Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Childbirth is an absolutely natural physiological act and usually does not require additional medical intervention, except for the assistance of a midwife. But in some cases, especially if the pregnancy was complicated by various diseases or there is an indication for a cesarean section, pain relief is simply necessary. Painful sensations in women occur during contractions, when the first stage of labor lasts and the cervix opens. They are associated with strong tension and contraction of the uterine muscles. Depending on the magnitude of a woman’s pain threshold, as well as on individual mental reactions, it can be either barely noticeable or unbearable.
Why is pain relief needed?
Since ancient times, humanity has been trying to find a way to reduce pain in women in labor. In ancient times, decoctions of herbs and smoking were used for this; later, synthetic painkillers appeared. Childbirth is one of the most painful processes, and the medieval concept of the need for female suffering is, fortunately, a thing of the past.
Research by modern scientists directly suggests that excessive pain during childbirth sharply increases the level of adrenaline and norepinephrine in the blood, and this can lead to disruption of oxygen transport in the body. As a result, the frequency of contractions may decrease with the possible development of fetal hypoxia.*
Non-drug methods of pain relief
First of all, it is necessary to apply the most physiological and safe methods. If there is no effect, drug anesthesia during childbirth is indicated.
Non-drug pain relief for childbirth is possible using several methods:
- Massage the sacral area yourself or ask a partner. During contractions it will help relieve the condition and reduce spasms. You can also stroke your stomach on the sides in a circular motion, neck, lower back;
- Breathing exercises - deep breaths, smooth exhalations lead to an increase in serotonin - the hormone of joy. The technique has a beneficial effect on the nervous system, psychological state, and has an analgesic effect. In addition, it prevents fetal hypoxia. The technique is this: first, take a deep, slow breath in through your nose and exhale through your mouth, while inhaling coincides with the onset of contractions. As contractions become more frequent, it is recommended to inhale through the mouth, but towards the end of each contraction, return to inhaling through the nose, exhaling through the mouth;
- Poses, when used correctly, relieve pain. Each woman is suitable for certain poses. For example, squatting, kneeling, standing on all fours with a raised pelvis, standing on your feet near the bed, leaning on its back, sitting and swinging on a fitball (gymnastic ball). According to research, the physical activity of a woman in labor and her vertical position reduce the duration of labor and reduce the risk of cesarean section;
- Water procedures are another effective way of natural anesthesia during childbirth, due to general relaxation and relief of muscle spasms. A warm shower is recommended, but not hot or cool - they will have the opposite effect. If contractions start at home and you decide to stand in the shower, monitor your condition and do not miss the moment the amniotic fluid breaks;
- The psychological component consists of eliminating stress and psychological preparation. It is carried out in a antenatal clinic or in special courses. The technique is based on the fact that stress leads to the release of adrenaline and cortisol: this leads to muscle spasm. Because of this, the dilation of the cervix, which means the passage of the baby through the birth canal, is difficult. By eliminating emotional tension, you relieve spasm, which means you will reduce pain, and the birth of your baby will be more comfortable.
What is epidural anesthesia
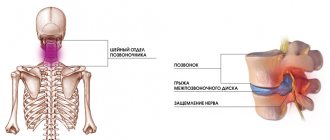
The epidural space surrounds the outside of the dura mater, which covers the entire spinal cord. In the epidural space of the lumbar region there are nerve endings that conduct pain impulses from the uterus. An injection is made in the lumbar region and an anesthetic is injected.
When painkillers are administered, sensitivity is temporarily switched off, which allows the woman in labor to stop feeling pain. The dose of the anesthetic drug is selected and adjusted for partial or complete pain relief.
Unlike general anesthesia, epidural anesthesia allows the woman in labor to remain conscious at all stages. Most often, such anesthesia, unless there are special indications, is used only for the period of contractions, which can last for several hours, and the woman gives birth without anesthesia.
Does anesthesia affect the fetus?
