JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) operates a Pain Treatment Center. More details about the Pain Treatment Center
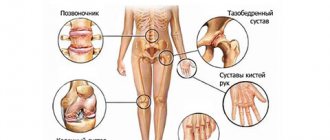
Pain in the hip joint, as a rule, indicates the appearance of a pathological process in the anatomical structures of the joint itself or adjacent tissues and organs. Most often, pain is caused by mechanical damage, an inflammatory process, an infectious or endocrine disease. It is possible that there are other factors that can trigger the appearance of this symptom. Let's look at why the hip joint hurts and how to deal with this problem.
Causes
Among the factors that provoke the appearance of pelvic pain, we should first of all mention:
- infectious inflammatory process in the tissues of the joint capsule (arthritis);
- degenerative tissue changes, osteoarthritis;
- traumatic injury - dislocation or fracture of the femoral neck;
- aseptic necrosis affecting the head of the femur;
- inflammatory process in the tissues forming the joint capsule (bursitis);
- non-infectious inflammation caused by an autoimmune disease;
- tuberculosis process;
- pregnancy.
Pain in the pelvic bones is much less common in young patients than in older people. In the older age category (over 60 years), it is periodically or constantly present in 60-60% of patients, while children under 18 years of age suffer from it in barely 10% of cases.
Diet
With the help of nutritional correction, the patient can not only reduce body weight, but also reduce inflammatory reactions, salt deposits in tissues and metabolic disorders. It is recommended to follow a balanced menu with sufficient, but not excessive amounts of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, as well as vitamins and minerals. Particular attention should be paid to unsaturated fats (olive and flaxseed oil), omega-3 acids (found in abundance in fish), collagen (jelly, aspic). It is recommended to minimize fast carbohydrates, alcohol, strong coffee, products with artificial flavors, preservatives and flavor enhancers.
Pelvic pain in women
The joint connecting the pelvic and femur bones bears the heaviest load in a woman’s body, so its wear and tear is also extremely high. A common cause of its damage is a fracture of the femoral neck - an injury that most often affects women over 60 years of age. At this age, many of them develop osteoporosis after menopause. Bones become fragile, and any fall from height can lead to a severe fracture. In old age, its treatment usually requires surgery.
Another disease that often affects women is coxarthrosis, which is characterized by the gradual destruction of interarticular cartilage tissue. One of the typical manifestations is pain in the hip joint when walking, which subsides with rest. In women, the disease begins during menopause and progresses steadily, sometimes leading to complete inability to move independently.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint
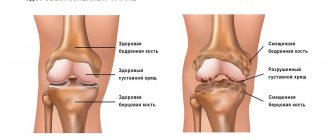
Arthrosis of the hip joint or coxarthrosis is a pathology of the musculoskeletal system. In an advanced stage, the disease leads to disability. The disease is accompanied by limitation or complete loss of motor function and joint deformation. The development of the disease involves thinning and destruction of cartilage tissue, as a result of which mobility deteriorates. This is a very common pathology.
The provoking factor is the person’s age. As the body ages, its tissues gradually wear out. The cartilage becomes thinner and begins to break down.
The development of coxarthrosis can be caused by:
- injuries of various types - fractures, bruises, dislocations;
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of the spine;
- overweight, obesity;
- disturbances in the endocrine system, hormonal imbalances;
- maintaining a sedentary lifestyle;
- deterioration of blood microcirculation in tissues;
- infectious diseases.
All these provoking factors lead to the fact that the cartilaginous structures are worn out and the articular surfaces begin to rub against each other. The bones become damaged and begin to deform. Movement is constrained and may be completely limited in the future.
This pathology can be primary or secondary. According to most doctors, primary coxarthrosis occurs when blood microcirculation in the joint area is disrupted. In the first two stages, the disease can be successfully treated with conservative methods. In the second two stages, a person needs surgery.
