Author of the article: Candidate of Medical Sciences O.Yu. Ermolaev
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
A paraovarian cyst is a round-shaped cavity filled with fluid, located in close proximity to the right and/or left ovary.
The paraovarian cyst is located between the broad ligament of the uterus, between the tube and the ovary.
A paraovarian cyst arises from rudimentary (rudimentary) periovarian tubules (from the epididymis). In other words,
A paraovarian cyst occurs as a result of a disruption in the process of embryonic development, i.e. does not depend on heredity and is not transmitted genetically (to offspring). About abnormal development of the genital organs in detail...
The epididymis reaches its greatest development during puberty, which explains the appearance of paraovarian cysts mainly at the age of 20-40 years.
Cases of detection of paraovarian cysts in girls 7-10 years old have been described.
Paraovarian cyst occurs in 10-12% of all identified tumor-like formations and ovarian tumors.
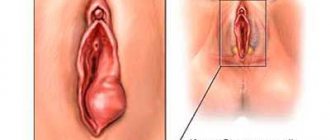
| 3D photo of a paraovarian cyst | |
| 3D photo of a paraovarian cyst of the left ovary. A paraovarian cyst is a round, thin-walled formation adjacent to the ovary. |
See all photos
Pay attention to the excellent quality of the photographs, testifying to the expert class of the equipment of the Women's Health Resort Clinic.
You can find photographs of paraovarian cysts taken by our specialists on many Russian and foreign websites and in textbooks.
A paraovarian cyst never becomes malignant (“does not turn into cancer”), since it is a tumor-like formation. Tumor-like formations grow due to the filling of the cyst and passive stretching of its walls, in contrast to true cysts, the walls of which consist of dividing (multiplying and growing) cells.
Paraovarian cyst never! independently or against the background of conservative (drug) treatment “does not resolve.”
The growth rate and maximum size of a paraovarian cyst are not predictable.
The growth of a paraovarian cyst can be promoted by insolation (sunbathing in natural conditions or in a solarium) and local hyperthermia (taking public baths with a water temperature above 38°C).
| REMOVAL of a paraovarian cyst or OBSERVATION - the gynecologist decides. It is IMPORTANT to start moving in the RIGHT direction! EVERYTHING you need to know about the right direction in the treatment of paraovarian ovarian cysts, see HERE: |
- Symptoms of a paraovarian cyst
- Complications of paraovarian cyst
- Treatment of paraovarian cyst
- Reasonable restrictions in the presence of a paraovarian cyst
- Questions and answers about paraovarian cyst
- Photo gallery paraovarian cyst
Treatment of paraovarian cysts by appointment by multi-line phone number 8 (800) 500-52-74 (toll-free within Russia), or +7 (for international calls).
| ONLINE information about the treatment of paraovarian cysts in Pyatigorsk can be found at REGISTER ONLINE for treatment of paraovarian cyst here. REGISTER online for treatment of paraovarian cyst here. |
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
Reviews about the treatment
Z.R., Nalchik
First of all, thank you very much for the positive experience that every patient receives. The friendliness and professionalism of the staff is already a guaranteed recovery. Oleg Yuryevich - You are a professional with a capital P, a very subtle psychologist, a real doctor. I wish you further expansion and more health, smiling, happy women around you.
Kh.M., Nazran
I am so glad that I found you, you are such a kind, good, bright person. I tell everyone about you. And they also ask me what I found there in this Pyatigorsk. I answer, “I found myself a doctor.” Thank you very much for everything, happiness, health and all the best.
All reviews about treatment in our Clinic
Symptoms of a paraovarian cyst
A symptom of a paraovarian cyst is periodic aching pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region (lower back), which intensifies during and after physical activity.
Pain with a paraovarian cyst, as a rule, stops (disappears) spontaneously (spontaneously) at rest and is not associated with the menstrual or ovulatory (during the release of the egg) periods. However, more often
A paraovarian cyst has no symptoms, i.e. an asymptomatic course is observed.