With spinal anesthesia during childbirth, with strict adherence to the technique and timely exclusion of contraindications, there are no consequences. Anesthetics act only locally; they enter the mother’s blood only in small quantities; this volume does not pass through the placental barrier.
When general anesthesia is used, the woman switches off completely, psychological stress is eliminated. Therefore, on the one hand, this method of anesthesia during childbirth is preferable. But on the other hand, the effect on the fetus is more pronounced. The longer the operation lasts, the more the drug enters the fetus’s body, breaking the placental barrier, and the more pronounced the side effects: depression of consciousness, cardiac activity and respiration.
The newborn will be lethargic. Respiratory and cardiac problems and breast refusal are possible. If ketamine is used for intravenous anesthesia, it, on the contrary, has a stimulating effect, unlike the others: on cardiac activity and the respiratory system. Gradually the concentration of the medicine ends, the baby’s condition returns to normal.
There is also a negative effect on the mother: the dilatation of the cervix slows down, which is why the total duration of labor is lengthened. Doctors select the dose of anesthetic individually to prevent overdose and inhibition of contractile activity. In such cases, additional stimulation and sometimes a caesarean section will be required.
Headaches and dizziness are common. With epidural and spinal anesthesia, blood pressure drops.
Spinal or epidural?
These two types of pain relief are very often confused, because they are really similar in appearance, especially for those who are far from medicine. However, there are differences between them.
Spinal . This anesthesia uses a thin needle through which an anesthetic is injected into the cerebrospinal fluid. Nowadays, this method is used less and less, because if performed incorrectly or if contraindications are not identified, it can lead to serious consequences.
Epidural . For this type of anesthesia, local anesthesia is first performed, after which a puncture is made at the puncture site with a special needle that penetrates to the dura mater. When performing this manipulation, it is very important not to move so that the doctor’s hand does not tremble. A catheter is inserted into the puncture through a needle, through which anesthetics enter the epidural space. His tube will remain in your back as long as necessary to maintain the pain-relieving effects of the medications. After removing the catheter, only a small puncture will remain, which will be treated and covered with a bandage.
How is epidural anesthesia given during childbirth?
Any intervention in a woman’s body during pregnancy and childbirth is coordinated with an obstetrician-gynecologist; the indications for this type of anesthesia, the condition of both the mother and the fetus are comprehensively assessed for maximum safety of the process. The patient is placed in a lateral position with her legs adducted, or sitting with her back arched. A venous catheter must be installed, followed by drip administration of at least 500 ml of crystalloid solution in order to prevent a pathological decrease in blood pressure after the manipulation.
The puncture site (the distance between the spinous processes of the lumbar vertebrae L2-L3) is treated with antiseptic solutions, anesthetized with local anesthetics, then a puncture is made with a special puncture needle, a catheter is inserted into the epidural space, an aseptic sticker is applied and the patient is placed in a lateral position, the first dose is administered through the catheter painkiller.
At this moment, it is very important to assess the condition of the woman and child - measuring pulse, blood pressure, monitoring the fetal heart rate.
Effect of anesthesia on a child
Proponents of “natural childbirth”, without any anesthesia, insist that drugs can negatively affect the fetus. However, modern research refutes this fact: as a result of the tests, it was found that epidural anesthesia does not affect the child in any way, but greatly facilitates the birth process.** In addition, for this type of anesthesia, drugs are used that do not penetrate the placental membrane of the fetus .
The main advantage of epidural anesthesia during childbirth is that a woman can relax, calm down and confidently move on to the process of expulsion of the fetus without neurosis and stress.
General anesthesia
This type of anesthesia is usually performed only in case of surgery, while the patient is under anesthesia, unconscious and does not feel anything. During the operation, food or liquid from the mother's stomach may enter the lungs, so the expectant mother is not recommended to eat or drink anything during labor. You can only rinse your mouth if you are very thirsty. If doctors do not know whether the patient has eaten food, then during a cesarean section a special tube will be inserted into her trachea to protect her lungs. General anesthesia usually does not affect the child’s condition, since the drugs are administered directly in the operating room and usually very little time passes.
