A biochemistry test is taken when diagnosing various diseases, in the presence of abnormalities in a general blood test, as well as to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment process.
Blood drawings are carried out by experienced nurses in our clinic or at home. The finished results are automatically sent to the patient’s email within 1-2 days.
On a note! Blood is the basis of life. The slightest change in its composition is a consequence of deviations in the functioning of internal organs, metabolic systems, or is due to the influence of negative environmental factors (poor ecology, hazardous production). A doctor of any specialization, using this analysis in his practice, receives a reliable diagnostic tool.
Depending on the list of complaints and the general clinical picture, the doctor may prescribe both a standard set of “blood biochemistry” and the study of individual indicators.
What are antibodies? And how to decipher the results of the analysis?
Why do men and women need regular laboratory screening?
Because sometimes only a test can reveal a health problem. For example, the same infections can cause such different symptoms that it is not easy to suspect one pathogen. In men, pathogenic microorganisms may not manifest themselves at all, but for their wives they become very dangerous (a classic example is the human papillomavirus). Therefore, men and women need regular examinations, with different diagnostic approaches. The same applies to hormonal studies: both men and women are tested for testosterone, but the norms for this hormone differ by more than 10 times. And even classic basic studies: biochemical and general blood tests for men and women have their own nuances... A general blood test is the basis of any serious examination of the body’s condition. Therefore, a general (or clinical) blood test is prescribed for almost all complaints and diseases by doctors of all profiles. It is included in the examination standards for medical examinations, urgent and planned hospitalizations. Unlike the general one, a biochemical blood test makes it possible to assess the functions of specific human organs, as well as the presence and quantitative parameters of basic microelements and vitamins in the body. The general test standards for men and women are not the same; this also needs to be taken into account when interpreting. We provide test standards and a list of blood parameters in the order in which they are usually indicated on the laboratory test form.
Hormones
Blood for hormonal studies must be donated on an empty stomach in the morning. If this is not possible, blood can be donated for some hormones 4-5 hours after the last meal in the daytime and evening (except for those studies for which blood must be donated strictly in the morning).
1-2 days before the test, exclude high-fat foods from the diet; the last meal should not be large. 1 day before the study, psycho-emotional and physical comfort (calm state without overheating and hypothermia) is necessary.
• Thyroid hormones
When initially checking thyroid hormone levels, discontinue medications that affect thyroid function 2-4 weeks before the test. When monitoring treatment, exclude taking medications on the day of the study and be sure to note this on the referral form (also note information about taking other medications - aspirin, tranquilizers, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives).
• Sex hormones
In women of reproductive age, the results of hormonal studies are influenced by physiological factors associated with the stage of the menstrual cycle. During the examination for sex hormones, the phase of the menstrual cycle should be indicated. Hormones of the reproductive system must be taken strictly on the days of the cycle:
- LH, FSH - 3-5 days of the cycle;
- Estradiol - 5-7 or 21-23 days of the cycle;
- Progesterone - days 21-23 of the cycle.
- 17-OH-progesterone, DHA - sulfate, testosterone - days 7-9 of the cycle.
- Prolactin - donate blood in the morning at rest; before the study, exclude palpation of the mammary glands.
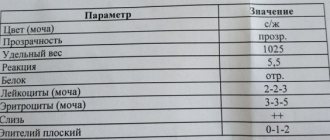
General tests: normal
Erythrocytes, or red blood cells, are the main transport vehicle for oxygen to tissues and organs. In a healthy body, the amount of the main protein of red blood cells, hemoglobin, varies from 13 to 18. It is this protein that attaches oxygen to itself. Deviations from the norm indicate a particular disease: a weakened immune system, a recent infection, or anemia. If a low level of hemoglobin is detected in the body, this is a reason for further examination. Elevated levels are extremely rare and usually indicate hematological diseases. If the level of red blood cells themselves is increased in the blood, then this may indicate pulmonary diseases, stressful situations, or heart disease:
- The norm of red blood cells in men and women is the same: 4.3-5.15 x 1012 cells/l;
- The hemoglobin norm in women is 120-140 g/l, and in men the hemoglobin norm is slightly higher: 135-160 g/l.
