Among all orthopedic disorders in children, the most common is planovalgus foot deformity. If it is not possible to correct the foot deformity in a timely manner using conservative methods, it is important to undergo surgery before the child reaches 16–17 years of age. At a later age, it becomes more difficult to completely correct the disorder, and the likelihood of complications due to disruption of the articular axis increases sharply. This can make it very difficult to carry out daily activities and even walk.
What is planovalgus foot in children?
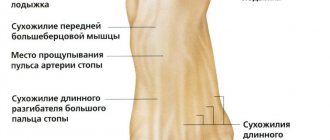
Plano-valgus foot deformity means a decrease in the height of the arches of the foot and a violation of the articular axis, as a result of which the child’s legs acquire an X-shape over time. At the same time, the presence of curvature of the ankles is indicated when, when the knees are tightly compressed in a standing position, the distance between the inner surfaces of the ankles exceeds 4-5 cm. Thus, with this orthopedic disorder, the foot rolls inward, which causes the heel and outer toes to deviate outward.
Sometimes both legs are deformed to the same extent, but more often one is more tilted inward. It is important to understand that all children have flat feet from birth and this is normal. Natural arches begin to form when the child stands on his feet and begins to take his first steps. Gradually they are strengthened naturally, and the foot is formed correctly. But if a child constantly walks on flat surfaces, for example, linoleum, laminate, parquet, tiles, etc., this impedes the development of muscles and ligaments. As a result, a flat-valgus foot occurs, especially if there are prerequisites. The situation is aggravated by choosing inappropriate shoes.
Causes
This type of deformity in children can be congenital or acquired during life. In the first case, it becomes a consequence of the occurrence of intrauterine developmental disorders of the bones of the foot. In this case, it is usually diagnosed during the first months of life during preventive examinations of the infant.
Acquired flat-valgus foot in children occurs against the background of weakness of the muscles and tendon-ligamentous apparatus and the occurrence of disturbances in the development of the musculoskeletal system.
Most often, plano-valgus foot deformity is observed in children:
- with muscle hypotonia;
- premature;
- those suffering from intrauterine hypotrophy, i.e., lack of body weight;
- having congenital weakness of connective tissue;
- weakened, often suffering from acute respiratory diseases, bronchitis, pneumonia at an early age;
- with diagnosed rickets;
- with neuromuscular diseases, including cerebral palsy, polyneuropathy, myodystrophy, poliomyelitis;
- having excess weight;
- those who have suffered injuries to the ligaments, muscles, bones of the foot and lower leg;
- with dysplasia or congenital dislocation of the hip joint.
Particularly noteworthy are the causes of flat-valgus feet in children, such as early standing of the infant, especially in a walker, and incorrect selection of shoes. Even in children without significant prerequisites for foot deformation, the foot can become flattened and fall inward. In the first case, this is due to the fact that the muscles and ligaments are not yet able to cope with the sharply increased load on them due to early standing on their feet and are stretched, while the arch of the foot remains flat. In the second case, shoes that are too soft or do not support the foot well cannot provide adequate support to the foot that is just beginning to form and leads to it falling inward. As a result, the ankle joint gradually shifts inward and the formation of an X-shaped deformity of the legs.
The first signs of acquired planovalgus deformity can be noticed during the first years of life, when the child begins to actively walk and run. However, they can also occur at a later age.
What causes?
The disease can be congenital or acquired. In the first situation, valgus is caused by malformations of connective tissue, genetic, chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus, and disorders of the nervous system. The pathology begins during the period of intrauterine development; the newborn is born with it.
Such violations include:
- innervation disorders;
- incorrect position of the femurs and pelvis, hip dysplasia;
- congenital hip dislocation;
- disorders in the lumbosacral spine;
- cerebral paralysis;
- spina bifida (incomplete closure of the neural tube in the spinal cord);
- adhesions in the pelvis;
- congenital weakness of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus.
