in women of reproductive age. Approximately every second patient with an ovarian cyst experiences menstrual irregularities. The most common complications of cysts include pedicle torsion and rupture. Rupture of an ovarian cyst (ovarian apoplexy) is a pathological condition characterized by rupture of the cyst membranes and hemorrhage into the pelvic cavity. This is a serious complication requiring immediate surgical intervention. According to statistics, pathology is observed in 1–2.5% of patients.
Most often, rupture occurs in the middle or in the second phase of the menstrual cycle.
Why do cysts rupture?
There are several reasons for the violation of the integrity of the walls. They can be divided into external and internal. External risk factors include:
- Physical exercise;
- Blows in the lower abdomen;
- Intense movements during sexual intercourse;
- Vaginal examinations;
- Surgical intervention.
Doctors include internal pathological processes leading to complications:
- Excessive growth of the cystic cavity due to an increase in the volume of secretions;
- Twisting of the cyst stalk (if present);
- Inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs;
- Polycystic ovary syndrome;
- Adhesive processes;
- Frequent abortions;
- Ovarian hyperstimulation during IVF and other manipulations;
- Stagnant processes in the pelvic organs.
Observations in gynecological practice have shown that the risk of cyst rupture increases when the neoplasm reaches a diameter of more than two centimeters.
Causes
Ovarian cysts develop for various reasons. Among them:
- pathologies of the endocrine glands;
- metabolic disorders;
- repeated artificial termination of pregnancy;
- surgeries on the pelvic organs;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs (in particular, the ovaries and fallopian tubes);
- heredity;
- taking certain medications;
- blood stagnation in the pelvis due to low physical activity, irregular sex life and other factors.
A rupture can be caused by:
- lifting weights or playing sports, as this increases intra-abdominal pressure;
- abdominal trauma, resulting in impaired blood circulation in the ovary;
- sexual intercourse;
- disorders of hemostasis (blood coagulation system);
- hormonal imbalance;
- pregnancy, when as the fetus grows, the enlarging uterus begins to compress neighboring organs.
Often, capsule rupture occurs under the influence of several factors at once.
Symptoms of a cyst rupture
The main sign of a ruptured ovarian cyst is acute, severe pain in the lower abdomen. It gradually intensifies and does not respond to analgesics.
The following symptoms may also indicate a problem:
- Unnatural vaginal discharge;
- Uterine bleeding;
- Hyperthermia;
- Reduced blood pressure;
- Weakness;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Paleness of the skin;
- Constipation, gas formation.
If such deviations occur, you should immediately consult a gynecologist.
What kind of prevention should be carried out?
In order for a woman not to suffer the sad fate associated with this pathology, it is necessary to take care of her health. Even if you feel excellent, go to the gynecologist for an examination every six months. If there are gynecological problems, be observed regularly. Patients with adnexitis, oophoritis, polyendocrine syndrome or STDs must definitely treat their disease.
Women who have suffered from ovarian apoplexy should take care to ensure that there is no relapse. One of the preventive measures is complex treatment to normalize the menstrual cycle and improve blood supply.
Patients who have undergone surgery are required to monitor the restoration of hormonal levels and the normalization of blood circulation. They are advised to take nootropics and tranquilizers. Under no circumstances should you refuse such drugs. The use of multiphase oral contraceptives will ensure normalization of hormonal levels and help prevent ovulation. It is better not to plan pregnancy during this period. It is necessary to wait for the body to fully recover and become stronger. Then you can confidently hope for a successful pregnancy and birth of a healthy baby.
Observation by a doctor is considered mandatory.
Diagnostics - how to determine a cyst rupture
If the gynecologist suspects a ruptured ovarian cyst, it is important to confirm the diagnosis as quickly as possible. To do this, doctors primarily choose instrumental research methods:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs, ovaries;
- Puncture (collection) of ruptured contents from the peritoneum through the vagina;
- Laparoscopic diagnosis: Using a laparoscope, doctors simultaneously remove fluid and evaluate the condition of the pelvic organs.
At the same time, during the examination, doctors refer you for a blood test, general and biochemical urine analysis.
Doctors also need to establish the form of the pathology: anemic - the main symptom is bleeding; pseudoappendicular – the main symptom is pain; mixed - both signs are observed. During the examination, gynecologists determine the severity level by the volume of blood loss: mild, moderate, severe (above 500 ml).
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of ovarian cyst rupture is based on the following algorithm:
- collecting complaints and studying anamnesis;
- gynecological analysis;
- additional examination.
Among the additional examination methods for suspected apoplexy of an ovarian cyst, the following are used:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- blood test for hCG;
- biochemical blood screening;
- ultrasonography;
- puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix;
- diagnostic laparoscopy.
In a general blood test with a cyst, a decrease in hemoglobin and hematocrit levels is noted. In a general urine test, the protein level increases, and red blood cells may appear. A blood test for human chorionic gonadotropin allows you to exclude ectopic pregnancy and rupture of the fallopian tube - a pathological condition, the clinical picture is extremely similar to a ruptured ovarian cyst. Biochemical screening indicates damage to kidney function.
