Homocysteine test
Homocysteine is an amino acid produced exclusively by the body. It does not come with food. Too high levels of homocysteine in the blood indicate that a person has homocysteinuria, an inherited autosomal recessive disease. Problems with the level of this amino acid can be caused by a lack of folic acid, vitamins B6 and B12, and genetic defects of folate cycle enzymes.
Elevated homocysteine levels significantly increase the risk of developing serious cardiovascular diseases, atherosclerosis, and venous thromboembolic complications.
During pregnancy, you need to carefully monitor the level of this acid. If the homocysteine content is elevated during pregnancy, blood microcirculation and nutrition of the placenta are disrupted, which can lead to such serious complications as fetoplacental insufficiency, intrauterine fetal hypoxia, gestosis, and miscarriage.
A test for homocysteine is prescribed to pregnant women in combination with other examinations. These include both routine tests and a study of the hemostasis system, studying biological material for the concentration of vitamin B12 and folic acid.
Homocysteine is a sulfur-containing amino acid in blood plasma. High homocysteine levels increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, Alzheimer's disease and osteoporosis.
Synonyms Russian
Sulfur-containing amino acid, a product of methionine metabolism.
English synonyms
Homocysteine, plasma total homocysteine.
Research method
Chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (CMIA).
Determination range: 1 - 500 µmol/l (Architect i2000SR analyzer, Abbott Diagnostics).
Units
μmol/L (micromoles per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Eliminate fatty foods from your diet the day before the test.
- Do not eat for 8 hours before the test; you can drink clean still water.
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
More about the study
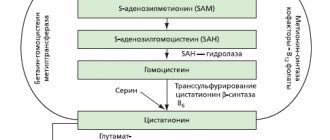
Homocysteine is a sulfur-containing amino acid, which is a product of the metabolism of the amino acids methionine and cysteine. Homocysteine is usually found in very small concentrations in the body's cells. Methionine is one of the eleven essential amino acids, that is, those that are not formed in the body and enter it only with food. In healthy cells, homocysteine is quickly transformed into its metabolic products.
For further metabolism of homocysteine, vitamins B6, B12 and folic acid are necessary. In patients deficient in them, homocysteine levels may be elevated.
Excess homocysteine is dangerous for the development of atherosclerosis due to damage to the walls of blood vessels and the formation of blood clots, although there is no direct connection between these two events. The feasibility of using homocysteine levels to assess the risk of cardiovascular diseases, peripheral vascular diseases and strokes is questionable, since, according to clinical studies, the introduction of folic acid and B vitamins into the bodies of patients did not reduce the number of cardiovascular diseases among them .
Levels of homocysteine in the blood and urine can rise sharply in homocysteinuria, a rare disease that is inherited. It causes changes in one or more genes. A person suffering from homocysteinuria develops a defective enzyme that prevents the breakdown of methionine. Because of this, homocysteine and methionine accumulate in the body. A child born with homocysteinuria looks healthy the first time after birth, but after a few years he shows signs of the disease: the eye lenses shift, the child becomes tall and thin, and his fingers become long and thin, he begins to suffer from skeletal abnormalities, osteoporosis, and Moreover, it greatly increases the risk of thrombosis and atherosclerosis, which can lead to early cardiovascular diseases. Further development of the disease threatens mental retardation, behavioral abnormalities and epilepsy.
What is the research used for?
- To diagnose homocysteinuria, in particular if there is a suspicion that the child has a hereditary predisposition to the disease.
- For some conditions in newborns, the test is performed as part of the infant examination. If a sample taken from a child gives a positive result for the presence of the disease, then a blood and urine test for homocysteine is prescribed to confirm the diagnosis.
- For the evaluation of patients at high risk of heart attack and stroke.
- To screen patients with a family history of coronary artery disease.
When is the study scheduled?
- If you suspect a deficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid in those who have had a poor diet, in the elderly (they usually have a slower absorption of vitamin B12 from food), as well as in people dependent on alcohol and drugs.
- When there is a high probability that a child (adolescent) may develop homocysteinuria.
- If a heart attack or stroke occurred without a predisposition to these diseases.
- When examining for the presence of cardiovascular diseases.
What do the results mean?
Reference values
| Floor | Reference values , µmol/l |
| Female | 4,44 — 13,56 |
| Male | 5,46 — 16,20 |
- Homocysteine levels may be elevated due to malnutrition or a lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid. In this case, the body cannot convert homocysteine into substances that the body can absorb, so the level of homocysteine in the blood increases.
