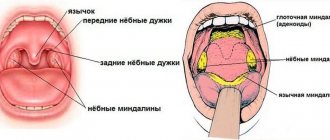
Symptoms of a sore throat
For tonsillitis, the incubation period ranges from 10 hours to 3 days. The disease is characterized by an acute onset, fever, chills, and pain when swallowing. An enlargement of the mandibular lymph nodes is also observed. As a rule, those lymph nodes that are closest to the source of inflammation become enlarged. After all, it is the lymphatic system that is responsible for capturing and destroying foreign organisms.
1
Otorhinolaryngology in MedicCity
2 Otorhinolaryngology in MedicCity
3 Otorhinolaryngology in MedicCity
Catarrhal tonsillitis is characterized by superficial damage to the tonsils. Catarrhal tonsillitis can begin suddenly, with a temperature of up to 37.5 degrees. A person with a sore throat feels unwell, chills, a severe headache and a sore throat, and has difficulty swallowing. The throat is red, the tonsils are loose and enlarged, there is a coating on the tongue. During pharyngoscopy, bright diffuse hyperemia and swelling of the tonsils are observed.
The patient may experience slight changes in the blood and mild signs of intoxication. Symptoms last 1-2 days and then disappear. After this, the disease can develop into a new form.
Lacunar tonsillitis is one of the common forms of catarrhal tonsillitis. With lacunar angina, the tonsils are affected in the area of the lacunae. The lacunae (depressions on the surface of the tonsils) are enlarged, the mucous membrane of the pharynx and tonsils turns red and swollen, the tonsils become covered with purulent plaque (which is formed from the contents of the lacunae). Plaque is removed easily, without bleeding marks.
Purulent (follicular) tonsillitis is much more difficult to treat. Follicular tonsillitis is characterized by deep damage to the tonsils. The mucous membrane of the tonsils is inflamed; many whitish-yellowish inclusions, similar to millet grains, are visible on it. These are suppurating follicles that gradually enlarge and burst, releasing pus into the pharyngeal cavity. The duration of the illness can be up to 10 days.
Follicular and lacunar tonsillitis is accompanied by a temperature of up to 39-40 degrees. Patients complain of general weakness, severe pain when swallowing, radiating to the ear, headache, pain in the heart, muscles and joints. The voice becomes unrecognizable and hoarse. Lymph nodes in the neck enlarge and become painful when palpated. Laboratory diagnostics reveals leukocytosis, traces of protein in the blood, red blood cells in the urine.
Necrotizing tonsillitis is distinguished from other forms by a more severe course and more pronounced symptoms. On the tonsils there are areas covered with plaque, spreading deep into the mucous membrane. The plaque has an uneven, pitted surface that is greenish-yellow or gray in color. When it is removed, the surface bleeds, and deep defects may remain on the tissues of the tonsils. Necrosis often spreads to the posterior wall of the pharynx and uvula.
Attention! If you have a sore throat, you need to consult an otolaryngologist! Along with the listed types of tonsillitis, there are also atypical tonsillitis , which require specific treatment, often with hospitalization.
How long does a sore throat last?
The duration of the disease depends on its form and severity. The total duration usually does not exceed 7 days4.
Regardless of how long a purulent sore throat is treated, the doctor states recovery only 5 days after the temperature normalizes. In this case, the patient’s sore throat should disappear, and the lymph nodes should become painless. In addition, the results of blood tests, urine tests and electrocardiograms are always taken into account3.
Up to contents
Factors in the development of sore throat
Sore throat is primarily an infectious disease. Inflammation of the tonsils can be caused by various microorganisms, primarily staphylococcus and streptococcus. In addition, the following factors can provoke a sore throat:
- hypothermia of the body;
- long exposure to polluted air;
- lack of sunlight;
- dampness;
- poor nutrition;
- unhealthy living conditions;
- overwork of a person.
Prevention and recommendations
Prevention of angina consists mainly in the general strengthening of the body's immunity. Therefore, preventive measures include:
- regular sports, gymnastics, hardening, walks in the fresh air
- avoiding hypothermia, careful use of air conditioning
- balanced diet with sufficient vitamins
- maintaining personal hygiene rules
- timely sanitation of foci of infection (for example, dental caries, chronic tonsillitis)
- in the event that one of the family members is sick, it is advisable to provide a ventilated separate room to avoid infecting others.
Treatment of sore throat
Sore throat is a fairly serious infectious disease that cannot be cured only by drinking herbal infusion and rinsing. Antibiotics for sore throat are mandatory. Treatment of sore throat in adults and children should be carried out under the guidance of a physician.
1 Diagnosis of sore throat
2 Diagnosis of sore throat
3 Diagnosis of sore throat
Our clinic uses all modern methods of diagnosis and treatment of ENT pathology. Otolaryngologists at MedicCity are professionals with extensive experience.
Attention! Sore throat is contagious, so the patient should be isolated from children and the elderly. He should have his own dishes and towel for the period of illness.
For mild cases, treatment of sore throat is outpatient. Severe forms of the disease require hospitalization in the infectious diseases department.
1 Diagnosis of sore throat
2 Diagnosis of sore throat
3 Diagnosis of sore throat
In the first days, bed rest, mild warm food, and plenty of fluids (fruit juices, compotes, milk, alkaline mineral water) are indicated. The prescription of antibacterial drugs is mandatory. Rinsing with antiseptic solutions and herbal decoctions is also used. Irrigation of the tonsils with various drugs is also prescribed. After a sore throat, it is necessary to follow a gentle regimen for some time to avoid complications.