The key manifestation of this disease is severe pain that appears in the thigh and groin area. At first, this symptom appears only after physical exertion, after prolonged standing or walking. In the future, the pain becomes more pronounced and persists constantly, even after rest.
It is very important to see a doctor in the early stages of the disease. This will stop further progression of the pathological process. If hip arthrosis is not treated, the severity of the disease will progress. The pain radiates to other areas - lower back, groin, spine, knee, lower leg.
Painful sensations are accompanied by:
- discomfort;
- feeling of fullness;
- crunch;
- clicks during movements.
At the initial stages of the disease, stiffness appears after waking up in the morning. In the future, mobility is limited, and gradually it becomes difficult for a person to move without a cane. At an advanced stage, the ability to move is completely lost.
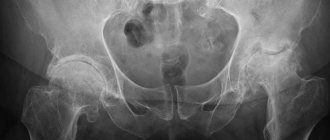
The presence of this disease can be determined using radiography, computer or magnetic resonance imaging, and ultrasound. Treatment in the early stages involves the use of conservative therapy. In the later stages, radical intervention can help.
Pelvic pain in men
The only pathology of the pelvic joint that affects only men is Perthes disease. This is a hereditary disease that consists of deformation of the head of the femur: it becomes flat rather than round. When walking, the patient has pain in the hip joint on the left side, if the pathology is localized on the left, or on the right side, if the head is deformed on the right.
A disease that is more common in men is tendonitis, or an inflammatory process that affects the tendons. This is a disease of athletes and people forced to perform heavy physical work for a long time - loaders, masons, heavy weights, etc. Pain appears during heavy exertion, during active movements. With moderate and light loads, as a rule, there is no pain.
The next typically “male” disease is necrosis of the femoral head, and about a third of patients become ill at a young age - up to 30 years. The disease goes through several stages, and already at the very beginning the patient has pain in the hip joint on the right side (or on the left), and the pain is felt in the groin area, less often it radiates to the hip, knee or lower back. If left untreated, lameness appears over time and disability develops.
Pelvic pain in pregnant women
There are several reasons why hip joints may hurt in women:
- in recent weeks - lack of calcium or vitamin D;
- increased production of the hormone relaxin, which promotes sprains;
- exacerbation of latent hip dysplasia or osteoarthritis;
- increased stress on the joint due to weight gain;
- old injury.
Women who have pelvic pain during pregnancy should be more attentive to their health, because this condition can lead to an exacerbation of even minor diseases.
Prevention
Lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of developing coxarthrosis, as well as the rate of its progression. It is important to strictly adhere to the rules:
- lead an active lifestyle: swimming in the pool, race walking, cycling - physical activity at an amateur level without racing for records helps improve blood supply and inhibits the processes of joint degeneration;
- normalize body weight to reduce the load on the legs;
- exclude injuries, hypothermia and occupational risk factors (vibration, heavy lifting, standing work);
- promptly treat all diseases, including those not directly related to the musculoskeletal system;
- Correct posture problems in a timely manner and wear comfortable shoes.
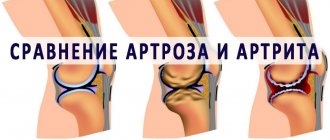
Chronic pelvic pain
Chronic is any pain in the pelvic area that continues with varying intensity for several months. Aching pain in the hip joint and surrounding area often occurs in women, but men also suffer from diseases that cause pain in the pelvic area. The causes of pain are varied, from osteochondrosis to urological and gynecological diseases. In each case, a thorough examination is necessary to identify the disease and prescribe adequate treatment.
Diagnostics
To determine the disease that causes constant pain in the hip joint, it is necessary to undergo a fairly extensive examination, which includes:
- X-ray of the hip joint, which allows you to detect or exclude traumatic damage, identify bone defects, growths and other pathologies;
- Ultrasound of the hip area, which reveals inflammatory processes and degeneration of soft tissues, calcified areas and other pathologies;
- CT scan of the hip joint, which is prescribed to clarify the diagnosis or in unclear cases;
- MRI to clarify the condition of the soft tissues of the joint capsule;
- puncture of joint fluid to remove effusion and study the composition of the infiltrate in order to detect the causative agent of infection;
- joint arthroscopy - endoscopic examination of the joint capsule using a probe inserted through a small incision.
