Detailed description of the study
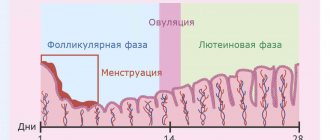
A healthy woman of reproductive age undergoes a set of sequential physiological changes every month, which is called the menstrual cycle. Its duration is 21-25 days, with an average of 28 days. The cycle consists of two phases: follicular and luteal. It's important to note that the length of the follicular phase can vary depending on the length of your cycle, while the luteal phase is usually stable and lasts 14 days.
The follicular phase is counted from the first day of menstruation until the onset of ovulation: day 14, if we consider the duration of the menstrual cycle to be 28 days. During the follicular phase, the follicle containing the egg grows and matures in the ovary. The process of an egg leaving the follicle is called ovulation. In the second phase of the menstrual cycle (luteal), the formation of the corpus luteum occurs. The corpus luteum is a temporary formation (gland) located in the ovary that synthesizes progesterone.
The endometrium, the inner layer of the uterus, also experiences cyclical changes. At the beginning of the follicular phase, detachment of the functional layer of the endometrium occurs, accompanied by bleeding, that is, menstruation. Next, the inner lining of the uterus restores its thickness. This provides the opportunity for implantation of the embryo in the subsequent luteal phase if conception has occurred. If pregnancy does not occur, the cycle repeats again, starting from the first day of menstruation.
The biological role of the menstrual cycle is to prepare the woman’s body for the possible onset of pregnancy - fertilization of the egg and implantation of the embryo in the uterine cavity.
The following hormones are involved in the menstrual cycle.
Estradiol is the active form of estrogen, a female sex hormone produced in the ovaries. During the follicular phase, its concentration increases, reaching a peak during ovulation. Its main function is to prepare the uterus for possible implantation of an embryo. There is a physiological decrease in the level of this hormone in a woman's life, in preparation for menopause (cessation of the menstrual cycle). Estrogen is formed from testosterone under the action of various enzymes.
The pituitary hormones are luteinizing hormone, prolactin and follicle-stimulating hormone. Luteinizing (LH) and follicle-stimulating (FSH) hormones influence the production of estrogen in the ovaries. Luteinizing hormone (LH) is produced in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. It is necessary to stimulate the production of estrogen. The action of LH is directed in women to the ovarian tissue and corpus luteum. A rise in LH levels occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle, followed by a peak in estradiol.
Follicle-stimulating hormone, produced in the pituitary gland, affects the growth of follicles in the ovary. In the middle of the menstrual cycle (towards the end of the follicular phase), the growth of this hormone reaches its peak, after which the follicle ruptures and the egg is released into the fallopian tubes.
Prolactin is necessary for the normal functioning of the mammary glands; it increases during lactation and pregnancy. In addition, prolactin affects the secretion of progesterone and follicle-stimulating hormone.
The production of sex hormones and the duration of the follicular phase are also influenced by thyroid hormones. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is a hormone produced in the anterior pituitary gland, its main function is to stimulate thyroid cells through receptors. In turn, these cells contribute to the production of thyroid hormones (T4, T3).
Free T4 is the active form of thyroxine, the main thyroid hormone. Thyroxine is necessary for the regulation of metabolic processes in the human body. It is synthesized in the thyroid gland. In women with reduced thyroxine production due to thyroid disease, the normal menstrual cycle is disrupted.
Testosterone is a hormone that is produced in small quantities by the ovaries and adrenal glands in women. It is involved in the regulation of the level of gonadotropic hormones of the pituitary gland; the maximum concentration of testosterone is determined during ovulation and in the luteal phase. In women, this hormone is converted into estrogen.
DHA-S (dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate) is produced in the adrenal cortex. Testosterone and dehydrotestosterone are formed from this substance. DHA-S is a low-active substance that must be determined if the development of adrenal tumors is suspected, as well as in women with menstrual irregularities and the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics, for example, male-pattern hair growth.
Sex hormone binding globulin is a protein produced in the liver. Its main role is the transport of sex hormones (estradiol, testosterone, progesterone). In combination with it, these hormones are in a bound, inactive state. If the level of this substance in the blood decreases, the amount of freely circulating hormones that it carries increases. At the same time, their biological effects are enhanced. A study of the level of sex hormone binding globulin is necessary if there is a suspicion of menstrual irregularities, the absence of menstrual bleeding, its irregularity, as well as if signs of hirsutism (male pattern hair growth) appear.
17-OH-progesterone (17-hydroxyprogesterone) is a hormonal substance that is necessary for the formation of steroid hormones. Cortisol and testosterone are synthesized from 17-OH-progesterone. This substance is determined if there is a suspicion of disruption of the normal functioning of the adrenal cortex, with the development of adrenogenital syndrome: the formation of a male physique, short stature, menstrual irregularities, infertility in women.
Timely diagnosis of hormonal disorders in a woman of reproductive age is necessary for a full life and the possibility of conceiving a child. Assessing the concentration of hormones in the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle will allow the doctor to identify changes in the production of these hormones and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
A detailed description of the studies and reference values are presented on the pages with descriptions of individual studies.