Whatever the reasons why a woman resorts to the use of pain relief during childbirth, she must certainly be informed about all possible complications and side effects of the drugs administered and their effect on the child’s body. It is unacceptable to use any type of anesthesia without the consent of the patient if she is conscious. The exception is emergency situations that threaten the life of the mother.
Indications for pain relief
Unfortunately, not all medical institutions can yet make an independent decision about the use of anesthetics. In most cases, the following situations are indications for the need for epidural anesthesia.
Premature pregnancy. Relaxing the pelvic floor muscles allows the baby to pass through the birth canal more easily without encountering resistance. For babies who were born prematurely, unnecessary stress is contraindicated, so if there are no indications for a caesarean section or other individual characteristics of the pregnancy, it is recommended to give birth with epidural anesthesia.
Discoordination of labor. This is the name of a condition in which contractions last longer than expected, but the dilation of the cervix is not sufficient. In this case, epidural anesthesia will relieve spasm and help labor.
High blood pressure. If you have hypertension, childbirth can lead to strokes or other dangerous consequences, so doctors may prescribe either a cesarean section or use an epidural, which will help normalize blood pressure levels.
The need for surgical intervention. In cases where general anesthesia cannot be used, but surgical assistance is required, epidural anesthesia is used as an alternative option.
Pain relief for childbirth
Ultrasound scanner HS50
Affordable efficiency.
A versatile ultrasound scanner with compact design and innovative capabilities.
Pain relief during childbirth is aimed at providing comfortable conditions for the laboring woman, avoiding pain and stress, and also helps prevent labor disturbances.
The perception of pain by a woman in labor depends on circumstances such as physical condition, anxious anticipation, depression, and characteristics of upbringing. In many ways, pain during childbirth is intensified by fear of the unknown and possible danger, as well as previous negative experiences. However, the pain will be reduced or better tolerated if the patient has confidence in the successful completion of labor and a correct understanding of the labor process. Unfortunately, so far, none of the currently existing methods of pain relief during childbirth is absolutely ideal. To achieve maximum effect, the choice of pain relief method should be individualized. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the physiological and psychological state of the woman in labor, the condition of the fetus and the obstetric situation. To increase the effectiveness of pain relief, prenatal preparation is important, the purpose of which is to remove the fear of the unknown of the upcoming birth. In the process of such preparation, the pregnant woman must be informed about the essence of the processes accompanying pregnancy and childbirth. The patient is taught proper relaxation, exercises that strengthen the abdominal and back muscles, increase overall tone, and different breathing methods during contractions and at the time of birth of the fetal head.
Acupuncture can be used as one of the methods of non-drug pain relief during labor. Most often, when using this method, only partial pain relief occurs, and most patients require the use of additional methods of pain relief. Another method of non-drug labor pain relief is transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), which has been used for many years. During labor, two pairs of electrodes are placed on the mother's back. The degree of electrical stimulation varies according to the needs of each individual woman and can be adjusted by the patient herself. This form of analgesia is safe, non-invasive, and can be easily administered by a nurse or midwife. The main disadvantage of the method is the difficulty in using electronic monitoring of the fetal condition, despite the fact that transcutaneous electrical neurostimulation itself does not affect the fetal heart rate.
However, the most important thing for pain relief during labor is the use of appropriate medications. Methods for pain relief during labor can be divided into three types: intravenous or intramuscular administration of drugs to relieve pain and anxiety; inhalation pain relief for labor; local infiltration use of anesthetics and regional blockades.
