Published: 10/22/2021 15:15:00 Updated: 10/25/2021
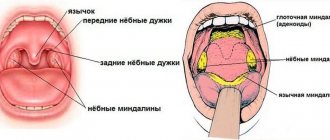
Sore throat is a disease of an infectious nature, manifested by acute inflammation of the lymphoid tissue of the pharynx. Most often the process affects the palatine tonsils, but other structures of the lymphadenoid pharyngeal ring can also be affected - the lingual and pharyngeal tonsils, lateral ridges or granules of the posterior pharyngeal wall.
The pathology in question is characterized by symptoms of intoxication, increased general temperature, sore throat that worsens during swallowing, enlarged and painful cervical lymph nodes. The palatine tonsils and arches are swollen, enlarged, bright red, and may have a white or dirty yellow coating.
Treatment of sore throat includes local treatment with antiseptics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotic therapy and detoxification measures. If complications develop or the process becomes chronic, surgical intervention may be required.
Causes of acute tonsillitis
A sore throat can be caused by a fungus or a virus, but most often the cause of the disease is bacteria. The most common variant is streptococcus. Quite often, sore throat is a complication of ARVI. In such situations, they usually talk about the addition of a bacterial infection.
Sore throat is transmitted by airborne droplets. Transmission of infection through household items is less common.
Most often, elderly people and children and people with weakened immune systems become infected. Why? Tonsils are organs that are part of the body's immune system. Their function is to protect the body from pathogenic bacteria. In fact, they are a kind of barrier that does not allow the “enemy” into the body. However, in cases with weakened immunity, the tonsils are not able to cope with the task and do not protect the body from pathogenic microflora. As a result, microorganisms attack the tonsils, causing them to become inflamed.
Sore throat can occur due to the following reasons:
- hypothermia, both of the throat and general;
- lack of vitamins;
- chronic tonsillitis is a sluggish inflammatory process in the tonsil area, which can result from untreated tonsillitis;
- poor air ecology - inhalation of polluted air in industries, etc.;
- foci of infection in the nasopharynx - caries, adenoids, sinusitis, etc.
Treatment
For proper treatment of sore throat, it is very important to correctly determine its causes. Several types of drugs are used in the process:
- Antipyretic.
- Antibacterial.
- Antiviral.
Only a doctor can prescribe a specific list of medications based on an analysis of the patient’s current condition. So, antibiotics and local medications are often used to treat herpes and purulent tonsillitis.
It is also important to create the right conditions for the patient. Isolation of the room with the patient, regular ventilation and wet cleaning of the room are indicated. You need to drink more water, food is consumed warm, brought to a puree state. In this case, the consumption of sour and spicy foods is contraindicated.
Complications
Sore throat is dangerous due to a large list of potential complications. These include phlegmon of the neck, bronchitis, otitis media, and laryngitis. If viral purulent tonsillitis is not treated, there is a high probability of a peritonsillar abscess.
There is also a list of general complications. These include:
- Severe inflammatory process in the kidneys.
- Lesions of the joints and heart of a rheumatic nature.
- Sepsis.
- Inflammation of the membranes of the brain.
There is also a great danger that the patient will experience infectious-toxic shock. It develops against the background of poisoning of the body by waste products of microorganisms.
Prevention
Anyone can get tonsillitis. Among the preventive methods are the following:
- Strengthening immunity.
- Control of personal hygiene.
- A varied, balanced diet.
- Insulation, avoiding hypothermia.
- Quitting bad habits - smoking, alcoholism.
Tonsillitis can also develop against the background of other diseases. These include such as pharyngitis, otitis media, caries and sinusitis. If you have such diseases, they need to be treated and not transferred to the chronic stage.
Share the article on social networks:
Types of sore throat
Sore throat differs in the degree of damage to the tonsils:
- catarrhal - the easiest option, in this case the inflammatory process affects only the mucous membrane, the tonsils are swollen and bright red
- lacunar – damage to the canals of the tonsils (lacuna), the tonsils are covered with a characteristic white coating;
- follicular - follicles are formed in the tonsils, which are filled with pus;
- combined - a severe form of tonsillitis, when both lacunae and follicles are affected on the tonsils.
