One of the most pressing problems of endocrine surgery is the diagnosis and treatment of a benign tumor of the thyroid gland - adenoma. This disease is quite common - it accounts for about a tenth of all nodular formations. Adenoma is often asymptomatic and has a risk of malignancy (malignancy), so the issue of its timely detection and treatment is extremely important.
- Causes of development and types of adenomas
- Symptoms of thyroid adenoma
- Diagnostic methods
- Who's at risk
- Types of operations for thyroid adenoma
- Features of the operation
- Recovery after surgery
Causes of development and types of adenomas
Possible causes of thyroid adenoma:
- Severe iodine deficiency.
- Environmental pollution from industrial waste.
- Impact of radioactive substances on the thyroid gland.
According to the histogenetic classification, the following forms of thyroid adenoma are distinguished:
- From A cells.
- 1.1. Follicular.
- 1.2. Papillary.
- 1.3. Trabecular.
- From B cells.
- 2.1. Follicular.
- 2.2. Papillary.
- 2.3. Trabecular.
- From C cells.
- 3.1. Solid.
The WHO classification divides benign thyroid tumors into two types:
- Follicular adenoma.
- Hyalinized trabecular tumor.
Follicular adenomas occupy first place in the frequency of detection. They can be represented by micro-, macrofollicular and solid tumors. Trabecular, embryonic, oncocytic and atypical types of structure are relatively rarely detected.
Separately, it is worth highlighting toxic or functioning adenoma. This type of tumor produces large quantities of thyroid hormones.
Such different adenomas
These dangerous tumors come in different types:
- follicular - looking like a rounded node. Their number is 15–25% of the total number of adenomas;
- papillary, which are papillary formations filled with dark brown liquid;
- toxic, accompanied by increased production of gland hormones (hyperthyroidism) and disruption of the endocrine system;
- oncocytic, consisting of B cells Hürthle-Askanasi. These formations got their name because of their aggressiveness and frequent progression to cancer.
Tumors are often asymptomatic, being detected by chance during an ultrasound examination or palpation of the gland. They represent a dense knot, delimited by a capsule from neighboring tissues. Large tumors put pressure on the trachea, causing a feeling of lack of air and difficulty breathing - such tumors need to be removed urgently.
Toxic adenoma is accompanied by signs of thyrotoxicosis - sweating of the hands, palpitations, arrhythmia, weight loss, a feeling of heat, increased blood pressure, dry eyes, and sexual dysfunction.
All of the listed types of adenomas, except toxic ones, require diagnosis by biopsy and removal. Only adenomas in the initial stages are treated conservatively if they are caused by removable factors, for example, hormonal imbalance.
Symptoms of thyroid adenoma
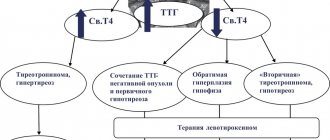
Thyroid adenoma most often occurs secretly. In most patients, the disease is not accompanied by changes in hormonal status, but in some cases the development of hypo- and hyperthyroidism is possible.
Some patients with adenoma experience symptoms such as discomfort and neck pain. As the tumor grows, signs of compression of the respiratory tract and esophagus (shortness of breath, dysphagia) may be detected. Neurological manifestations of compression, for example, Horner's syndrome, are even less common.
Toxic adenoma is always accompanied by symptoms of thyrotoxicosis of varying severity. When the tumor is located in the right lobe of the thyroid gland, concomitant hyperthyroidism is usually more severe.
An objective symptom is the identification of a round-shaped nodule in the thyroid gland with clear contours. On examination, in most cases, asymmetry in the neck area is noticeable. Palpation of the tumor is dense and elastic, usually painless.
The disease progresses extremely slowly. Thyroid adenoma has the ability to gradually increase in size over several years or periodically stop growing.
Diagnostic methods
The problem of diagnosing thyroid adenoma is very relevant, since recently there has been an increase in the percentage of these tumors in the structure of nodules. In addition, there are significant difficulties in the process of differential diagnosis of follicular adenoma and follicular type cancer.
If a dense formation with clear contours is detected by palpation in the thyroid gland, it is necessary to determine its size, location, and consistency. It should also be noted the presence or absence of pain during palpation and the relationship of the detected compaction to other tissues in the gland (mobility, adhesion).
Further diagnosis is carried out using the following laboratory tests:
- Determination of free thyroxine and triiodothyronine to assess thyroid function.
- Test for antibodies to thyroglobulin. Performed to exclude a possible autoimmune process.
In addition, to establish and clarify the diagnosis of thyroid adenoma, instrumental diagnostic methods are indicated:
- Ultrasound examination with color Doppler mapping.
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy (under palpation and ultrasound control).
- Urgent histological examination.
- Intraoperative laser autofluorescence spectroscopy (IOLAS).
If a patient is diagnosed with hyperthyroidism in combination with a single nodule in the thyroid gland, then the likely diagnosis is a toxic adenoma. To confirm it, scintigraphy is indicated, which reveals a “hot node” with an increased level of iodine absorption.
In some patients, the adenoma is detected by chance. In these cases, a thyroid tumor is detected, for example, during an ultrasound or MRI of the cervical region, which were prescribed for another purpose.
Who's at risk
According to research results, women suffer from thyroid adenoma 5 times more often than men. This disease is most often diagnosed between the ages of 51 and 60 years.
Based on the presumed causes of tumor development, the risk group also includes all residents of goiter-endemic areas and places that have been contaminated with radiation waste. For example, after the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in the adjacent territory, the percentage of people who became ill with thyroid adenoma increased noticeably.
Read also
Symptomatic arterial hypertension
Arterial hypertension is a very common disease of the human cardiovascular system.