- Severely elevated homocysteine levels in a newborn indicate a high likelihood that the baby has homocysteinuria, so further tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis.
Explanation of the homocysteine test
| Age | Floor | Homocysteine level, µmol/l |
| 5 days - 1 year | both | 2,87 – 9,99 |
| 1 year – 7 years | both | 2,76 – 7,62 |
| 7 – 12 years | both | 3,43 – 8,45 |
| 12 – 15 years | female | 4,07 – 10,36 |
| male | 4,71 – 10,40 | |
| 15 – 19 years old | female | 4,92 – 11,88 |
| male | 5,5– 13,39 | |
| >19 years old | female | 4,44 – 13,56 |
| male | 5,46 – 16,20 |
Homocysteine. Interpretation of test results
Indicators obtained during the study may vary significantly. This is influenced by the gender and age of the patient. For example, in men the concentration of homocysteine in the body is an order of magnitude higher than in women. The same applies to age - the older a person is, the higher the level of this substance in his body will be.
Reduced homocysteine levels: what does it mean?
If during the study it was discovered that the concentration of homocysteine in the patient’s body is reduced, this may indicate a number of abnormalities. Among them are the initial stages of diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction, the first trimesters of pregnancy, and Down syndrome.
In addition, the concentration of homocysteine in the body is directly affected by taking certain medications. These include estrogen preparations, expectorants and a number of others.
What does an elevated homocysteine concentration indicate?
If the study revealed that the level of homocysteine in the patient’s body is increased, this may indicate: severe complications of pregnancy, decreased cognitive abilities in old age. Also, this indicator can increase significantly during the period of taking medications such as cytostatics, sugar-lowering drugs, androgen hormone, etc.
If the homocysteine test shows abnormalities, the patient must undergo a series of additional examinations.
This analysis can be taken on a state basis only with the direction of a specialized specialist. The paper can be prescribed by a general practitioner, neurologist, obstetrician-gynecologist, endocrinologist. In some cases, other doctors also issue a referral.
This analysis is also necessary to assess cardiovascular risks. However, it is not prescribed separately - the study is always carried out in conjunction with other tests.
Treatment of hyperhomocysteinemia
If hyperhomocysteinemia is detected, specially selected therapy is carried out with high doses of folic acid and B vitamins (B6, B12, B1). Since a vitamin deficiency state is often associated with impaired absorption of vitamins in the gastrointestinal tract, treatment, as a rule, begins with intramuscular administration of B vitamins. After homocysteine levels have decreased to normal (5-15 mcg/ml), maintenance doses of vitamins per os are prescribed. This treatment is characterized by the absence of side effects, and in addition, it is incomparably cheaper than pharmacotherapy for risk factors such as hypertension and hyperlipidemia.
Tests for coronavirus
- Test for coronavirus
- Coronavirus test for organizations
- Testing for coronavirus at home
- Testing for coronavirus at home in 12 hours!
- Testing for coronavirus in Lyubertsy in 12 hours!
- Testing for coronavirus in Nekrasovka in 12 hours!
- Testing for coronavirus in Korolev in 12 hours!
- Test for coronavirus on the Sokol metro station
- Coronavirus test at Kolomenskaya metro station
- Coronavirus test at Voykovskaya metro station
- Test for coronavirus in Nekrasovka
- Coronavirus test in Korolev
- Test for coronavirus in Lyubertsy
- Test for coronavirus in Mytishchi
- Test for coronavirus at home Mytishchi
- Test for coronavirus at home Korolev
- Test for coronavirus at home Lyubertsy
- Test for coronavirus at home Nekrasovka
Any tests can be taken at clinics in the East Clinic network.
