Pain, numbness, burning muscle in the thigh area is one of the common symptoms of diseases of the spine, femur and muscles, and pelvis. At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors identify the cause of muscle pain in the thigh using modern examination methods. Comprehensive diagnostics allows you to timely determine the cause and stop the disease.
All conditions have been created for the treatment of patients:
- Chambers of European comfort level;
- The use of the latest drugs with a minimal range of side effects;
- Innovative methods of rehabilitation therapy.
Doctors take an individual approach to choosing a treatment method for each patient. Professors and doctors of the highest category discuss all cases of severe pain in the thigh muscle at a meeting of the expert council and make a collegial decision regarding further tactics for managing the patient.
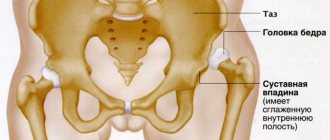
Causes of hip pain
The causes of hip pain (as well as its nature) can be different. The hip may hurt on the side of the joint or in the soft tissues, and the discomfort can occur periodically and be intense, acute or chronic. Both the right and left hip can hurt; in addition, pain can be localized in the groin area.
At CELT you can get advice from a specialist algologist.
- Initial consultation – 4,000
- Initial consultation with the head of the Pain Clinic - 4,500
Make an appointment
Hip injuries
Hip injuries include:
- bruises of the pelvis, hip joint, upper thigh;
- fracture in the area of the trochanters of the femur;
- sacrum fracture;
- dislocations of the femur;
- sprains and tears of muscles and ligaments;
- fracture of the femoral neck;
- compression fracture of the 5th lumbar vertebra.
It is worth noting that rupture of the hip ligaments can occur not only due to injury, but also due to the emergence and development of degenerative processes in them. A rupture is characterized by acute pain and impaired joint mobility.
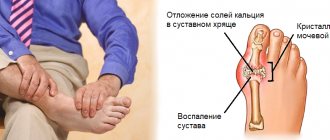
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint
Coxarthrosis, or arthrosis of the hip joint, is a disease in which wear and tear occurs on the hip joint. It is one of the most common causes of pain in the right and/or left hip. A distinctive feature of this disease is pain localized in the groin and radiating down the lateral and anterior femoral surface. Often the sensations can be projected onto the buttock or radiate to the knee; they appear when walking or getting up from a chair. Other clinical manifestations of coxarthrosis include:
- significant limitation of mobility of the affected limb (inability to perform rotational movements, pull the leg towards the chest or move it to the side);
- crunch in the hip joint;
- shortening of the leg (appears in advanced stages of the disease).
More about coxarthrosis
Arthritis of the hip joint
There are a number of arthritis that can cause inflammation of the hip joints. Despite the fact that this phenomenon is quite rare, it exists and is mainly affected by people aged 15 to 40 years.
Painful symptoms are felt most strongly at night and their intensity is quite high. They do not subside even when changing body position. When walking, the pain subsides somewhat, and in the evening (after the patient has “dispersed”) they can completely disappear, but at night they will make themselves felt again.
Hip infarction – aseptic necrosis of the femoral head
Hip infarction - this is the diagnosis given to five percent of patients who complain of hip pain. This disease is characterized by rapid development; pain symptoms increase over 1–3 days and become almost unbearable at night. Their weakening is observed at 4–5 am. Men suffer from this disease 8 times more often than women.
Inflammation of the femoral tendons
This disease is diagnosed in 25–30% of the number of patients who come with complaints of pain symptoms. Most often, women suffer from this disease, and the peak incidence occurs during menopause, during which weakening of muscles and tendons is often observed. The development of the disease occurs rapidly - within a period of 3 to 15 days. The hip hurts on the side in the soft tissues along the outer surface, either on one side or on both. The discomfort is quite intense; they appear when walking or lying on the affected side. There is no limitation of movement in the hip joint.
More about trochanteritis
Piriformis syndrome
Another very common cause of hip pain is piriformis syndrome. It occurs during pathological processes in the lumbar spine and, as a rule, is one-sided. An increase in pain occurs within 1 to 3 days due to:
- stress;
- lifting weights;
- sudden unsuccessful movement.
