Abstract
Oxidative stress is considered one of the causes of impaired melanogenesis, leading to the development of vitiligo. There are reports in the scientific literature that in foci of vitiligo melanocytes retain their viability, but their pigment-forming function is suppressed. Under the influence of certain stimuli, they can restore their activity; in particular, a therapeutic effect is noted not only from the use of selective phototherapy with UV radiation, but also from the use of antioxidants.
In this article, the author describes his own clinical experience of successfully treating patients with vitiligo using intradermal injections of an antioxidant cocktail.
Key words: vitiligo, antioxidants, mesotherapy.
Causes
An interesting fact is that this pathology is not congenital; white spots have to be treated after exposure to not only external, but also internal factors. Race is not particularly important, however, the disease is more often diagnosed in patients with dark skin.
The following reasons can provoke the development of the disease:
- Heredity.
- Endocrine and hormonal disorders.
- Exposure to chemicals that may be used in the production of low-quality cosmetics.
- Prolonged exposure to the sun.
- Use of certain pharmaceuticals.
- Pathologies of the digestive system.
- The presence of autoimmune processes in the body, in which antibodies tend to attack healthy cells instead of pathological ones.
- Various damage to the skin, burns - inflammatory reactions with an autoimmune component are triggered in the affected areas, most often it is the cells that produce pigment that react in this way.
The development of vitiligo can begin completely unnoticed by a person. Sometimes it is preceded by slight itching, increased sensitivity of the skin, a tingling sensation, “goosebumps”. Each spot that appears has a clear outline; more often, such spots with smooth or scalloped edges have a rounded shape. Apart from the white color, there are no changes in the skin, no peeling or atrophy.
With further development of the pathology, the spots begin to merge, increase in size, and can be observed on any part of the body. Lack of pigmentation is not the only sign of the disease; sometimes skin irritation is observed.
Introduction
Vitiligo
- one of the most common types of hypomelanosis. According to official data, it affects from 3 to 6% of the world's population (the largest number of cases was recorded in Asia and the Middle East). However, in recent years, it appears that the number of patients with vitiligo has been steadily increasing. Let us recall that dyschromia is manifested by spots of depigmentation due to the loss of the ability of certain areas of the skin to produce melanin. This is due to the absence of the enzyme tyrosinase in melanocytes, which stimulates the process of pigment formation. Due to the presence of a pronounced cosmetic defect, patients with vitiligo experience severe stress and psycho-emotional discomfort. This dictates to clinicians and researchers the need to find new ways to treat this disease.
Currently, the lack of a holistic concept of the pathogenesis of vitiligo makes it difficult to develop a unified approach to treatment and predict the clinical course of this disease. In a number of scientific studies of the pathogenesis of vitiligo, preference is given to various theories: genetic, neurogenic, autoimmune, theory of oxidative stress, etc. All these theories have been repeatedly confirmed experimentally, but scientists have not yet come to a consensus. In addition, there are also a number of provoking factors: exposure to UV radiation, psycho-emotional stress, changes in the state of the peripheral nervous system, etc.
Surgical intervention
In 20% of cases, conservative treatment of vitiligo does not give the desired result, then surgery is considered. Surgical treatment consists of transplanting one's own healthy melanocytes onto lesions devoid of pigment. After surgery, new melanocytes are formed in the deep layers of the epidermis. The process of restoring pigmentation takes several months.
Indications for surgical treatment of vitiligo
- The lesions are located on open areas of the body (face, neck, décolleté, arms). They are a significant cosmetic defect and violate the psychological status of the patient.
- Lack of results from local and systemic therapy for 12 months.
- The disease is in remission. Over the course of 1-2 years, new spots do not appear, and existing ones do not grow.
There are several methods of surgical treatment of vitiligo.
- Epidermal transplantation. The affected areas of skin are excised. In their place, an autograft prepared by the PUVA method is placed (a flap of epidermis from a healthy area of the body).
- Minitransplants. Areas of healthy skin less than 1 mm in size are transplanted into depigmented lesions.
- Transplantation of cultured or uncultured melanocytes. Individual cells that produce pigment are implanted into the skin.
Side effects of surgical treatment may include:
- The appearance of scars;
- Uneven pigmentation;
- Rejection of transplanted areas of the epidermis;
Contraindications:
- Tendency to the appearance of scars;
- Intolerance to ultraviolet radiation and laser therapy.
