Due to its complex structure and function, the knee joint is very susceptible to injury, which can cause pain. Many people, especially the elderly and athletes, often complain of this disease. Overuse, bruises, sprains, sprains, strains, and tears are the most common causes of knee pain. What other reasons can cause knee pain? Do I need to visit a doctor? How to care for your knees? What should I do to prevent them from getting sick?
Knee structure
The knee joint is the largest joint in the human body and is most often affected by various types of injuries. Thanks to it, you can straighten and bend your leg, as well as perform rotational movements.
The knee is located between the femur and the tibia, has a width of 11-22 cm. The design of the knee is distinguished:
- meniscus,
- ligaments,
- knee cap.
Meniscus
The meniscus consists of two rigid plates with flexible cartilage.
There are lateral and medial meniscus. By adapting to the articular surface, they can move when the knee bends backward by 12 mm. These properties allow them to act as shock absorbers during jumps and distribute body weight evenly.
If your meniscus is damaged, you may experience the following symptoms:
- difficulty flexing and extending the joint;
- acute pain in the knee;
- difficulty moving;
- edema;
- a feeling of stiffness and an audible clicking sound.
Meniscus damage can be caused by:
- degenerative changes;
- cyst inside the joint;
- severe flexion and torsion injuries;
- disruption of the meniscus structure,
- overload.
Ligaments
The knee is strengthened by external collateral ligaments and joint capsules, as well as internal ligaments: the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments. The first prevents the tibia from moving forward, the second prevents the tibia from sliding backward.
The cruciate ligaments protect the knee joint from wearing out too quickly and support a smooth gait.
Damage to the knee ligaments causes instability of the knee, that is, excessive mobility in relation to the physiological state.
The most common injury is the anterior cruciate ligament, which prevents the tibia from moving forward in relation to the femur.
Knee ligament injuries are most often indicated by severe knee injury, a feeling of dislocation, and a hematoma in the joint.
Knee cap
The kneecap is a flat bone located in front of the knee. Together with the femur, it forms the patellofemoral joint. Under normal conditions, the kneecap moves in the groove of the knee joint.
When it slips out of the groove, pain and problems with walking occur. The most common diseases are chronodromalacia patella and lateral support syndrome of the patella.
Chondromalacia is a condition of the cartilage surrounding the kneecap. The cause of this condition is the improper angle of movement of the kneecap by the quadriceps muscles, which causes the kneecap to rub against the bone instead of sliding.
Causes of knee pain
Knee pain can be caused by many reasons. The pain can be painful after intense running, climbing, heavy exercise and sprain injuries. Knee pain also occurs due to bacterial inflammation, metabolic disorders such as gout, and chronic diseases such as degenerative joint disease.
However, knee pain most often affects athletes who put weight on their knee joints, especially so-called "chair athletes" who do not engage in any activity and suddenly decide to ski or run. Knee pain is characterized by limited joint mobility and swelling of the knees, which often occurs after intense exercise.
Causes
Injury
Knee structure
Knee pain can be caused by injury. This is the most common reason. A knee injury usually occurs under one of the following circumstances:
- a strong blow to the knee or a blow to the knee against a hard object;
- a fall;
- sharp excessive or uncharacteristic bending of the joint.
As a result of the injury, a bone fracture, dislocation, damage to tendons or ligaments, or damage to the meniscus (shock absorber cartilage that acts as a lining between the bones in the joint) can occur.
In case of injury, there is acute pain and the knee swells. Hematoma (bruising) and impaired blood supply are also possible (in this case, the skin turns pale, the knee becomes numb, and a feeling of cold and tingling may occur).
With meniscopathy (damage to the meniscus), acute pain goes away after 2-3 weeks. But the consequences of the injury can be felt for years, in the form of exacerbations - the return of pain during exercise or unsuccessful movement.
Excessive loads
Knee damage can be caused not only by a one-time impact (trauma), but also by factors acting over a long period of time. After all, the knee joint is not only one of the most complex in the human body, but also bears significant loads, especially when walking - here almost the entire load falls on it. The load may be excessive. Diseases of the knee joint are possible in professional athletes, as well as in people whose work involves carrying heavy objects or long walking.
As a result of such stress, bursitis of the knee joint (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the synovial bursa), tendonitis, tendinosis (diseases of the connective tissue of the joint), and some other diseases can develop.