The size of a paraovarian cyst can vary from small to gigantic (1.0-30.0 cm in diameter).
Paraovarian cysts 0.5-2.5 cm in diameter do not cause discomfort and are most often an “accidental finding” during ultrasound or laparoscopic examination.
“Accidental finding” is usually called data obtained during a methodically correctly performed study by a diagnostician. At the same time, there was no indication of the possible presence of “accidentally” obtained data in the form of complaints or results of other studies.
The diameter of a symptomatic (causing complaints) paraovarian cyst is often 5-15 cm.
As the paraovarian cyst grows, it is accompanied by symptoms of compression of neighboring organs and an increase in the size of the abdomen.
In rare cases, menstrual irregularities and infertility are observed against the background of a paraovarian cyst.
What studies are carried out for ovarian tumors
- Bimanual examination remains relevant even with the most modern equipment, as it allows one to obtain important information.
- Speculum examination provides access to the cervix for examination, allows you to take aspirate and examine the endometrium.
- Washing and puncture of the abdominal cavity for cytological examination.
- Ultrasound using vaginal and abdominal sensors.
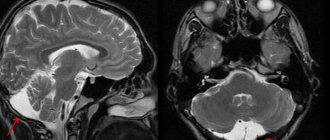
- Nuclear MRI and computed tomography allow for precise layer-by-layer studies to identify the presence of metastases in the lymph nodes.
- Ultrasound and mammography - examination of the mammary glands.
- Study of the condition of the endometrium.
- Examination of the intestine for the presence of a tumor (irrigoscopy, rectromanoscopy).
- Examination of the gastrointestinal tract, since the appearance of a metastatic tumor in the pancreas, intestines, and stomach is possible.
- Tumor markers. Increase in tumor marker CA-125 - more than 35 units. indicates an increased risk of developing an oncological process. But this statement is not always true, since there are cases where a significant excess of the tumor marker norm in endometrial ovarian cysts and endometriosis is not related to oncology.
- Carrying out laparoscopy
Complications of paraovarian cyst
CYST TORSION is a rare complication of paraovarian cyst.
Cyst torsion occurs when there is a sudden change in body position (sexual intercourse, somersaults, snowboarding, etc.).
Torsion of the cyst always occurs with the tube of the same side, less often with the ovary of the same side and is accompanied by sudden acute colicky PAIN in the corresponding groin area, a drop in blood pressure, and symptoms of SHOCK. About cyst torsion in detail...
Torsion of a paraovarian cyst is an indication for urgent surgical treatment.
Torsion of paraovarian cysts in children is observed much more often than in adults. This is explained by the greater mobility of cysts in CHILDREN due to the relatively longer ligamentous apparatus of the ovaries, the location of paraovarian cysts outside the pelvic cavity, as well as the increased activity and sharpness of the child’s movements.
A small paraovarian cyst, as a rule, does not interfere with pregnancy. But during PREGNANCY, due to the enlargement and exit of the uterus from the small pelvis, the risk of twisting or twisting of the paraovarian cyst increases significantly with the need for urgent surgical treatment.
A paraovarian cyst of any size during pregnancy does not have a negative effect on the fetus.
The risk of strangulation, torsion and/or rupture of the paraovarian cyst during CHILDREN exists, but in the absence of sudden changes in body position, it is low.
A paraovarian cyst does not affect hormonal levels, does not cause the formation and growth of acne on the face, and does not affect the growth of hair on the body and head. Thus,
A paraovarian cyst does not cause a delay in menstruation, does not cause intermenstrual bleeding (“bleeding”) and does not contribute to lengthening or shortening the duration of menstruation and increasing or decreasing the amount of menstrual blood.
Lead tactics
- Surgery for a malignant ovarian tumor.
The uterus and cervix, appendages, as well as the greater omentum are removed. Removing the oil seal is important because... In some cases, it contains micrometastases. In addition, the omentum promotes the production and accumulation of ascityl fluid.