Pathogenetic features of vitiligo
In recent years, scientists around the world are increasingly inclined to the dominant role of oxidative stress in the development of vitiligo. Humans, like other aerobic organisms, need oxygen for their vital functions. however, a significant increase in oxygen levels in tissues is detrimental to aerobes. The toxic effect is not caused by oxygen itself, but by its so-called reactive forms (ROS), some of which are free radicals. Normally, the formation and breakdown of ROS are in a state of balance, and they do not accumulate in cells. The content of ROS can increase with an increase in the rate of their formation or a decrease in the ability of cells to neutralize them. The combination of these processes creates conditions for oxidative stress. At the cellular level, there are disturbances in the functioning of the electron transport chains of mitochondria or microsomes, changes in the activity of enzymes (including dehydrogenases - enzymes that catalyze reactions of biological oxidation and reduction), lipid peroxidation.
The trigger factor for the formation of ACF in the body is exposure to UV radiation. In moderate doses, it stimulates melanogenesis, which manifests itself in the form of tanning. But with increasing intensity and duration of exposure, direct damage to melanocytes is possible, including due to disruption of the cell’s own antioxidant systems [7]. In addition, under the influence of UV rays, the activity of the sympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system increases and the synthesis of catecholamines, which suppress the production of melanin, the main chromophore that absorbs UV rays, increases. All this together leads to an increase in the level of ACF in the blood plasma, epidermis, interstitial fluid of depigmented areas of the skin of patients with vitiligo, contributing to the development and progression of the disease.
Last news
Scientists have created a genetically modified protein that treats vitiligo in mice. Previous studies have shown that HSP70i, a stress-inducible heat shock protein (its synthesis is activated when the temperature rises), plays a key role in the disease vitiligo.
- HSP70i consists of 641 amino acids. Researchers at Loyola University New Orleans replaced one of these amino acids, creating a genetically modified version of HSP70i. The new modified protein displaces its normal predecessor and stops the development of the autoimmune reaction.
- Scientists injected the modified HSP70i into experimental mice suffering from vitiligo and having a salt-and-pepper coloration. After some time, the mice's fur returned to its normal black color. Similar effects were obtained in experiments on human skin cell cultures.
Experimenters hope that human studies will confirm the effectiveness of the new method and finally make it possible to find a cure for vitiligo. True, the experiments were carried out back in 2013, and nothing more was heard about them. Perhaps the experiments stopped due to the unsafety of genetically modified developments.
Drug of choice and treatment tactics
There are reports in the scientific literature that in foci of vitiligo melanocytes retain their viability, but their pigment-forming function is suppressed. however, under the influence of certain stimuli they can restore their activity [9]. In particular, there is a therapeutic effect from the use of not only ultraviolet light (selective phototherapy), but also antioxidants.
The idea of using the drug NCTF135 (FILLMED, Laboratoires Filorga) in the treatment of vitiligo to reduce the effect of oxidative stress on melanocytes arose naturally when analyzing its composition. it includes a polyrevitalizing complex of 55 active ingredients (13 vitamins, 23 amino acids, 6 minerals, 6 coenzymes, 5 nucleotides, glutathione and hyaluronic acid at a concentration of 0.025 mg/ml). It is known that the body’s antioxidant system is multicomponent and is divided into extra- and intracellular protection. it is represented by non-enzymatic substances (for example, tocopherols, carotenoids, ascorbic acid, uric acid, glutathione) and true enzymes (superoxide dismutase, catalase, transferase, etc.) [8]. If you carefully study the components of the drug NCTF135, it contains glutathione, hyaluronic and ascorbic acids, and tocopherol (vitamin E) as antioxidants. All of them are the most important link in protecting cells from ROS. With an increase in the intracellular concentration of glutathione, the antioxidant protection of cells increases and their trophism improves. In addition to antioxidants, NCTF135 contains hyaluronic acid - it activates neoangiogenesis, improving blood circulation in the injection area. Against this background, the administered vitamins and microelements are better absorbed, cell proliferation is activated and the main metabolic processes in them occur more intensely.
The drug NCTF135 has proven itself in the treatment of a number of skin diseases, but we did not find any mention of the use of intradermal injections of antioxidants in vitiligo lesions. In addition, vitiligo is also not included in the list of indications for use of the drug NCTF135. Therefore, in this case we can only talk about “off label” therapy, i.e. use of the drug for indications not approved by government regulatory authorities and/or not mentioned in the instructions for use. It is worth noting that many medications are used in the “off label” mode in modern medical practice in the Russian Federation, so our observation is not something extraordinary from a legal point of view.
