Immunology is a medical branch that studies the functioning of the immune system, the body's reactions to a number of autoimmune processes and the production of antibodies. In addition, she is developing methods for the treatment and prevention of many diseases associated with immunity.
This area of medicine is developing very rapidly, as microorganisms constantly undergo mutations and it is necessary to respond to these changes in a timely manner.
An immunologist is a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of pathological conditions affecting the immune system. Also within his competence is the study and prevention of allergic reactions, the development of all kinds of vaccines against viral infections. Immunologists can not only practice in clinics, but also engage in scientific activities in research centers.
In what cases should I contact
Often a situation arises when a person’s health deteriorates, and a problem arises with making a diagnosis. In such a case, the attending physicians refer the patient to an immunologist. His consultation is required if the following symptoms appear:
- general weakness, feeling of fatigue;
- pain in the eyes, dry sclera, tearing;
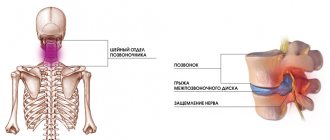
- dyspnea;
- prolonged cough, asthma attacks;
- headache;
- aching joints;
- constant low-grade fever;
- sleep disorders (drowsiness, insomnia, frequent awakenings);
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
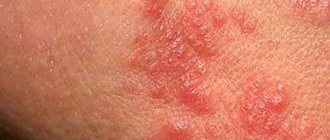
- herpetic rashes;
- the appearance of papillomas and warts.
It is also recommended to visit this specialist if there are deviations from the norm in the general blood test, or the body’s immunity to medications (antifungal, antibacterial, antiviral).
It is the immunologist who is able to clarify the picture of the course of the disease and identify the underlying pathology.
Advantages and disadvantages
pros
- High level of remuneration when compared with doctors of broad specialization.
- There are many vacancies for immunologists in all regions of Russia.
- Opportunity to form a stable circle of patients.
- Work in a clinic or private practice.
- The immunologist receives standard social guarantees.
- Regular professional development.
- Modern research methods significantly simplify the diagnostic process.
- The work is interesting and important.
Minuses
- Difficult, non-communicative, disobedient patients who often neglect doctor’s instructions.
- There is a fairly high risk of infection with various diseases, especially when it comes to working with patients who are carriers of HIV/AIDS.
- The doctor is responsible for the life and health of each patient he provides care to.
What diseases does it treat?
An immunologist is competent to treat the immune system, lymphatic vessels and nodes. Here is a specific list of diseases:
- lymphadenitis and lymphangitis;
- autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma);
- urticaria (acute and recurrent forms);
- allergic conjunctivitis;
- sinusitis,
- pharyngitis;
- otitis;
- furunculosis;
- stomatitis;
- pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- candidiasis;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- HIV infection;
- recurrent herpes infection;
- chronic acute respiratory viral infections;
- bronchial asthma;
- itchy dermatitis;
- all types of allergies (food, insect bites, medicinal);
- serum sickness;
- fever of unknown origin;
- secondary immunodeficiency due to psoriasis, hepatitis, urogenital papillomatosis and other chronic diseases.
Sometimes it is recommended to consult an immunologist in case of infertility, after radiation therapy, or after organ transplantation operations.
Training to become an immunologist
Every graduate of a medical university who has received an education within the specialty “Pediatrics” (code: 05.31.02) or “General Medicine” (code: 05.31.01) . For admission, you must pass the Unified State Exam in chemistry and the Russian language (major and compulsory subjects, respectively), as well as several additional exams: physics, biology, mathematics (major), foreign language. The competition for a place is very high, so you need to prepare well for the Unified State Exam in order to score 70-85 points in each subject!
The duration of training in these specialties is 6 years, the form of training is full-time only, which is due to the large volume of the program and disciplines, and practical training. After graduating from medical school, certified doctors choose a narrow specialization by entering residency in the profile “ Allergology and Immunology” (code: 08/31/26) .