Narcotic analgesics are the most effective drugs used to relieve labor pain. However, these drugs are used to reduce pain rather than completely stop it. With established labor in the active phase of the first stage of labor, these drugs help correct uncoordinated uterine contractions. The choice of drug is usually based on the severity of potential side effects and the desired duration of action. Intravenous administration of drugs is preferable compared to intramuscular administration, since the effective dose is reduced by 1/3 - 1/2, and the effect begins much faster. Tranquilizers and sedatives are used during childbirth as components of drug pain relief to relieve agitation, as well as to reduce nausea and vomiting. In the active phase of labor, when the cervix is dilated more than 3-4 cm and painful contractions occur, sedatives with narcotic analgesics in combination with antispasmodics (No-spa intramuscularly) are prescribed. The use of narcotic analgesics should be stopped 2-3 hours before the expected moment of expulsion of the fetus, to prevent possible narcotic depression.
Inhalation pain relief for labor
Inhalation analgesia of labor by inhaling painkillers is also widely used in obstetric practice. Inhalational anesthetics are used during the active phase of labor when the cervix is dilated by at least 3-4 cm and in the presence of severe painful contractions. The most common are nitrous oxide (N2O) with oxygen, trichlorethylene (trilene) and methoxyflurane (pentrane). Nitrous oxide is a colorless gas with a slight sweetish odor that is the most harmless inhalational anesthetic for mother and fetus. The most common ratios of nitrous oxide to oxygen are: 1:1, 2:1 and 3:1, allowing for the most optimal and sustained analgesia. During the process of inhalation anesthesia, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the woman in labor by medical personnel. The effectiveness of pain relief largely depends on the correct inhalation technique and rationally selected ratios of the components of the gas-narcotic mixture. Three options can be used to achieve an analgesic effect.
Options for labor pain relief using inhalational anesthetics
- Inhalation of the gas-narcotic mixture occurs continuously with periodic breaks after 30-40 minutes.
- Inhalation is carried out with the beginning of the contraction and ends with its end.
- Inhalation occurs only in pauses between contractions, so that by the time they begin, the required degree of pain relief is achieved.
Autoanalgesia during labor with nitrous oxide can be performed throughout the active phase of the first stage of labor until the cervix is fully dilated. Due to the fact that nitrous oxide is eliminated from the body through the respiratory tract, this provides greater control over the pain relief process. During pain relief during childbirth, after stopping inhalation of nitrous oxide, consciousness and orientation in the environment are restored within 1-2 minutes. Such analgesia during labor also has an antispasmodic effect, ensuring coordinated labor, preventing abnormalities in uterine contractility and fetal hypoxia. The use of a gas-narcotic mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen is the most acceptable in obstetric practice for pain relief during labor. In addition to nitrous oxide, drugs such as trichlorethylene (has a more pronounced analgesic effect compared to nitrous oxide) can also be used for inhalation anesthesia; methoxyflurane (use is less controlled than nitrous oxide and trichlorethylene).
Epidural analgesia
Regional analgesia can also be successfully used to relieve labor pain. The cause of pain in the first stage of labor is contraction of the uterine muscles, stretching of the cervix and tension of the uterine ligaments. In the second stage of labor, due to stretching and elongation of the pelvic structures during the advancement of the fetus, additional pain sensations arise, which are transmitted along the sacral and coccygeal nerves. Therefore, to achieve pain relief during childbirth, the transmission of pain impulses along the corresponding nerve bundles should be blocked. This can be achieved by a pudendal nerve block, a caudal block, a spinal block, or an extended epidural block.
Epidural analgesia is one of the popular methods of labor pain relief. Performing epidural analgesia involves blocking pain impulses from the uterus along the nerve pathways entering the spinal cord at a certain level by injecting a local anesthetic into the epidural space. Indications for epidural analgesia are: severe painful contractions in the absence of effect from other methods of pain relief, incoordination of labor, arterial hypertension during childbirth, childbirth with gestosis and fetoplacental insufficiency.
Contraindications to labor analgesia using epidural analgesia
- Bleeding during pregnancy and shortly before childbirth.
