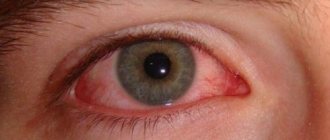
Visual fatigue syndrome (“Chronic eye fatigue”) is one of those conditions that can exist for a long time, causing discomfort in a person and gradually leading to serious visual impairment.
Fatigue that quickly sets in during visual work has a medical name - “asthenopia”. Eye fatigue is not an independent disease; it is a borderline condition, the consequences of which in the form of decreased visual acuity can be avoided with the right approach and timely prevention.
Asthenopia (visual fatigue)
“Our eyes are tired,” we say when we read for too long, or work at the computer, or repair our watches, or sew. This is usually followed by a gesture that, again, is familiar to everyone: rub the inner corners of the eyes with the tips of the index and thumb (the physiological meaning of this instinctive gesture is to stimulate blood circulation and eliminate mechanical stagnation). However, the eyes can get tired after four hours of continuous concentration, or after ten minutes. In the latter case, they talk about rapid fatigue of the visual system, or asthenopia (the well-known cognate word “asthenia” translated from Greek means “lack of strength”; asthenopia, accordingly, is “powerlessness of the eyes”).
Delfanto® capsules - a modern way to get rid of eye fatigue
If your eyes are dry from the computer, exercises to relieve eye fatigue and improve blood circulation can be combined with the use of special medications, for example, drops. An alternative is Delfanto® capsules for oral administration, based on Aristotelia Chilensis extract (MaquiBright®).
The active ingredient contains at least 35% polyphenolic anthocyanins, which help eliminate the effects of oxidative stress. It is known for its damaging effect on the cellular structures of the cornea. The antioxidants present in Delphanto® quickly spread through the bloodstream and have a complex effect:
- restore lacrimal gland cells damaged by free radicals;
- normalize the functions of the lacrimal glands;
- increase the production of your own tears.
It is enough to take 1-2 Delfanto® capsules a day to forget about visual fatigue and dry cornea. The first positive changes will be noticeable within 2 weeks after the start of the course. The recommended course of treatment is 4 weeks.
Symptoms of asthenopia
As a rule, patients with asthenopic syndrome complain of heaviness, pain, tension, double vision, increased lacrimation, an irresistible desire to close the eyes, noticeable redness of the sclera, inability to concentrate the gaze at a close distance; the most eloquent (or simply prone to introspection) also talk about a sharp decrease in general mental performance, an increase in the number of “careless errors,” headaches, creeping drowsiness, “sand” or a foreign body in tired eyes. With all the variety of symptoms, these uncomfortable sensations in various combinations always arise as a result of more or less prolonged visual concentration - otherwise one has to think not about asthenopia, but about some other ophthalmopathology that manifests similar manifestations.
Speaking about the most tiring loads for the eyes, one cannot help but refer to statistical data, known and understood by many, as they say, from their own experience: sadly, working on computer monitors (even the most modern and “safe for the eyes”) is still exhausts the visual system faster than any other work. Among the sad leaders in this list, driving a car at night is also mentioned (which is easily explained, given the highest concentration of visual attention and the sharp, traumatic contrast between absolute darkness and the blinding headlights of cars oncoming or reflected in the mirror); then comes reading, and only after this comes the actual professional types of “visual” activities, such as text proofreading, sewing, radio editing, etc.
Reasons for appearance
At the first warning signs, it is necessary to eliminate or at least minimize the factors that led to eye fatigue. This can be either one reason or a whole complex of them. It is important to understand that any visual stress is already a prerequisite for asthenopia. The following causes of eye fatigue have the most negative impact on the organs of vision:
- long-term work with a computer, tablet or smartphone, especially if the font on the screen is small;
- watching TV for a long time. The greatest fatigue occurs when watching movies and programs with 3D glasses;
- long (more than 3-4 hours) reading of paper and electronic books, printed media, especially with small print and in uncomfortable conditions, for example, in moving vehicles;
- incorrectly selected glasses. If, after putting them on, you feel discomfort, headache and dizziness, you should consult an ophthalmologist;
- poor workplace lighting. In addition to the main light source, it is necessary to use background lighting, ideally LED bulbs. It is advisable to place the desktop next to the window;
- insufficient air humidity in the room. Staying in such conditions for many hours leads to the development of dry eye syndrome. At the same time, the protective tear film of the visual organs becomes thinner, which causes discomfort and fatigue of the visual organs;
- work requiring long-term concentration;
- driving a car for a long time, especially in bright sunlight, at night, in snowy weather, in extreme conditions.