A doctor who has completed residency in the areas of “General Medical Practice (Family Medicine)”, “Pediatrics” and “Therapy” can undergo a short retraining, after which he will have the opportunity to work as an allergist-immunologist. Only one retraining program is available for immunologists - “Osteopathy”, as specified in Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated October 8, 2015 N 707n.
Courses
CHTA (Modern Scientific and Technological Academy) (Full-time, remote)
CHTA provides training in the field of “Immunology”:
- Training;
- Professional retraining;
- Preparation for passing initial and recurring accreditation;
- Educational seminars with CME credits.
24/7 customer support.
Delivery of documents throughout Russia. Office in the center of Moscow. More than 7 years in the field of additional professional education. AMO (Academy of Medical Education)
Professional retraining, advanced training, seminars, preparation for accreditation in the field of Immunology. includes:
- Individual selection of programs according to your specialty.
- Compiling a portfolio.
- Entering all the necessary information for you on the Rosminzdrav portal.
- Support until successful accreditation.
Every month, the Academy of Medical Education conducts more than 20 educational events (seminars and webinars) with the issuance of CME points.
AMO is in the FRDO register, and in 2021 it passed a scheduled inspection by the Moscow Department of Education. MUIR
Features of clinical laboratory diagnostics for the new coronavirus infection COVID-19. The goal of the program is to develop and improve the ability and readiness of medical specialists for prevention, early diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and the new coronavirus infection COVID-19. The course consists entirely of practical online webinars. If it is not possible to attend an online webinar, everything is saved in video files in your personal account.
Russian Institute of Professional Education "IPO"
Russian Institute of Vocational Education, NANO "IPO" Enrolls students to receive a specialty in professional retraining and advanced training: Professional retraining "Immunology" Studying at NANO "IPO" is a convenient and quick way to receive distance education. 2000+ training courses. 15,000+ graduates from 200+ cities. Short deadlines for completing documents and external training, interest-free installments from the institute and individual discounts. Contact us! Each document issued by the Institute of Vocational Education is entered into the unified register “FRDO”.
Universities
Bashkir State Medical University
General Medicine (Faculty of Medicine, BSMU, Ministry of Health of Russia)
Northwestern State Medical University named after I.I. Mechnikov
General Medicine (Medical Faculty of Northwestern State Medical University named after I.I. Mechnikov)
Saratov State Medical University named after V. I. Razumovsky
General Medicine (Saratov State Medical University named after V.I. Razumovsky)
Dagestan State Medical University
General Medicine (Faculty of Medicine, DSMU)
Ural State Medical University
General Medicine (Faculty of Treatment and Prevention of USMU)
Diagnostics
This specialist has several laboratory and instrumental methods to establish an accurate diagnosis. Among them:
- Comprehensive determination of immune and interferon status.
- A scratch test is an allergy test, the essence of which is to introduce an allergen by means of a superficial scratch and observe the local reaction.
- Prick test ─ application of an allergen to the skin using a puncture.
- Taking scrapings from the skin or mucous membranes for cytological examination (from the oral cavity, external auditory canal).
- Determination of sensitivity to allergens.
- Bacteriological blood culture.
- PCR diagnostics and serological studies. They allow you to accurately determine the type of pathogen, virus or bacteria.
- Test for inhibition of natural leukocyte migration with various drugs.
- Bronchoscopy is an examination and assessment of the condition of the mucous membranes of the trachea and bronchi using a special device.
- Computer spirometry ─study of external respiratory function with tests (to detect hidden bronchospasm).
- X-ray of the lungs.
- Analysis of stool for dysbacteriosis.
If necessary, the immunologist refers the patient for consultation with doctors of other specialties: otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist, allergist, dermatologist.
How does an appointment or consultation with an immunologist proceed?
The initial appointment with an immunologist takes into account the rules of medical examination:
- Collecting anamnesis and listening to patient complaints.
- General examination with assessment of the condition of the skin and mucous membranes. Using the method of palpation and tapping, the tonsils, the presence of swelling of the lymph nodes, the thymus gland (only in children and adolescents), the spleen, and the liver are checked.