The pain is localized in the gluteal and lumbar region, and the sacrum often hurts. Sometimes painful sensations descend along the back surface of the lower limb to the heel.
Other reasons
In addition, the hip can hurt inside or outside and for a number of other reasons:
- pathologies of the endocrine system, leading to the destruction of cartilage and bone tissue;
- pathology of arterial vessels;
- infectious processes in the bone tissues of the hip and pelvis;
- malignant bone tumors.
Description and symptoms of pathologies of the articular zone of the musculoskeletal system
Prolonged manifestations of pain are the reason for an MRI of the hip joint. The bone joint itself is not penetrated by nerve fibers, so some diseases can be asymptomatic for a long time. Soreness appears at the stage of damage or compression of the nerve canals passing in the “hinge” region of the body. At the initial stage of the appearance of disorders, unpleasant sensations arise in a limited area of the connection of the femur with the pelvis. If the disease is ignored, the source of inflammation grows and spreads to neighboring tissues: muscle and tendon fibers, cartilage formations, nerve and blood tracts.
A person may experience the following sensations:
- prolonged radiating pain that does not go away within several days, the cause of which can be identified on an MRI of the hip joint;
- night pain leading to insomnia;
- the desire to change positions as often as possible in order to relieve the pelvic joint with constant discomfort in it.
These signs serve as a reason for a thorough diagnosis, and emergency clinical care is required if the patient complains of the following conditions:
- Irradiation to the groin. Through the conductive canal of the nerve, pulsating sensations spread to the lower abdomen and groin area; with inflammation of adjacent fibers, the sciatic nerve is affected.
- Shootings in the lower part of the back. They can be both sharp and dull, pulsating, leading to limited movement of the body and pelvis.
- Spread of pain to the leg, including the knee area. It may manifest itself as muscle weakness or itchy sensations in the skin.
- A “hinge” clutch that prevents free movement of the limb. It is a sign of arthritic and arthrosis lesions.
- Partial or complete lack of mobility associated with the destruction of pelvic tissues or trauma experienced.
- Lameness associated with low intensity pain. It requires correction, since a change in motor habit leads to deformation of the entire musculoskeletal system.
Most patients describe the phenomenon of crunching sounds when changing body position or movement. A kind of crunching sound is produced by individual ligaments. If the sound is not accompanied by unpleasant sensations, there is no need to worry. Additional pain requires contacting a medical specialist.
Diagnosis of hip pain
The specialists of the CELT Pain Clinic, like no one else, know how important it is to correctly diagnose such clinical manifestations as hip pain. The similarity of symptoms requires differentiation of different diseases, which will result in the prescribing of effective treatment.
In addition to taking an anamnesis, an examination is carried out by one of the following specialists:
- neurologist;
- traumatologist-orthopedist;
- rheumatologist;
- surgeon;
- oncologist.
In addition, our Pain Clinic performs the following diagnostic tests:
- X-ray of the hip, pelvis, lumbar spine;
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the lumbosacral spine.
If necessary, laboratory tests may be prescribed.
How to get rid of pain?
For the most part, the treatment process is directly dependent on the causes of pain, however, in all pathological conditions, the use of anti-inflammatory drugs (Movalis, Diclofenac Sodium, Ibuprofen, Nimesil) is possible.
The analgesic effect is ensured, and at the same time the level of inflammation decreases. Different pathological conditions are treated in their own way:
- Surgeries are required for malignant process in the hip joint. The tumor must be removed followed by chemotherapy.
- Repositioning of the bone, its realignment and immobilization for months.
- Drainage of the bone cavity and opening are carried out in case of purulent inflammation. This is followed by antibacterial therapy (Cefoperazone, Cefazolin, Ceftriaxone, Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Moxifloxacin).
- Regeneration drugs that improve blood circulation, for example, Pentoxifylline, restore bone tissue.
- Tivortin is the best medication for normalizing blood flow in the limb; in combination with physiotherapy it gives good results.
The use of all painkillers is completely justified and relevant after surgery, joint replacement or metal osteosynthesis.
