Vaginal and Bartholin's gland cysts are formations on the vaginal wall or in its vestibule, filled with liquid secretion. A vaginal cyst can be located on the surface, but sometimes it penetrates deep into the tissue and can reach the size of a chicken egg. Its increase occurs due to the accumulation of serous or mucous contents in it. As for Bartholin gland cysts, their formation can be caused by their blockage, narrowing or overgrowth.
The gynecological service of CELT invites you to undergo diagnostics and treatment of cysts in Moscow. Our multidisciplinary clinic has been operating in the capital's market for more than 25 years and offers paid medical services of a high professional level. We guarantee correct and accurate diagnosis, as well as treatment in accordance with modern international standards.
At CELT you can get advice from a gynecologist.
- Cost of initial consultation - 3,000
- Cost of consultation with ultrasound - 4,200
Make an appointment
Etiology of vaginal cysts and Bartholin glands
| Initiating factors for vaginal cysts | Initiating factors of glandular cysts |
A cyst is not a tumor of the vagina and can be:
| Blockage or narrowing of the glands can occur due to:
|
Symptoms of bacterial vaginosis
With the development of bacterial vaginosis, many patients note the appearance of an increased amount of vaginal discharge, which may have an unpleasant odor (the smell of rotten fish) and/or be accompanied by slight itching in the external genital area. Some patients may have only one of the symptoms: increased discharge or an unpleasant odor, or mild itching. These symptoms may bother a woman constantly, or appear periodically.
It should be noted that the majority of women (50-75%) who are diagnosed with bacterial vaginosis do not have any symptoms of this condition at all. In this case, we talk about the so-called asymptomatic form of bacterial vaginosis.
Clinic of vaginal cysts and Bartholin's glands
| Symptoms of a vaginal cyst | Symptoms of glandular cysts |
Most often, vaginal cysts do not manifest themselves in any way and can be discovered accidentally during an examination by a gynecologist. However, if they have a large diameter, the patient may feel:
If the cyst is infected, leucorrhoea and symptoms of colpitis appear, and the pain becomes stronger. | Small cysts have virtually no clinical manifestations and can be detected accidentally during hygiene measures. Cysts of large diameter are characterized by pain and discomfort, which increases when sitting and walking. Due to its blocking of the entrance to the vagina, unpleasant sensations arise during sexual intercourse. If the cyst is infected, the pain becomes stronger and does not stop. Complications can include infection and abscess. |
Methods of treating pathology: surgery
Gynecologists, for the most part, are of the opinion that small cysts with an asymptomatic course do not require surgical removal - they only need to be observed over time, using drug therapy if necessary.
Indications for surgical removal of the tumor are:
- increase in size;
- the appearance of unpleasant or painful symptoms;
- diagnosed signs of purulent cyst lesions;
- manifestations of colpitis.
As for contraindications to the procedure, surgical removal of the tumor is not performed if the woman has acute infectious processes in the genital organs. To carry out the operation, it is necessary to carry out a course of treatment, and only after achieving a positive result is it possible to proceed with removal.
Diagnosis of vaginal cysts and Bartholin glands in CELT
| Diagnosis of vaginal cyst | Diagnosis of glandular cysts |
| Diagnosis occurs during a gynecological examination using speculum. The doctor detects a formation of a round or oblong shape, which needs to be differentiated from diverticula, prolapse of the walls of the bladder or vagina. In addition, colposcopy, smear examination and ultrasound scanning are performed. |
|
Causes
Vaginal cyst, urethral diverticulum, paraurethral cyst in women are diseases that are simultaneously within the competence of a urologist and gynecologist. Due to the low prevalence of these diseases, the vast majority of staff doctors in local clinics today do not have the necessary experience in differentiating these pathologies. Conventional diagnostic methods do not allow us to identify the characteristic features of these diseases.
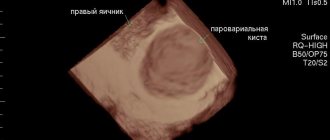
Vaginal cyst
- This is a hollow tumor-like formation filled with watery or mucous fluid. The cyst can reach 9-10 cm in diameter and be located both on the surface of the vaginal walls and in the depths of the tissues. This disease occurs in 1-2% of patients. Experts identify the following types of cystic formations of the vagina:
- Congenital.
Most often they are localized in the middle lateral or posterior walls of the vaginal cavity. Less common is a congenital cyst of the anterior vaginal wall. Formed due to intrauterine developmental anomalies.
- Traumatic or implantation
. Most often they are located much lower than congenital cysts in the posterior walls of the vaginal cavity. Formed as a result of surgery, birth injuries, abortions.
- Vaginal vestibule cysts.
Formed due to inflammation of the Bartholin gland. The cause of inflammation can be injuries, sexually transmitted infections, and failure to comply with intimate hygiene rules.
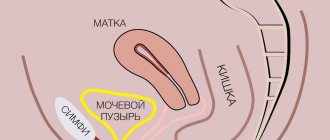
Paraurethral cyst
- This is a round, hollow formation formed from the glands of the urethra. A urethral cyst in women is filled with mucous fluid and can reach 2-4 cm in diameter. Most often it develops at the external opening of this canal and much less often in the depths of the tissue. Formed as a result of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system, birth or surgical trauma, due to decreased immunity (including due to diabetes mellitus). Urethral cyst occurs in 2-6% of women.