Diagnostics
Vitiligo spots at first glance can be confused with spots that occur with lichen or syphilis. However, the latter two diseases are characterized by symptoms other than skin discoloration. Thus, with syphilis, specific lesions of the mucous membrane are observed, and with lichen, the surface of the spots peels off.
The most accurate way to determine vitiligo is by shining a Wood's lamp on the spots. Under it, the affected areas will be highlighted blue-white, and areas where the pigment has just begun to disappear will also become visible. When visiting a dermatologist, it is better to insist on this diagnostic method.
Clinical observations
We observed 7 patients (all women) aged from 25 to 54 years. Complaints upon presentation include rashes in the form of multiple white spots of various shapes and sizes on the skin of the face, neck, torso and limbs. Most of them have been ill since childhood; one patient noted the onset of the disease during pregnancy. In all patients, the rash (at the start of therapy) was progressive. Heredity is not burdened: blood relatives do not have vitiligo. There is no allergic history.
All patients we observed were examined to exclude concomitant diseases. In particular, a clinical blood test, a biochemical blood test were carried out, and the function of the thyroid gland was checked (including ultrasound). In all patients, the blood levels of TSH, free T3, free T4, AT to TPO and AT to TG were determined in the blood. In 2 of 7 patients, an increased level of antibodies to TG was detected (in one patient the norm was exceeded by 3 times, in the second by 50 times). both patients were consulted by an endocrinologist with a diagnosis of autoimmune thyroiditis. These patients were observed by an endocrinologist without prescribing symptomatic therapy. No other pathology of the internal organs was identified. Before starting mesotherapy, the patients received the treatment presented in the table.
- Patient 1: a course of vitamin therapy (3 months), a 2-month course of topical medications (Protopic ointment 0.1%) 2 times a day. The treatment was completed 4 months before the start of mesotherapy and, according to the patient, had no effect.
- Patient 2: previously used celandine tincture for 1.5 months without any visible effect. Treatment was completed 2 months before the start of mesotherapy.
- Patients 3 and 4: not previously treated. The diagnosis was made initially.
- Patient 5: received a course of selective phototherapy 311 nm (3 times a week, 20 sessions) without any visible effect. Treatment was completed 5 months before the start of mesotherapy.
| Patient, N | Previous therapy |
| 1 | 3-month course of vitamin therapy + 2-month course of Protopic ointment 0.1%, 2 times a day |
| 2 | 1.5-month course of celandine tincture |
| 3 | not previously treated |
| 4 | not previously treated |
| 5 | 1 course of selective phototherapy 311 nm (3 times a week, 20 sessions) |
| 6 | 1 course of excimer laser (10 sessions) with 1st and 2nd degree burns in the area of the lesions |
| 7 | 1 course of excimer laser (10 sessions) with 1st and 2nd degree burns in the area of the lesions |
rice. 1. Patient 3: vitiligo lesions in the area of the hands before (a) and 2 weeks after the NCTF135 course (B)
rice. 3. Patient 5: vitiligo lesions in the décolleté area before (a) and 2 weeks after the NCTF135 course (B)
rice. 4. Patient 7: vitiligo lesions in the face and neck before the NCTF135 course (a, B) and 2 weeks after the end of the NCTF135 course (c, D)
Patients 6 and 7: received a course of excimer laser (10 sessions each) with 1st and 2nd degree burns in the area of the lesions. however, according to the patients, they did not observe repigmentation after restoration of the integrity of the skin in the lesions. Treatment was completed 8 and 12 months before the start of mesotherapy, respectively.
Despite the lack of clinical improvement after previous treatment, all patients were motivated to undergo mesotherapy.
At the time of examination, depigmented white spots were localized on the skin of the periorbital and perioral areas, neck and décolleté, hands, axillary areas and inner thighs (Fig. 1a, 2a, 3a, 4a, B). Photo recording of the lesions was carried out before the start of therapy and 2 weeks after the 5th procedure.
“Mom has white bangs, and so do I.”
Alina, 28 years old - I have had vitiligo since birth.