Aggravating and provoking factors can also be:
- high or low blood pressure;
- increased intracranial or intraocular pressure;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- headaches, migraines;
- hormonal imbalance, diseases of the endocrine system;
- osteochondrosis;
- malnutrition of the visual organ associated with poor nutrition of the body;
- farsightedness, nearsightedness and astigmatism;
- age-related changes in the body.
Types of asthenopia
Despite the apparent “simplicity” of such a phenomenon as eye fatigue, it is by no means, firstly, harmless, and secondly, simple. Asthenopia (like any other local “powerlessness” in the body) can be based on various, including quite serious, reasons. Thus, according to the etiological, causal principle, several variants of asthenopia are distinguished.
Accommodative asthenopia
An increased load on the eyes is any refractive error, be it myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism, presbyopia, which a person does not consider necessary to correct with glasses or lenses. In such cases, the visual system reflexively, regardless of consciousness, overstrains itself in an attempt to ensure the maximum possible visual adaptation to the environment. This evolutionary mechanism was formed in those times when the life of a given individual literally depended on the vigilance, attentiveness and “resolving power” of the eyes. Therefore, the ciliary (“ciliary”) body, which performs several functions in the eyeball, including accommodation, will in any case be excessively strained or, conversely, stretched in order to give the lens the necessary curvature of the surface, i.e. the refractive power required for a given case.
If the focal point, despite all efforts, still ends up behind, in front of or to the side of the macular region of the retina (or there is no single focus at all, as happens with astigmatism), the ciliary muscle still does not give up its attempts to accommodate and adjust vision at the required distance. Obviously, such a regime is completely anomalous for the delicate ocular biomechanics; overload will increasingly deplete muscle fibers, leading to increased concentrations of lactic acid (“fatigue hormone”) and the development of asthenopic symptoms.
Accommodative asthenopia often manifests itself at school age, which is due to a combination of a number of unfavorable factors for the eyes: rapid growth of the body, hormonal instability and endocrine changes, traditional school overload, passion (sometimes manic) for TV or computer games, lack of sleep, etc. This pathogenic combination is well known, but is not always taken into account by parents when organizing the child’s study, recreation, physical and mental activity regime. In fact, have all parents tried to at least approximately track how many hours a day the child spends almost motionless, peering at the small screen of a smartphone?
The most favorable, but, unfortunately, far from guaranteed outcome may be a spontaneous reduction of asthenopia with further growth and formation of the eyeball, as well as strengthening of the accommodating muscles.
In adulthood (usually after 40 years), even against the background of normative visual acuity, ocular weakness and fatigue may be accompanied by the initial stage of presbyopia, i.e. farsightedness due to age-related weakening of the ciliary muscle. In such cases, asthenopia progresses in parallel with the worsening of farsightedness.
A person may not immediately notice rapid visual fatigue, but gradually the problem becomes too obvious to ignore. Needless to say, this kind of symptom complex requires, at a minimum, an examination and consultation with an ophthalmologist, and you should contact it as early as possible.
Patients with suspected accommodative asthenopia must undergo visimetry - a thorough measurement of visual acuity and refractive parameters of the eye. For this purpose, special diagnostic glasses with a set of replaceable lenses are used, and mydriatic drops are instilled into the eyes, providing cyclopegia (essentially artificial paralysis of the accommodating muscle in its extremely relaxed state) and pupil dilation.
If the doctor establishes a clear connection between asthenopic symptoms and existing ametropia (refractive error), i.e. the accommodative nature of asthenopia will be confirmed, the first and most important therapeutic step is the appointment of optical correction - glasses or contact lenses - without which any further steps will be meaningless. As a rule, constant wearing of glasses is prescribed in childhood or adolescence; for adults, provided the acuity of “distant” vision is relatively preserved, glasses can be selected for reading or for working with small objects at a short distance.
In addition, a patient with this type of visual fatigue is strongly advised to pay attention to how his usual working day is organized; how long do intensive loads on the visual system alternate and with what? how the workplace is lit; how many hours a day are devoted to rest and how much, in particular, to sleep; whether there is activity in his life that can be considered generally strengthening (amateur sports, tourism, summer cottage, etc.). It is impossible to imagine a situation where all these factors cannot be optimized in principle: even basic eye gymnastics, taking just a few minutes, can radically relieve eyes that have become petrified in constant tension.
Any doctor knows the latent (and sometimes openly manifested) irritation that such “banal” and “primitive” recommendations cause in many patients: unfortunately, we often prefer to believe in expensive imported tablets or drops, although much better and longer lasting ( and most importantly, an effect that is natural for the eyes) could be achieved by overcoming elementary laziness and thinking about what our vision will be like in three, five or ten years.