References
1. Clinical aspects of hyperhomocysteinemia: monograph / V.A. Snezhitsky [and others]; under general editorship V.A. Snezhitsky, V.M. Pyrochkina. – Grodno: GrSMU, 2011. – 292 p. 2. Kostyuchenko G.I. Hyperhomocysteinemia: clinical significance, age-related characteristics, diagnosis and correction // Clinical gerontology. 2007. No. 4. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/gipergomotsisteinemiya-klinicheskoe-znachenie-vozrastnye-osobennosti-diagnostika-i-korrektsiya (date of access: 08/30/2020). 3. EC/EOA GUIDELINES FOR THE DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF DYSLIPIDEMIAS 2021 Original publication European Heart Journal (2016), 37 (39): 2999-3058, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehw272
Homocysteine and dementia
Dementia is a condition in which the ability to think is impaired. Dementia manifests itself in a decrease in memory, attention, and ability to perform daily activities. There are many forms of dementia, but the most common is Alzheimer's disease. This is a disease in which abnormally folded proteins accumulate in neurons, which leads to impaired intelligence. The main reason for the development of this disease is currently unknown. Research around the world is looking at various factors that may play a role in the development of Alzheimer's disease. One possible reason is a disruption of the folate cycle. It is believed that high levels of homocysteine can damage neurons and cause their death.
Why does Alzheimer's disease occur and how can sleep protect against dementia?
Normal for men and women
GC is measured in micromoles per liter. The norm for a healthy woman is no less than 4.6 µmol/l and no more than 12.4 µmol/l. In men, values vary from 6.2 µmol/l to 15 µmol/l.
Minor deviations from the norm - up to 1-2 units up or down - may be a consequence of the individual characteristics of the body. If there is an increase or decrease of more than 3 units, you should pay close attention to your health. With such indicators, the risk of developing vascular atherosclerosis in women increases by 80%, and in men by 60%.
How to control homocysteine levels
- Introduce into the diet foods containing vitamins B6, B12, folic acid;
- All women of reproductive age should consume a daily dosage of folic acid of 400 mcg per day;
- Reduce consumption of foods containing the amino acid methionine:
- Fish,
- Meat,
- Cheese,
- Eggs,
- Nuts.
Any diet is prescribed individually, so to change your diet you should contact a specialist.
Sources:
- Kim, J., Kim, H., Roh, H., Kwon, Y., Causes of hyperhomocysteinemia and its pathological significance, 2021.
- S. Brustolin, R. Giugliani, and T. M. Félix, Genetics of homocysteine metabolism and associated disorders, 2010.
- Andrey N. Gaiday, Akylbek B. Tussupkaliyev, Saule K. Bermagambetova, Sagira S. Zhumagulova, Leyla K. Sarsembayeva, Moldir B. Dossimbetova, Zhanibek Zh Daribay, Effect of homocysteine on pregnancy: A systematic review, 2021.
- Elena Voskoboevaa, Alla Semyachkinab, Maria Yablonskayab, Ekaterina Nikolaevab, Homocystinuria due to cystathionine beta-synthase(CBS) deficiency in Russia: Molecular and clinical characterization, 2021.
- Natassia Robinsona, Peter Grabowskib, Ishtiaq Rehman, Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis: Is there a role for folate?, 2017.
- Nadia Bouzidi, Majed Hassine, Hajer fodha, Mejdi Ben Messaoud, Faouzi Maatouk4, Habib Gamra, Salima ferchichi, Association of the methylene-tetrahydrofolate reductase gene rs1801133 C677T variant with serum homocysteine levels, and the severity of coronary artery disease, 2021.
- NHS, Homocystinuria
What else should you know?
If the results of laboratory tests confirm the diagnosis of homocystinuria, then in some cases genetic testing is performed. Genetic testing is ordered to identify one or more of the most common genetic mutations. If the patient has an unfavorable family history of early atherosclerosis or one of the family members has been diagnosed with homocystinuria, then the patient should be tested for the genetic mutation that was found in the family member.
Homocysteine levels can increase with age, as well as with smoking, drinking alcohol, drinking large amounts of coffee, or using drugs such as carbamazepine, methotrexate, or phenytoin. Its concentration in women is lower than in men, but increases after menopause, possibly due to a decrease in estrogen production.
Homocysteine levels may increase in some diseases, for example, hypothyroidism, renal failure, proliferative diseases.
Interpretation of results
Reference values vary depending on age. To correctly interpret the results, you must consult a doctor; self-diagnosis is unacceptable. Elevated levels of homocysteine may indicate a deficiency of B vitamins, kidney failure, diabetes, psoriasis, senile dementia, and pregnancy complications. They can also be elevated due to malnutrition. Significantly elevated levels in a newborn indicate homocysteinuria. To confirm this diagnosis, additional examination is required. Amino acid deficiency is observed in Down syndrome and hyperthyroidism.
The test results may be affected by long-term use of a number of medications, so you should inform your doctor if you are taking any medications.