Arthrosis of the knee joint is a degenerative-dystrophic pathology that leads to deformation and destruction of articular cartilage. Gradually the limb loses mobility. According to statistics, almost every third person on the planet suffers from arthrosis, and this number is not decreasing. Elderly people, especially those who are overweight, are at risk. After 65 years, arthrosis is diagnosed in 70-85% of cases of treatment for knee pain.
A rheumatologist helps maintain a patient’s quality of life with joint pathology.
Causes of arthrosis
- Destruction of the joint due to natural wear and tear (aging of the body).
- Hormonal disorders (menopause, endocrine diseases).
- Congenital defects of the musculoskeletal system.
- Injuries, surgery on the knee joint.
- Professional sports.
- Monotonous physical work with increased load on the knee joints.
- Excess body weight.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Autoimmune diseases.
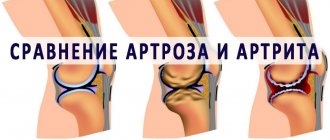
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis in many cases does not cause great difficulties. But there are exceptions, for example, patients with damage to the shoulder joint and symptoms of joint inflammation. Difficulties may also arise in diagnosing primary and secondary osteoarthritis, the occurrence of which is associated with metabolic or other diseases. During X-ray examination, signs of osteoarthritis are detected quickly (especially in older people) if clinical signs of osteoarthritis are present. In order to make a final diagnosis, X-ray and laboratory data are not enough. To do this, it is necessary to conduct a number of additional studies to identify the exact cause of joint pain.
Symptoms of the disease
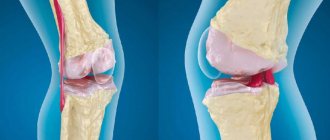
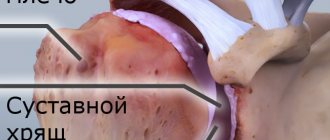
Deforming arthrosis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis) develops slowly and is chronic. In the early stages, the disease does not cause pain: the person feels only discomfort and stiffness in the lower limb. Gradually, motor restrictions increase. Without adequate treatment, the knee becomes noticeably deformed. Motor functions are so impaired that it is difficult for a person to walk, sit down, or stand up. Deforming arthrosis progresses to the point of disability of the patient. To preserve the joint, you must consult a doctor when the first symptoms of pathology appear.
Depending on the severity, there are three degrees of arthrosis of the knee joint:
- 1st degree. Clinical manifestations of the disease are mild. Most patients do not pay attention to the symptoms and continue to lead their usual lifestyle. With grade 1 arthrosis, a person may feel discomfort in the knee after standing for a long time, intense walking, or physical activity. On an x-ray, a narrowing of the joint space is visible, osteophytes growing inside the joint are visible. If arthrosis is accidentally detected in the first stage, for example, during a medical examination, its development can be significantly slowed down and even stopped.
- 2nd degree. Pain with arthrosis of the knee joint becomes intense and difficult to ignore. The leg is especially bothersome early in the morning or in the evening. During the day, at rest, aching pain persists. Degenerative processes in the joint are reflected in the gait: the person begins to limp. When moving, a crunching sound is heard in the knee. Arthrosis of the 2nd degree can be complicated by a “joint mouse” - this is a condition in which a particle of bone or destroyed cartilage enters the synovial cavity. A foreign body causes severe pain that interferes with the movement of the limb. On examination, deformity of the knee is obvious. Possible inflammation and swelling. The x-ray shows a narrowed joint space and osteophytes, thickening of the bone.
- 3rd degree. A severe form of the disease that develops without treatment. Arthrosis of the 3rd degree is the cause of permanent disability. The pain in the knee is very severe, mobility is limited, the person cannot walk independently, every step is painful. The leg becomes deformed and begins to crunch heavily. On an x-ray, the doctor determines degeneration of cartilage tissue, destruction of ligaments, menisci, and proliferation of connective tissue.
What should I do?
Instead, you need to add dairy and fish dishes, buckwheat, beans, lentils, as well as products containing fiber and sulfur (flax seed, bran, onions, garlic) to the menu. They take an active part in the construction of cartilage and connective tissue.