Muscular asthenopia
The muscular variant of asthenopia, as the name suggests, is associated with dysfunction of the muscular system of the eyeball; in this case we mean not internal accommodating, but external oculomotor muscles, which ensure rotation of the eye in all planes.
If a myopic person does not resort to optical correction, relatively successful functioning of the visual system at close distances can be achieved at the cost of excess convergence: the eyes, when the oculomotor frame is tense, are reduced to the bridge of the nose. With normal vision, focusing is achieved by the effort of the ciliary muscle and an increase in the curvature of the lens; with myopia, the accommodating muscle is relaxed, and stereoscopic (3D) vision is ensured precisely by convergence. This is especially true for those cases where the degree of myopia in the right and left eyes is different: to form a binocular image, the brain “requires” an equally clear signal from both retinas. The development of the asthenopic symptom complex is thus caused by a discrepancy between the degree of tension of the accommodative and oculomotor muscle systems.
It is also possible to develop heterophoria, or latent (hidden, implicit) strabismus. This variant of strabismus is not noticeable with open eyes, but if one of them is closed, it turns out that the axis of the open eye is still directed straight, while the axis of the closed eye deviates, i.e. leans to the side. This ophthalmopathological phenomenon is due to the uneven development and different functional state of the oculomotor muscles. The fact is that the “rotary” system, fused with the outer surface of the eyeball, consists of six separate muscles, and if some of them are more developed than others, the rest have to overexert themselves to compensate for this difference in strength. Accordingly, constant excess tension inevitably depletes muscle tissue and leads to asthenopic symptoms.
Closing the eye relieves excess tension, the extraocular muscles (including the weaker and, therefore, more tired ones) relax, and the rotation of the closed eye may be inconsistent with the movement or gaze of the open one. It should be noted that heterophoria is not a condition that can be dismissed with disdain; with long-term existence of hidden strabismus, true strabismus easily develops.
The therapeutic strategy for muscular (as well as for accommodative) asthenopia includes, as a first-priority measure, optical correction of myopia. If latent strabismus is detected, the best and most effective remedy is a system of eye training exercises. For these purposes, special devices have been developed and used. Often, for example, synoptophore training is prescribed; the principle of its operation is the separate presentation of two images to the right and left eyes - a person, observing these images through the eyepieces, must, through an effort of will, merge them into a single visual image, which can only be ensured by coordinated tension (and therefore training) of the oculomotor muscular system . Such trainings are prescribed in the form of a more or less long series; if necessary, a repeated course can be prescribed, which in most cases makes it possible to achieve pronounced and stable therapeutic success: strabismus is gradually reduced. If the desired result is not achieved, the ophthalmologist calculates and prescribes special glasses with prismatic curvature, which, even with deviation of one of the eyes, allow you to see quite well without overworking the eye muscles.
Asthenic asthenopia
Eye fatigue can be a consequence and one of the manifestations of systemic asthenia - general exhaustion, weakening, "weakening" of the body - which manifests itself in a wide range of mental and physiological disorders. Asthenopia as part of a general asthenic symptom complex occurs, as a rule, after suffering systemic diseases, severe infections, various intoxications, as well as due to chronic physical or intellectual fatigue or an unhealthy regime of workload and rest. From here the necessary response measures naturally follow: massive restorative therapy, rationalization and normalization of the daily routine, vitamin therapy, and, if possible, long-term rehabilitation and restorative rest (for example, sanatorium treatment). But the first and mandatory step is to treat the underlying asthenic pathology, if any.
Symptomatic asthenopia
Asthenopia of the symptomatic type is a local reaction to infectious and inflammatory diseases of the eye and adjacent organs (ear, nasopharynx, oral cavity, etc.). Often, visual fatigue is one of the earliest symptoms of incipient inflammation of the intraocular structures, which also involves the ciliary body. With symptomatic asthenopia, high-quality diagnosis (if necessary, with the involvement of related specialists), localization of the inflammatory focus and its adequate treatment are crucial.
Nervous asthenopia
If all the reasons described above are reliably and reliably excluded, all that remains is to assume the psychogenic origin of eye fatigue. Indeed, in certain forms of neurotic disorders and personality anomalies (primarily neurasthenic and hysterical types), asthenopia is one of the components of the general neurotic syndrome. Obviously, in such cases, etiopathogenetic (aimed at eliminating the causes) therapy should be provided by a neuropsychiatric specialist.
If you notice signs of visual fatigue (asthenopia), contact the specialists of our ophthalmology center: modern equipment and extensive practical experience of doctors will help you quickly determine the cause and effectively eliminate the problem.
