When it's hot, you want to cool down. Air conditioners, ice cream and ice drinks, dousing and bathing in cold water are used. And the payback could be a sore throat.
Hypothermia is a predisposing factor that sets the stage for bacteria and viruses to more easily penetrate the body and stay there longer. Maybe it only takes one exposure to hypothermia to get sick.
How to distinguish a sore throat and how to treat it? Associate Professor of the Department of Ear, Nose and Throat Diseases at Sechenov University, Candidate of Medical Sciences Eduard Sinkov spoke about this .
The main causes of sore throat in children
What exactly caused a child’s sore throat may depend on age, time of year and climate zone. Most often, a sore throat is caused by viruses, while bacteria are the second most likely cause of the disease. All pathogens are transmitted mainly by contact, when a child touches his nose, eyes or mouth with hands that have been in contact with an infected person or contaminated objects (toys, door handles, cutlery). To determine the causes of sore throat, laboratory tests are recommended.
There are many viruses known to cause pain and swelling in the throat. The most common respiratory viruses cause ARVI. Other viral pathogens that can cause symptoms of a sore throat include herpes influenza viruses, enteroviruses, adenoviruses, and the Epstein-Barr virus (the cause of mononucleosis).
The most common bacterial causative agent of sore throats is group A streptococci. In winter or early spring, up to a third of sore throats in school-age children are caused by streptococci. Streptococcal sore throat is uncommon in children under 2-3 years of age.
Bacterial tonsillitis is characterized by a sudden onset of the disease, with sore throat, nausea and vomiting, and fever above 38.3°C. In young children, streptococcal infection can occur with a temperature of less than 38.3°C. Infants under one year of age with sore throat may have a low-grade fever.
Most cases of sore throat are viral and do not require treatment. But children with group A strep throat need to be treated with antibiotics to prevent the infection from spreading and potentially dangerous complications such as rheumatic heart valve disease.
Why do you need to undergo streptotest?
Sore throat is very contagious. The severity of the disease depends on how long the contact with the sick person was and how many viruses the person received from him. And here the principle is the same as with any infectious disease, including coronavirus. The lower the dosage, the better. It is clear that the mask does not completely save, but nevertheless reduces the amount of virus or microbe that has entered the body. This means that a person will get sick more easily.
If you have a sore throat, it is fundamentally important to understand what caused the disease - a virus or a microbe. The choice of drugs depends on this - antiviral or antibiotics. This certainly cannot be done without special tests. One can only guess. For example, with the mildest, viral form of tonsillitis (catarrhal), when the mucous membrane that covers the tonsils (tonsils) and the back wall of the pharynx becomes inflamed, the throat usually just turns red, hurts and feels sore.
Many faces of sore throat. The doctor talks about 7 types of disease and the difference in treatment Read more
But if white plaques appear on the tonsils, most likely, bacterial tonsillitis. Usually in this case there is a very severe sore throat, high temperature, severe intoxication (nausea, muscle aches). Before buying antibiotics, it is better to purchase a streptotest at the pharmacy and carry out a diagnosis. A swab is taken from the throat and the color of the strip determines whether it is streptococcal sore throat, the most severe, or viral inflammation. But it is better to do this together with your doctor in order to choose the right treatment.
What symptoms indicate a child has a sore throat?
To assume that a child has a dangerous form of streptococcal tonsillitis, one or more of the following symptoms must be present:
- Temperature ≥ 38.3°C
- Season: late autumn, winter or early spring.
- The child does not have a cough
- The child's age is from 5 to 15 years.
- Recent exposure to someone with a sore throat
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- The child's voice sounds muffled
- Stiffness in the neck or difficulty opening the mouth
Types of sore throat
The most important difference is the difference between a sore throat caused by streptococcus and a sore throat caused by other microbes. Depending on this, streptococcal and non-streptococcal tonsillitis are distinguished, since this is of fundamental importance for further treatment.
In Russian medicine, a classification of angina has been adopted, based on the stage of the inflammatory process and the appearance of the tonsils.