- Surgery for a benign tumor
Adnexectomy is performed - removal of appendages. Simultaneously with surgical treatment:
- the internal lining of the formation is examined in detail for malignant growths;
- Histological examination is performed.
A modern approach to diagnosing and treating cysts and other diseases of the female genital area is offered by gynecologists at the RAS clinic in Moscow. Here you can undergo a preventive examination by a gynecologist and have a pelvic ultrasound performed. You can make an appointment for a consultation on the website or by calling the numbers provided.
Treatment of paraovarian cyst
Paraovarian cysts 0.5-2.5 cm in diameter that do not cause inconvenience (asymptomatic) do not require treatment and are not able (never!) to “resolve.”
MONITORING the condition of the paraovarian cyst with regularity once every 5-6 months.
Paraovarian cysts 2.5-5.0 cm in diameter are symptomatic and large symptomatic paraovarian cysts 5.0 cm or more in diameter, causing pain, painful menstruation or infertility, require surgical treatment, since they fundamentally cannot “resolve” (even with “good treatment”).
The prognosis after surgical treatment is favorable. Relapse (reoccurrence) is never noted, because rudimentary (rudimentary) formations from which the paraovarian cyst is formed are completely removed during surgery.
Treatment of paraovarian cysts by laparoscopy is preferable.
Before IVF, during the period of preconception preparation, the paraovarian cyst is usually removed.
After removal of a paraovarian cyst using the laparoscopic method, it is advisable to plan pregnancy after a course of restorative treatment.
The DURATION of restorative TREATMENT at the Women's Health Resort Clinic in Pyatigorsk is 12 days.
COMPLETE RECOVERY in most cases occurs 2 months after removal of the paraovarian cyst.
Cystoma
Cystoma is an enlarging tumor, often having a multi-chamber cavity. Growth occurs both due to the accumulation of fluid inside the cavity and as a result of the division of cells that make up the formation. This tumor is real. Can be benign, malignant or potentially malignant.
There are groups of patients whose risk of developing cysts is especially high:
- patients with chronic diseases of the genital area, as an addition to complex therapy, such women are recommended to use hormonal contraceptives;
- patients with hormonal disorders: lack of pregnancy (hormonal infertility), disrupted menstrual cycle;
- patients who have undergone ovarian surgery, incl. cystectomy;
- Bad heredity – endometriosis and ovarian tumors in the family;
- Patients with breast cancer;
- Women who have had a pathological pregnancy.
There are difficulties in finding screening - identifying certain signs in many patients. It is necessary to conduct an in-depth examination of women if there is a formation larger than 3 cm on the uterine appendages during a two-hand examination.
Reasonable restrictions in the presence of a paraovarian cyst
In the presence of a paraovarian cyst, intense physical activity associated with straining and sudden changes in body position is undesirable: rotation, jumping, somersaults, falls, etc.
The possibility of performing physical exercises (types of exercises and intensity of the training process) and other physical activity should be individually agreed with the attending physician.
Sexual activity with a paraovarian cyst is not contraindicated. However, during sexual intercourse, it is advisable to refrain from positions that cause or intensify discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen.
If you have a paraovarian cyst, it is advisable to refrain from thermal procedures, including taking general baths with a water temperature above 38°C.
It is advisable to refrain from sunbathing in natural conditions and solariums.
There are no special features or dietary restrictions for paraovarian cysts.
The presence of a small paraovarian cyst (up to 2.5 cm in diameter) is not a contraindication for sanatorium treatment in Pyatigorsk.
A paraovarian cyst is not a contraindication for travel by underground (metro), land (car, train and other rail transport), river, sea and air transport. Horseback riding is not recommended.
A paraovarian cyst is not a contraindication to the insertion of an IUD (intrauterine device, “spiral”).
At the Women's Health Resort Clinic, you can conduct an ultrasound examination using an expert-class device with 3D/4D, elastography, power Doppler and color Doppler mapping modes in order to identify a paraovarian cyst.
