Synonyms: ACTH, Adrenocorticotropic hormone, Corticotropin, ACTH, Adrenocorticotropic hormone, Corticotropin,
Scientific editor: M. Merkusheva, PSPbSMU named after. acad. Pavlova, medical practice.
An analysis for adrenocorticotropic hormone is carried out to identify pathologies in the functioning of the endocrine system and adrenal glands.
The hormone is produced by the gland of the brain - the pituitary gland, namely, its frontal part (anterior lobe). ACTH acts on the adrenal cortex, causing the production of hormones necessary for health: androgens, cortisol, estrogens.
Indications for analysis
A test for hormone levels is prescribed for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases associated with dysfunction of the adrenal cortex. Monitoring indicators is also necessary to assess the effectiveness of therapy for oncological pathologies.
In women, ACTH is performed in case of menstrual irregularities, excessive hair growth, and infertility.
What symptoms and activities may be a reason for getting tested:
- abnormal pigmentation of the epidermis;
- acne in adults;
- early puberty in adolescents;
- Cushing's disease (fat deposition on the face, neck, abdomen, purple stretch marks on the abdomen, thinning limbs, increased blood sugar, high blood pressure);
- diseases of the skeletal system (osteoporosis), as well as muscle weakness and pain;
- causeless weight loss accompanied by high blood pressure;
- regular attacks of hypertension;
- severe fatigue, weakness and lethargy for a long time;
- deviation from the norm of cortisol in the blood;
- monitoring the patient’s rehabilitation after removal of corticotropinoma (tumor in the pituitary gland);
- long-term treatment with medications (for example, glucocorticoids);
- dysfunction of the adrenal cortex;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment for cancer patients.
For a doctor, the reason for referring a patient to ACTH may be:
- test with corticotropin-releasing hormone;
- changes in cortisol levels;
- suspected ACTH-producing tumor.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone in women's health
Corticotropin is released in the body cyclically throughout the day. Its maximum concentration in the blood is detected at 4-6 o'clock in the morning, and the lowest - from 18 to 23 o'clock. Fluctuations in the hormone during the day directly depend on the woman’s waking hours. ACTH also increases significantly during severe stress and slightly during pregnancy and menstruation.
After 45 years, 60% of people experience deviations in the normal amount of ACTH due to hormonal fluctuations, as well as during pregnancy or menopause. To accurately determine the concentration of this hormone, it is necessary to donate venous blood for immunoradiometric analysis.
Content:
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone in women's health
- Indications for hormone testing
- Increased hormone level
- Decrease in ACTH level
- Preparing for the ACTH test
Due to its peptide nature, the ACTH hormone is capable of producing many biological effects. It consists of 39 amino acid residues, which determines the complexity of its structure. Among the main functions of the hormone, experts call stimulation of the formation of proteins and adrenal nucleic acids, an increase in the synthesis of cortisol, an effect on the synthesis of mineralocorticoids, activation of androgen precursors, an increase in cholesterol synthesis, and a melanocyte-stimulating effect.
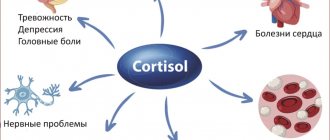
Long-term exposure to corticotropin causes hypertrophy of the adrenal cortex, and, as a result, an increase in the concentration of those hormones that are produced by the adrenal glands (testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, cortisol). When the production of cortisol is mobilized in the human body, processes such as increased blood flow into muscle organs and tissues, an increase in blood glucose levels, which contributes to an increase in muscle energy, and activation of anti-allergenic, anti-inflammatory and anti-stress effects are triggered.
In addition to the above positive qualities, cortisol can also have a negative effect:
- suppressing immunity by reducing antibodies and lymphocytes in the blood;
- reducing muscle mass by increasing protein breakdown processes;
- slowing down digestive processes and inhibiting cognitive thinking.
In medicine, mineralocorticoids are commonly referred to as hormones that can regulate mineral metabolic processes. One of these hormones, aldosterone, promotes the development of inflammation in the body, disrupts the excretion of potassium and sodium salts in the urine, which often leads to hypertension. The second mineralocorticoid, deoxycorticosterone, has a similar effect.
When androstenedinone and dihydroepiandrostenedione (androgen precursors) are activated in the body, the level of male hormones in the female body increases, which often manifests itself in disruptions of the menstrual cycle, increased oily skin, hair growth in atypical places, and impaired ovarian function.
With increased synthesis of cholesterol in the body, the walls of cells and nerve fibers are strengthened, and the level of vitamin D increases. The melanocyte-stimulating effect promotes the production of melanin, which leads to saturation of the color of the skin, hair and iris of the eyes.
In addition to all of the above, the ACTH hormone affects brain cells, improving memory and the ability to perceive information.
It should also interact productively with other hormones:
- prolactin, responsible for the productivity and growth of the mammary gland, menstruation;
- somatotropin, which is responsible for activating growth processes in children;
- vasopressin, which increases the circulating vascular volume of blood and affects pressure and vascular tone.
Female reproductive cells do not show sensitivity to ACTH, but it enhances the action of other hormones of the anterior pituitary gland, which affects the functioning of the ovaries, ovulation processes and the regularity of menstruation.
It is especially important to monitor the level of ACTH in adolescents, since hormonal fluctuations during this period of time lead to the formation of infantilism, or an advance in the physical development of girls, a late onset of menstruation and other pathologies. An increased level of adrenocorticotropic hormone in adulthood provokes a decrease in the level of female and an increase in male sex hormones in the body, which leads to ovarian dysfunction and infertility.