Arthrosis
Arthrosis of the knee joint (osteoarthrosis of the knee joint, gonathrosis) is a degenerative-dystrophic disease of the joint, that is, pathological changes caused by destruction (primarily physical wear and tear) and malnutrition of joint tissues. Primary arthrosis is usually caused by age-related changes and is bilateral. Secondary arthrosis is also possible - a consequence of other joint diseases, for example, arthritis, gout, etc.
The first symptoms of gonarthrosis are pain in the knee, which appears when climbing stairs, getting up from a squatting position, or walking long distances. The pain is usually accompanied by a crunching sensation and a feeling of tightness in the joint. At the initial stage of the disease, the knee does not hurt at rest.
More about arthrosis
Arthritis
Arthritis of the knee joint is an inflammatory disease of the joint, which can be caused by various reasons - degenerative changes in the articular cartilage (that is, in this case, arthritis is preceded by osteoarthritis), and infection. There are different types of arthritis - post-traumatic, reactive, rheumatoid, gouty. The most common type is rheumatoid arthritis, which is caused by disorders of the immune system.
With arthritis, pain can also be observed at rest (the pain intensifies at night). Physical activity (walking) also leads to increased pain. Pain occurs with full flexion or extension of the knee. The patient feels most comfortable if his knee is bent.
Knee pain is accompanied by swelling (edema) of the joint and redness in the joint area. The joint may be hot to the touch.
Isolated inflammation of the knee joint is rare and most often occurs at a young age. In most cases, arthritis of the knee joint is only a special case of multiple joint damage (polyarthritis), and then the pain in the knee is combined with pain in other joints.
More about arthritis
Other causes of knee pain
Knee pain can also be caused by:
- coxarthrosis (arthrosis of the hip joint). In this case, the pain in the knee is of a reflected nature (radiates to the knee from the hip joint);
- circulatory disorders of the knee joint. Such pain is typical for adolescents during a period of active growth;
- bone tumors (benign and malignant);
- some other diseases.
Why do knees hurt at a young age?
The most common causes of knee pain, especially in young people, are physical activity and joint strain. If it is not caused by direct injury, it is most likely due to training errors:
- Incorrect running technique
- Poorly fitting shoes (not designed for running or that do not take into account foot defects such as flat feet),
- Running on a surface that is too hard (such as asphalt or cobblestones),
- Lack of proper warm-up
- Exercise intensity is too high.
Overuse of the knee can also occur as a result of frequent and prolonged standing and obesity.
Knee pain treatment
Before starting treatment for knee pain, you should consult a specialist. Depending on the extent of the injury and symptoms, conservative or surgical treatment is performed.
Conservative treatment of knee pain contains an algorithm of the following actions:
- First and foremost, the limb must be protected from further injury. The knee is given rigidity and the load is relieved with the help of crutches.
- It is necessary to avoid putting stress on the limb and avoid activities that cause pain, which promotes tissue healing.
- The temperature of the tissues is lowered in order to minimize the risk of edema or reduce the existing one. In addition, it has an analgesic effect. Cooling is carried out in the first 48-72 hours after injury for 10-15 minutes, approximately every 2 hours.
- It is necessary to apply moderate pressure in the form of a bandage of the limb. This prevents swelling.
- It is advisable to place the limb on high pillows in a supine position. This will help prevent the tumor from spreading to the damaged area.
- Using ointments and tablets prescribed by a professional doctor will help the pain area heal faster.
Surgical treatment for knee pain is considered when conservative treatment has failed and surgery or reconstruction of the damaged structure of the knee is necessary, such as cruciate ligament reconstruction, meniscectomy, repair of a torn tendon or bone fracture.
Pain in the knee joint: treatment at the Yusupov Hospital
The main goals for the treatment of pain in the knee joint, which the doctors at the Yusupov Hospital Therapy Clinic set for themselves, are the following:
- eliminate swelling;
- relieve the patient from discomfort;
- restore the functions of the knee joint;
- prevent new attacks.
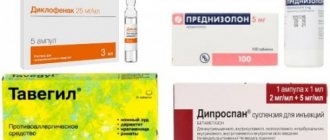
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics are used to relieve pain. The use of warming and distracting ointments, as well as restorative drugs, is effective.
In the remission stage, patients are prescribed the use of physiotherapeutic techniques, massages, and therapeutic exercises.
In the absence of effectiveness from conservative therapy, specialists, taking into account all the pros and cons, consider the advisability of surgical treatment.
