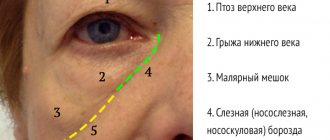
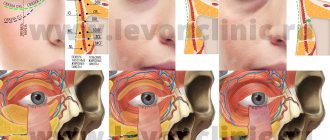
Dark circles under the eyes of a child
If the skin under your baby's eyes has changed color, it means that not everything is in perfect order. The presence of dark circles under the eyes is a consequence of illness or illness in a child. Therefore, when they appear, it is imperative to conduct an examination and identify the cause. You shouldn’t worry too much or let everything take its course. The diagnostic capabilities of medicine and the competence of doctors will help both identify the cause and eliminate it.
Causes
Unfortunately, dark circles under a child’s eyes indicate an unhealthy condition and a malfunction in the body’s performance.
Lack of oxygen
The root causes of deterioration in the natural balance of the skin under the eyes in children are varied. It can darken, Obaglaza believes, if there is a lack of sleep or rest for a sufficiently long time. The skin, which is only 0.5 mm thick, acquires a dark tint due to a change in the color of the blood in the translucent vessels. This occurs when stagnation occurs in the capillaries of venous blood (with carbon dioxide). This is why the skin in these areas looks a little darker than the cheeks and chin. Forming circular areas.
Hereditary
Why a child has such a feature may have a fairly simple explanation. From his relatives he could have inherited a fairly close arrangement of blood vessels to the thin skin. The lower eyelid is devoid of fatty cell tissue, which is how the effect of coloring this place in a shade darker than the entire face occurs. So if he is not the only one in the family who has such signs, then this is the reason.
Fatigue
The appearance of “black circles of fatigue” is associated with cortisol. Its main function is to preserve energy reserves. Therefore, when they are overused, its production exceeds the permissible level by a factor of two. In this way, OglazaRu thinks, he helps the child not fall asleep. In addition, it helps to increase the amount of blood in the body and congestion of the blood vessels located on the lower eyelids.
Chin tremor in a newborn: the child's chin trembles
In most cases, these symptoms disappear completely with timely diagnosis and treatment, especially if treatment is started in the first six months of the child’s life.
When a newborn baby's chin trembles, this almost always indicates increased stimulation of the nervous system. If the chin trembles frequently or constantly, it means that excitation in the child’s central nervous system significantly dominates inhibition. And this, in turn, may indicate a history of brain damage: intrauterine infection, intrauterine and/or birth hypoxia, birth trauma, increased intracranial pressure, etc. In this case, the child’s chin shakes while crying or spontaneously. Other neurological symptoms may also appear. An increase in muscle tone is often observed; the baby does not form the correct reflexes inherent in newborns: proboscis reflex, palmar-mental, palmo-oral, support reflexes. There may also be other neurological signs indicating that the nervous system has been damaged in some way. In more serious cases, early development may be impaired.
Where to start and who to contact? If a child often experiences chin trembling, first of all, he should get an in-person consultation with a pediatric neurologist. The doctor will examine the baby and, if necessary, prescribe an ultrasound of the brain and ultrasound of the cerebral vessels to look at the situation with intracranial pressure and cerebral circulation. If epilepsy is suspected, encephalography (EEG) is advisable. As a rule, the most relevant age for research and determination of the causes of this problem is up to six months, since most of the consequences of intrauterine and birth damage to the nervous system are well restored during the first 6-12 months of life (the so-called “therapeutic window”). It is at this moment that every effort should be made to ensure that the damaged functions are fully restored and continue their development as normal.
Symptoms
Symptoms of circles and spots
Now is the time to describe the main symptoms of the appearance of frightening “color” signs.
Nervous system disorders
Often, the main cause of circles appearing under the eyes of a child is impaired functioning of the nervous system. With this disease, the child often gets tired and feels lethargic during the day and is less mobile. In this case, ObaGlazaRu notes, the skin is dry and pale, as the normal functioning of individual organs is disrupted.
Anemia
The presence of anemia, associated with a decrease in the content of a microelement such as iron, also forms dark circles in a child, since this disease is directly related to a change in the amount of iron-containing protein.
Hypoxia
When an insufficient amount of oxygen is supplied, hypoxia develops. Frequent colds and dizziness accompany the course of this disease. Therefore, if school-age children or teenagers have such symptoms, they should definitely be taken to the doctor.
