Red eye syndrome
- a condition that is characterized by redness of the ocular surface and signals inflammation of the anterior segment of the eye.
Red eye is a symptom of various infectious and non-infectious ophthalmological diseases. The syndrome occurs due to excessive expansion and filling with blood of small blood vessels that are located in the conjunctiva or sclera of the eye and are responsible for its nutrition. Redness is manifested by an increased vascular pattern on the ocular surface.
This condition may be accompanied by:
- yellow, green, white, or brown discharge from the eye;
- increased sensitivity to light;
- swelling of the eyelid;
- profuse lacrimation;
- pain in or around the eye, etc.
Symptoms of red eye syndrome
In addition to the main symptom - hyperemia of the skin or mucous membrane of the eye, there may be symptoms such as: pain in the eyes (aching or cutting), swelling of the eye tissue, itching, a “feeling of sand” in the eyes, lacrimation, photophobia, blurred vision. Discharge from the eyes during red eye syndrome is one of the most important criteria in the correct diagnosis of diseases. The nature of the discharge is mucous, purulent, foamy, copious, the color is yellow, green, whitish, helps to establish the cause of the disease.
The most common factors for tear film disruption are:
- menopause,
- endocrine ophthalmopathy,
- pregnancy,
- kidney pathology,
- exhaustion of the body,
- chronic fatigue syndrome,
- infectious diseases,
- skin diseases,
- other systemic and chronic diseases.
Also eye diseases:
- lagophthalmos,
- chronic diseases of the conjunctiva / eyelids / cornea,
- dysfunction of the lacrimal gland.
Dry eye syndrome can be aggravated/manifested by wearing soft contact lenses and laser vision correction.
Important
Separately, it is worth mentioning the course of the disease in Cicatricial Pemphigoid and Sjögren's syndrome (Sjögren), in which DES is particularly pronounced and leads to serious complications.
Most of the population is susceptible to DES to varying degrees. For some people, DES is uncomfortable, for others it is not. There are cases when the patient does not notice discomfort, although there are manifestations of dry eye syndrome in the eye. Dry Eye syndrome worsens in the autumn-winter period. Prevention methods
- Prevention of dry eye syndrome comes down to humidifying the air in the room where you spend most of the time, correct vision correction, work breaks during prolonged visual stress, and treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases, if any.
- Treatment uses tear replacement drugs that lead to stabilization of the tear film.
- Complaints with dry eye syndrome are very similar to complaints with chronic conjunctivitis, blepharitis and ametropia (insufficient vision correction), but the drugs prescribed are different.
Diseases manifested by red eye syndrome
- Acute inflammatory diseases of the eyelids, lacrimal organs and orbital tissues (edema of the eyelids, blepharitis, barley, chalazion, eyelid abscess, acute dacryoadenitis, acute dacryocystitis, orbital phlegmon, lacrimal sac phlegmon).
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye and cornea (conjunctivitis, keratitis).
- Inflammation of the membranes of the eye itself (scleritis, episcleritis, iridocyclitis).
- Eye injuries (contusions, penetrating and non-penetrating wounds and eye burns).
For a correct and accurate diagnosis of the cause of red eye syndrome and successful treatment, it is necessary to promptly consult an ophthalmologist and strictly follow the recommendations of a specialist without self-medicating.
Causes of redness
From the very beginning, it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with other serious diseases accompanied by redness of the eye, among which are:
- Acute iritis;
- An attack of glaucoma;
- Corneal ulcer;
- Corneal injury;
- Scleritis;
- Episcleritis.
Bacterial inflammation of the conjunctiva can be caused by any of the widespread pathogens of purulent infection. Cocci, primarily staphylococci, are the most common cause of the development of infectious lesions of the conjunctiva (the course is favorable). The most dangerous pathogens are Pseudomonas aeruginosa and gonococcus, which cause severe acute conjunctivitis, which often causes damage to the cornea.