Parents often think that some of the congenital abnormalities have nothing to do with foot pathology. However, all musculoskeletal structures in the body are interconnected, so the causes of hallux valgus can be quite unexpected. For example, valgus can be caused by a birth injury such as a displacement of the bases of the skull bones, namely a change in the position of the occipital bone. Such trauma causes a chain reaction. The vertebrae of the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spines become abnormal, the sacrum, pelvic bones, hips, and lower legs rotate. And so the deformation reaches the feet. In the same way, sometimes valgus can be a consequence of a diagnosis such as torticollis.
Acquired valgus foot placement in a child is caused by errors in the development and functioning of the musculoskeletal system, injuries, and excessive stress on a weakened muscular-ligamentous system.
It is facilitated by early standing in a vertical position and early walking. The risks are especially high if the baby is chubby or overweight. There is no need to rush to teach him to walk, to be equal to other children. It is much more beneficial for the musculoskeletal system to encourage the baby to actively crawl. The child’s body is ready to stand on its feet and begin walking only at 10–12 months. Some babies take their first steps at 9 months, while others at 15–18 months. And these are all variants of the norm. Remember that different walkers, jumpers, and reins can do harm, not good. Before using them, consult your pediatrician.
Unformed, fragile ligaments, tendons, and muscles with weakened tone are not able to hold the legs in the correct position, so the feet become deformed under the weight of the body. The situation is worsened by poor coordination and the baby's rocking gait, when he spreads his legs wide apart for stability.
A common cause of hallux valgus is rickets suffered in infancy. Oddly enough, this pathology occurs in mild severity in almost 30% of children under 3 years of age. The cause of rickets is a deficiency of vitamin D, which leads to impaired absorption of calcium, insufficient mineralization and bone strength.
Another common reason is unsuitable, tight or, conversely, too loose shoes. It leads to improper distribution of the load on the foot while walking, the formation of a gait that causes the appearance of curvature of the legs. Choose high-quality and good shoes for your child with an elastic hard back, a small heel, an orthopedic insole, and made from natural materials. It is strictly not recommended to give the shoes of older brothers, sisters, nephews, etc. to your child.
Favorable conditions for the development of pathology are created by:
- prematurity;
- excessive joint mobility;
- flat feet;
- calcium and vitamin D deficiency;
- frequent infectious diseases;
- weakened immune system;
- obesity;
- disorders in the nervous system;
- leg and foot injuries (fractures, dislocations, sprains);
- kidney diseases;
- genetic predisposition, the presence of valgus in parents, grandparents;
- endocrine disorders leading to disturbances in calcium metabolism.
Symptoms
In addition to the outwardly noticeable incorrect positioning of the feet with plano-valgus deformity, other manifestations of the disorder may be observed in children. This is due to the fact that deviations from the norm in the configuration of the foot lead to changes in the articular axis. As a result, the load on the joints of the lower extremities is distributed incorrectly, which leads to the following symptoms:
- uncertainty, clumsiness of gait, frequent falls when walking and especially running;
- shuffling when walking;
- rapid fatigue of the child, which is especially noticeable when playing with peers;
- pain in the legs and back that occurs after short physical activity and walking;
- curvature of the legs with the formation of an X-shaped deformity;
- cramps and swelling of the legs, which is not always observed.
With plano-valgus deformity of the feet, children do not step on the entire foot, but mainly on its inner edge. This will be confirmed by shoes, upon inspection of which uneven wear will be noticeable, namely the greatest abrasion along the inner surface.
Prognosis and likelihood of cure
The sooner you go to the clinic, the faster and more effectively it is possible to correct all problems. When diagnosed within a year, the probability of eliminating the defect is almost one hundred percent.
If the abnormal development is detected late or treatment is refused, problems with the spine (scoliosis, osteochondrosis), arthritis, and joint dysfunction are guaranteed. Everything can be cured only in childhood.
Degrees of hallux valgus in children
Depending on the severity of the deviation, the following degrees of hallux valgus in a child are distinguished:
- 1st degree – the angle of deviation from the norm is 10-15°;
- 2nd degree – the angle is within 15-20°;
- 3 degree – curvature is 20-30°;
- 4th degree – the foot deviates from the normal position by more than 30°.