- Use of anticoagulants or decreased activity of the blood coagulation system. 3. The presence of a focus of infection in the area of the proposed puncture.
- A tumor at the site of the intended puncture is also a contraindication to epidural analgesia.
- Volumetric intracranial processes accompanied by increased intracranial pressure.
Relative contraindications to epidural analgesia
- Previous extensive back surgery.
- Extreme obesity and anatomical features that make it impossible to identify topographic landmarks.
- Past or existing diseases of the central nervous system (multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, muscular dystrophy and myasthenia gravis).
Epidural analgesia is carried out when regular labor is established and the cervix is dilated by at least 3-4 cm. Only an anesthesiologist who knows this technique has the right to perform epidural anesthesia.
The advantages of epidural anesthesia include: high efficiency of pain relief; the patient is conscious during analgesia; the possibility of long-term maintenance of analgesic effects throughout childbirth; absence of a depressing effect on labor, the condition of the mother and the fetus; optimization of blood supply to the uterus and kidneys against the background of sympathetic blockade. If it is necessary to perform an emergency caesarean section, the epidural block can be strengthened, which allows for the proper level of anesthesia during the operation.
As an anesthesia during the active phase of the first stage of labor when the cervix is dilated from 4 to 6 cm, a paracervical block can be used, in which pain impulses from the body of the uterus and its cervix can be blocked by introducing a local anesthetic on both sides of the cervix.
If in the second stage of labor the sensitivity of the perineum should be preserved, which allows the woman in labor to push, then additional analgesia to that given in the first stage of labor is not required. If it is necessary to continue pain relief or there is a need for surgical intervention (application of obstetric forceps), then the methods of choice are an epidural block of the pudendal nerve or inhalation analgesia.
The pudendal nerve block is performed 10-20 minutes before the moment when perineal anesthesia is required. Pain relief is achieved by injecting a local anesthetic into the pudendal canal on both sides of the pelvis. The combination of a pudendal nerve block with inhalational analgesia is advisable when managing vaginal delivery in high-risk patients, since the block does not have a negative effect on the hemodynamics and respiratory system of the woman in labor, or on the condition of the fetus.
Certain advantages of different types of pain relief for certain obstetric complications during childbirth should be taken into account. So, in particular, for gestosis, it is advisable to use epidural analgesia. The advantages of using this method of pain relief in this case are: the ability to control blood pressure levels; optimization of uteroplacental blood flow; improved kidney function; reducing the need for additional use of depressants that have a negative effect on the condition of the fetus. If there is a need for emergency delivery by cesarean section, then the already installed block allows this surgical intervention to be performed immediately, even if it is necessary to increase the level of the block.
If labor during gestosis develops very quickly, or epidural analgesia is contraindicated for some reason, then inhalation analgesia using nitrous oxide can be successfully used to relieve labor pain. Such analgesia can be enhanced by small doses of narcotic analgesics, and in the second stage of labor supplemented with a pudendal nerve block.
Pain relief for labor disorders
Disorders of labor also deserve attention. Adequate timely treatment of labor incoordination, as a rule, contributes to its normalization. The choice of appropriate therapy is carried out taking into account the age of the women, obstetric and somatic history, the course of pregnancy, and an objective assessment of the condition of the fetus. With this type of abnormal labor, the most reasonable method of treatment is long-term epidural analgesia. A common anomaly of labor is weakness, which is corrected by intravenous administration of drugs that enhance uterine contractility. Before prescribing birth-stimulating drugs if the patient is tired, it is necessary to provide the woman with rest in the form of pharmacological sleep. Proper and timely provision of rest leads to the restoration of impaired functions of the central nervous system. In these situations, rest helps restore normal metabolism in the uterus. For this purpose, a wide arsenal of medications is used, which are prescribed by the doctor on an individual basis, depending on the current obstetric situation and the condition of the woman in labor. In obstetric practice, the method of electroanalgesia is also used, the use of which allows one to achieve stable vegetative balance and avoid allergic reactions that may occur when using pharmacological drugs (neuroleptics, ataractics, analgesics). Unlike pharmacological drugs, the use of pulsed current makes it possible to obtain the so-called “fixed” stage of therapeutic analgesia, which makes it possible to maintain consciousness during the birth act, verbal contact with the woman in labor without signs of her excitement and transition to the surgical stage of anesthesia.
