The approaching birth can not only be a source of joyful anticipation of meeting your baby soon, but also cause a certain amount of anxiety. This is especially true for the first pregnancy. While waiting for the baby to appear, the expectant mother increasingly wonders how to understand that contractions have begun. It also happens that at the first urge, a woman rushes to pack her things for the maternity hospital, but then the discomfort disappears and causes bewilderment.
Let's talk about how to distinguish real contractions, whether you should be afraid of them, and when you really need to rush to the hospital.
Contractions: how to understand that they have begun
When contractions begin, a woman may feel them in different ways.
Sensations can be of three main types, which are often described by women in labor:
- Pain in the lumbar region.
- Pain as during menstruation.
- Cramping pain that spreads throughout the abdomen.
It is impossible to predict how much a woman will be bothered by contractions.
Much depends on the physiology and position of the child in the womb. But, despite the different nature of the sensations, every woman goes through three natural phases of the process: 1. Initial. The pain is mild. The contractions are short, and there are quite long breaks between them. This condition can last up to 8 hours. At this time, the expectant mother can take a warm shower or begin to gradually get ready for the maternity hospital. It is advisable to start marking the time intervals of contractions so as not to miss their transition to the next phase.
2. Active. The duration of contractions increases, the breaks become shorter. A woman may feel discomfort for up to 1 minute, after which a new contraction begins after a short period. The condition lasts from 3 hours. By the time only 5 minutes pass between contractions, it is highly advisable for a woman to already be under the supervision of a doctor.
3. Transitional. This phase is easy to skip on your own - it takes from half an hour to 2 hours and helps the cervix open to a state of full readiness (7-19 cm). At the same time, the woman notices the release of the mucus plug, which at other times “closes” the cervix. The time for the baby's birth is approaching2.
Specialists
Egorova Elena Borisovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest qualification category.
Specializes in peritoneal factor of infertility in women and management of problematic pregnancies.
It will provide effective help if, before conception, you were diagnosed with adhesions, endometriosis, erosion or other pathologies of the cervix.
Akinshina Svetlana Vladimirovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, hemostasiologist with an academic degree.
Pregnancy management S.V. Akinshina will help avoid severe complications: gestosis, placental insufficiency, fetal loss syndrome.
The doctor's expertise includes hemostasis disorders and immunological infertility.
Margiani Fatima Abdurashidovna
Doctor of Medical Sciences, qualified diagnostician of female infertility factors.
Provides competent support for late, multiple or problematic pregnancies. A consultation and examination with Fatima Abdurashidovna will help determine the cause of failure to conceive a child or recurrent miscarriage.
Petreykov Evgeniy Rafailovich
If you are planning a pregnancy, IVF, or have a history of fetal failure in the first trimester, contact Dr. Petreikov.
A gynecologist of the highest category, Candidate of Sciences, will help determine the risk and cause of obstetric complications, and also prescribe supportive treatment for a genetic predisposition to thrombosis.
False contractions
Above we gave an example of how prenatal contractions begin. However, in obstetrics there is also the concept of false contractions.
False contractions are exactly the same process of contraction of the uterus. However, they do not lead to dilatation of the cervix, therefore they are considered “training”. False contractions can cause the expectant mother to rush to the maternity hospital, although in fact it is not difficult to bring them to light. Firstly, a woman, as a rule, does not experience pain. Secondly, the intervals between “training” contractions are not shortened, and they do not intensify.
Usually, starting from the end of the second trimester, a woman begins to feel uterine contractions, which become stronger and longer as the baby grows. If such contractions do not cause pain or increased discomfort, then this is the absolute norm. Shortly before childbirth, such uterine contractions intensify, gradually developing into real contractions.
When to go to the maternity hospital
When visiting your doctor in the third trimester, find out his recommendations for when you need to go to the hospital and stick to them. At the same time, ask what number to call if you go into labor while your doctor is not open. In many cases, the recommendation is to call your doctor when you notice signs of labor, such as your water breaking, mucus plug, or contractions starting. Be prepared to tell your doctor how often contractions occur and how long each contraction lasts, as well as other signs, if any. If you notice bleeding, call your doctor immediately. Based on the information you tell him, the doctor will tell you whether you should go to the maternity hospital or whether it’s better to stay at home for now, in a calmer and more comfortable environment for you, suitable for the first stage of labor.
What to do when contractions start
When the interval between contractions becomes less than 5 minutes, the woman needs to be under the supervision of a doctor as soon as possible. Until this time, if the mother is not bothered by severe pain, it is enough to simply relax and calm down, count down the time intervals and get ready for the hospital. Calmness and proper breathing play a big role in how easily discomfort will be tolerated. Fear of pain can only intensify spasms - this has long been a known fact.