Symptoms of a sore throat
Sore throat is an acute infection, and therefore the onset of the disease is rapid. Typical symptoms are:
- temperature rise to 38 degrees and above, depending on the type of disease;
- chills;
- malaise and weakness;
- headache;
- redness of the throat with catarrhal tonsillitis and the appearance of a white coating with lacunar, ulcers with follicular;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- the appearance of bad breath.
The first four symptoms are quite typical for influenza and ARVI, but a sore throat is characterized by a severe sore throat. It is pain, and not soreness, which is more typical of pharyngitis or ARVI. It hurts not only to swallow food, but also to simply swallow.
Angina
Angina
Sore throat is an infectious disease that develops acutely and begins with inflammation of the palatine tonsils (most often), as well as the lingual, laryngeal and nasopharyngeal tonsils. Then, due to intoxication, general symptoms of the disease develop and a high body temperature (38-41 C) occurs. Prevalence of the disease
Sore throat most often affects children of preschool and school age and adults under 35-40 years of age, especially in the autumn and spring periods.
Etiopathogenesis (why and how tonsillitis occurs)
Initially, against the background of hypothermia, infection (contamination) of the tonsils occurs with various microorganisms (staphylococcus, streptococcus, pneumococcus). Infection can be from one’s own microbes (caries, chronic tonsillitis) or from outside (airborne and foodborne routes). Multiplying microbes release toxins that enter the blood and cause intoxication (weakness, loss of appetite, high fever).
Symptoms of a sore throat
Main symptoms: headache, sore throat, joint pain, chills, weakness. The temperature during a sore throat reaches 38.5-40 degrees during the day. After 1-2 days, small white lesions (necrotic follicles) appear on the surface of the tonsils. This is follicular tonsillitis. The appearance of grayish-white purulent contents in the lacunae (folds of the tonsils) is a symptom of lacunar tonsillitis. Changes in the tonsils can be necrotic in nature - this is a purulent-necrotic form of tonsillitis.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of angina is not difficult; the main diagnostic technique for recognizing it is examination of the pharynx - pharyngoscopy, as well as assessment of complaints and medical history. It is necessary to make a differential diagnosis of lacunar tonsillitis and diphtheria of the pharynx, as well as catarrhal tonsillitis and acute pharyngitis. To clarify the diagnosis, swabs from the throat and nose for diphtheria and laboratory tests for hemolytic staphylococcus are used. During the course of the disease, it is necessary to monitor peripheral blood counts.
Treatment of sore throat
At the onset of the disease, it is necessary to observe bed rest (to reduce the possibility of developing complications - from the heart, kidneys, joints). Spicy, rough foods are excluded from the diet. It is recommended to drink plenty of warm drinks (milk with honey, tea with lemon), broth, liquid porridge, jelly (all from a separate container). Drug therapy involves the use of antibacterial drugs (selected on the basis of culture, or broad-spectrum antibiotics) and anti-inflammatory drugs, desensitizing drugs. A treatment regimen can only be prescribed by an experienced doctor after an examination. Self-medication can lead to undesirable outcomes. In the case of the development of phlegmonous tonsillitis, the first step is opening the abscess.
Concomitant therapy:
rinsing: various antibacterial solutions are used for rinsing. As antiseptics, use a 1% solution of iodinol for rinsing the throat, a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide, a 0.1% solution of potassium permanganate, a 2-4% solution of boric acid, a solution of bicarmine, 0.05-0 ,1% solution of rivanol, calendula tincture, aqueous solution of chlorhexidine and dioxidine; inhalations: for inhalation use decoctions of the following herbs - chamomile, eucalyptus, marigold flowers, Siberian elderberry, caragona mane (camel's tail), blueberry, etc.; compresses: it is recommended to use compresses locally, especially with enlarged regional lymph nodes. Apply a mixture of alcohol (100 ml), menthol (2.5 g), novocaine (1.5 g), anesthesin - menovazin (1.5 g) to the front of the neck, wrapping the neck with a scarf or scarf.