Pain relief during childbirth with diabetes mellitus
In case of diabetes mellitus at the beginning of the active phase of the first stage of labor, it is advisable to avoid the use of narcotic analgesics and the use of epidural analgesia is more preferable. This is due to the fact that the negative impact of systemic analgesics and sedatives is reduced, the mother’s stress response to pain is less pronounced, and better control over the mother’s condition is ensured while consciousness is preserved. In addition, epidural analgesia helps prevent the development of rapid and rapid labor and allows for painless, controlled completion of labor. If necessary, against the background of epidural analgesia, surgical delivery is possible both through the natural birth canal (obstetric forceps, vacuum extraction) and by emergency cesarean section (after quickly strengthening the block). If there is no possibility and conditions for performing a regional block, it is possible to use inhalation analgesia, enhancing it with a block of the pudendal nerve.
Pain relief for childbirth due to heart disease
For rheumatic heart diseases, pain relief should be carried out until delivery and continue in the early postpartum period. These requirements are best met by an extended lumbar epidural block. This technique allows you to eliminate pushing in the second stage of labor, and provides the necessary conditions for the application of obstetric forceps and the use of vacuum extraction. If a caesarean section becomes necessary, an extended lumbar epidural block can be extended to the required level. This method of pain relief helps prevent the development of acute heart failure with pulmonary edema and decreased venous return. In a patient with a prosthetic valve and using heparin, it is advisable to use tranquilizers and narcotic analgesics or inhalational analgesia without hyperventilation to relieve labor pain. In the second stage of labor it should be supplemented with a pudendal nerve block.
Anesthesia and premature birth
In the management of preterm labor, the use of narcotic analgesics and sedatives during labor should be avoided. Carefully performed regional anesthesia is the best type of pain relief for the delivery of a premature fetus. An extended lumbar epidural block, maintained throughout labor, is an ideal form of analgesia, as it allows for strict control of the course of labor and perineal dissection. If a cesarean section is necessary, the epidural block can be quickly reinforced.
Ultrasound scanner HS50
Affordable efficiency.
A versatile ultrasound scanner with compact design and innovative capabilities.
When not to use
Any medical intervention has its contraindications, and this includes epidural anesthesia. However, even the presence of contraindications is not a reason to give birth without anesthesia. In this case, doctors can choose alternative ways to reduce the pain threshold.
Low blood pressure. With low blood pressure, the administration of painkillers can cause a sharp drop in blood pressure.
Spinal deformity. If a woman has degenerative disorders in the spinal column, it is extremely curved or abnormal, access for a boat will be difficult. This means that when the drug is administered, it may end up in the wrong place or may not block pain.
Inflammation in the puncture area. In case of any inflammatory processes in the lumbar region (the site of epidural anesthesia), injections are prohibited, as they can provoke suppuration or other unpleasant consequences of infection in the blood.
Blood clotting disorder. Some painkillers can thin the blood, which is especially dangerous if uterine bleeding occurs during childbirth.
Intolerance to a certain group of drugs. Usually analogues are simply used, but in rare cases epidural anesthesia becomes impossible
Unconscious state. Firstly, an unconscious woman, in principle, does not feel pain, and secondly, she cannot give her consent to the use of anesthesia, which is required when prescribing a certain group of drugs
Choosing a pain relief method
When choosing a method of anesthesia during childbirth, they rely on how the birth will take place, take into account risk factors, and the general condition of the woman and fetus. During natural childbirth, anesthesia is often epidural, unless there are medical indications for the use of other types. When a woman is preparing for a caesarean section, the anesthesiologist, depending on the situation, the presence or absence of hypoxia in the fetus, and the wishes of the patient, chooses general or epidural anesthesia.