In addition, with planovalgus deformity, flat feet are also observed, which can also be of varying degrees of severity. It is determined by the angle of the longitudinal arch of the foot. Thus, during the plano-valgus deformity the following stages can be distinguished:
- 1 – the angle of the arch of the foot is 130-140°, and the valgus deviation of the heel bone is 5-10°;
- 2 – the angle of the arch of the foot is in the range of 141–160°, and the valgus deviation of the heel bone is 10–15°;
- 3 – the angle of the arch of the foot is 161-180°, and the valgus deviation of the heel bone is more than 15°.
Since the feet are the only supporting point of the human body, the health of the entire musculoskeletal system largely depends on the correctness of their anatomy. Therefore, in the absence of competent treatment to eliminate plano-valgus foot deformity, children subsequently develop pathological changes in the remaining joints of the lower extremities and even the spine. As a result, you may experience:
- pain in the ankle, knee and hip joints;
- back pain, most often in the lower back;
- curvature of the spine with the formation of a scoliotic arch;
- persistent pain when walking in the area of the 3rd interdigital space;
- formation of heel spurs;
- hallux valgus deformity of the 1st toe, etc.
Deformation of the feet in children can reach severe degrees, which will lead not only to a cosmetic defect, but can even cause disability at a young age. Therefore, it is extremely important to pay attention to the signs of flat-valgus foot in children in a timely manner, get advice from an orthopedist and then strictly follow the recommendations received from him.
With this approach, there is a high probability of complete restoration of the normal supporting function of the foot, elimination of discomfort in the legs and prerequisites for the development of complications. But the more severe the deformity, the more difficult and lengthy the treatment will be, and sometimes it will require further surgical intervention. Therefore, you should not hope that foot problems will disappear on their own. It is better to consult an orthopedist at the first suspicion of abnormalities.
Danger
If the degree of deformity is mild, a complete recovery is possible. Severe hallux valgus is not an ordinary cosmetic defect. The disease causes serious functional impairment of the limbs, which can lead to disability.
Lack of proper treatment of the abnormality can cause:
- flat feet;
- constant pain in the legs;
- osteochondrosis;
- arthrosis;
- shortening of limbs;
- poor posture (scoliosis);
- deformation of the pelvis, ankle and knee joints.
Diagnostics
Usually, the first signs of changes in the condition of children's feet are discovered by parents or a pediatrician during a preventive examination. However, to accurately confirm the diagnosis and prescribe treatment, you should consult an orthopedist. The doctor will conduct an examination, during which he will pay attention to the deviation of the toes and heels to the outside, the smoothing of the natural arches of the foot, and the displacement of the inner part inward. These data are usually sufficient to diagnose a child with a planovalgus foot. But in order to determine the degree of deformation and develop the most effective treatment tactics for a particular child, a comprehensive examination of the feet should be carried out, which may include:
- radiography of the feet, performed in 3 projections, which allows you to evaluate changes in the position of the feet relative to each other;
- computer plantography is a modern method for diagnosing deviations from the norm in the condition of the feet, which allows you to accurately calculate various morphological parameters, on the basis of which you can then create individual orthopedic insoles;
- podometry is a diagnostic method that makes it possible to accurately assess the nature of the load distribution on different parts of the foot and even detect pathological changes that have not yet manifested themselves externally;
- Ultrasound of the joints is a simple and accessible method, thanks to which you can assess the condition of the joints of the lower extremities and detect changes in them caused by foot deformation that require correction.
Thus, diagnosing feet for suspected planovalgus deformity in children does not require any painful or unsafe procedures and can be performed in the shortest possible time.
In order to exclude pathologies of the central and peripheral nervous system, children are advised to consult a neurologist.
How to prevent the appearance of a bulging bunion?
Prevention of pathology involves following simple rules:
- Attentive attention to the condition of the feet - when the first signs of increased fatigue, discomfort and inflammation of the feet appear, you must immediately contact an orthopedic traumatologist. By diagnosing the disease in the early stages, you can avoid surgery and restore the health of your feet using conservative treatment methods.
- Wearing comfortable shoes - experts recommend choosing shoes very carefully, in strict accordance with your foot size. It is also important to avoid prolonged wearing of uncomfortable shoes with pointed narrow toes and high thin heels (above 7 cm). Wearing shoes made of non-breathable synthetic materials can also accelerate the development of various foot pathologies.