But you don’t need to take painkillers yourself. The very first advice to a woman giving birth is to “breathe deeply.” Proper breathing and focusing on exhalation not only prevents stress, but also relaxes the pelvic floor muscles. A light massage of the lower back also helps. And most importantly, don’t overexert yourself. It is important to use the time between contractions to rest before the most important thing - childbirth3.
What to do at home during the first stage of labor
From the time you start having contractions until the time you need to go to the hospital, your doctor may recommend that you stay home for now. Here's what you can do during this time:
- do breathing and relaxation exercises;
- go for a walk;
- take a nap;
- take a shower or bath;
- listen to relaxing music or watch a movie;
- finish packing for the maternity hospital
How to Reduce Pain When Contractions Start
Today, there are relatively safe ways to relieve a woman in labor from severe pain during childbirth. However, many doctors are wary of these activities. The point is not only in the risk of side effects (which, although not great, still exists), but also in the fact that the drugs can lead to a weakening of labor functions.
If the doctor nevertheless decides on the need for pain relief, the choice is given to one of the groups of drugs:
1. Drug pain relief. This includes various analgesics, taken mainly orally (with water).
2. Epidural anesthesia. An anesthetic substance (lidocaine, ropelocaine, etc.) is delivered under the membrane of the spinal cord using a thin needle, which the doctor inserts between the vertebrae. The method is effective (after administration, sensitivity below the back disappears completely), but due to a number of nuances it is used only in exceptional cases. For example, as a result of such anesthesia, a woman can no longer push effectively, so instrumental intervention may be required.
It is preferable when childbirth occurs naturally, without drug intervention3.
The birth of a child: a happy ending
If the birth proceeded normally and the baby cried immediately after birth, he is placed on the mother's stomach. The joy of this moment completely overshadows and erases from memory the pain and fear just suffered. After the birth of the baby, there is a short break in pushing (up to 15 minutes), and then, when the separated placenta enters the vagina, the woman again feels the desire to push. But these attempts are much weaker and do not require much physical effort. The woman strains slightly and the placenta (placenta and membranes) is born. The birth is over. Now you are a mother and the owner of the most expensive treasure in the world. Congratulations!
1 The most favorable presentation (i.e., position in the uterus) of the fetus is considered to be cephalic presentation (position with the head down). If the baby's buttocks or legs are felt in the lower segment of the uterus, they speak of a breech presentation. You can read more about this in the articles by E. Chernukha “Belvic presentation of the fetus” (No. 11/2001) and “Childbirth with breech presentation” (No. 12/2001).
2 See V. Zaborsky, N. Kuznetsova, “Vertical childbirth”, No. 2, 2002.
What to do if contractions have not started?
It also happens that the due date has approached, but contractions have not started. This phenomenon is not necessarily a cause for concern, but requires medical supervision. The causes of decreased labor function may be previous inflammatory diseases, menstrual irregularities or hormonal disorders.
Typically, birth occurs at 37-40 weeks. If this does not happen, but the doctor does not detect pathologies of the placenta, the baby has enough oxygen and nutrients, and the amniotic fluid is clean, then natural induction of labor will do. Women are advised to take easy walks and stay in an upright position. Sex can also have a positive effect on stimulating labor: substances contained in semen have a softening effect on the cervix, and sexual arousal and orgasm are natural muscle stimuli. The main thing is to take precautions.
What you definitely shouldn’t do is dabble in traditional methods of stimulation. Especially when it comes to herbs. They have a strong and not always controllable effect, so it is generally better for pregnant women to protect themselves from using any infusions and decoctions.
If a decision has been made to medically induce labor, one of the following methods is selected:
1. Taking prostaglandins (if the cervix is not ready to dilate).
2. Amniotomy (opening of the amniotic sac) - used to reduce the contractile functions of the uterus.
3. Administration of oxytocin (intravenously or in tablets) - to stimulate the process of contractions4.
Childbirth is an exciting and responsible event. And the best thing an expectant mother can do in this situation is not to be afraid of the accompanying manifestations. You need to try to perceive contractions not as a source of pain, but as a natural process that contributes to the birth of a tiny beloved baby.