When the situation is urgent, the woman’s opinion does not matter. Doctors begin to save her life and the life of the child immediately after entering the maternity ward and assessing the danger. In this case, you cannot hesitate.
According to the recommendations of the American Society of Anesthesiologists, of all the methods used in obstetrics and gynecology, neuraxial methods (epidural, spinal and combined spinal-epidural) are the most flexible, effective, with the fewest negative consequences.
Contraindications
Absolute contraindications to anesthesia during childbirth:
- lack of conditions for the procedure and sufficient competencies of medical personnel;
- refusal of the woman in labor;
- bleeding disorders, including those caused by treatment with anticoagulants;;
- risk of bleeding;
- severe condition caused by sepsis,
- rash, purulent lesion at the injection site;
- intracranial pressure;
- liver failure;
- pathology of the cardiovascular system, including AV block, coarctation of the aorta, aortic valve stenosis;
- abnormal condition of the fetus - decreased heart rate, prolapse of the umbilical cord;
- drug intolerance.
Relative contraindications are those that require a thorough examination, stabilization of the condition to avoid worsening the situation, or additional consultation with specialists:
- unstable psychological state;
- mental disorders;
- previous injuries of the spine, its deformation;
- fetal malformations;
- the likelihood of expanding the scope of the operation;
- demyelinating diseases of the nervous system, peripheral neuropathy;
- tattoo at the puncture site.
Consequences and complications
In most cases, epidural anesthesia is well tolerated without negative consequences for mother and child. However, there are situations when unpleasant complications actually occur, usually in the woman in labor.
Entry of drugs into the venous system. If the doctor gets into a vessel during a puncture, and the anesthetic ends up in the bloodstream, the woman will feel weakness, dizziness, and numbness of the limbs. Fortunately, this is all fixable: usually such reactions occur instantly, even when the catheter is installed, and if the anesthesiologist is notified in a timely manner, unpleasant consequences can be avoided. Therefore, if you experience any of the above symptoms during epidural anesthesia, you should inform your doctor.
Allergy. Unfortunately, no one is protected from possible negative reactions of the body to the anesthetic. If you have allergic reactions (especially to medications or, for example, anesthesia administered during dental treatment), you must tell your doctor about it. This will greatly help the doctor, who will select the correct drug and its dosage, and will protect you from allergic reactions and anaphylactic shock.
Back pain. Some women, in reviews of the use of anesthesia during childbirth, complain that after an epidural the lumbar spine hurts. This happens at the site of puncture and installation of the catheter. This pain usually goes away quickly in the postpartum period. But you should definitely tell your doctor about it.
Fall in blood pressure. Most painkillers actually lower blood pressure significantly. To avoid dizziness, doctors usually recommend that their patients lie down and drugs are administered through a catheter in small doses.
Other disadvantages of anesthesia
Most of the consequences depend on whether the anesthesiologist performs his manipulations correctly and whether the woman in labor follows all the doctors’ recommendations. The fact is that if the drug is administered incorrectly, pain relief may occur partially (in 15% of cases) or not at all (5%). Often, incorrect insertion is due to a woman’s excess weight or abnormalities in the development of her spine.
Another rare phenomenon is “mosaic” anesthesia. It occurs due to the fact that there are partitions in the epidural space that do not allow the medicine to be evenly distributed throughout the fluid. Loss of sensation on one side of the body should be immediately reported to the anesthesiologist, and he will adjust the dose of drugs.