In addition, the orthopedist, surgeon or rheumatologist prescribes laboratory tests for the patient in accordance with the presenting symptoms:
- general urine and blood tests;
- immunological blood test;
- biochemical blood test for rheumatic markers, etc.
Advantages of the clinic
No matter what problem the patient comes to the Health Energy clinic with, we will do everything to cope with the disease. We offer:
- the opportunity to be examined by doctors of various specializations;
- take tests and perform diagnostic procedures of varying complexity;
- use the services of a day hospital;
- evaluate the possibilities of physiotherapy and massage.
“Health Energy” means affordable prices and the highest level of service. Don’t let coxarthrosis ruin the life of you and your loved ones. Make an appointment at our orthopedic center!
Treatment
Clinic JSC "Medicine" offers the services of the "Pain Treatment Center". Experienced specialists will help solve the problem with any type of pain.
Since there are quite a lot of diseases that cause pelvic pain, the methods of treating them depend on the symptoms and disorders detected during diagnosis. For pathologies of bone and joint tissue, the following are usually prescribed:
- chondroprotectors, complexes of minerals and vitamins to strengthen bones, cartilage tissue and ligaments;
- muscle relaxants to reduce muscle spasms and relax tense muscles;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, in case of severe symptoms - steroids;
- drugs that improve capillary circulation to reduce swelling and manifestations of hypoxia;
- diuretics to stimulate fluid exchange and reduce swelling.
For inflammatory diseases, physiotherapeutic sessions have a good effect. Patients are prescribed electrophoresis, laser therapy, medicinal phonophoresis and other procedures. They are carried out at the end of the acute phase of inflammation to stimulate the recovery process.
If conservative methods are not effective enough, the patient may be prescribed:
- therapeutic blockade - the introduction of an anesthetic drug into the selected area to block the transmission of pain impulses along the nerve fiber, due to which spasmed muscles relax, the trophism of periarticular tissues improves, and blood flow normalizes;
- radiofrequency denervation - elimination of nerve fibers using a radiofrequency pulse through needles inserted into the joint tissue, which allows the patient to permanently relieve pain in the hip joint, radiating to the groin, knee or lower back;
- surgical opening and drainage - for purulent inflammation of the joint, followed by antibacterial therapy;
- removal of the tumor - in case of a malignant tumor process, after which chemical and radiation therapy is carried out to reduce the risk of relapse;
- hip replacement - in case of destruction, the head of the femur is removed and an implant is installed in its place, but in some cases not only part of the femur is replaced, but also the acetabulum of the pelvic bone.
The choice of method depends on the degree of damage to the joint and other tissues.
General information
Coxarthrosis belongs to the group of dystrophic diseases. It begins gradually with microscopic changes in the structure of the cartilage. Increased load, inflammatory diseases, and blood supply disorders lead to structural transformations and thinning of cartilage tissue, and these, in turn, deform the contours of the articular site. As a result, the distribution of load on the contacting surfaces of the bones changes, and areas with maximum pressure begin to wear out faster. This triggers a whole cascade of pathological reactions:
- the appearance of microcracks and areas of compaction in cartilage tissue;
- decreased smoothness of articular surfaces;
- the growth of cartilage in the place of thinning and its replacement with bone tissue;
- the appearance of osteophytes (bone growths) along the edges of the articular area;
- thickening and decreased elasticity of the joint capsule;
- sclerosis and decreased strength of ligaments;
- changes in the composition of synovial fluid (natural lubrication inside the joint);
- narrowing of the joint space;
- fusion of all joint elements (ankylosis).
Without treatment, coxarthrosis inevitably becomes a cause of immobility and disability.
Make an appointment