- In women, hemoglobin may decrease during pregnancy and with heavy menstruation.
Disturbed pigment metabolism
In the human body there are specifically colored proteins. These are peptides that contain a metal (for example, copper or iron). Such peptides include cytochrome, hemoglobin, myoglobin, etc. As a result of the breakdown of peptides, bilirubin and its fractions are formed.
Free bilirubin appears after the breakdown of red blood cells in the spleen. This bilirubin is very toxic, especially to the human brain. However, the body is not poisoned due to the rapid connection of free bilirubin with albumin. In liver diseases such as cirrhosis and hepatitis, the concentration of bilirubin in the body increases due to a decrease in the amount of albumin and the predominance of glucuronic acid.
Indirect bilirubin binds to this acid, which loses its toxicity. It then enters the bile and is converted into urobilinogen. This enzyme, in turn, penetrates through the small intestine into the blood and then into the kidneys. It is urobilinogen that colors urine yellow.
ESR: blood normal
The main role of IgG antibodies is the long-term protection of the body from most bacteria and viruses - although their production occurs more slowly, the response to an antigenic stimulus remains more stable than that of IgM class antibodies.
ESR stands for erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Laboratory assistants measure this parameter when introducing certain reagents.
The norm for ESR in women is up to 15 mm/h. In men, the rate is lower - up to 10 mm/h. High levels indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. Despite the fact that ESR is a nonspecific indicator, that is, it can indicate a whole range of diseases, it has remained an extremely popular and in-demand laboratory diagnostic method for several decades.
Alpha amylase
This enzyme is special. It breaks down complex carbohydrates into simpler compounds. Alpha amylase is concentrated in the salivary glands and pancreas. When examining blood, the doctor will definitely pay attention to the decrease and increase in the level of this enzyme.
Alpha-amylase exceeds the normal level in hepatitis, pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis, mumps, and renal failure.
A decrease in the level of the enzyme is observed with alcoholism, myocardial infarction, toxicosis during pregnancy, thyrotoxicosis, pancreatic necrosis, and taking steroid drugs.
Leukocyte formula: test norms
Leukocytes are white blood cells; they protect the body from viruses, bacteria, fungi, foreign agents and its own altered cells. Leukocytes come in several varieties: for example, monocytes are responsible for antifungal immunity (their increased level can also indicate infectious mononucleosis), neutrophils activate antibacterial immunity, and lymphocytes activate antiviral immunity.
The number of leukocytes is not as constant as, for example, the number of red blood cells. The level of white blood cells varies depending on the condition of the body, time of day, hormonal levels and other factors. It is best to take a test to determine the leukocyte formula in the morning on an empty stomach. You can only drink water before the test. At Lab4U you can take a general blood test with leukocyte count and ESR at any time convenient for you at the nearest medical center.
The quantitative and qualitative composition of lymphocytes allows a specialist to judge what the body is currently struggling with and suggest the dominant problem and the main cause of a particular condition. A general blood test may not contain a leukocyte formula, but if you want to find out the state of your immunity, it is better to do a general analysis with a leukocyte formula. As a rule, the blood standards for women and men in terms of the number of leukocytes are the same.
However, before the start of the menstrual cycle in women, the permissible norm of leukocytes increases by 2 times to 20 x 109/l - instead of the usual norm of 109/l.
An excess in the number of leukocytes indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body; its localization can be identified through a more detailed examination of the body. A decrease in the number of white blood cells in both men and women can be caused by autoimmune diseases - for example, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune thyroiditis, as well as malaria or salmonellosis.
Blood biochemistry: indications for testing
A diagnostic test is required in the following cases:
- The presence of persistent pain in patients in the head, back, muscles, joints, and so on.
- Frequent disruptions in the functioning of the digestive tract: dyspeptic syndrome, heaviness and bloating in the abdomen, belching, difficulty swallowing.