Until I was six years old, I was taken to doctors, we tried all the folk remedies and even went to my grandmother to remove the damage. As a result, my family reconciled, realizing that it was all useless, and stopped tormenting me. I can say that I was lucky: my hands and face were not affected by vitiligo, but there are light strands on my head - such a white bang. On the arms, spots extend from the wrist to the elbow, and they are also present on the stomach and legs. At school, the teachers were indignant about why my mother dyed my bangs blonde, but she explained everything to them, and it ended. I don’t remember any reaction from my classmates.
Of course, in adolescence there was a rejection of appearance, there were complexes. I tried to wear clothes that were as closed as possible so that the stains would not be visible, and I used self-tanner. Vitiligo also affects your lifestyle - it’s better not to sunbathe, because you can instantly get burned. As a child, I was always burned.
There were no problems in my personal life or with friends. The only thing that bothered me was strangers who could look at me on the street. But the older you get, the less you care what others think. Previously, I hid the spots when strangers looked, but now, when they look at me, I look straight in the eyes - interest in me instantly disappears.
Now I have another problem: I worry about my daughter, how she will cope with the same situations that I had. She was also born with white bangs. While she is four years old, she doesn’t ask any questions, she just says: “Mom has white bangs, and so do I.” The husband reacts calmly to all this: he says that he got two such beauties.
Procedure protocol
Before starting therapy, all patients participating in the study signed informed consent for the “off label” procedure and permission to publish their photographs in scientific journals.
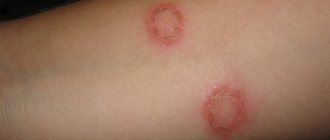
The course of mesotherapy procedures with NCTF135 consisted of 5 sessions, once a week. Emla cream was previously used as local anesthesia for patients for 30–45 minutes. Then, NCTF135 was administered in a volume of 3.0 ml intradermally, using a papular technique, at a distance of approximately 1.0 cm from each other (Fig. 5). A 30G × 13 mm needle was used for injections. The duration of the procedure was 15–20 minutes (excluding anesthesia time).
Symptoms of the disease
First signs
The first sign of vitiligo can be considered the disappearance of pigmentation on any part of the skin. The lesion will necessarily be symmetrical, most often it first appears on the face near the eyes and mouth or on the palms, soles and genitals.
Sometimes an intensely colored border appears around discolored skin spots on healthy skin. If vitiligo begins to appear on the scalp, then the hair may also become discolored. When vitiligo is detected, new spots may appear in places where there have been recent injuries, cuts, bruises, or sunburn. Therefore, if there is a manifestation of vitiligo in the form of small spots, you should not get carried away with sunbathing, otherwise there is a risk of their spreading throughout the body.
Vitiligo spreads quite quickly, the skin rapidly loses melanin and, for this reason, pigmentation in the affected areas of the body. At a certain point, this process may slow down, but at any opportunity (exacerbation of a chronic disease, influenza, etc.), the prevalence of vitiligo can expand again. Cycles of disease development can be repeated many times, but it is completely impossible to predict or explain their occurrence, which makes it difficult to effectively treat the disease.
In the area of discolored skin, the activity of the sweat glands is disrupted. When exposed to sunlight, areas of the skin with white spots will never develop a tan, although in unaffected areas the epidermis will darken. Each case of vitiligo is unique; sometimes the process of skin discoloration may begin with redness, which will gradually lose pigment and become white.
Often, along with vitiligo, patients develop diseases such as porphyrin disease, alopecia areata, white skin atrophy, scleroderma and others. The main distinguishing feature of vitiligo is the complete absence of peeling when affected. The chronic nature of vitiligo prevents its rapid and complete cure. Even the smallest unnoticeable spot can begin to grow and discolor over the rest of the skin over time.
The spread of vitiligo usually occurs slowly; it can take several years from a small spot to noticeable manifestations, and sometimes the development takes the entire life of the patient. There are cases in medicine when the clinical picture of vitiligo disappeared on its own without any therapy, but this is extremely rare. To date, no effective and reliable remedy has been found to treat the disease in question.
Difference from other diseases
A feature of the manifestation of vitiligo is a clear contrast in the color of the spots in relation to healthy skin. The smooth surface of milky-white or snow-white spots with pityriasis-like edges has no redness or signs of inflammation. It is easy to distinguish vitiligo from birthmarks - all spots with this disease are exactly the same in color.
In most dermatological diseases, the surface of the skin begins to peel off and itch, the person sleeps poorly and constantly scratches the damaged areas. With vitiligo, such problems do not exist; the spots do not make themselves known in any way, except for visual perception. Their only “live” manifestation is a periodic increase in the size of the white zones. Therefore, it is very easy to distinguish vitiligo from any skin problems; it is almost impossible to confuse the symptoms; they are characteristic exclusively of the problem under consideration.