Lack of vitamins
Another important reason for darkening of the skin around the eyes in the form of circles sometimes occurs due to a deficiency of vitamins (C and B). And as a consequence of this, poor absorption of iron microelements.
Helminths
Obaglaza notes that dark circles under a child’s eyes become an alarming sign when foreign creatures begin to parasitize in a fragile body, poisoning healthy tissue with the results of their vital activity. At the same time, appetite worsens, the absorption of beneficial microelements obtained from food is delayed, an allergic reaction is present, and the plant process and development are disrupted.
Lower blood pressure
Water depletion is also signaled by darkened skin around the eye sockets, as a rapid decrease in the overall pressure in the vessels and local circulation begins.
Obsessive neuroses
In most cases, the problem of obsessive-compulsive neurosis and tics is solved by play psychotherapy or a course of medical treatment, and most often by a combination of drug treatment and psychological work with suppressed nervous tension in the child.
Obsessive neuroses in children manifest themselves in the form of obsessive movements and thoughts. Obsessive states (obsessions) manifest themselves as irresistible and involuntarily arising thoughts, fears, and, as a result, obsessive movements.
Intrusive thoughts
- when a child fears for the health and safety of himself and his family
- constantly thinks or imagines that something bad might happen to them
- always remembers negative events that happened to him or his family in the past
Typical obsessive mental actions
- reading license plates, signs, operations with numbers and letters from license plates and signs
- counting lamp posts, houses, lawn fences, etc.
- constant search for “favorite” and “unfavorite” letters and numbers
Obsessive movements and actions.
The scope of their manifestations is very extensive. This could be a nervous tic in a child, or obsessive movements. The most typical obsessive movements and actions in children:
- biting nails and lips
- hair pulling
- thumb sucking, sucking or biting a pencil, pen, button, edge of clothing
- coughing, grunting, or making noises
- twitching of limbs
- blinking and/or stereotypic eye movements
- circling
- tapping, clapping
- rocking
- squatting, limping when walking
- rubbing the body or objects
- shaking and shaking hands and objects
- jumping and skipping for no reason
- muscle contractions of the arms and legs, as well as the face.
Typical complex ritual actions
- Children can walk on certain floor tiles
- walk around, twist, stroke the object a certain number of times
- jump up and clap your hands, pronounce phrases, etc.
Also, neuroses can have a different course:
- episodic
- chronic
- progressive
Neurosis in a child can have different causes
. The most common is the presence of any mental trauma in the child, as well as the presence of emotional factors. Such as: a tense and conflictual situation in the family, incorrect and too harsh and authoritarian upbringing of children.
Often this list also includes physiological reasons: heredity and genetics, previous diseases, physical overload of the child, lack of sleep.
One way or another, all this is due to the fact that the child has increased arousal in certain areas of the brain. Basically we are talking about dysfunction of the subcortical nuclei of the brain, which are responsible for posture and facial expressions, muscle tone and global motor acts. The child is forced to somehow relieve this excitement. Thus, this discharge occurs precisely through actions.
These may be: tics (the child twitches or jerks with some part of the body), fast stereotypical movements, there may be obsessive postures, obsessive movements; the child may sit down, jump, make some sounds, pronounce words or even swear words (with Tourette syndrome). Very often such manifestations are not taken seriously in the initial stages.
Tourette's syndrome is a genetically determined condition associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder and tics, or stereotypical tic-like movements.
Also, neurosis-like obsessive states are largely provoked by chronic streptococcal infection with an increase in antistreptolysin O (ASLO) in chronic tonsillitis, the so-called PANDAS syndrome, ongoing neuroinflammation with an increase in markers such as NSE and S100 protein. We also often see such manifestations in children who are carriers of neuroinfections, that is, infections that have a toxic effect on the nervous system.
EEG (electroencephalography) for children at the Echinacea clinic
We advise you to contact a child neurologist, child psychiatrist and allergist-immunologist. For convenience and coordination of assistance to the child, we practice a consultation of all three specialists. Thanks to this, the appointments are more informative, and the effect of the prescribed therapy occurs faster.
Obsessive neurosis responds well to treatment in the early stages, especially in preschool age.