Womenfirst
- PROBLEMS OF FALSE CONTRACTIONS IN MODERN OBSTETRICS - Buzumova Zh.O., Bazarbaeva Zh.U., Nurmanalieva E.B., Kanigaeva A.M., Seksenova A.B. – 2021 – Bulletin of the Kazakh National Medical University / No. 3 2018
- QUICK BIRTH IN MODERN OBSTETRICS - Zhelezova M.E. – 2021 — Practical medicine / '1 (93) 2016
- RATIONALE FOR THE APPROPRIATENESS OF PARAVERTEBRAL BLOCK FOR ANALGESIA OF SPONTANEOUS LABOR - Neimark M.I., Ivanova O.S. – 2018 — Bulletin of anesthesiology and resuscitation / Volume 15 / No. 3/2018
- Obstetrics: national guide / ed. E. K. Ailamazyan, V. I. Kulakov, V. E. Radzinsky, G. M. Savelyeva. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2014. - 1200 p.
RUS2124800-2 from 03/20/2020
TIME OF LABOR
During pregnancy, a woman is concerned about many issues, but most of all she is interested in the time of birth. This is usually associated with the fear of pain, any complications and the most important question - how will childbirth end for mother and child? All these fears are in vain. Modern obstetrics has extensive experience in preparing pregnant women for childbirth and special monitoring of the progress of labor, allowing timely diagnosis of complications from the mother or fetus and providing both with adequate care. Finally, methods have been developed by which a woman herself can contribute to the successful course of labor and reduce pain.
Pregnancy lasts on average 280 days (40 weeks), counting from the first day of the last menstrual period. If you count back 3 months from this date and then add 7 days, this will be the approximate due date. For example: the last menstruation was on December 10, therefore, birth can be expected on September 17.
It is advisable to remember the day of the first fetal movement. Primiparous women feel it in the middle of pregnancy (20 weeks), and multiparous women feel it a little earlier (18 weeks).
It will be possible to speak most accurately about the date of birth if the gestational age is established. It can be determined by a doctor based on the size of the uterus, which corresponds to certain stages of pregnancy.
With sufficient reliability, it is possible to determine the duration of pregnancy and, therefore, delivery based on ultrasound examination of the fetus.
Childbirth occurring before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature, and after 42 weeks - late.
Term birth, that is, occurring on time, is considered to be a birth that began during a full-term pregnancy. It is known that the duration of full-term pregnancy varies from 37 completed weeks (259 days) to 42 weeks (294 days). Starting at 38 weeks of pregnancy, you can expect to give birth every day.
Precursors and onset of labor.
It is impossible to determine the day of birth in advance, but there are a number of signs by which one can judge its approach.
Harbingers of childbirth:
1. The pregnant woman feels that it has become easier for her to breathe; this is due to the fact that the fetal head has dropped lower and pressed tightly against the entrance to the bony pelvis. ;
2. The amount of vaginal discharge increases, it may become brown or pink;
3. Individual contractions of the uterus appear - “training” contractions - irregular, short and quickly passing when stroking the abdomen;
4. Weak, dull, quickly passing pain often occurs in the lumbar region;
5. As a rule, a pregnant woman experiences weight loss.
When these warning signs appear, you should prepare for a trip to the maternity hospital. You cannot travel outside the city or leave the house for a long time, as contractions may suddenly begin or amniotic fluid may leak. But it is quite possible that you will have to be patient and wait. The interval between the appearance of precursors and childbirth can be several days or 2-3 weeks.
Start of labor
The onset of labor is indicated by the appearance of bloody, spotting discharge from the vagina. This is the release of the “birth plug”, that is, the contents of the cervix, which begins to open; the appearance of a “birth plug” means that labor will begin in the next 24-48 hours.
Rush of amniotic fluid
It is important to pay attention to the amount of water that can “gush out” unexpectedly or pour out in a thin stream. Normally, the waters are light or slightly pinkish, without any admixture of bright blood; in them you can see white lumps of vernix lubrication of the fetus. However, the waters may have a greenish or brown color, which is due to the ingress of original feces - meconium. You should definitely inform your doctor about this, since meconium in the water may indicate fetal discomfort.
After the discharge of water, you must immediately go to the maternity hospital, since a long period without water is fraught with the danger of infection of the fetus and the mother’s birth canal. To avoid infection, you do not need to tightly close the vagina with a pad or insert a tampon; you cannot take a bath, only a shower.
Regular labor pains
The main thing that is characteristic of labor contractions is their regularity, repetition at first every 15-20 minutes, then more and more often, longer and stronger. These are true labor contractions that open the cervix. In contrast, false contractions usually have an irregular rhythm, do not intensify, and can stop if you change your body position. However, false contractions also perform an important function - they prepare the cervix for childbirth, which becomes soft, short, its canal opens, that is, it matures for childbirth.