In addition, there are a number of traditional medicine that help reduce pain, but their use must first be discussed with specialists who monitor the progress of treatment aimed at eliminating pain in the knee joint. How to treat this pathology should only be decided by an experienced, highly qualified doctor who is familiar with the patient’s research results, the individual characteristics of his body and many other important nuances.
Which doctor should I consult for knee pain?
First, it is best to visit your general practitioner, who will conduct an initial examination of the injured knee, based on which it will be possible to diagnose its possible cause. The doctor will examine the sore spot and, if possible, prescribe appropriate pharmacotherapy (most often these will be anti-inflammatory and painkillers) or rehabilitation. If the problem is more complex, your GP will refer you to an orthopedist or rheumatologist for a more in-depth diagnosis.
If you suspect that your knee may have been damaged as a result of an injury, you should not delay visiting your doctor. Quickly identifying the cause of your pain will not only help you combat it, but most importantly, it will save you from serious consequences such as joint damage and disability.
How to get rid of pain
First of all, you need to consult a doctor (initially a therapist or orthopedist-traumatologist, in the future you may need the help of a phlebologist or rheumatologist) to find out the causes of pain. Urgent treatment to a medical facility is required in case of unexpected sharp pain, fever and injuries. After examination and questioning, the doctor will refer you for diagnostic procedures. It can be:
- laboratory tests (general and biochemical blood tests, joint puncture);
- radiograph;
- arthroscopy;
- densitometry;
- Ultrasound of joints and blood vessels.
Cure for knee pain
If you have pain in your knees, it is best to consult a doctor who will prescribe you the necessary pharmacological medications. Self-medication may not give you any results, and more often it can only worsen the problem.
To improve the motor system and relieve pain, it is recommended to use nutritional supplements for joints (with glucosamine, collagen, hyaluronic acid, chondroitin), which support the production of synovial fluid necessary for the proper functioning of the joints. To temporarily relieve pain, you can use painkillers or topical gels (with paracetamol, ibuprofen, diclofenac). In addition, patches and warming ointments applied to the sore area relieve pain in bones and joints, allowing effective movement.
Treatment and prevention
Most joint diseases in the early stages respond well to treatment using conservative methods - medication, physiotherapy, exercise therapy and massage. In advanced cases, joint replacement surgery and long-term rehabilitation are often required, and full restoration of health will no longer be possible. This is why it is so important to start treatment on time for joint pain.
- Among the medications, anti-inflammatory drugs, chondroprotectors and some other drugs are usually prescribed. Hyaluronic acid injections reduce friction, relieve pain and stiffness during movements, and improve the quality of synovial fluid
- Physiotherapy (electrophoresis, UHF, magnetic therapy, laser therapy and other procedures) helps eliminate pain and swelling, stop inflammation, improve blood circulation and speed up tissue repair
- Therapeutic exercise normalizes blood flow, eliminates stiffness of movement and strengthens the muscle corset. When doing exercise therapy, it is important not to achieve record results, but to perform all the exercises correctly
- To speed up recovery, you need a therapeutic diet. Eating vitamin-rich plant foods, fish and other seafood has a beneficial effect on the restoration of articular cartilage
The best ways to prevent knee diseases are a healthy lifestyle and moderate physical activity. To keep your knees healthy:
- maintain a normal weight;
- eat a balanced diet;
- go swimming;
- choose comfortable shoes with orthopedic insoles;
- Strengthen your leg muscles as recommended by your doctor.
Network of clinics “Hello!” specializes in the treatment of joint diseases. All clinics are located near metro stations, which is especially important for visitors who experience pain while walking. Modern diagnostic equipment and the use of the latest treatment techniques help experienced doctors successfully relieve patients of joint pain of various origins.
Knee pain when bending
Knee pain when bending can be caused by overuse during daily life or sports. In this case, rest and peace to the damaged area helps.
Many patients with knee pain are diagnosed with various conditions that affect knee dysfunction. Such diseases include:
- Degenerative changes. A degenerative disease affecting the knee joint is gonarthrosis.
- Chondromalacia patella - This condition causes the articular cartilage that covers the kneecap to soften.
- Baker's popliteal cyst - with this disease, fluid accumulates in the popliteal fossa. The cyst is treated surgically.
- Jumper's knee is an occupational disease that most often affects very active people. Occurs as a result of overload of the upper part of the kneecap.