As for Tourette's syndrome, even if there is a genetic predisposition, this syndrome can become silent. After all, until the debut of Tourette syndrome, the child lives with the same genetic makeup, but there are no tics or vocalisms. This is not only a matter of genetic predisposition to Tourette's syndrome, but also related problems and the current state of the child's health. Working with provoking factors (obsessive-compulsive disorder, infections, concomitant inflammatory diseases, sleep disturbances, high levels of anxiety, etc.) usually leads to gradual improvement, often until the complete cessation of tics and vocalisms.
We widely practice play therapy for the treatment of obsessive neuroses in children
When to worry
When parents need to make a decision
To avoid blue dark circles under the baby’s eyes, it is necessary to provide the child with time for sleep and simple mental or physical inactivity during free hours.
If this is not the reason, then it may be associated with diseases of the cardiovascular system. During periods of impaired blood circulation, dark cyanosis may occur, which informs about a change in the amount of iron-containing protein, without the content of oxygen molecules.
Improper functioning of the gallbladder changes the composition of the liquid part of the blood and causes a yellow-gray tint in the lower part of the eye sockets, forming a kind of circles. A brownish tint reflects liver pain or excess bile, if this additionally causes swelling of the lower eyelids. Such manifestations, ObaGlazaRu believes, are also possible due to infections of the nose or throat in the form of tonsillitis, pharyngitis (the presence of streptococci). The main indicators of a healthy body are violated:
- Weakness appears;
- The temperature rises;
- There is pain in the lumbar region and abdomen;
- Presence of headaches;
- The occurrence of shortness of breath and difficulties with urine output.
Black circular formations in children are a consequence of:
- cysts on the liver;
- the presence of infectious liver diseases;
- hepatolenticular degeneration;
- bronchus diseases;
- manifestations of chronic inflammatory disease of the skin (dermatitis);
- having an allergic reaction to pollen;
- inflammation of the frontal sinus;
- sinus inflammation;
- sinusitis.
Children's mild myopia: causes and prerequisites
There are many causes of myopia in children, both external and internal. In addition, there are always risk factors that increase the possibility of developing and progressing the disease. The main causes of myopia and factors of its progression are:
- Heredity is considered by many doctors to be the main cause of the disease. If at least one of the parents has this pathology, the child’s risk of getting the disease increases to 33%; if both parents have the disease, this figure increases to 50%. As an important genetic factor, studies point to a collagen defect, which plays an important role in the formation of the sclera, the outer layer of the eye that performs a protective function.
- Age of onset of myopia . In preschoolers, the percentage of myopia is much lower than in school-aged children and fluctuates at the level of 2-3%. The earlier myopia is identified, the more likely it is to develop into high myopia by the time the child reaches adulthood.
- Floor . Girls are slightly more likely to develop the disease than boys. The percentage is approximately 55:45.
- Race - according to statistics, the occurrence of myopia in people of the Mongoloid race occurs several times more often than in representatives of other races. And the spread of the disease among children in the Asian region reaches 80%.
- Unfavorable conditions for the eyes - frequent use of phones, computers, poor lighting, uncomfortable furniture, prolonged reading in an uncomfortable position or working with small parts, insufficient time outside during daylight hours
Who to contact?
Which doctor should I contact for help?
You should not self-medicate, ObaGlazaPy draws your attention. This is a serious reason to contact the diagnostic center and undergo all the necessary tests. This will allow for a proper examination. You can find a good clinic in our catalog.
It is impossible to identify the cause solely by external signs. Therefore, the pediatrician will need to track the history of diseases that the baby has suffered from, starting from the first days of life. In this case, the doctor must clarify what diseases the parents had, as well as the characteristics of the child’s behavior, his regime, food intake, and more.
At the same time, the body is completely examined, not excluding tests (blood, urine, feces). Sometimes you need to take an x-ray of the organs in the chest cavity or perform an ultrasound of the tummy. It may be necessary to consult with specialists in cardiology, otolaryngology, gastroenterology or nephrology.
Hyperactive child and restless child. Increased excitability in a child
Symptoms and causes.
A hyperactive child cannot sit for a long time and do work associated with a static body position, often screams loudly and violently expresses emotions, has an attention deficit that does not allow him to concentrate on one thing, and is forced to discharge accumulated tension through physical activity.
That is, in the child’s nervous system, excitation significantly dominates over inhibition. The danger of increased excitability is a decrease in learning ability and, as a result, a child falling behind his peers in development.
It is important to understand the source of increased excitability and restlessness.