Urethral diverticula in women
- This is a hollow round formation, most often formed in the area of the posterior wall of the urethra, usually communicating with the urethra. The diverticulum cavity can be up to 3 cm in diameter, and the wall of the diverticulum is similar to the wall of the urethra. When urinating, the diverticulum may become larger as some urine may be retained in the cavity. Urethral diverticula occur in 1.6-5% of women. Experts identify the following types of this disease:
- Congenital. They are formed as a result of intrauterine development disorders: expansion of paraurethral cysts, improper fusion of the embryonic folds of the urethra.
- Purchased. They are formed as a result of the transformation of paraurethral cysts, with a communication between the cyst and the urethra.
Treatment of vaginal cysts and Bartholin glands in CELT
The development of treatment tactics in our clinic is based on the diagnostic results and individual indications of the patient.
| Treatment of vaginal cysts | Treatment of glandular cysts |
Cysts of small diameter that do not cause unpleasant symptoms do not require treatment, but require observation. If they grow and manifest themselves, they are removed surgically using various techniques:
Depending on the situation, laparotomy or vaginal access is used. | Conservative treatment methods are not able to give the desired result, since they do not eliminate the violation of the outflow of secretions from the glands. However, if there are inflammatory processes, the patient is prescribed antibiotics. Surgical techniques include the following:
|
The gynecological service of CELT receives doctors of the highest category and candidates of science with over thirty years of practical experience. You can make an appointment with them online through our website or by contacting our operators.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Bacterial vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis is a disruption of the normal balance between “good” and “harmful” microorganisms that are usually present in the vagina.
Normally, there are quite a lot of different microorganisms in the vagina. Among them, lactic acid bacteria, called lactobacilli, dominate in number. The content of other microorganisms, many of which belong to the so-called anaerobic group, is much lower in the vagina of a healthy woman. But both lactobacilli and anaerobes are components of the normal vaginal microflora.
With bacterial vaginosis, there is a violation of the ratio between lactobacilli and anaerobes in the vagina: the number of lactobacilli is less than normal, while the number of anaerobes is sharply increased. There is no inflammation in the vagina with bacterial vaginosis.
Bacterial vaginosis is a quantitative change in the flora of the vagina.
According to statistics, 40-50% of all cases of the appearance or change of vaginal discharge are caused by bacterial vaginosis, approximately 25 to 50% of all women of reproductive age have bacterial vaginosis one or more times.
Causes of bacterial vaginosis
- taking antibiotics
- climate change
- change of sexual partner
- using an intrauterine device
- using menstrual tampons
Contraindications
Surgery should not be performed during menstruation. There is also a list of contraindications:
1. Bad urine and blood tests.
2. Lack or excess of platelets, leukocytes, and erythrocytes in the blood.
3. Low or elevated hemoglobin levels.
4. Severe cardiovascular insufficiency.
5. Infectious disease.
6. Drug intolerance.
7. Old age.
8. Oncology.
Prevention
First of all, it is necessary to promptly diagnose cystic formations in the vagina, which will allow you to avoid problems with pregnancy in the future. In order to avoid their occurrence, it is recommended to carry out all vaginal manipulations with extreme caution and listen to all instructions from the midwife during childbirth.
In the absence of pronounced symptoms, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the cyst on the vaginal wall over time.
Cystic formation does not in any way affect a woman’s ability to give birth to a child, but can cause the accumulation of purulent exudate inside. If the enucleation or aspiration is not thorough enough, there is a high probability that the cyst will reappear in the vagina.
Compliance with preventive measures allows you to avoid the development of pathology and dangerous complications.
Progress of the operation
The anesthesiologist administers local anesthesia to the patient. The surgeon makes a longitudinal incision with a scalpel in the desired area. Performs the necessary actions with the cyst shell. Then, catgut or silicone threads are used to stitch the wall incisions. The seam is treated with an antiseptic. The patient is brought back to his senses.
The prospect of a complete cure is quite high. In most cases, no complications arise and the healing period occurs as quickly as possible. The cyst is a benign tumor, so its transformation into a cancerous tumor is completely excluded and has not been encountered in medical practice. If the fluid is not completely cleared, there is a possibility that the vaginal cyst will reappear.
You should not touch the cyst if it does not cause any complaints. There is a possibility that complications will occur after surgery. Formation of suppuration or fistula.
The Gartner cyst is the safest. It is not a contraindication for conception, pregnancy and childbirth. Does not disrupt the menstrual cycle. But the woman should be under constant supervision of a specialist.
Getting rid of a cyst at home and using folk methods can lead to complications or bleeding. Do not use any medications or supplements without a doctor's prescription.
Rehabilitation
The period of rehabilitation and therapy is short. Healing and resorption of sutures occurs quickly. The woman has been in the hospital for a couple of days. Next, as you feel better and have the doctor’s permission, you can switch to a day hospital.
Already after 2-3 days, movement is allowed. Without making sudden movements or bending. Do not lift heavy objects. Within a month, the menstrual cycle is restored. Supportive housing may be worn after surgery.
The seams are treated with antiseptic solutions to prevent infection. Do not drink alcoholic beverages and stop smoking. Do not take vasodilators.