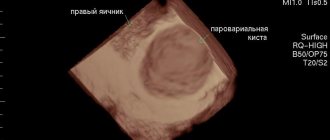
Using an ultrasound examination, the doctor can see the accumulation of fluid in the pelvis. The doctor will also notice that one of the ovaries is enlarged in size, this will make it possible to suspect a cyst. In order for OMT ultrasound to provide more information, it is recommended to perform it transvaginally. In this case, the gynecologist can much better assess the condition of the female genital organs, in particular the damaged ovary.
Puncture of the posterior vaginal vault is a minimally invasive manipulation that is necessary to examine the contents of the pelvic cavity. The procedure is performed in a manipulation room, with strict adherence to the rules of asepsis and antiseptics. In emergency cases, the puncture is performed without prior preparation. If necessary, the woman should empty her bladder and rectum. Since the procedure is quite painful, it is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia.
The patient is placed in a gynecological chair, and the external genitalia are treated with an antiseptic solution. The cervix is shifted towards the pubis, and the posterior vaginal vault is stretched. Then the gynecologist makes a puncture and sucks out the contents of the pelvic cavity using a syringe. The resulting liquid is sent to the laboratory for testing. As a rule, the doctor is able to obtain blood, which confirms the fact of internal bleeding. However, with a pronounced adhesive process in the pelvis, provided that the adhesions impede the free flow of blood, the procedure may not be informative.
Diagnostic laparoscopy is an endoscopic examination that allows you to directly examine the pelvic and abdominal organs and see the ruptured cyst. Instruments are inserted into the body through small punctures in the anterior abdominal wall, after which the abdominal cavity is filled with a special gas, and the doctor begins the examination. Using magnifying optics, a gynecologist can examine the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries in detail, assess the contents of the pelvic cavity and draw final conclusions about the woman’s health. The manipulation is carried out only under general anesthesia.
Treatment of cyst rupture. What to do?
If the rupture of the ovarian cyst is minor, for example, the contents of the tumor were small or the affected area was minimal, conservative treatment is possible.
After laparoscopy, it is possible to eliminate the contents of the cyst from the peritoneal space, and with the help of micro-instruments, remove the neoplasm tissue.
For mild pathology, gynecologists prescribe strict bed rest in the hospital and medication:
- Antispasmodics;
- Hemostatic;
- Anti-inflammatory;
- Painkillers.
Nurses administer medications intravenously, intramuscularly, and also prescribe tablets and capsules to patients. If a hormone imbalance is diagnosed, specialists provide hormonal therapy. Additionally, physiotherapists are involved, who organize a course that promotes the restoration of the body. At the same stage, doctors prescribe vitamin complexes.
Surgical treatment of ovarian cysts
If the degree of rupture is serious, gynecologists decide to perform surgery:
- Tubovariectomy – complete removal of the uterine appendage;
- Unilateral oophorectomy – removal of the ovary;
- Ovarian resection - excision of the affected tissue while preserving the ovary.
Typically, surgeons choose minimally invasive techniques: laparoscopy - through three punctures on the abdomen; laparotomy - through an incision in the lower abdomen. Doctors usually remove the uterus or ovary only in patients over childbearing age. In other cases, they try to preserve elements of the reproductive system.
After the operation, gynecologists prescribe conservative treatment, which is aimed at restoring hormonal balance and eliminating symptoms.
Treatment of the disease
Before prescribing therapy, the nature of apoplexy is established. Experts divide it into the following types:
- Painful. It is caused by severe pain in the lower abdomen, the presence of blood loss, and its detection in the abdominal cavity. The doctor will prescribe conservative treatment for this type.
- Hemorrhagic appearance. It produces severe hemorrhages and vascular damage. Hemorrhagic apoplexy is treated with surgery.
- Mixed look. Therapy is carried out exclusively surgically.
When the cyst ruptures and there is minor hemorrhage, the symptoms are mild, which is why patients often do not take the problem seriously and refuse surgical treatment. However, the best option for eliminating apoplexy is urgent surgery.
If you choose therapeutic treatment instead of surgical treatment, there is a possibility of formation of adhesions of the fallopian tubes, which in 40% of cases provokes infertility in the patient. Additionally, relapse of apoplexy often occurs during therapeutic treatment.
If a specialist determines a rupture of a cyst on the right or opposite ovary with complications, the patient requires qualified assistance with mandatory hospitalization. Therapy for apoplexy includes:
- Medication course.
- Monitor vital signs (pressure, pulse, etc.).
- Taking a blood test to track the red blood cells in your blood.
If repeated hemorrhage is detected, the attending physician prescribes laparoscopy. The essence of the operation is that the patient is placed under general anesthesia, and the surgeon makes small incisions on the abdomen. Through them, with the help of special instruments, bleeding is stopped, and fluids and blood clots formed as a result of the rupture are removed. The specialist then removes the cyst. In severe cases of apoplexy, when it is no longer possible to save the ovary, it can also be removed.