Do vitiligo spots itch?
The patient does not feel any subjective sensations when vitiligo occurs. This applies to pain, itching, and swelling of the skin in the affected areas. However, very rarely, some patients complain of itching of vitiligo spots. This is evidence of secondary damage to the skin, the influence of the sun, cosmetics, and other aggressive influences on it, but not vitiligo. The dermis, which has lost melanin, loses its own protective functions along with it, which means it becomes sensitive to even the weakest influence.
results
During the therapy, all 7 patients noted the disappearance of the sharp boundary between the lesions and healthy skin (“leveling” of the external boundaries of the lesions), as well as complete or partial repigmentation in lesions that were previously devoid of pigment. natural pigmentation was restored both along the periphery and in the central part of the lesions [10]. Moreover, in 6 patients spotty (“mosaic”) repigmentation was visually recorded in all lesions in which intradermal injections of the drug were performed (Fig. 1B, 2B, 3B), and in one patient there was almost complete repigmentation in the lesion at the right corner of the mouth. In addition, in the last patient, on the lateral surface of the neck on the left, the lesion decreased in size, partially repigmented and was divided into two parts by an “isthmus” (Fig. 4 c, D).
After the therapy, the patients began to notice a decrease in the sensitivity of depigmented lesions to sunlight. Short-term interaction with UV light no longer caused significant long-term hyperemia in the lesions, as it did before treatment. During the mesotherapy course, no allergic reactions or exacerbation of the underlying disease (appearance of new spots) were noted. Upon completion of the course of therapy, patients were recommended sunscreen with SPF 50+ as a preventive measure.
During further observations (6 months after completion of the course of mesotherapy), repigmentation in all patients was persistent and amounted to about 30% of the entire affected area. Six months after 1 course of mesotherapy with antioxidants, 2 out of 7 patients received a second course of mesotherapy with the same drug. As a result, the process of repigmentation in the lesions continued and amounted to another 15–20% of the total area of depigmentation. the remaining 5 people refused to continue treatment due to financial difficulties.
Thus, in a total of 2 patients, after two courses of mesotherapy with antioxidants, persistent repigmentation amounted to up to 50% of the total lesion area. This allows us to talk about a persistent effect of repigmentation in vitiligo lesions after an injection course of antioxidants, as well as an increasing effect with repeated course use of the drug.
rice. 5. intradermal injections (patient 7) in lesions on the skin of the face (a) and neck (B)
Classification
Vitiligo, depending on the location of the spots, is divided into three main types:
- localized form: spots are located in certain places;
- generalized form (the most common form): spots are located throughout the body;
- universal form (occurs least often): almost complete loss of pigment (more than 80% of the body area).
In turn, the main types are divided into subgroups. The generalized form includes acrofacial vitiligo (face and limbs only), vitiligo vulgaris (spots scattered symmetrically throughout the body), mixed vitiligo (a combination of different types). The localized form includes focal vitiligo (spots are present in 1–2 areas), segmental vitiligo (spots are located on one side of the body), mucosal vitiligo (spots are present only on the mucous membranes).
There is also a division according to the type of spots:
- blue spot - spots have a bluish tint;
- inflamed spot - the border of the spot is inflamed and raised;
- tricolor spot - between healthy skin and the spot there is a medium pigmented zone;
- four-color spot - in addition to three colors, a zone of strong pigmentation appears around the spot.
The course of the pathological process with vitiligo is divided into types:
- stable appearance: a white spot appears and remains unchanged for a long time;
- progressive type: there is a constant progress of the depigmentation process, sometimes it happens quickly, sometimes slowly;
- unstable appearance: some spots disappear, while other formations increase.
Possible complications
At first glance, the disease does not pose a danger, but if it develops unfavorably, the following complications are possible:
- Ophthalmic disorders. Depigmentation of the iris or inflammation is possible.
- Aseptic meningitis. When the melanocytes of the meninges are damaged, inflammation of the meninges can develop.
- Hearing disorders. Melanocytes are involved in the transmission of auditory stimuli, so hearing impairment is possible.
In clinical practice, these complications are rarely detected.
Psoberan
Psoberan is available in the form of ointment and solution. A drug of combined action, of plant origin, increases the body's sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation.