According to statistics, 20-30% of the population suffers from arterial hypertension, aged 60 years and above... Read more
Hyperprolactinemia
Hyperprolactinemia is a persistent increase in the level of the hormone prolactin in the blood. Hyperprolactinemia syndrome is a complex of symptoms that occur against the background of increased prolactin levels, the most characteristic...
More details
Metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a “pandemic of the 21st century.” The prevalence of metabolic syndrome is 20–40%. In the Russian Federation, 40% of the population have 2 components of metabolic syndrome, 11% –...
More details
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a progressive metabolic disease of the skeletal bones, which results in a decrease in bone density and disruption of its internal structure. The result of osteoporosis is...
More details
Diabetes mellitus, type 2
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by chronic hyperglycemia, which results from impaired insulin secretion, insulin action, or both...
More details
Types of operations for thyroid adenoma
Surgical options for removing a benign thyroid tumor:
- Extracapsular hemithyroidectomy with resection of the isthmus.
- Subtotal thyroidectomy.
The extent of surgical intervention is determined by the size of the tumor and its histological characteristics. Preference is given to organ-preserving surgery. The technical advantages of removing one of the lobes of the gland with resection of the isthmus over subtotal thyroidectomy are obvious: the risk of injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerve and parathyroid glands is minimized. However, it has been observed that approximately a quarter of patients who underwent lobectomy experienced growth of a nodule in the remaining lobe of the thyroid gland within 4 years.
Conditions for hemithyroidectomy for adenoma:
- Reasoned diagnosis of a benign tumor.
- The node is no more than 1 cm in diameter.
- The contours of the formation are clear and even.
- Homogeneous isoechoic structure and “hypoechoic corolla”.
- Absence of atypical cells in the examination of histological material.
In all other situations, subtotal thyroidectomy is considered to remove the adenoma. The reasons for such an operation are:
- Bilateral localization of thyroid adenoma.
- Benign formation in combination with multinodular goiter.
- Detection of malignant cells in a histological specimen.
In some cases, according to indications, total removal of the gland with lymph node dissection is performed due to suspicions of a pronounced malignant process. Radical operations are rare; surgeons usually try to preserve at least a small part of the gland parenchyma.
How to prepare for an ultrasound
The method is accessible and simple, does not require special preparatory operations. You can eat absolutely any food product. But there are a number of restrictions:
1. Regardless of the feeling of nausea, older people are not recommended to eat before the procedure. Age-related changes may have an effect.
2. Women are recommended to undergo examination on days 7-9 of the menstrual cycle to avoid inaccurate results.
3. Immediately before the procedure, you need to free your neck from elements that interfere: jewelry, collars, etc.
4. Preparation for an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland in children is no different from the procedure for adults. The child must be psychologically prepared for the procedure so that he is not afraid of either the doctor or what he will do.
Doctors recommend that women undergo testing both during pregnancy and at the planning stage. If it is impossible to get pregnant, gland pathology may be one of the possible causes.
After the child has suffered stress, it is also worth going to the clinic so that an endocrinologist can perform an ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
Features of the operation
Surgical interventions that are carried out to remove a thyroid adenoma are quite labor-intensive and require clear and precise actions by the surgeon. Such operations are accompanied by the risk of damage to the recurrent laryngeal nerve and parathyroid glands, which are located next to the thyroid gland. In this regard, many endocrinological surgeons use magnifying devices (binocular magnifying glasses, operating microscope). The introduction of neuromonitoring devices into practice also greatly facilitates the visualization of the recurrent nerve.
After surgery using the classical approach, a fairly noticeable scar remains. In order to minimize the consequences of such cosmetic defects, an endoscopic treatment method using minimally invasive access is being introduced into practice. Removing tumors using endoscopy guarantees the absence of noticeable postoperative scars, but surgeons note an increased risk of complications from such operations.
When removing a toxic form of thyroid adenoma, preoperative preparation is carried out, the essence of which is to take hormonal drugs. Surgical intervention is carried out after normalization of the gland.
The main thing is the experience of the surgeon
Such interventions are very complex: small errors can cause damage to the nerves and muscles of the larynx. The person’s voice disappears, it becomes difficult for him to swallow and breathe.
Most complications are associated with improper treatment and insufficient qualifications of the surgeon. According to statistics from world medicine, to successfully perform interventions on the gland, a doctor must perform up to 50 such operations per year. You should not trust your health to a surgeon who has removed a thyroid adenoma two or three times.
If the operation to remove the adenoma went well, patients tolerate the postoperative period easily and go home within 2–3 days. Physical activity and sports are prohibited until the doctor's permission. After treatment, you need to periodically donate blood for thyroid hormones.
Recovery after surgery
Provided there are no complications during and after thyroid surgery, the patient needs about 10-12 days to recover. The beginning of the rehabilitation period may be accompanied by hoarseness. This complication is temporary and develops as a result of compression of the recurrent laryngeal nerve by edematous tissue of the gland. The voice returns as the swelling decreases over several days.
If the thyroid gland has been completely removed, the patient is prescribed lifelong hormone replacement therapy. The drug of choice is L-thyroxine in an individual dose, which is selected taking into account body weight and metabolic characteristics, as well as concomitant pathology.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Are there any ways to protect yourself from these formations?
The most important thing is a healthy lifestyle :
proper and nutritious nutrition, sufficient physical activity. You need to eliminate trigger factors - bad habits. Do not consult with “all-knowing” neighbors and friends, do not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication - but consult a doctor in a timely manner if you have complaints. It is also important not to take iodine preparations and other vitamins and microelements without a doctor’s prescription.
You can make an appointment with Tatyana Pugavko or another endocrinologist by calling the center: +375 29 311-88-44 ;
+375 33 311-01-44 ; +375 17 299-99-92 .
Or through the
online registration
on the website.