Correction of different degrees of farsightedness
When correcting hypermetropia, it is important to adhere to the wearing regime of glasses. In mild cases, not all patients wear them. As a rule, accommodative abilities are sufficient to compensate for the visual defect. With second degree farsightedness, glasses must be worn almost always. They are removed when reading. Severe forms of hyperopia require constant use of optics. At the same time, glasses with strong diopters cause dizziness and eye fatigue in many patients, so it is recommended to wear contact lenses.
If the optics are chosen correctly, all doctor’s recommendations for the treatment of asthenopia are followed, visual discomfort will not occur with eye strain. Although a complete cure for asthenopia requires a lot of time and effort.
Prevention of asthenopia
An attentive reader has long noticed that in descriptions of generally accepted therapeutic protocols (for almost any variant of asthenopia), optimization of the work and rest regime is most often mentioned. Of course, first of all, this applies to those types of activities that involve continuous, monotonous and intense visual load. Prevention measures are just as simple and just as effective: regular eye rest - at least once an hour, lasting at least ten minutes, preferably with your eyes closed or performing some simple relaxation exercises (for example, alternately shifting your gaze from nearby objects into the distance and back). A very important factor is the illumination of the working field: there should be enough light, but not too much, and, in addition, the sharp contrast between the local bright spot and the surrounding twilight is very harmful to the eyes. We should not forget about the optimal distance from the eyes to the object of visual concentration (at least 30-40 cm); It is with this in mind that work furniture should be selected and configured.
Finally, it is extremely necessary to organize good nutrition to ensure a sufficient amount of proteins, vitamins and microelements entering the body; A deficiency of these substances affects the state of the visual system no less (and in some cases more) detrimentally than the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, heart or brain. Therefore, in winter and especially in early spring, it is advisable to take a course of nutritional and vitamin complexes for the eyes prescribed by an ophthalmologist.
How to deal with fatigue? Basic methods
It is necessary to take care of prevention. It includes regular breaks when working at the computer, special exercises and vision correctors. Medicines are selected for chronic fatigue. Typically, local medications are used for these purposes, such as eye drops or ointments, which are divided into several groups:
- Moisturizing compositions . They compensate for dry mucous membranes and are suitable for the prevention and treatment of dry eye syndrome.
- Vasoconstrictor compounds . Eliminate redness and tissue swelling.
- Vitamins . Improve vision, enhance the performance of the visual organs. If your eyes get tired quickly, they may be lacking useful microelements.
The duration of treatment for eye fatigue depends on how severe the symptoms are and what stage of development the pathology is at. Therapy includes several areas at once.
Eye drops
The main medications to combat fatigue and discomfort are eye drops. They improve the condition of the mucous membrane during tension, reduce dryness and burning that appears at the end of the day. They can be used when wearing contact lenses.
A good option would be Gilan eye drops. The drug does not contain preservatives; it contains hyaluronic acid, which saturates the cornea with moisture and micronutrients. The drops relieve fatigue, help fight dryness and redness, and reduce pain and burning. When used regularly, they protect the mucous membrane from drying out. Suitable for children, pregnant women.
Before using drops, you must make sure there are no contraindications!
Gymnastics to prevent eye strain
Therapy may include exercises that relieve tension, reduce discomfort and fatigue, and relieve dry mucous membranes:
- Make circular movements with your eyes regularly, first 10 times in one direction, then 10 in the other.
- Keeping your head still, look to the left as much as possible, then in front of you, then move your gaze to the right. This needs to be done slowly, calmly. The exercise can be alternated with moving the eyes up and down.
- Squeeze and relax your eyelids 20 times, tensing your eye muscles.
- Blink about 50 times quickly to increase tear production.
- Place the paper on the window. Then, approaching the glass, focus your gaze on it, and then transfer it to an object in the distance.
- Massage your eyebrows with your index and ring fingers, placed at the beginning and end of the eyebrow arch.
- Don't forget exercises to warm up the upper shoulder girdle and neck: twists, bends or rotations.
Immediately after gymnastics, place tea bags or cotton wool soaked in a decoction of medicinal plants on your eyelids.
Eye masks for fatigue
Cooling gel masks for eye strain are an excellent choice. They are stored in the freezer and taken out at the right time to apply to the area around the eyelids. Thanks to the effects of cold, swelling is reduced, the skin is tightened and smoothed. In case of severe fatigue, the gel mask has a refreshing and invigorating effect and reduces stress on the visual organs.
An alternative to masks is a cooling cream. It affects the skin around the eyes, reduces the feeling of fatigue. This is a temporary help that only removes the symptoms, but does not eliminate the cause of the discomfort!