- The use of orthopedic insoles - special insoles help reduce the load on the forefoot, evenly distribute the person’s weight and soften mechanical shocks.
- Regular rest - if the patient’s professional activity involves long periods of standing, it is very important to provide the feet with proper rest.
Treatment
Based on the research results obtained, the orthopedist develops an individual program for the conservative treatment of planovalgus foot in a child. Since the foot continues to develop up to 12 years of age and remains quite plastic, until this period treatment involves the use of only conservative methods. In most cases, with the correct selection of means and strict adherence to the recommendations of the orthopedist, up to this age it is possible to completely restore the normal shape and function of the foot, or at least significantly bring them closer to normal, as well as strengthen the muscular and ligamentous apparatus.
Conservative treatment of flat valgus foot in children is always complex and may include the following measures:
- selection and constant wearing of orthopedic shoes, including at home using individually made orthopedic insoles;
- massage of the feet, as well as the lower extremities, and sometimes the lower back;
- physiotherapy;
- Exercise therapy.
If indicated, children may be prescribed foot immobilization by applying a plaster cast.
If, by the age of 12 years, conservative methods have not been used to eliminate planovalgus deformity of the foot, which is observed in less than 7% of cases, the issue of surgical intervention is considered. If indicated, it is important to perform it before the child turns 16-17 years old.
Orthopedic shoes and insoles
Orthopedic shoes are the basis for the treatment of plano-valgus foot deformity. You will definitely need to buy it, and you will need 2 pairs: for the street and for the house.
Distinctive features of proper orthopedic shoes are:
- high-quality, elastic instep support;
- a hard, high, fixed heel that will tightly grip the ankle joint and ensure it remains in the correct position;
- Thomas heel, the inner part of which is 1.5 times longer than the outer part;
- dense side part;
- the presence of at least 3 convenient fasteners;
- dense, elastic sole;
- widened bow;
- naturalness of all materials in contact with the foot.
In some cases, the orthopedist may limit himself to prescribing individual orthopedic insoles, which will take into account the structural features of the right and left feet separately and compensate for existing deficiencies. They will need to be put into the shoes instead of the insoles that come with them.
Massage
For flat-valgus feet, massage is an essential component of treatment. Moreover, if to prevent the formation of this type of deformity, the usual techniques of stroking and rubbing, which every parent can master, are sufficient, then if you already have valgus, it is recommended to visit the office of a professional massage therapist at least several times. The doctor will show you what techniques should be used to strengthen the muscles and ligaments of the foot and lower leg, and improve the quality of blood circulation in the lower extremities. After just a few sessions of observing the professional actions of a specialist, parents usually fully master the proposed techniques and can massage the child themselves.
For flat-valgus feet, the following is usually indicated:
- stroking, kneading the feet;
- providing a light vibration effect on certain areas;
- tapping on the legs alternating with stroking;
- massaging the toes and ankle joints with rotational movements, including those involving the knee joint;
- massaging the heels and supporting area of the foot in the area of the metatarsophalangeal joints;
- light kneading of the front and back surfaces of the thighs, buttocks, lower back, avoiding impact on the spine.
After completing the massage session, foot baths will help enhance its effect.
It is very useful to buy a special massage mat with different types of irregularities or make it yourself using pillows filled with chestnuts, peas, buckwheat, beans, sand and other objects of different sizes. Walking on such a mat will neutralize the negative impact of walking on a flat surface and actively promote the proper development of muscles, ligaments of the foot and the formation of arches. In this case, children under 3 years old should choose products with a protrusion height of up to 2 cm, and older ones - up to 3 cm.
It is useful to simply walk barefoot on such a massage mat, stand, shift from foot to foot, slide one foot along the mat, and also rise on your toes and lower on your heels.
Exercise therapy
Since weakness of the muscular system plays a large role in the formation of flat-valgus foot in children, exercise therapy plays a significant role in combating this. For each child, the exercise complex is selected individually, taking into account his age, as well as the severity of the deformity. As a rule, they are simple and can be performed under parental supervision at home. But you should do therapeutic exercises every day, and its effectiveness depends not on the number of exercises, but on the regularity of their implementation.