Actions for sore throat
If you notice the first symptoms of the disease, you should consult a doctor. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate or try to overcome the disease with folk remedies. Sore throat is a serious disease that is dangerous to joke with.
If a sore throat is not treated or acted incorrectly, a number of complications can occur:
- chronic tonsillitis - in this case you will remain with this disease for life;
- laryngitis or bronchitis;
- abscess;
- rheumatism of the heart or joints;
- glomerulonephritis;
- pyelonephritis.
For a sore throat, a specialist prescribes antibiotics depending on the clinical picture and individual characteristics of the patient. Gargling is also prescribed every hour to remove suppuration and inflammation. To do this, use herbal decoctions, salt with soda, furatsilin, chlorhexidine. Do not eat or drink for half an hour after rinsing.
In addition to rinsing, the tonsils are irrigated with antimicrobial agents. If the temperature rises above 38 degrees, antipyretics are taken. Children are recommended to use wraps to relieve fever.
Antihistamines will help relieve swelling, and special lozenges will reduce pain.
It is important to ensure you drink plenty of fluids. In this case, warm fruit drinks will be most useful.
Food during illness should be dietary, soft and warm, so as not to irritate a sore throat.
Features of diagnosis and treatment of sore throat in children
Sore throat is one of the most common childhood diseases. Most often this happens in spring and autumn, when children's immunity is especially weakened. Weakening of the immune system occurs as a result of the following reasons:
- poor nutrition;
- non-compliance with sleep and rest schedules;
- hypothermia of the child’s body as a result of being outside;
- drinking cold drinks from the refrigerator;
- frequent viral infections.
- chronic inflammation of the tonsils (tonsillitis).
If a sore throat is suspected, the doctor may take a swab from the child’s throat for flora and diphtheria and ask for a general blood test, since certain signs may not only have a sore throat. Symptoms in the form of a white-gray coating on the tonsils are also characteristic of diphtheria. Only sore throat is treated with antibiotics, and diphtheria is treated with anti-diphtheria serum.
Similar symptoms may appear in acute tonsillitis, which is caused by viruses and fungi and requires antiviral treatment.
Sore throat in children is especially dangerous due to possible complications. The main target organs for complications of angina are the heart and kidneys. The cause of such complications is inadequate or untimely initiation of treatment for sore throat!
Treatment of sore throat in children has its own characteristics. A course of antibiotics, gargling with sage, chamomile, and a solution of soda and salt are prescribed. Children under 2 years of age are not recommended to irrigate the throat with antiseptic spray or use medications with essential oils, as this can cause spasm of the larynx. If the child’s temperature continues to rise, then you need to urgently call an ambulance.
Types of most likely complications
Tonsillitis develops due to the penetration of bacteria and viruses into the oropharynx, which cause pain and symptoms of intoxication. Timely intake of antibacterial agents and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations allows you to destroy the causative agent of the disease in the primary focus of microbial development. If this does not happen, there is a high probability that bacteria will spread throughout the body through the blood or lymph flow, which leads to inflammation of the internal organs.
All possible complications of any type of tonsillitis are divided into local and systemic (general). Local ones are easier to tolerate, although they lengthen the recovery time and significantly weaken the immune system. General complications are less common, but they are much more dangerous for the patient.
Complications of sore throat
Complications can be early or late. Early ones (peritonsillitis, peritonsillar abscess, etc.) are caused by the spread of infection to neighboring organs and occur during illness. Late ones appear after 3-4 weeks and are of infectious-allergic origin (articular rheumatism, rheumatic carditis, streptococcal glomerulonephritis).
Attention! Complications of tonsillitis most often occur during self-medication. Only timely comprehensive treatment of sore throat under the supervision of an otolaryngologist will protect you from the serious consequences of the disease!
Causes of acute tonsillitis
A sore throat can be caused by a fungus or a virus, but most often the cause of the disease is bacteria. The most common variant is streptococcus. Quite often, sore throat is a complication of ARVI. In such situations, they usually talk about the addition of a bacterial infection.
Sore throat is transmitted by airborne droplets. Transmission of infection through household items is less common.
Most often, elderly people and children and people with weakened immune systems become infected. Why? Tonsils are organs that are part of the body's immune system. Their function is to protect the body from pathogenic bacteria. In fact, they are a kind of barrier that does not allow the “enemy” into the body. However, in cases with weakened immunity, the tonsils are not able to cope with the task and do not protect the body from pathogenic microflora. As a result, microorganisms attack the tonsils, causing them to become inflamed.
Sore throat can occur due to the following reasons:
- hypothermia, both of the throat and general;
- lack of vitamins;
- chronic tonsillitis is a sluggish inflammatory process in the tonsil area, which can result from untreated tonsillitis;
- poor air ecology - inhalation of polluted air in industries, etc.;
- foci of infection in the nasopharynx - caries, adenoids, sinusitis, etc.
Mistake 7 - trying to pick off plaque that has formed in the throat with a spoon
Firstly, plaque is very difficult to remove, so trying to pick it off can cause bleeding in your throat. And secondly, plaque creates a protective film on the tonsils, which prevents the spread of infection. When you begin to recover, the film will come off on its own. Therefore, the most you can do to get rid of plaque is to gargle with soda solutions or salted water with a drop of iodine. In this case, only that part of the film that is ready to fall off will be washed off.
And finally, at home it is difficult to achieve complete sterility of instruments. Therefore, when trying to pick off plaque, you risk introducing an additional infection into your throat.
Dagger in the throat. Why is a sore throat dangerous in a child? Read more