- Runner's knee is an injury to the joint between the kneecap and the thighbone, commonly affecting people who exercise.
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Bacterial infections
- Lyme disease is a disease that in many cases affects the joints, including the knees.
How to independently determine the cause of pain
Each disease has its own clinical manifestations and pain of a certain nature.
- With gonarthrosis, there is a constant dull pain during movements, the discomfort intensifies after waking up in the morning, accompanied by a crunching sound.
- With arthritis, swelling is noticeable and body temperature rises.
- With vein thrombosis, women complain of constant or periodic aching pain at night.
- Intense sharp pain will indicate damage to the meniscus.
- Rheumatism and rheumatoid arthritis cause symmetrical severe pain in both knees.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is well “camouflaged”: it does not cause swelling or fever
Knee pain when walking
Pain in the knees when walking is characterized by a characteristic crunching and cracking sound. It tends to get worse when running, playing sports, climbing stairs or walking. Painful symptoms also appear when sitting in one place for a long time, for example, when working for many hours at a computer or while driving a car.
Internal knee pain when walking is often caused by damage to the kneecap, meniscus (the elastic component of the knee), or ligaments. To avoid the development of physiopathological processes, treatment must be started as early as possible, otherwise there is a risk of surgical intervention.
Knee pain when going down stairs can cause what is called synovial plica syndrome, which occurs in people who are very physically active and constantly bend and straighten their knees. Sharp pain in the outside of the knee when walking is usually closely associated with lateral damage to the meniscus, which is more mobile and therefore more susceptible to injury. Older people mostly complain of pain under the knee when walking. This is because the level of cells that form the vascularized meniscus decreases with age.
Knee pain on the inside
The cause of knee pain can be a pathology of the knee joint, for example, as a result of injury or osteoarthritis. Sometimes knee pain can be the result of a rheumatological condition, such as gout, or other diseases, such as Lyme disease. A common cause of knee pain is overuse due to excess weight or sports. Pain in the knee or calf area may indicate vascular disease. In addition to the presence of pain, accompanying symptoms are also important. Therefore, it is worth visiting a therapist who, after meeting the patient, will order possible diagnostic tests and refer, for example, to an orthopedist and traumatologist or rheumatologist.
Complex therapy for joint diseases may include the following methods:
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs and chondroprotectors;
- injections into the joint of liquid endoprostheses - synovial fluid substitutes, for example, Fermatron, Sinokrom or Noltrex;
- physiotherapy - UHF, electrophoresis, laser, magnetic therapy (eliminate swelling, stop the inflammatory process, improve blood circulation);
- physical therapy – normalizes blood flow, strengthens the muscle corset;
- therapeutic diet - eating plant foods, fish and seafood to restore articular cartilage.
What is indicated for arthritis is prohibited for arthrosis: do not self-medicate
To keep your joints healthy, you need to take care of them from a young age. Lifestyle matters – diet, exercise. Excess weight has a detrimental effect on joint health, so this problem must be solved first. It is equally important to wear comfortable shoes and protect yourself from injury. If, despite your efforts, you notice pain in your knee, do not panic, but go for a consultation with a specialist as soon as possible.
Side knee pain
Lateral knee pain is one of the most common pain complaints after injury. It may happen suddenly or develop gradually. These types of symptoms are quite common in runners and people who participate in sports that require activity, such as twisting or sharply turning a limb. Pain on the side of the knee can cause limited mobility and other symptoms such as swelling or jerking in the joints (knee twitching, popping).
The most common symptoms reported by patients are tingling on the side of the knee, a burning sensation, knee pain after running, walking or at rest. As a rule, imaging allows you to very accurately determine the extent of damage to the structures of this joint. They use X-rays, ultrasound of the knee joint and the most accurate magnetic resonance imaging. Sometimes a diagnostic procedure called exploratory arthroscopy is necessary. This is the case when the clinical picture is unclear and there is insufficient information from studies conducted to date.
External knee pain
There is no single cause of pain, but there are several reasons why you may have knee pain. More common:
- Athletes: runners, cyclists, martial artists, gymnasts.
- After an injury that pushes the knee outward (away from the other leg).
- In those who do exercises that involve twisting or rotating the knees
- In people who tend to be bent at the knees or bow-legged, putting stress on the outer knee
Also, pain in the knee on the outside can be caused by injury. Only a professional doctor can make a diagnosis.