- Making a preliminary diagnosis and prescribing diagnostic tests.
Consultation with an immunologist requires preliminary preparation. Standard list of recommendations:
- If possible, stop taking medications 1-2 weeks in advance (or notify your doctor about the composition of the medications).
- During the last week, do not eat foods that are not typical for your standard menu; give up alcohol and energy drinks, including tea and coffee.
- 3 days before the examination, try to eliminate physical activity and stressful situations.
- When conducting diagnostics, blood is taken on an empty stomach, so do not eat anything 12 hours before the procedure. It is allowed to drink a small amount of clean still water.
- Before taking and subsequent diagnostics, try not to smoke.
Making a diagnosis and choosing a treatment strategy are possible only after studying the immunogram data, accompanying tests and instrumental examination methods.
What diagnostic methods does an immunologist use?
Basic set of methods for studying immunity:
- general blood test with a detailed leukogram - to identify general immune pathology;
- immunogram – to assess the patient’s immune status;
- HLA typing (detection of histocompatibility complex) - before organ transplantation, for the diagnosis of autoimmune conditions, in case of immunological infertility;
- skin allergy tests - to quickly determine the list of allergens;
- bacterial culture from the skin and mucous membranes - to identify infections;
- bone marrow puncture – before transplantation and to clarify the diagnosis in hematology;
- biopsy of lymph nodes/thymus - if a malignant process is suspected and to identify characteristic changes in primary immunodeficiencies.
Depending on the situation, the doctor may prescribe X-ray diagnostics, ultrasound, gastro- and colonoscopy, computed tomography (CT), tests for tumor markers and gene mutations.
Treatment
Depending on the established diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a treatment regimen. This may include the following:
- medications with antihistamine effect;
- enterosorbents;
- external preparations for treating the skin (ointments, gels, emulsions, creams);
- bronchodilators;
- sedatives;
- calcium gluconate injections;
- immunomodulators;
- hypoallergenic diet.
It is also necessary to give up bad habits, eliminate potentially dangerous allergens, and keep your home clean (regular wet cleaning is required).
Important personal qualities
The immunologist is constantly in contact with representatives of different social groups, therefore self-control, discipline, tact, as well as the following traits should prevail in his character:
- desire to help people,
- analytical thinking,
- erudition,
- empathy,
- resistance to stress.
A doctor should not be squeamish, sloppy, or impolite. He must inspire trust and respect in patients, possessing communication skills.
Treatment price
Prices for immunologist services depend on the city and the reputation of the clinic. In the provinces, the cost of consultation is lower than in the capital. The average cost of admission is from 2 to 5 thousand rubles. You can also make an appointment with an immunologist at a regular public clinic at your place of residence. It will be completely free, but most likely you will have to wait your turn.
An immunologist is an important and sought-after specialist in the modern world. Living in megacities, unfavorable ecology and a sedentary lifestyle often affect the health of the population and cause disturbances in the functioning of the immune system.
Consultations with a doctor online Taking care of your health is a life priority for everyone.
Communicate with doctors online and receive qualified assistance without leaving your home. Try it Please note! The information on this page is provided for informational purposes only. To prescribe treatment, you must consult a doctor.
Characteristics of the work of an immunologist
An immunologist is a doctor whose focus is the treatment of diseases of the human immune system, as well as carrying out preventive measures regarding diseases and pathologies of the immune system, in order to minimize the consequences of immunological problems and their impact on the functioning of other important organs and systems of the patient.
Content:
- Characteristics of the work of an immunologist
- Symptoms and diseases
- Methods for diagnosing diseases by immunologists
- Recommendations from immunologists
Preventive immunization is not only a medical, but also a socially useful task for immunologists, which includes the timeliness of vaccination and the prevention of complications in the post-vaccination period.
Since the immune system takes an active part in the work of absolutely all organs and systems of the human body, an immunologist must very skillfully assess the impact of immune problems on the course of various processes.