Do your joints hurt? Eat less meat
4. Orthopedic shoes without prescription.
For arthrosis of the ankle, knee or hip, orthopedists often recommend wearing orthopedic insoles, or arch supports. They support the arch of the foot and reduce stress on the joints of the lower extremities. This is true provided the selection is correct. If insoles are chosen at random, they can cause harm.
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint
Therapy includes a set of procedures, medication, and recommendations for lifestyle changes. It is important not to try to treat arthrosis on your own. Often, patients in the first stages of the disease use painkillers and consult a doctor when the joint is already destroyed. The earlier treatment is started, the more effective it is.
Drug treatment
The doctor prescribes medications to relieve inflammation, swelling, reduce pain, activate metabolic processes and tissue regeneration. Medicines are selected individually.
The following medications can be taken:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in the form of tablets, ointments, injections. The drugs relieve pain and swelling well, and improve the patient’s well-being.
- Glucocorticosteroids in the form of injections directly into the knee joint. Injections are indicated for severe cases of the disease, when the limb is practically immobilized.
- Painkiller blockades. They help cope with symptoms and alleviate the course of the disease.
- Chondroprotectors. The drugs help restore cartilage tissue and slow down the destruction of the joint.
Conservative treatment
Shock wave therapy
The method is non-invasive, helps remove salt deposits and improve the trophism of connective tissue. Physiotherapy improves blood circulation and has a beneficial effect on the elasticity of ligaments. Shock wave therapy is carried out in courses of 4-10 procedures.
Plasmolifting (PRP therapy)
The patient's own platelet-rich plasma is injected into the joint. A course of plasma lifting accelerates tissue regeneration.
Phonophoresis
The method combines the effects of ultrasound and medicinal ointments. Physiotherapy products, as a rule, have a complex composition and are prepared in a pharmacy according to a prescription. Ultrasound increases the penetrating ability of the active substance.
Massage
The procedure is contraindicated in the acute stage of arthrosis. When the inflammation is relieved and the pain is reduced, you can begin a massage course. Lymphatic drainage technique helps prevent the accumulation of synovial fluid. Massage also improves blood circulation in the knee and relieves muscle spasm. The procedure is most effective after performing special exercises for arthrosis of the knee joint.
Taking a bath
You can conduct the course at home as prescribed by a doctor or as part of a spa treatment. For arthrosis, radon, turpentine, and hydrogen sulfide baths are indicated. The procedures have a beneficial effect not only on the knees, but also on the hip and ankle joints.
Hirudotherapy
Medical leeches are placed around the deformed joint. The saliva of these creatures contains active substances that promote the restoration of cartilage. Hirudotherapy is usually prescribed for grade 1 and 2 arthrosis to relieve swelling and reduce pain.
Physiotherapy
Gymnastics for arthrosis of the knee joint is an essential part of complex treatment. Special exercises help maintain muscle tone in the sore limb and prevent congestion. They begin to do gymnastics in the morning, without getting out of bed. Then during the day, perform another 3-4 sets of exercises for several minutes. It is useful to supplement therapeutic exercises for arthrosis of the knee joint with swimming.
Surgery
Surgery is indicated for grade 2 and 3 arthrosis:
- Puncture. Using a syringe, the accumulated fluid is pumped out of the joint cavity. Internal pressure decreases, swelling and inflammation decrease, and mobility improves. The procedure is carried out on an outpatient basis, at the surgeon's appointment.
- Arthroscopy. The method is used for rehabilitation of the knee joint. Arthroscopy is performed through small punctures, so the operation is quite easy to tolerate and the recovery period is short.
- Corrective osteotomy. A classic method of treating deforming arthrosis, which consists of correcting the deformed anatomical axis of the lower limb, followed by fixation of the wedge-shaped resection of the bone with a titanium plate. After osteotomy, the patient requires rehabilitation for several months.
- Endoprosthetics. Installation of an artificial joint is performed in extreme cases of deforming arthrosis of the knee joint and allows the knee to return to its previous range of motion without pain. After total endoprosthetics, the patient requires long-term (about 2-3 months) rehabilitation.
Cost of services
price 532 — Consultations with an orthopedic traumatologist.
You can see
more detailed prices for services Literature:
- Bozabaev B.U. Method of treatment of deforming arthrosis of the knee joints [Electronic resource] // Bulletin of the Kazakh National Medical University. 2013. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/metod-lecheniya-deformiruyuschego-artroza-kolennyh-sustavov.