The remote high-density LED monitor of the ultrasound machine allows the doctor to comment on the “live” image, and the Patient to actively participate in the discussion of what she saw.
The ability to record ultrasound data on a disk and/or flash card (USB drive) allows you to save objective information for doctors and an electronic medical history. Cost of the study
The cost of a pelvic ultrasound is 1,550 rubles.
The resort clinic for women's health operates both for paid services and in the voluntary health insurance system.
Each doctor at the Clinic has long-term experience, several specializations and is able to comprehensively assess the situation.
Methods of carrying out operational actions
Laparoscopic removal
Laparoscopy involves the removal of ovarian cysts through three or four small incisions. Initially, the abdominal cavity is examined, after which the neoplasm itself is monitored. The final stage is liquidation. The operation to remove an ovarian cyst is performed under anesthesia, and the duration varies from half an hour to 60 minutes.
laparoscopy of ovarian cysts
This operation is carried out using special medical equipment - a laparoscope. It is equipped with special mechanisms, which helps to obtain high-quality images of internal organs.
Types of laparoscopy for ovarian cysts :
- Scrape out formations without damaging tissue. This surgical treatment is called cystectomy.
- Removal of a specific component of the ovary where the cyst is located.
- Removal of the tumor and ovary is called oophorectomy. It is worth noting that this operation is characterized by preservation of the pipe.
- Adnexectomy is the removal of the ovary and tube from the side of the injury.
Leading specialists in the treatment of paraovarian cysts in the North Caucasus
Ermolaeva Elvira Kadirovna A well-known and recognized specialist in the treatment of paraovarian cysts in the North Caucasus. An experienced ultrasound diagnostic doctor. Desperate and frightened girls and women turn to her.
Ermolaev Oleg Yurievich Candidate of Medical Sciences, gynecologist-endocrinologist with 25 years of successful experience. Experienced ultrasound doctor.
Shchepkin Petr Sergeevich Gynecologist, specialist in the diagnosis and treatment of paraovarian cysts. Experienced ultrasound doctor.
More information about experienced gynecologists
| INTERNATIONAL RECOGNITION of the reputation and achievements of the Women's Health Resort Clinic in the development and implementation of effective and safe treatment methods and the quality of medical services provided is the AWARDING of the Women's Health Resort Clinic in Pyatigorsk with the SIQS International QUALITY CERTIFICATE in the field of medicine and healthcare. International Socratic Committee, Oxford, UK and Swiss Institute for Quality Standards, Zurich, SWITZERLAND. |
We work seven days a week and on holidays:
Monday - Friday from 8.00 to 20.00, Saturday, Sunday, holidays from 8.00 to 17.00.
Treatment of paraovarian cysts by appointment by multi-line phone 8 (800) 500-52-74 (toll-free within Russia), or +7.
| ONLINE information about the treatment of paraovarian cysts in Pyatigorsk can be found at REGISTER ONLINE for treatment of paraovarian cyst here. REGISTER online for treatment of paraovarian cyst here. |
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
We accept girls, young women and women from all cities of Russia, near and far abroad.
We are at your FULL DISPOSAL if you have any doubts or wishes.
Causes
Among the causes of ovarian cysts are:
- hormonal disorders;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- obesity;
- history of abortion;
- congenital anomalies in the development of tissues of the pelvic organs;
- early onset of menstruation (before 11 years);
- taking certain medications (including oral contraceptives);
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the intestines and bladder;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- history of surgical interventions on the pelvic organs;
- smoking.
Diagnostics
At the initial consultation, the gynecologist listens to your complaints, collects an anamnesis of the disease, and performs an objective examination. Be sure to tell your doctor the time of onset of symptoms and the possible causes of their occurrence.
To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an examination, which includes:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- pregnancy test/hCG blood test;
- X-ray or CT (if necessary).
At the discretion of the doctor, a blood test for tumor markers, hormones, and laparoscopy with collection of material for histological examination may be prescribed. Also, if there are concomitant diseases, consultation with specialists may be required.