- Respiratory system disorders: shortness of breath, chronic cough syndrome, bronchospasm.
- Pathological symptoms from the cardiovascular system: hypo- or hypertension, chest pain, brady- or tachycardia, coldness of the extremities, heart rhythm disturbances.
- Problems with the urinary system: poly-, oligo- or anuria, nocturia, pain, cramps and other discomfort during urination.
- Weakening of the immune system and frequent ARVI.
- Reproductive function disorders: decreased libido, menstrual irregularities, infertility.
- Hormonal imbalances: constant feeling of thirst, hunger, cold or heat, sudden weight loss or spontaneous weight gain, drowsiness during the day and insomnia at night, dry skin, increased sweating, irritability, unreasonable attacks of panic or fear.
- Pregnancy. Expectant mothers are required to donate blood twice before the baby is born, in the first and third trimester.
Platelets: general norms
Platelets are blood cells that participate in blood clotting processes and prevent extensive blood loss.
General norms of platelets in men and women suggest the content of these cells in the blood in an amount of two hundred to four hundred thousand per microliter.
A smaller number indicates insufficient blood clotting and can be caused by blood diseases. An increased platelet count can indicate a number of diseases - from autoimmune pathologies to tuberculosis, enteritis and colitis. A deviation from the normal platelet content in one direction or another requires further detailed examination of the blood coagulation system - a coagulogram.
| Analysis indicator | Norm | |
| Men | Women | |
| Hemoglobin | 130-170 g/l | 120-150 g/l |
| Red blood cells | 4.0-5.0 x 1012/l | 3.5-4.7 x 1012/l |
| Leukocytes | 4.0-9.0 x 109/l | |
| Hematocrit (the ratio of the volume of plasma and cellular elements of blood) | 42-50% | 38-47% |
| Average red blood cell volume | Within 86-98 µm3 | |
| Leukocyte formula | Neutrophils:
| |
| Platelet count | Within 180-320 x 109/l | |
| Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) | 3-10 mm/h | 5-15 mm/h |
Biochemical blood test for women and men
A biochemical blood test in women and men shows how well certain organs function. It is from biochemical analysis that one can assume, for example, diagnoses such as renal failure, diabetes mellitus or viral hepatitis. A reduced level of total protein in the blood along with an increase in creatinine and urea levels may indicate kidney disease. Excess or lack of glucose may indicate diabetes.
Deficiency is also observed with prolonged fasting. Excessive amounts of bilirubin indicate liver problems. And an increased level of total cholesterol indicates the presence of a large amount of saturated fat in your diet or thyroid disease.
Biochemical blood test standards are common for both sexes:
- total protein - 63-87 g/l;
- urea - 3.4-8.6 mmol/l;
- creatinine - 15-75 µmol/l;
- total bilirubin - 8.49-20.58 µmol/l;
- ALT - up to 37 units;
- AST - up to 42 units.
Regular laboratory diagnostics can help you monitor your health and begin timely prevention of the most common diseases. But what to do if the clinic does not have a medical examination program? For your convenience, the online laboratory “Lab4U” has developed an Annual Medical Examination complex. It includes more than 30 blood parameters, reflecting the functioning of all body systems, and allows you to detect diseases at the earliest stages before the appearance of clinical signs.
Why does jaundice appear?
There are several mechanisms for the occurrence of jaundice.
| Cause of jaundice | What's happening? |
| Increased breakdown of hemoglobin | Due to the too active production of indirect bilirubin, the liver simply cannot cope with its processing and excretion |
| Liver diseases | The amount of bilirubin produced does not exceed the norm, but the affected liver cells are not able to fully function and cope with their work |
| Impaired flow of bile | Instead of entering the intestines, bile accumulates in the liver and provokes its destruction. Bilirubin then enters the blood again. |
Jaundice is an indication for a biochemical blood test to determine the level of bilirubin in the blood. These indications also include liver tumors and cirrhosis, hepatitis, and hemolytic anemia.