The most commonly prescribed exercises include:
- alternate walking on the inside and outside of the foot;
- rolling the feet of a rolling pin;
- grasping and lifting small objects with the toes (when working with young children, you should monitor them very carefully, preventing attempts to put a small object in the mouth or nose);
- crushing a newspaper sheet or towel with your toes;
- thumb painting;
- performing rotational movements with the foot;
- run the toe along the shin, as if clasping it with your toes;
- lift your toes slightly turned inward while standing straight.
So that the child does not resist physical therapy classes and willingly performs useful exercises for him, it is worth carrying out them in a playful way at a time when he is cheerful and in a positive mood.
In general, any physical activity has a beneficial effect on the condition of the feet: walking, outdoor games, jumping, cycling, wall climbing, rope climbing. But if the child is tired, you should not force him to be active.
In addition to exercise therapy, kinesio taping can be used. The method involves gluing special breathable elastic bands, called tapes, to the feet. They are made from hypoallergenic materials and help to correctly distribute the load on the supporting points of the foot and muscles, but only with proper gluing. With tapes you can swim, wear any shoes, run, jump and perform any other actions. On average, they are applied for 5 days, after which replacement is required.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are indicated when there is a significant angle of deviation of the foot from the normal position. But they should be considered only as an auxiliary method of treating the disease, and not the only necessary one. Thanks to properly selected physical effects, it is possible to increase the effectiveness of other measures taken, reduce the severity of pain, fatigue and swelling of the legs.
The following have a positive effect on the condition of the feet with plano-valgus deformity:
- electrophoresis;
- diadynamic therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrical stimulation of the muscles of the lower leg and foot;
- paraffin therapy;
- ozokerite and mud applications;
- IRT.
Prevention
To avoid the formation of flat-valgus foot in a child, you should:
- eliminate stress on the legs for up to 7-8 months;
- Do gymnastics with your baby every day and carry out preventive massage;
- provide the child with adequate nutrition appropriate for his age;
- spend enough time outdoors;
- avoid overtiring the baby and create conditions for proper sleep;
- prevent rickets and, if necessary, give the child vitamin D supplements;
- Encourage your child to walk barefoot on sand, pebbles, grass, etc.
It is very important not only to independently monitor the child’s condition, but also not to neglect preventive examinations, not only by the pediatrician, but also by specialists. As soon as the child begins to attempt to walk, it is necessary to carefully and scrupulously choose shoes. It must exactly match the leg in size and width (extra room for growth is not allowed), have a rigid fixed back, tight instep support, and also be made of high-quality materials that allow air to pass through.
How to detect?
Signs of hallux valgus in a child appear by the age of 1 year, when the baby learns to walk and tries to take his first steps. To check for deformity, measure the distance between your ankles while standing with your feet tightly pressed together. If it is more than 5 cm before the age of 4 years, it means the child has hallux valgus.
In addition, the following symptoms are characteristic:
- complaints of fatigue and pain in the legs;
- lack of interest in walking, the child chooses to move in a stroller or in the arms of his parents;
- support on the inside of the foot in a standing position;
- X-shaped position of the legs (knees closely touching each other, ankles widely spaced);
- trampling of shoes from the inside.
What a hallux valgus looks like in a child, look at the photo below:
As a rule, hallux valgus is easy to notice visually by the feet turning outward. The main load or body weight falls on the inner edge of the foot, and the gait changes. The child may shuffle their feet a lot when walking or running.
If the deformity is congenital, it is noticeable almost immediately. At the first examination at 1 month, a pediatric surgeon or orthopedist will see this deviation. With a mild congenital abnormality, the pathology can be detected after the first year of life, when the baby begins to walk.
With planovalgus deformity, the child complains of dull, aching, throbbing pain, cramps in the foot, fatigue in the legs, and pain in the lower back. He will avoid stress, active games, and feel more comfortable in larger shoes.
Valgus is not only an aesthetic problem, but also a medical one. The child quickly gets tired when moving, sometimes even experiences pain while walking or after it.