- Ingredients: bergapten and psoralen of plant origin (from fig leaves).
- Manufacturer: no information.
- Contraindications: do not use for children under 5 years of age, people over 60 years of age, or pregnant women. Exhaustion - cachexia; Acute diseases of the gastrointestinal tract; diseases of the central nervous system; hypertension; tuberculosis; blood diseases; diabetes; nephritis - acute and chronic.
- Price: not specified.
- Course of treatment: treatment is carried out in courses of 2-3 months. Duration of therapy is 10-12 months.
- Side effects: nausea, heaviness in the abdomen, diarrhea, headache, palpitations, insomnia and irritability, allergic rash. Redness, erythema, burns due to excessive exposure to UV rays.
- Doctors' opinions: Doctors use the drug in PUVA therapy.
Reviews from forums
Psoberan is not used as an independent remedy, but only in combination with ultraviolet radiation during PUVA therapy. Therefore, read in detail about this method and its effectiveness.
Review of PUVA therapy by user Katish from the provitiligo.com forum
conclusions
Psoberan belongs to a group of drugs that increase sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation. Self-medication with such means is not effective without special lamps. And without the constant supervision of a doctor it can be dangerous.
Beroxan
Beroxan is a solution for external use. The drug increases sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation due to parsnips in the composition.
- Ingredients: parsnip (active ingredients - xanthoxin and bergapten).
- Manufacturer: no information
- Contraindications: cataracts, gastric and duodenal ulcers, nephritis, liver cirrhosis, gastritis, hepatitis, hypersensitivity, diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis, blood diseases, tumors, diabetes mellitus, cachexia, hypothyroidism, thyrotoxicosis, CHF, arterial hypertension, multiple pigmentary disorders nevi. Do not use for pregnant and lactating women, children under 5 years of age, people over 60 years of age.
- Price: no information.
- Course of treatment: 1-2.5 months. If necessary, repeat the course with a break of 1.5-2 months.
- Side effects: headache and dizziness; heartbeat; dyspepsia, nausea, gastralgia. Acute dermatitis due to an overdose of UV rays.
- Doctors' opinions: the drug is used in clinics as a photosensitizer - a substance that enhances the effect of UV rays.
Reviews from forums
The drug is not used separately; see reviews of PUVA therapy.
Review of PUVA therapy by user Gallina from the provitiligo.com forum
conclusions
Beroxan enhances the effects of ultraviolet radiation during PUVA therapy and is not used separately (not sold in pharmacies). The method gives results in 85% of cases, but has many contraindications and side effects. Consultation with a doctor is required here.
Psoralen
Psoralen is available in the form of an alcohol solution. The drug increases sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation, therefore it is used in PUVA therapy.
Psoralen solution
- Ingredients: psoralen - obtained from the plant Psoralea drupaceae; 70% alcohol.
- Manufacturer: no information.
- Contraindications: cataracts, gastric and duodenal ulcers, nephritis, liver cirrhosis, gastritis, hepatitis, hypersensitivity, diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis, blood diseases, tumors, diabetes mellitus, cachexia, hypothyroidism, thyrotoxicosis, CHF, arterial hypertension, multiple pigmentary disorders nevi.
Do not use for pregnant and lactating women, children under 5 years of age, people over 60 years of age.
- Price: 600 rub.
- Course of treatment: 3-3.5 months. If necessary, a repeat course is prescribed.
- Side effects: headache, dizziness, palpitations, cardialgia, dyspepsia, nausea, gastralgia. In case of an overdose of ultraviolet radiation - acute dermatitis (skin hyperemia, blisters).
- Doctors' opinions: psoralen is used to treat vitiligo as a drug that enhances the effect of ultraviolet radiation. For example, with PUVA therapy. Safety when used in the clinic is guaranteed by constant medical supervision.
Reviews from forums
The drug is useless to use separately from UV therapy. Look at reviews of the use of PUVA therapy.
Review of PUVA therapy by user MaSulKa from the provitiligo.com forum
conclusions
The drug is intended to enhance ultraviolet exposure and there is no point in using it separately. At the clinic, a qualified doctor will select the dose and will constantly monitor you. This is the only way to guarantee the safety of using psoralen.
Vitix gel
Vitix is a non-greasy gel that contains antioxidants, plant extracts and trace elements (potassium, magnesium, sodium).
Vitix gel
- Ingredients: Cucumis Melo melon extract
- Manufacturer: ACM (France).