Cons of the procedure
Most opponents of epidural anesthesia insist that during childbirth, a woman produces large amounts of the hormone oxytocin, which causes attachment to the child. And if you “block” pain with painkillers, its production will stop, and the “maternal instinct” will not work. Women who have given birth with an epidural and are raising children will easily destroy the myth of absent attachment.
Possible negative consequences are complications from inappropriate medications. Therefore, questions about allergies need to be addressed in advance. So there are practically no downsides to epidural anesthesia, and conclusions about “irreparable harm” that are not supported by facts should not be taken into account.
Pros of the procedure
We live in a modern world in which everything is done for maximum comfort. Outdated ideas that a woman in labor must suffer in order to have the right to be called a mother are today considered extremely inhumane. The advantages of epidural anesthesia are:
- pain relief during labor, which can be truly unbearable for the mother
- the opportunity to take a break when contractions have been going on for several hours, and even sleep
- lowering blood pressure in hypertensive patients
- preventing the negative consequences of excessive pain, which can provoke fetal hypoxia
- normalizing uterine contraction, relaxing the cervix and helping the baby pass through the birth canal
- relief of nausea and vomiting
- absence of depression of the respiratory centers in the mother and newborn
In addition, if an emergency caesarean section is necessary, the anesthesiologist will simply increase the dose of drugs and the operation can begin immediately.
When is epidural anesthesia given during childbirth?
According to the World Health Organization, 25–30% of women in labor rate pain during natural childbirth as unbearable. According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, namely Article 19 of Federal Law No. 323 “On the fundamentals of protecting the health of citizens in the Russian Federation,” every patient has the right to pain relief. Thus, in the absence of medical contraindications, a woman’s desire for pain relief during childbirth is a sufficient indication for the use of epidural anesthesia and other modern methods of pain relief. In addition, there are generally accepted indications and contraindications for regional anesthesia methods. The absolute indications for epidural anesthesia during childbirth are:
- Increased blood pressure of any etiology (preeclampsia, hypertension, symptomatic arterial hypertension).
- The presence of somatic diseases: heart defects (not all), respiratory diseases - bronchial asthma, kidney diseases - glomerulonephritis, high degree of vision loss, increased intracranial pressure.
- The presence of current or previous venous or arterial thrombosis.
- Young women giving birth under 18 years of age.
- Intrauterine fetal death, where the main aspect is the psychological state of the woman.
The consequences of the lack of epidural anesthesia after childbirth for mother and baby in the above clinical situations can be very serious.
Relative indications for epidural anesthesia are:
- Anomalies of labor, namely discoordinated labor.
- Premature birth (birth at gestational age earlier than 37, but later than 22 weeks).
- Large fruit.
- Caesarean section operation.
Epidural anesthesia during childbirth ensures a minimal drug load on the fetus and newborn, which is a huge advantage during premature birth, when the baby’s nervous system is especially vulnerable. The level of stress hormones in the mother’s blood is reduced, disruption of fetoplacental blood flow and disruption of oxygen transport to the child are prevented due to excessive contractions of the uterus. Also, according to statistical data, there is a decrease in injuries to the birth canal (ruptures of the cervix, vagina and perineum) due to muscle relaxation and a softer, smoother flow of the birth process. With maximum adherence to pain management technology, there is no deterioration in the condition of the fetus and newborn, the frequency of surgical delivery does not increase, and the risk of neurological consequences is minimal.
How else to make childbirth easier
Not all women necessarily want to give birth using anesthesia. However, even in this case, you can make the birth process easier for yourself.
- Pregnancy needs to be planned well in advance, giving up all bad habits, building a diet and daily routine, seeing a doctor and trying to avoid stress if possible.
- Before giving birth, you need to attend training courses in it, where you will be told in detail about how to breathe correctly and what to do when contractions begin. Such lessons are needed in order to prepare not only physically, but also emotionally.
- During contractions, you can use some massage techniques: they are usually discussed in courses. In addition, it is very important to breathe properly and try not to scream, as this takes oxygen away from the child