Corticotropin releasing hormone test
In rare cases, ACTH can be produced not only by the pituitary gland, but also by a malignant tumor in any organ. Tests show high levels of ACTH and cortisol. To diagnose the pathology, a test with corticotropin-releasing hormone is prescribed. After it, the ACTH level either increases (indicating Itsenko-Cushing's disease) or remains at the same level (ectopic production syndrome).
To carry out the test, venous blood is taken in the morning on an empty stomach and ACTH is measured. Then 100 mcg of corticotropin-releasing hormone is injected into a vein and blood is drawn after 30, 45 minutes and 1 hour, determining the ACTH level for each time.
general information
Adrenocorticotropic hormone is involved in many processes that occur in the body unnoticed by humans. From what we can feel is a deterioration or improvement in memory, learning ability, motivation (good mood, inspiration - loss of strength, depression). The hormone activates adenylate cyclase, which in turn catalyzes the conversion of adenosine triphosphate, which is of great importance for metabolism in the body. As a result of the chain of reactions, ACTH is involved:
- in protein kinase stimulation;
- transfer of free cholesterol;
- accelerating the formation of steroids;
- cholesterol decomposition;
- formation of pregnenol and corticosteroids.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone is important for the normal functioning of the entire body. It does not play a leading role, but still takes part in the synthesis of adrenal catecholamines, which are designed to respond to factors such as ischemia (decreased blood supply) and hypoglycemia (decreased glucose concentration).
However, at elevated concentrations that persist for a long period of time, it can cause harm to the body. Cause an increase in the mass of the adrenal glands, leading to the creation of reserves of cholesterol, pantothenic and ascorbic acids. At the same time, increased concentrations of the hormone can slow down inflammatory reactions.
ACTH norms
Standard reference values
The norm for the ACTH test is an absolute value of 9-52 pg/ml.
Reference values of the Invitro laboratory Invitro values are somewhat different from the standard ones, since the more modern equipment of this laboratory allows measurements to be taken with greater accuracy.
- <46pg/ml
Factors influencing the result
- failure by the patient or medical staff to comply with the rules of preparation for the procedure;
- taking medications;
- recent injury or surgery;
- inappropriate phase of the menstrual cycle;
- the patient has a high temperature;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- unstable mental state;
- time zone change;
- sleep disorder;
- hemolysis (destruction) of red blood cells.
Important! The interpretation of the results is always carried out comprehensively. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on only one analysis.
ACTH is elevated
Pathology is indicated by a 1.5-fold increase in hormone levels:
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease. It occurs against the background of various pathologies (the most common is pituitary adenoma). Increased iron volume produces more hormone, which means it stimulates excess cortisol production - ACTH increases up to 2 times;
- Addison's disease (cortisol deficiency), as well as congenital adrenal hyperplasia. In these pathologies, the adrenal cortex does not produce cortisol, shifting the function to the pituitary gland. In this regard, the level of ACTH rises sharply; — 2-2.5 times (> 1000 pg/ml);
- paraneoplastic syndrome. It is a consequence of the reaction of the pituitary gland to an oncological formation in any organ;
- Nelson's syndrome. Develops in patients with Cushing's disease, in the presence of a pituitary tumor, after amputation of the adrenal glands. The patient experiences secondary adrenal insufficiency and ACTH levels increase;
- syndrome of ectopic production of adrenocorticotropic hormone - 1.5 times the norm. In rare cases, ACTH can be produced not only by the pituitary gland, but also by a malignant tumor in any organ. Tests show high levels of ACTH and cortisol. To diagnose the pathology, a test with corticotropin-releasing hormone is prescribed. After it, the ACTH level either increases (indicates Itsenko-Cushing's disease) or remains at the level (ectopic production syndrome);
- taking medications. Lithium-based drugs, insulin, ethanol, calcium gluconate, amphetamines, aminoglutethimide, levodopa, metoclopramide, metyrapone, pyrogens, vasopressin can artificially increase ACTH levels.
Artificial ACTH
Artificial ACTH, consisting of the first 24 amino acids of the natural hormone, was first prepared by Klaus Hoffmann at the University of Pittsburgh. In synthetic forms, ACTH is known as Synacthen or Cortrozine. These two substances are used in Australia and the UK to perform ACTH tests, which show the effectiveness of the adrenal glands in stressful situations.
At first, artificial ACTH was used as a replacement for the so-called Actar gel for the treatment of epileptic spasms. But due to sharply increased prices, the medicine lost popularity. It was soon also proposed for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and nephrotic syndromes.
ACTH is low
Insufficient production of the hormone is associated with the following processes:
- secondary hypocortisolism. If the functioning of the pituitary gland is disrupted (insufficient production of ACTH), atrophy of the adrenal cortex occurs (lack of cortisol synthesis). Functional failure of other glands of the endocrine system may also occur;
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome. The level of adrenocorticotropic hormone falls in the presence of a malignant tumor in the adrenal glands. It differs from Cushing's disease in that there is excessive production of cortisol and, as a result, a reduction in the production of ACTH by the pituitary gland;
- benign formations in the adrenal glands. The tumors in this case perform the function of the organ and produce additional cortisol, which reduces ACTH levels;
- taking medications from the glucocorticoid group, cryptoheptadine.
1.What is ACTH?
ACTH is a hormone that can be tested to test the condition of the pituitary and adrenal glands.
ACTH is produced by the pituitary gland.
The adrenal glands respond to ACTH levels in the blood and produce cortisol, which helps your body cope with stress. Cortisol is a vital hormone,
so its level in the blood should be monitored. When cortisol levels are elevated, ACTH levels fall and vice versa.
Cortisol and ACTH levels change throughout the day.
As a rule, the ACTH hormone is elevated in the morning (from 6 to 8 am) and decreases by 6 pm. If the doctor wants to check the ACTH level, then it is measured in the morning and evening. Cortisol levels are usually checked along with ACTH.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!