Immunologists also work in research centers, studying the variability of diseases and developing the latest effective vaccines.
The main sections of immunology as a science are classified into separate specialized areas.
General immunology, which examines the molecular structure of human immune cells, pathological immunology or immunopathology, which examines disorders of the immune system of an individual patient, infectious, non-infectious immunology.
The list also includes immunochemistry, allergic immunology, which studies, prevents and eliminates allergic reactions.
Transplantation immunology considers the immunological aspects of organ transplantation, radiation immunology deals with the restoration of immunity after irradiation, embryoimmunology is aimed at determining the compatibility of the fetus and mother.
Pediatric immunology stands out separately, the task of which is to study the development of immunity in children, their timely immunization and the determination of specific methods of treating young patients.
Another global role of immunologists in modern medicine is direct participation in the development of vaccines against severe infectious diseases.
Immunodeficiency conditions
Immunodeficiency is a state of insufficient immunity. There are primary and secondary immunodeficiencies. Primary immune deficiency is mainly caused by severe congenital diseases and genetic pathologies. These include Louis-Barr syndrome, agammaglobulinia and others. Secondary immunodeficiencies are much more common and differ in duration and severity. The following can lead to decreased immunity:
- infectious diseases;
- long-term use of corticosteroids, drugs to suppress the immune system;
- alcohol and other types of intoxication;
- metabolic disorder;
- lymphomas, leukemias, hemoblastoses;
- radiation therapy.
The most severe form of secondary immunodeficiency is caused by HIV infection.
Immunity deficiency can be suspected if the patient often experiences relapses of infectious diseases of the respiratory tract and urinary tract. Immunodeficiencies are also accompanied by generalized herpes, cardiasis, and furunculosis. Patients with this pathological condition are susceptible to the development of eczema and severe allergic reactions. With congenital or acquired deficiency of immunological factors, the risk of developing cancer increases.
Immunologist services at GMS Hospital
GMS Hospital Medical Center provides a wide range of services for the diagnosis and treatment of immunological diseases. When you visit an immunologist, you will receive professional advice from a specialist, and in just one day you will be able to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis, take tests for allergens, have an immunogram and a number of other specific tests.
After a detailed examination using innovative diagnostic techniques and technically advanced equipment, the immunologist will develop an individual treatment regimen. In addition to medical and advisory assistance, experienced immunologists at GMS Hospital will help you understand the variety of vaccines when carrying out immunoprophylaxis.
Immune disorder or common morbidity: how to distinguish?
There are criteria by which you can distinguish a serious immune failure from ordinary recurrent diseases. Its main manifestation is the presence of frequent infectious diseases with a severe course in a person.
An occasional runny nose, cough, or fever is a normal protective reaction of the body; they are not a reason to visit an immunologist. Doctors tend to consider 4-6 episodes of uncomplicated illnesses per year in an adult as the norm, even if one day bronchitis or pneumonia occurs, requiring the use of antibacterial therapy.
Immunity disorders are evidenced by frequently occurring severe illnesses that are difficult to treat with antibiotics.
to contents ^
When should you contact an immunologist?
It is necessary to visit a specialist in the case when there is a deterioration in the condition, and the reasons explaining this fact have not been found. It is possible that another doctor will independently redirect the patient for a consultation with an immunologist.
The patient himself should be alert to the following body conditions:
- The body temperature remains at low-grade levels for a long time (from 3 to 7 days), but there is no explanation for this fact.
- A person suffers from a chronic feeling of fatigue; he becomes easily fatigued, even after a short period of mental or physical activity.
- There are problems with sleep such as insomnia or, on the contrary, constant drowsiness.
- There is a feeling of aching in the body and joints.
- Colds often recur and are protracted.
- Recurrent fact of herpetic infection.
- Purulent infections of the oral cavity and nasopharynx.
- Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
- A blood test indicates the presence of inflammation.
- Frequent relapses of any disease.
- Lack of sensitivity of the body to treatment - antiviral, antibacterial, antimycotic.