Consequences of a breakup
The most beneficial consequence for the body is the development of anemia as a result of blood loss. The problem is solved by restorative conservative treatment. It is also possible that adhesions may appear in the fallopian tubes and other organs due to the insertion of a laparoscope. In this case, after simple surgical operations, the body returns to normal.
If the cyst is large, the most common consequence is acute peritonitis, an inflammatory process of all organs of the peritoneum. No less dangerous complications are also possible:
- hemorrhagic shock;
- infertility if the ovary is severely affected;
- sepsis when cyst secretion enters the bloodstream.
In 25% of cases, due to late access to doctors, sepsis or hemorrhagic shock lead to death.
Types of cysts
A cyst is a benign formation in the ovary, shaped like a bubble and filled with liquid or jelly-like contents. It appears from the follicle, which matures in the tissues and is filled with secretions. Some cysts do not change in size and resolve over time, while others continue to grow and may eventually rupture.
Ovarian cysts are one of the most common diseases of the reproductive system. With the onset of menopause, the risk of such formations decreases.
Cysts themselves do not pose any threat to health. And if the size of the bubble is small enough and does not increase over time, most doctors opt for routine observation. Concerns arise from large cysts, which can burst and lead to dangerous consequences for a woman’s health.
The formations can be either very small (2-7 mm) or quite large, reaching a diameter of 10 and sometimes 20 cm. Depending on the size and contents, cysts are divided into several types:
- Follicular (functional) - usually occurs without any noticeable symptoms. As a rule, this is a small formation that does not grow and goes away on its own over time. Formed when there are deviations in a woman’s hormonal background.
- Corpus luteum cyst (hemorrhagic) is a follicular type of cyst. Appears in the second half of the menstrual cycle due to disruptions in the endocrine system. After a failed conception, hemorrhage occurs at the site of the corpus luteum and a cavity is formed.
The size of this cyst is about 5-8 cm. It is most common in women aged 16 to 45 years.
- Endometrioid is a formation that consists of the endometrium, the inner layer of the uterus, and is filled inside with blood clots. Often such cysts are bilateral and can grow up to 20 cm in diameter.
- Mucinous - a bubble consisting of a thick transparent gel-like content - mucin. Its walls are capable of stretching, which is why the formation can reach enormous sizes and consist of several chambers. This type of cyst is the most dangerous for a woman’s health, as it can develop into a malignant tumor.
- Paraovarian – located on the fallopian tubes. Its diameter ranges from 12 to 20 cm. It can grow to such large sizes that it begins to imitate a belly, as during pregnancy. Most often it occurs in young women aged 20-30 years.
- Dermoid is a congenital type of pathology that occurs when fetal development is disrupted. Contains cartilage, hair tissue, nails, bones and teeth. The size of this cyst can reach 15 cm. Very rarely it develops into a malignant tumor.
- Thecal lutein cyst is a cyst that occurs in the early stages of pregnancy. Appears due to malfunction of the corpus luteum and insufficient amounts of hormones. Rarely seen.
Photo source: shutterstock.com
Prevention of ovarian cysts
Prevention of cysts and ovarian cysts includes:
- Healthy lifestyle (proper nutrition, absence of bad habits, regular physical activity).
- The use of contraceptive methods to avoid unwanted pregnancy and, as a consequence, abortion.
- Normalization of weight.
- Timely treatment of gynecological and other inflammatory diseases.
If your menstrual cycle is irregular, you should contact a gynecologist as soon as possible. Regular preventive examinations are also important - at least 1-2 times a year.
Leading specialists in the treatment of paraovarian cysts in the North Caucasus
Ermolaeva Elvira Kadirovna A well-known and recognized specialist in the treatment of paraovarian cysts in the North Caucasus. An experienced ultrasound diagnostic doctor. Desperate and frightened girls and women turn to her.
Ermolaev Oleg Yurievich Candidate of Medical Sciences, gynecologist-endocrinologist with 25 years of successful experience. Experienced ultrasound doctor.
Shchepkin Petr Sergeevich Gynecologist, specialist in the diagnosis and treatment of paraovarian cysts. Experienced ultrasound doctor.
More information about experienced gynecologists
| INTERNATIONAL RECOGNITION of the reputation and achievements of the Women's Health Resort Clinic in the development and implementation of effective and safe treatment methods and the quality of medical services provided is the AWARDING of the Women's Health Resort Clinic in Pyatigorsk with the SIQS International QUALITY CERTIFICATE in the field of medicine and healthcare. International Socratic Committee, Oxford, UK and Swiss Institute for Quality Standards, Zurich, SWITZERLAND. |
We work seven days a week and on holidays:
Monday - Friday from 8.00 to 20.00, Saturday, Sunday, holidays from 8.00 to 17.00.
Treatment of paraovarian cysts by appointment by multi-line phone 8 (800) 500-52-74 (toll-free within Russia), or +7.
| ONLINE information about the treatment of paraovarian cysts in Pyatigorsk can be found at REGISTER ONLINE for treatment of paraovarian cyst here. REGISTER online for treatment of paraovarian cyst here. |
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
We accept girls, young women and women from all cities of Russia, near and far abroad.
We are at your FULL DISPOSAL if you have any doubts or wishes.