Therefore, the first thing we will offer you is to find out the reason for what is happening. There are three main options:
- This is your child’s normal natural temperament
and the intervention of a psychiatrist or doctor is not required. The child is mentally healthy and psychologically well-being. In this case, we will give you some recommendations, and you and your child will become noticeably more comfortable. - There is some psychological problem
that increases the child’s level of emotions, anxiety or aggression, for example.
Emotion requires release (discharge, realization), hence increased excitability and restlessness. The child is mentally healthy and does not need any medical treatment.
These kinds of psychological problems are quite easily diagnosed during a conversation with the child and parents, and then gently corrected. - Increased excitability and restlessness are a consequence of a medical problem.
We can talk about, for example, increased intracranial pressure, chronic inflammation somewhere (adenoids, tonsils), neuroinflammation, the consequences of birth hypoxia or trauma, childhood neurosis, a latent form of epilepsy. We also encounter more serious problems in our practice, such as autistic disorder and childhood schizophrenia. In this case, it is very important to find the true cause of what is happening, and only then will the treatment work effectively and safely.
Hyperexcitability, restlessness and hyperactivity as character traits
. If we talk about increased excitability and restlessness as characterological characteristics, this is possible if the child is extroverted and temperamental by nature. Or the child may copy this style of behavior from one of the family members. But we can talk about the norm only if this type of hyperactivity does not lead to health problems and if the child is not so excited that he stops sleeping normally, begins to get sick often, or lags behind in general development. Having severe disinhibition and excitability, the child cannot concentrate and master the skills that he is supposed to master by age.
Hyperactivity test
Active attention deficit:
1.Cannot concentrate on one thing, it is difficult to maintain attention;2.May forget what he was assigned or asked for;3.Likes to start a new activity, but cannot finish it;4.Cannot organize clearly his activities and maintain a routine; 5. It is difficult to maintain order, he may lose all his things; 6. Does not like monotonous tasks that require mental effort and attention; 7. May forget what he was assigned or asked for; 6. Doesn't respond immediately when approached.
Motor disinhibition:
1. Often moves restlessly (runs, jumps, climbs somewhere, fidgets in a chair and at the table); 2. Takes a long time to fall asleep and sleeps poorly, may wake up often4. Likes to talk a lot and uncontrollably.
Impulsiveness:
1. Poor control of one’s behavior; 2. Can’t regulate one’s actions and most often does not follow rules; 3. Poorly concentrates attention; 4. Can’t wait for something to finish or reward; 5. No precise line of behavior, strong variability in results and states; 6. May begin to answer without listening to the question; 7. Often interferes in someone else’s conversation and interrupts it; 8. Doesn't know how to wait, can run without waiting for the start.
If you find at least six of the listed signs in a child under the age of 7, we can assume that there is a tendency to hyperactivity. But only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis. Where to start and who to contact with an overly excitable child?
If we are talking about a hyperactive, excitable and restless child, then it all starts with a detailed identification of the reason for what caused the child’s nervous system to remain in a state of excitement for such a long time. Most often in such cases, we recommend starting with an appointment with a pediatric neurologist and/or a child psychiatrist, and we also suggest getting a joint appointment with these two experts. This makes it easier and faster to determine the cause of increased excitability, to avoid treatment that is unnecessary in many cases, or to select exactly the treatment that your child needs. Based on the results of the initial examination, we can recommend additional laboratory and instrumental studies. We can also save you time and send a laboratory examination form to your email address for your initial appointment; to do this, you can fill out the “ask a doctor a question” form
.
Treatment
Why is there no clear way in medicine to treat circles aimed at eliminating one or more manifestations when blue or black colors appear in a child’s lower eyelids? This happens, notes Obaglaza.ru, due to the presence of various diseases.
Therapy for children with such circles is carried out using effective methods for treating each individual case, taking into account the identified and established causes of circular color manifestations under the eyes.
What examinations are needed?
The following directions are usually given:
- General blood analysis. It will show whether there is inflammation in the body, and will also help determine the baby’s hemoglobin level.
- General urine analysis. It will help detect problems in the kidneys and the entire genitourinary system.
- Feces for worm eggs and scraping for enterobiasis, which will indicate the presence or absence of parasites in the child.
If abnormalities are found in the tests, the pediatrician may prescribe additional examinations and consultations with the following specialists:
- neurologist;
- endocrinologist;
- nephrologist;
- Ultrasound specialist.