Prevention of sore throat
General and local hardening of the body is important: systematic physical education and sports, morning hygienic exercises, air baths, rubdowns and showers with gradually decreasing water temperature. In order to increase the resistance of the pharyngeal mucosa to cooling, local hardening is carried out - gargling with water of a gradually decreasing temperature (from warm to cold). It is necessary to remember the basic rules of hardening: gradualism, systematicity and taking into account individual characteristics. General UV irradiation contributes to increasing the protective properties of the body, especially in the autumn-winter period. Treatment of concomitant diseases of the oral cavity and nose. Carious teeth, sore gums, purulent lesions of the paranasal sinuses predispose to the development of sore throat. Various pathological conditions of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx that interfere with nasal breathing (deviated nasal septum, polyps, adenoids, hypertrophic rhinitis, etc.) force the patient to breathe through the mouth, and at the same time the mucous membrane of the oropharynx cools and dries out. Treatment of sore throats must begin as early as possible after diagnosis. In this case, it is possible to shorten the recovery time and reduce the likelihood of complications.
Doctors of OJSC CDC Euromedservice are ready to help you in the diagnosis and treatment of sore throats. It should also be noted that during the febrile period of sore throat it is necessary to observe bed rest. In this case, it is preferable to invite a doctor to your home rather than attend an outpatient appointment.
Sore throat without hyperthermia
There are also cases of atypical course of the disease. For example, at a slightly elevated temperature or even at normal temperature. As a rule, this happens in adults with catarrhal tonsillitis. In addition, people with acutely reduced immunity get sick without a rise in temperature. This applies to those diagnosed with cancer, hepatitis C, HIV, etc. The infection can also occur in older people.
Sore throat can occur at normal temperatures and in pregnant women, since hormonal changes in the body can also affect the activity of the immune system.
In such cases, a sore throat may be mistaken for a simple cold and not treated. However, this can be dangerous, since sore throat can cause serious complications and often becomes chronic.
A sore throat without fever can also be caused by a fungal infection. In this case, there are no other symptoms - pain when swallowing, headache and other discomfort. Symptoms include a cheesy coating on the tonsils, bad breath and dry mucous membranes.
Causes of sore throat
Most often, inflammation is caused by the activity of beta-hemolytic streptococcus group A. Among the possible causative agents of the disease are also adenovirus, staphylococci, pneumococci, parainfluenza virus, mycoplasma, chlamydia, rhinovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, spirochete, Epstein-Barr virus, diphtheria bacillus, enterovirus Coxsackie B, fungi.
The risk of developing a sore throat increases when exposed to the following factors:
- general or local hypothermia;
- weakened immunity due to acute respiratory infections;
- fungal diseases;
- chronic pathologies of the nasopharynx, difficulty in nasal breathing, purulent processes and inflammation in the paranasal sinuses;
- caries;
- systematic exposure to irritating substances on the body, work in a smoky or dusty room;
- increased air dryness;
- regular drinking of alcohol, smoking;
- acute and chronic intoxication;
- poor nutrition, lack of vitamins in the diet.
Actions for sore throat
If you notice the first symptoms of the disease, you should consult a doctor. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate or try to overcome the disease with folk remedies. Sore throat is a serious disease that is dangerous to joke with.
If a sore throat is not treated or acted incorrectly, a number of complications can occur:
- chronic tonsillitis - in this case you will remain with this disease for life;
- laryngitis or bronchitis;
- abscess;
- rheumatism of the heart or joints;
- glomerulonephritis;
- pyelonephritis.
For a sore throat, a specialist prescribes antibiotics depending on the clinical picture and individual characteristics of the patient. Gargling is also prescribed every hour to remove suppuration and inflammation. To do this, use herbal decoctions, salt with soda, furatsilin, chlorhexidine. Do not eat or drink for half an hour after rinsing.
In addition to rinsing, the tonsils are irrigated with antimicrobial agents. If the temperature rises above 38 degrees, antipyretics are taken. Children are recommended to use wraps to relieve fever.
Antihistamines will help relieve swelling, and special lozenges will reduce pain.
It is important to ensure you drink plenty of fluids. In this case, warm fruit drinks will be most useful.
Food during illness should be dietary, soft and warm, so as not to irritate a sore throat.
Contraindications for sore throat
Sore throat is a disease that cannot be carried on your feet. Even in cases where it occurs in a mild form. This can trigger the infection to become chronic or severe, and also contributes to complications.
If you feel better, you should not stop taking antibiotics. It is also not recommended to smoke or drink alcohol, as smoke and alcohol can irritate a sore throat. It is necessary to exclude fatty, spicy, sour and solid foods from the diet for the same reason - so as not to irritate the throat.
It is extremely important to completely cure the disease so that it does not become chronic. Otherwise, you will face the fact that the infection will torment you regularly.