- Klimenko I.G. Method of treatment of deforming arthrosis of the knee joint [Electronic resource] // Siberian Medical Journal (Irkutsk). 2007. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sposob-lecheniya-deformiruyuschego-artroza-kolennogo-sustava-soobschenie-1.
- Zorya V.I., Lazishvili G.D., Shpakovsky D.E. Deforming arthrosis of the knee joint // Littera. 2010.
- Makushin V.D., Chegurov OK, Kazantsev V.I., Gordievskikh N.I. On the role of intraosseous hypertension in the genesis of pain syndrome in gonarthrosis // Genius of Orthopedics. 2000.
Endoprosthetics - a modern alternative to surgery
At the second and even third stage of arthrosis, progressive doctors recommend their patients intra-articular injection of a synovial fluid substitute, for example the drug Noltrex. The procedure is carried out in a dressing room, under local anesthesia, for 20-30 minutes. The full course involves several administrations at weekly intervals.
After a short period of time, the person forgets about the pain, mobility is restored, and the result lasts for 1-2 years. Endoprosthetics of synovial fluid is a relatively new treatment for arthrosis, however, due to its long-term effect and the absence of side effects, it is increasingly preferred instead of drugs based on hyaluronic acid.
Treatment with Noltrex is focused on long-term effects rather than temporary relief of symptoms.
The second degree of arthrosis is a certain intermediate stage. The period when it is not too late to start treatment, recover and return to a healthy lifestyle without pain and restrictions. The main thing is not to miss the first signs and take action in time, since otherwise the consequences for the joints can be unpredictable.
Knee replacement for deforming gonarthrosis
Non-invasive or minimally invasive treatment that was not successful at stage 2 is pointless to use anymore. To effectively help the patient restore their quality of life, experts recommend undergoing high-tech arthroplasty. This surgical intervention allows in 95% of cases and above to achieve complete restoration of the limb’s functionality. Intraoperative and postoperative complications are minimal: negative phenomena practically do not occur with correctly performed intervention and impeccably organized rehabilitation.
Very often surgery is the only option.
The procedure for replacing a failed biological joint is the only real salvation for many patients with an incurable chronic pathogenesis. The productivity of such implantation has been reliably confirmed by multicenter clinical studies. According to many years of practical observations, with an artificial left-sided and/or right-sided analogue joint, the amplitude of movements is restored to full volume.
Simplified implant installation diagram.
A minimum of 15 years must pass before the next reinstallation of the prosthesis, although in most cases the non-native structure serves well on average for 20-25 years. We will once again emphasize that the main conditions for the long service life of a unique device that functions similarly to a healthy joint and a favorable prognosis are high-precision placement of an artificial prosthesis and high-quality postoperative rehabilitation of the patient.
Knee implant in mock-up.
The implanted product, which is placed instead of a destroyed knee joint, comes in various types, depending on the degenerative-dystrophic specifics. The most widely used types of endoprosthetic systems are:
- unicondylar prosthesis – the lateral or medial condyle of the tibia is subject to prosthetics;
- total implant with a movable platform - such models involve a complete replacement of articular surfaces (the most expensive, but considered the most physiological);
- linked endoprosthesis - used in situations where the ligamentous apparatus of the knee is additionally damaged (mechanical stabilizers in this device will play the role of ligaments).
The structure of knee prostheses follows the natural configuration of the joint or its individual part, which needs to be replaced due to irreversible changes that have occurred. Modern endoprostheses are made from ultra-technological metal alloys based on titanium, chromium, cobalt, molybdenum or high-strength ceramics.
A unicondylar implant made of black ceramic is subject to longer wear.
The implant model and attachment method are selected by the operating surgeon at the preoperative stage of preparation. Based on the type of fixation, innovative designs are:
- cement – bonded to the bone using medical cement;
- cementless – fixed by hammering;
- hybrid - one of the elements is placed on cement, the second is hammered into the bone using the “press fit” technique.
The surgery is performed under spinal (most often) or general anesthesia. The entire replacement process takes approximately 2 hours. The essence of the procedure is the resection of the deformed end elements of the articular bones, followed by the correct installation and rigid fixation of the endoprosthesis components. Immediately after prosthetics, they begin to implement a rehabilitation program, which provides for intensive prevention of all possible complications and high-quality development of the operated limb.