- Contraindications: hypersensitivity.
- Price: 2300 rub.
- Course of treatment: from 6 to 12 months.
- Side effects: rarely - skin redness (erythema), itching, peeling.
- Doctors' opinions: medical studies on the effectiveness of treatment were conducted in 2001-2002. Of the 49 selected patients, in 30 the pigment began to recover after application, and in 1 the spots disappeared.
Reviews from forums
Mostly negative.
Review of Vitix gel by pearl from the provitiligo.com forum
Review of Vitix gel by KashaK from the provitiligo.com forum
Review of Vitix gel by user raisa from the provitiligo.com forum
Review of Vitix gel by Allo from the provitiligo.com forum
conclusions
The effectiveness of Vitix gel is based on the action of antioxidants. People's reviews say it's a waste of money. The drug generally does not give any results.
Vitiskin gel
Vitiskin is a gel containing antioxidants, copper, zinc, vitamins B5 and B12. Antioxidants prevent oxidative processes in the body and prevent the formation of free radicals.
Gel Vitiskin
- Ingredients: water, alcohol, superoxide dismutase, clacium pantothenate, zinc acetate, copper acetate and other substances.
- Manufacturer: Isis Pharma (Switzerland).
- Contraindications: not recommended for pregnant and nursing mothers.
- Price: 3300 – 3500 rub.
- Course of treatment: six months.
- Side effects: burning, itching, erythema, dryness and flaking of the skin.
- Doctors' opinions: a detailed report from a study of 79 patients is posted on the manufacturer's website. According to the results, the gel eliminates stains on the chest and hips in 90% of cases, and on the feet in 20%.
Reviews from forums
Reviews are contradictory, but there is a positive experience with using the gel.
Review of Vitiskin gel by Sergik from the provitiligo.com forum
Review of Vitiskin gel by Gallina from the provitiligo.com forum
Review of Vitiskin gel by ISB user from the provitiligo.com forum
conclusions
The use of Vitiskin gel together with ultraviolet irradiation of 311 nm evens out the skin color on the chest and hips. However, when comparing effectiveness with other vitiligo treatment methods and medications, Vitiskin loses.
Vitilemna
Vitilemna gel is a preparation that contains duckweed extract and is easily absorbed into the skin.
Gel Vitilemna
- Ingredients: duckweed extract.
- Manufacturer: Medin Terra SRO (Czech Republic).
- Contraindications: none found.
- Price: 3500 rub. for 150 ml. drug.
- Course of treatment: 6-12 months.
- Side effects: none identified.
- Special instructions: for results in treatment, it must be used in combination with Vitilemna tablets and ultraviolet irradiation.
Reviews from forums
There are not enough reviews on the use of the drug on the forums to evaluate the effectiveness.
Review of Vitilemna gel by user natasha19916 from the provitiligo.com forum
Review of Vitilemna gel by Senya from the provitiligo.com forum
conclusions
Vitilemna gel is suitable for supporters of natural treatment methods - due to the extract of duckweed in the composition.
However, no studies have been conducted on the effectiveness of the drug. There are few reviews from the forum, and they are contradictory. Our conclusion is that the drug is ineffective when used separately from other methods of treating vitiligo.
Cream Ideal legs - Coverderm
Ideal Legs Cream is a foundation that smooths out skin imperfections and evens out its color.
Foundation Ideal legs
- Waterproof, UV protection level - SPF 40.
- Dries in a few seconds and stays on the skin all day.
- Can be used on any skin type.
- Can be used every day
Application:
- Vitiligo
- Dark spots
- Acne
- Stretch marks, varicose veins
- Tattoos, bruises, burns
Composition: non-toxic dyes Shades:
Shades of Coverderm cream “Ideal legs”
Directions for use: Apply evenly to skin using fingers or a sponge. In these cases, we recommend using two shades:
- Vitiligo, psoriasis, acne, burns, freckles, rosacea. Before applying the main shade, soften the affected areas with shade No. 8.
- Pimples, bruises, tattoos. Apply shade #0 before your base color.
- Burns, stretch marks, scars. Fill the affected areas with shade No. 0 cream before applying the main shade.
If using two shades, cover the first layer with Kaverderm powder. Then apply the second shade. Contraindications: none identified. Special instructions: use two shades of cream to get an even color.
conclusions
Reviews about Coverderm foundation are generally negative. Those who have tried it note that the texture is too thick and has a mask effect. The choice is yours.