Arthritis treatment
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are appropriate for severe pain to relieve inflammation and reduce the pain effect:
- Xefocam;
- Nise;
- Ibuprofen;
- Ortofen.
Additionally, antibiotics, drugs to improve immunity, antiallergic drugs, and drugs that improve metabolism are prescribed.
It is forbidden to work on the problem joint; the affected limb must be at rest.
The effectiveness of treatment is predetermined by a correctly identified cause of hip arthritis.
Treatment of coxarthrosis
To treat this pathology, surgery is required, but in the early stages you can start with conservative treatment.
- to eliminate inflammatory processes and relieve pain symptoms, muscle relaxants, steroidal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used;
- plasma lifting should be done to stimulate regenerative processes;
- chondroprotectors and vasodilators to restore cartilage tissue and activate blood supply in the problem area.
Kinesitherapy and physiotherapy are used as additional therapeutic measures. Diet correction is required.
Treatment of bursitis of the trochanteric bursa
Conservative treatment involves the following measures:
- restriction of physical activity;
- local anesthetics in combination with hormonal drugs;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- physical therapy, gymnastics, ultrasound and electrophoresis;
Compresses with calendula, sage, pine buds and plantain will not only relieve the inflammatory process, but also prevent the chronic development of pathology. These herbs have anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effects. In rare cases, doctors resort to surgery if inflammation and pain persist even after long-term conservative treatment. Removing the bursa is the only option, while the hip joint will still function fully.
Treatment for hip pain
The specialists of the CELT Clinic will help you get rid of hip pain forever. To do this, they not only act on the pain syndrome, but eliminate its cause. Of course, in case of severe pain, efforts are initially aimed at eliminating it. The course of treatment prescribed directly depends on the pathology that caused the pain. Typically, these are conservative methods that include:
- exercise therapy;
- massage;
- manual therapy;
- systemic therapy.
In addition, a blockade of the hip joint can be performed, which can completely eliminate pain and reduce inflammation. At the same time, the risk of side effects is practically eliminated. In extreme cases, our specialists resort to surgical intervention.
Modern treatment methods, a large arsenal of medical equipment, knowledge and experience of doctors at the CELT Pain Clinic allow our patients to forget about pain forever!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
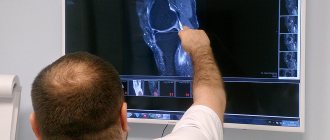
Evaluation of treatment effectiveness using MRI of the hip joint
After undergoing restorative manipulations, it is important to carry out repeated diagnostics to verify the correctness of the prescribed treatment course. The best way to compare the rate of tissue regeneration is MRI. If there are images from a previous study, the functional diagnostician compares the stage of the disease, identifies the absence or presence of relapses (tumors or infections affecting the pelvis), and migration of metastases.
After surgery, the composition of the fluid in the joint cavities and the degree of fiber restoration are examined. In some cases (with cancer of the bone), it is necessary to remove the hinge part of the hip and replace it with a prosthesis. The implant material is a metal alloy, so MRI scanning of the hip joint is contraindicated. An alternative is the same informative examination as a computer scan.
Hardware examination can be carried out in specialized diagnostic centers containing tomography rooms. You can select the nearest medical facility on the website of the Moscow Unified Recording Center. An expanded list of clinics makes it easier to compare by ratings, location addresses, and prices for services. Mark the best offers and sign up for diagnostics through the service. This will open access to additional discounts on the selected type of tomography.
How is diagnostics carried out?
Hip and groin pain can occur for numerous reasons. Initially, the patient needs examination to establish the correct diagnosis. This directly determines what therapy will be prescribed.
To determine the disease you may need:
- radiography of the hip joint;
- Dopplerography to examine vascular patency;
- CT and MRI;
- electromyography to examine tendon reflexes;
- clinical analysis of urine and blood;
- Ultrasound to determine fluid in the joint cavity;
- osteoscintigraphy to detect bone and joint abnormalities;
- densitometry to determine bone density and strength;
- biochemical, bacteriological and immunological research.
An x-ray of the hip joint is usually sufficient to identify the problem. If necessary, the doctor can prescribe a full diagnosis of the spinal column.