Why eyes turn red: common causes
Red eyes are an unpleasant symptom that often occurs when sleep patterns are not followed, as well as when blood pressure rises, a viral infection occurs, or a seasonal allergic reaction occurs. In addition, this situation can occur due to excessive physical stress. In this case, not only redness of the proteins is observed, but also small hemorrhages in the scleral area. As a rule, they do not pose a danger and go away on their own within 2-3 weeks.
The cause of changes in the color of the protein shell can also be traumatic damage to the organs of vision, for example, when foreign bodies enter them. In addition, eyes often turn red after excessive visual stress: prolonged work at the computer, driving at night, and other situations. When using contact vision correction products, redness of the sclera is also possible if the rules of care, wearing regimen and replacement schedule are not followed.
Typically, in the situations described above, the protein shell returns to its usual color after eliminating the main cause of irritation (virus, allergen, foreign body in the eye).
If a change in the color of the protein membrane occurs systematically, it is necessary to consult an ophthalmologist and undergo an examination of the visual organs to exclude or confirm the presence of inflammatory processes.
Why do the whites of the eyes turn red?
- Poor sleep patterns and chronic fatigue.
- The appearance of viral diseases (flu, acute respiratory infections).
- Mechanical damage to the cornea caused by a foreign body entering the eye.
- Seasonal allergic reaction.
- Increased visual load.
- Taking medications that reduce blood clotting.
- Failure to comply with the rules of care, wearing regimen and replacement schedule for contact correction products.
- Inflammatory processes in the eyes caused by various infections.
Diagnosis of red eyes
To establish an accurate diagnosis, a complete examination is required. After collecting anamnesis, a primary ophthalmological examination is performed, including:
- visual acuity test;
- assessment of the oculomotor system;
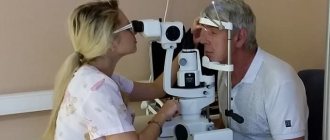
- slit lamp examination;
- eye pressure test;
- fundus examination.
Bacteriological analysis is carried out if an infectious disease is suspected. The composition of the tear film is determined using the Schirmer test - this is a test using special paper strips. Other diagnostic methods may be required: gonioscopy, ultrasound of the eye.
Treatment
Non-infectious and infectious forms of keratitis require long-term hospital treatment. On average, it takes from 2 to 4 weeks to completely restore the cornea and eliminate the causes of the disease. The basis of therapy is conservative methods, mainly drug treatment. The drugs are prescribed by an ophthalmologist; if necessary, specialists from other medical fields are involved in the process: phthisiatricians for tuberculous origin of keratitis, allergists and immunologists for non-infectious forms of the disease, venereologists for detection of specific microorganisms, etc.
What groups of drugs treat inflammation of the cornea:
for the viral form of keratitis - interferon preparations and acyclovir in the form of local instillations, placing ointments with acyclovir under the eyelid, oral administration of immunomodulators (Levamisole and its analogues);
- for bacterial forms of keratitis - instillation of drops into the eye, intraocular injections and antibiotics from the groups of penicillins, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, etc., and in severe cases - intravenous infusion of antibiotics;
- for tuberculous forms of keratitis - anti-tuberculosis chemical drugs orally and intramuscularly, therapy is carried out under the supervision of a phthisiatrician;
- for allergic inflammation - local and systemic antihistamines, instillation of hormonal agents;
- for specific bacterial inflammations of the cornea (if pathogens of syphilis and gonorrhea are detected) - specific antibiotics, selected taking into account the sensitivity of the microflora to them in the form of local agents, intravenous and intramuscular injections.
Regardless of the origin of inflammation, therapy is supplemented with drugs to accelerate epithelization and prevent complications:
- mydriatics (atropine and its derivatives, scopolamine) in the form of drops and ointments;
- preparations with taurine to accelerate corneal regeneration;
- local enzyme preparations for decreased visual acuity.