Why are hormones important?
A lack of hormones in the body leads to serious diseases such as diabetes. Due to disruption of the hormonal system, people can be born dwarfs; women can have problems with pregnancy, the menstrual cycle, excess weight, increased hair growth, acne on the face, and premature ovarian failure.
Based on what complaints the patient receives, the doctor determines which hormones the woman should be tested for.
References
- Ilyasova, N.A., Burlev, V.A. Clinical and endocrine features of the menstrual cycle of women. Gynecology, 2015. - No. 6.
- Khasanov, A.A., Zhuravleva, V.I. Modern ideas about the regulation of menstrual function. PM, 2009. - No. 34.
- Pereira, H., Larson, R., Bemben, D. Menstrual Cycle Effects on Exercise-Induced Fatigability. Front Physiol., 2021. - Vol. 11. – 517 p.
- Monis, C., Tetrokalashvili, M. Menstrual Cycle Proliferative And Follicular Phase., 2021.
Preparing for hormone tests
Assessing a patient’s hormonal background is an important point in diagnosing many diseases. What hormone tests are needed in a particular case is determined by the doctor. The patient is only required to comply with the rules for preparing for research, which are given below.
In order to get a reliable picture as a result of hormonal tests, the patient must take into account the basic rules for preparing for them.
- For a few days, heavy physical activity is excluded, situations that cause nervous tension are prohibited.
- Two days before the study you need to give up alcoholic beverages.
- Two hours before taking biological material, you should stop smoking.
- The analysis is carried out in a state of absolute calm, therefore, you need to sit and relax 15 minutes before it is carried out.
- Distortion of the results is possible if the patient is taking medications; you should definitely discuss this situation with your doctor.
Some types of hormonal tests
It is advisable to carry out only on specific days of the cycle (if we are talking about a woman), the doctor will definitely warn you about this.
A man can take hormone tests
any day.
To obtain a correct interpretation of the results of hormone tests, strict adherence to the following rules is necessary.
- It is advisable to donate blood in the morning (8-11). The analysis must be carried out on an empty stomach, which means that at least 8 hours must pass between the collection of biological material from the patient and the last meal. At the same time, it is not prohibited to consume water in any quantity; it does not in any way affect the study on the concentration of hormones.
- On the eve of the study, it is recommended to limit yourself to a light dinner; it is advisable to avoid fatty foods in order to avoid distorting the results.
- Approximately two days before the hormone test, doctors advise you to stop drinking alcohol. Excessive physical activity is also prohibited.
- The use of medications is not recommended. In some cases, you can take medications after first discussing this with your doctor. It is advisable to conduct the study before drug treatment or two weeks after its cessation.
- About two hours before the test is due, you need to stop smoking cigarettes. You should also not drink coffee, tea, juice, or sparkling water. There should be no physical stress (climbing stairs too quickly, running), as well as emotional arousal. It is advisable to relax and rest a little 15 minutes before the analysis.
- Donating blood after an instrumental examination, various physiotherapeutic procedures, ultrasound or X-ray examination, massage and other medical procedures is not recommended; you need to wait a certain time.
- If laboratory parameters are checked over time, it is preferable to carry out repeated studies under the same conditions, that is, at the same time of day, in the same laboratory, and so on.
- In some cases, laboratory analysis of hormones
must be carried out strictly on certain days of the cycle.
The attending physician will warn the patient about this. As a rule, we are talking about tests for hormones of the reproductive system.
In order for anal analysis to be carried out on the main hormones
turned out to be as informative as possible, it is very important to prepare for them correctly.
Where are hormone tests done?
Diana Medical Center offers its patients a full range of hormone tests. The drug and hardware base of our laboratory allows us to quickly and reliably determine the concentration of hormones in blood, urine and other biological fluids. In addition, the results are deciphered by our specialists, who, if necessary, will develop an optimal scheme for correcting hormonal levels.
Get tested for hormones
You can skip the line for adults, children, and pregnant women at a convenient time by making an appointment on any day - we work seven days a week. You can find out the cost of the listed studies on our website in the price list of services.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Complexes with this research
Fitness control of sports nutrition Assessment of liver function, hormone levels and metabolism when taking sports nutrition RUR 5,140 Composition
Male confidence Prostate cancer risk assessment and testosterone level control RUR 1,190 Composition
Check-up No. 1 for children and adolescents Annual preventive examination program RUB 10,950 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Male infertility. Extended examination RUB 29,030
- Female hormones. Follicular phase RUB 5,930
- Preventative check-up RUB 11,960
- Advanced male anti-aging diagnostics RUB 33,710
- Anti-aging diagnostics. Hormonal balance RUB 6,250
Testosterone
This hormone can be tested in both men and women any day. Testosterone is needed by both spouses, but is a male sex hormone. In the female body, testosterone is produced by the ovaries and adrenal glands. Exceeding the normal concentration of testosterone in a woman can cause irregular ovulation and early miscarriage, and the maximum concentration of testosterone is determined in the luteal phase and during ovulation. A decrease in testosterone concentration in a man causes a decrease in sperm quality.