There are the following types of sore throat:
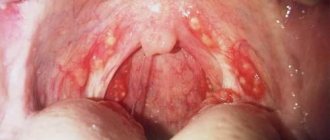
- Catarrhal tonsillitis - the tonsils are enlarged, red, there are no plaques, it is considered the mildest form.
- Follicular tonsillitis - a small, pinpoint purulent plaque appears.
- Lacunar tonsillitis - the lacunae of the tonsils are filled with pus, is considered the most severe form.
In European and American medicine, this type of classification is not given importance. In Russia, you can often hear the word “angina” as a designation specifically for streptococcal tonsillitis, although in fact this word does not have such a meaning.
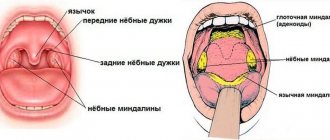
Depending on whether one or both tonsils are inflamed, tonsillitis can be unilateral or bilateral. In many cases, angina is combined with pharyngitis - inflammation of the posterior wall of the pharynx; the lingual tonsil, palatine ridges, etc. can also be involved.
What studies confirm that a child has a sore throat?
If there is a suspicion that the child may have streptococcal or the child may have streptococcal tonsillitis or scarlet fever, tests may be carried out to confirm the diagnosis: a rapid test (Strep test) and culture. For both types of tests, the doctor takes a swab from the back and sides of the child's throat. The results of the rapid test are obtained within a few minutes, and the culture will be ready within two days. If the research confirms the streptococcal nature of the disease, the child is prescribed antibiotic therapy. If the result of the Strep test is negative, then an additional culture is done to avoid false negative results.
Diagnosis of sore throat
If you suspect a child has a sore throat, parents should immediately seek advice from a qualified specialist.
An experienced doctor will help determine the type and stage of the disease and, accordingly, select the optimal treatment. At the initial appointment, the doctor listens to the complaints of the little patient and his parents, examines the child’s oral cavity using a laryngeal speculum or pharyngoscopy (visual examination of the pharynx using artificial light), palpates the lymph nodes, and also asks about contacts with patients. Based on the medical history, the doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis, after which he refers the patient for additional studies to confirm the initial assumption. The following methods are used in diagnosing angina:
- Bacteriological examination of a throat smear to determine the type of pathogen and determine sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Clinical blood test.
- Blood test for C-reactive protein, ASL-O, rheumatoid factor.
The method of treating acute tonsillitis will depend on the results of laboratory and instrumental studies.
Symptoms of the disease
Depending on the form of the disease, the type of pathogen and the degree of angina, the general clinical symptoms will differ:
- Catarrhal. With this form of sore throat, the infection spreads to the mucous membrane of the tonsils. The main symptoms are: sore throat, which reaches maximum strength during swallowing, redness and swelling of the tonsils. Against the background of the inflammatory process, an increase in temperature is observed.
- Follicular. With angina, not only the mucous membrane is affected, but also the lymphoid follicles. The primary symptom is a sore throat, which begins acutely and is accompanied by a sharp rise in temperature to high levels. A person feels weakness, aches in muscles and joints, and headaches. On the tonsils, festering follicles measuring 1–3 mm appear, which open on the second to fourth day.
- Lacunar tonsillitis, which is characterized by a deep degree of damage to the tonsils, accompanied by the accumulation of pus in the lacunae. The tonsils become bright red, with a yellow-white coating clearly visible on them. Sore throat is accompanied by general intoxication of the body.
- Necrotizing tonsillitis is quite rare and is characterized by the presence of necrotic areas.
The onset of symptoms begins after the end of the incubation period. Against the background of elevated temperature, febrile convulsions may occur - severe tension in the muscles, followed by shuddering and twitching.
The mechanism of development of sore throat in children
The infection reaches the tissues of the lymphoid pharyngeal ring through the respiratory tract, where it adheres, multiplies and releases toxic products. At the site of introduction of the pathogen, an inflammatory focus is formed with local changes - swelling of the lymphoid tissue, accumulation of purulent masses in the lacunae.
With the accumulation of exotoxins, tissue breakdown products and microbial bodies, a toxic and allergic syndrome develops. The infection from the source of inflammation spreads through the bloodstream throughout the body, affecting internal organs and systems. With a strong immune system, early and properly selected treatment, inflammation can be stopped at any stage.