Surgical interventions are not performed for uncomplicated forms of inflammation of the cornea. They are resorted to in case of deepening of the pathological process and the appearance of ulcers and deep erosions on the surface of the cornea. Such neoplasms threaten not only a deterioration in visual acuity, but also damage to the outer shell of the eye, followed by leakage of the vitreous body and clouding of the lens.
If, after eliminating the acute inflammatory process, deep ulcers are discovered, the following types of operations are performed:
- Microdiathermocoagulation
is a microsurgical intervention using high-frequency currents. The method allows you to remove scar and necrotic tissue in the area of the most severe clouding of the cornea. After 5 days, the scab is rejected, and a cleared area of the cornea appears in its place. Complete healing occurs 2 weeks after surgery. - Laser coagulation
is a microsurgical effect on a corneal defect, which allows you to “evaporate” it layer by layer and simultaneously sanitize the tissue. Such an intervention also makes it possible to stimulate regenerative processes: full-fledged transparent corneas are formed at the site of the defect, rather than a scar. - Cryoapplication
is a localized, low-traumatic effect on an ulcerative defect with ultra-low temperatures. The technique is comparable in effectiveness to thermocoagulation with electric waves, but has a less pronounced coagulating effect. - Laser treatment
is a low-traumatic procedure for glaucoma and other diseases associated with decreased vision due to clouding of the lens. - Keratoplasty
is the restoration of the cornea with donor or artificial materials.
Removal (enucleation) of the eyeball is carried out in complicated and severe forms of keratitis, when the infectious process spreads to all the membranes of the eye, the vitreous body and intraocular structures. Such a complication can threaten the infection to penetrate the eye socket and then the brain, so the only correct solution is to radically eliminate the problem.
Why do my eyes turn red after using contact lenses?
Many people with refractive errors (farsightedness, myopia, etc.) prefer contact lenses. These optical products provide high quality not only central, but also lateral vision, which allows for the widest possible viewing angle. In addition, they do not restrict freedom of movement and do not compress the bridge of the nose, unlike glasses.
Patients often wonder why their eyes turn red in the evening when using lenses. This may be due to several factors. One of them is non-compliance with wearing optical products.
For example, continuous use of colored lenses for more than 4-5 hours causes oxygen starvation of the cornea. If you sleep with lenses worn during the day, you will experience dryness and redness in the morning. With prolonged use of correction products in rooms with excessively hot and dry air, a change in the color of the sclera is also observed due to drying out of the cornea. To eliminate this uncomfortable phenomenon, it is necessary to additionally use moisturizing drops.
Some believe that the eyes turn red in the evening due to an allergy to contact lenses. However, this is quite rare. As a rule, it is confused with individual intolerance to the components of a multifunctional solution. In this case, the care product should be replaced. Also, an allergic reaction may occur to protein and lipid deposits that accumulate over time on the surface of optical products with a long period of use. To avoid this, it is necessary to carry out enzymatic cleaning in a timely manner using special means. It is also important to maintain a replacement schedule for optical products. After their expiration date, they must be disposed of and replaced with a new pair.
Redness of the eyes is also observed when the cornea is damaged, which is associated with violation of the rules for wearing lenses. For example, this may occur if you wear cracked optics.
In this case, as a rule, the eye becomes very red, and pain and tearing are also observed. This indicates that you need to immediately remove the lenses and seek help from an ophthalmologist.
In addition, redness occurs when the parameters of optical products are incorrectly selected (diopters, curvature, etc.). You may need contact correction products with a higher level of oxygen permeability and moisture content. Patients with hypersensitive eyes are recommended to buy daily lenses. They are the safest and easiest to use.
Reasons why the whites of the eyes turn red when wearing lenses:
- Incorrect selection of contact correction products.
- Violation of the wearing regimen or replacement schedule for optical products.
- Lack of professional and systematic care for contact lenses.
- Individual intolerance to the components included in the optical care solution.
- An allergic reaction to deposits that accumulate over time on lenses with a long period of use.
- Mechanical damage to the cornea due to violation of the rules for using optical products.