Fatigue glasses
Modern optics with special coating are great for working at a computer. It acts as a light filter, helps to distinguish colors more clearly, and enhances visual acuity. Thanks to this, reading from the monitor screen becomes more comfortable and your eyes get less tired.
To select suitable glasses, you should consult an ophthalmologist, who will evaluate the patient's vision. He will determine concomitant diseases, a tendency to farsightedness or myopia, and identify why the eyes get tired. Based on the results of the examination, the doctor will write a prescription, according to which you can order suitable glasses from the optician.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are suitable for home treatment. They can be used as a complement to primary therapy after consultation with a doctor.
The simplest recipe is used tea bags that can be applied to the eyelids. Green tea is best suited for these purposes, as it contains the most nutritional components.
Let us note a few more effective recipes that can be used at home.
Propolis on water
Propolis has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. To treat eye fatigue, an aqueous solution of propolis is used, which should be instilled onto the mucous membrane.
Chamomile compresses
Pharmacies sell ready-made bags of chamomile flowers. Brew two bags in 250 ml of boiling water and leave for a while. Cotton pads are moistened in the prepared decoction and applied to the eyes for 20 minutes. Chamomile has anti-inflammatory properties, so it will be useful not only for eye fatigue, but also for certain diseases. For example, with conjunctivitis.
Cornflower tincture
To prepare the tincture, you need to take a spoonful of cornflower flowers, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water over them, and leave them in a dark place for an hour. The prepared infusion should be filtered through cheesecloth. They need to wipe their eyelids twice a day. You can gently rinse your eyes.
What is the tear film and why is it necessary?
The tear film is a liquid, constantly renewed biostructure, which is part of the ocular surface, covers the cornea and performs important functions for the life of the eyes: optical, protective, immune, respiratory and nutritional.
The tear film is necessary for the proper, full functioning of the eyeball. Structurally, it is heterogeneous and consists of three layers. The tear film also has a very complex chemical composition, including water, numerous nutrients and special protective substances, all the necessary and balanced components for the normal functioning of the anterior surface of the eye. It also provides support for local immunity, antibacterial and respiratory functions. The tear film, leveling the surface of the cornea, provides its optical function and is a refractive medium, while having on its surface at the border with the air the highest refractive power of the order of 60D. In this regard, even minor disturbances in the tear film can greatly reduce visual acuity.
The amount of basic tear secretion per day is up to 2 ml, while the tear film has nothing in common with the tear produced by the lacrimal gland in a reflex state.
Need to know! The lacrimal gland provides only reflex lacrimation only for a protective purpose in response to physical or other irritation of reflexogenic zones (foreign body, volatile chemicals, thermal effects), as well as due to a psycho-emotional response.
The lacrimal gland is capable of secreting up to 30 ml of tears per minute, depending on the intensity of the irritating agent. Its secretion has a higher osmolarity and therefore moderately irritates the ocular surface and cannot replace the tear film.
Mucin layer of the tear film
The mucin layer is produced by goblet and granule cells, glands of Manz (limb) and crypts of Henle.
A gel consisting of mucin forms a smooth surface of the epithelium, facilitates the sliding of the eyelids along the cornea, cleanses and moisturizes the epithelium, and imparts hydrophilic properties to the epithelium.
The mucin layer makes up only 0.5% of the total thickness of the tear film. Its main task is to impart hydrophilic properties and adhesive ability to the primarily hydrophobic corneal epithelium. It is for this reason that the tear is held quite firmly on the cornea. In addition, mucin smoothes out all micro-irregularities of the epithelial surface and gives the cornea its characteristic mirror shine.
Aqueous layer of the tear film
The aqueous layer is the most prominent, produced primarily by the tear glands (95% of the aqueous component of the tear film), with the additional glands of Krause and Wolfring producing the remaining 5%. The aqueous layer consists of water-soluble electrolytes and organic low-molecular and high-molecular substances. Continuously updating, this layer ensures, on the one hand, the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the epithelium of the cornea and conjunctiva, and on the other, the removal of carbon dioxide, metabolic products and exfoliated epithelial cells.
Lipid layer of the tear film
The lipid layer is produced by the Meibom glands located in the upper and lower eyelids. Normal meibomian gland secretion is formed from unsaturated fats, and its oleic acid content determines its melting point. When the amount of oleic acid decreases, the secretion hardens (compacts) due to an increase in the melting point of lipids and normal body temperature becomes insufficient to maintain lipids in a liquid state. Under the influence of body temperature, the meibomian glands become denser, causing secondary blockage of the excretory ducts, which leads to inflammation. The lipid layer prevents excess evaporation of the aqueous layer and gives the outer surface of the tear film a smooth appearance.