Treatment of sore throat in children
Mild and moderate forms of tonsillitis are treated on an outpatient basis. If the disease is severe, therapy is ineffective, or a purulent complication is suspected, the patient is hospitalized in the infectious diseases department. During a sore throat, the child is isolated for 3-4 days, bed rest, plenty of fluids, and gentle nutrition are prescribed.
When a bacterial infection is isolated, antibacterial drugs are taken taking into account the resistance of the pathogen - macrolides, penicillins, cephalosporins. The course of treatment is 5–15 days. For viral sore throat, antiviral drugs are indicated.
To alleviate the severity of symptoms and prevent the development of a secondary bacterial infection, local treatment is carried out:
- gargling with antiseptics and herbal decoctions;
- dry heat and warming compresses on regional nodes (unacceptable for fever, body temperature above 37°C);
- irrigation of the pharynx, treatment of the back wall of the pharynx and tonsils with antimicrobial drugs;
- resorption of lollipops, tablets with antiseptic action;
- vitamin therapy;
- aromatherapy with essential oils;
- inhalation.
Taking into account the specifics of the disease and its clinical manifestations, the therapist prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antipyretics, immunomodulators, and antihistamines. In the subacute period, physiotherapy is included - ultraphonophoresis, laser radiation, UV therapy, UHF therapy.
For frequently recurring tonsillitis, the issue of complete removal of the tonsils along with adjacent tissues using a laser, radiofrequency electrode, or ultrasonic scalpel is resolved. If complications develop in the form of a peritonsillar abscess, it is opened.
Treatment of viral and bacterial sore throat
Treatment of sore throat (for example, catarrhal) caused by a virus consists of alleviating the symptoms of the disease, because Viral sore throat usually goes away on its own. In this case, to relieve the symptoms of the disease, it is recommended to: gargle with salt water, drink plenty of warm tea, take painkillers, and use other treatment methods at home.
If the cause of a sore throat is streptococcus, then antibiotic therapy is necessary to treat a sore throat (for example, follicular or lacunar). Taking antibiotics will help control the spread of infection and prevent rare but serious complications (for example, rheumatism, myocarditis).
When frequent relapses of tonsillitis occur, the disease becomes chronic, creating conditions for local destruction of the tonsils. Which in turn leads to the inability of the tonsils to perform their protective functions of the immune system. In addition, the constant presence of infection in the tonsils allows microbes to enter the general bloodstream, thereby affecting other organs and systems. To exclude complications associated with this phenomenon, doctors recommend removal of pathologically altered tonsils.
Contraindications for surgery to remove tonsils are: heart defects of 2-3 degrees of severity; hemophilia - a blood clotting disorder; severe diabetes mellitus.
Treatment of viral pharyngitis.
As already mentioned, antibiotic therapy for viral pharyngitis will not be an effective treatment. Moreover, there is no so-called causal treatment. Viral pharyngitis is a disease that goes away on its own; treatment is symptomatic. The most widely used antipyretic drugs are those whose active ingredient is paracetamol. Antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs are also used
- these include, for example, compounds related to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the active ingredient of which is ibuprofen.
For nasal discharge, topical medications are used to relieve nasal congestion. Thanks to local action, active ingredients
almost immediately enter the infected area. In case of fever, it is also recommended to drink plenty of fluids to keep the body hydrated.
Many medications used to treat viral pharyngitis are available without a prescription. So you can buy them yourself without visiting a doctor. However, you should read these instructions carefully and adhere to the prescribed doses. In addition to symptomatic treatment
Rest and reduction in physical activity are also necessary.
Causes of sore throat
The root cause of this disease is viruses and bacteria. The most common of them are beta-hemolytic streptococcus and staphylococcus. They can enter the body from the environment or from sources of chronic infection within the body itself. The immune system of a healthy person should suppress pathogenic microorganisms, but there are provoking factors for the development of sore throat:
- smoking;
- deficiency of vitamins and balanced nutrition;
- hypothermia;
- throat trauma;
- the presence of other inflammatory processes.