Normal labor for primiparous women lasts on average 12-14 hours, and for multiparous women 6-8 hours.
Periods of labor
The onset of labor is considered to be the appearance of uterine contractions, rhythmically repeating every 10-15 minutes. Contractions gradually intensify, and the interval between them decreases. With the onset of labor, a pregnant woman is already called a woman in labor.
If labor is delayed too much, the woman is given help. Doctors of Ancient Greece said that the sun should not rise twice over the head of a woman in labor.
There are three stages of labor: cervical dilatation, expulsion of the fetus and the postpartum period.
The first stage of labor - gradual dilatation of the cervix
It occurs under the influence of regular contractions. Contractions over and over again stretch the circular muscles of the cervix, making it thin and pliable. Wedging of the amniotic sac into it and pressure from the fetal head are also aimed at this. Slow, gradual dilation of the cervix begins 2-3 weeks before birth. In most women, the cervix “ripens” before childbirth, that is, it becomes short, soft, with the canal dilated to the 2nd.
The period of dilation is the longest during childbirth. It lasts about 9-10 hours in primiparous women and 6-7 hours in multiparous women. The duration of contractions during this period increases to 1.5 minutes, and the interval between them decreases from 10-15 minutes to 1 minute.
In the first stage of labor, the woman in labor must follow the recommendations of the doctor and midwife and actively help herself: breathe calmly and evenly through her nose, relax outside of contractions. When the cervix opens completely, the fetal head can descend into the pelvic cavity.
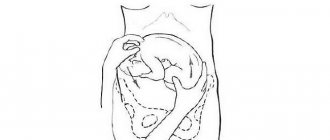
Second stage of labor - expulsion of the fetus
When the fetal head reaches the outlet of the pelvis, that is, sinks to its bottom, contractions are joined by pushing - contractions of the abdominal muscles. Due to this, intra-abdominal pressure increases, which helps expel the fetus from the uterus.
The duration of the expulsion period is on average 1-2 hours in primiparous women and less than an hour in multiparous women.
During the period of exile, it is especially important to follow the instructions of the doctor and midwife, helping yourself and the child to safely pass this very important stage. An experienced doctor and midwife will receive the baby after birth, lightly pat his buttocks, the baby will cry, his lungs will expand, and he will begin to live extrauterine life.
The birth is not yet over - the baby is still connected to the mother by the umbilical cord, and the placenta is in the uterine cavity. The placenta (baby place) is the placenta, umbilical cord and membranes of the fetus.
In the third, successive period, the umbilical cord is crossed
However, neither the mother nor the child will feel pain - there are no pain nerve fibers in the umbilical cord. A baby's cry immediately after birth is a good reaction to a new external environment. A sign is placed on the child’s arm indicating the mother’s last name, first name and patronymic, the year, day and hour of the child’s birth, as well as his gender.
The third stage of labor lasts on average 5-10 minutes, but can last up to 1 hour. The woman in labor feels weak contractions that separate the placenta from the walls of the uterus, and then with one or two light attempts the baby’s place comes out. Now the birth is over.
After giving birth, a woman (she is now called not a woman in labor, but a postpartum woman) remains in the maternity ward for two hours under the careful supervision of medical personnel, who monitor the woman’s condition and the amount of bloody discharge from the genital tract. At this time, the soft birth canal is examined and, if there are ruptures, sutures are placed with preliminary anesthesia. After the examination, the postpartum woman is transferred to the postpartum ward.
How can you make childbirth easier?
Childbirth is a severe physical strain. A pregnant woman needs to learn how to use her energy sparingly. Fear of labor pain interferes with the proper course of labor. To learn how to manage labor pain, a pregnant woman must master some techniques.
First of all, this concerns posture during childbirth. At the beginning of labor, when contractions are still irregular and short, you can choose the body position that will be most comfortable. However, lying on your back is not recommended because in this position the fetal head puts pressure on the mother's large blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the placenta.
A simple and important rule is to urinate frequently. It is necessary to urinate every two hours, since a full bladder prevents the fetal head from descending into the pelvic cavity.
In the active stage of labor, when contractions are repeated frequently, you also need to regularly change your body position, trying not to lie on your back. If doctors allow you to walk around, you should take advantage of it. You can kneel in bed, leaning on a chair, that is, you tend to change your body position more often.
Recently, some maternity hospitals have recommended spending the first stage of labor in a bath with warm water. Immersion in warm water eases painful contractions and has a calming effect on the woman in labor. However, the second stage of labor must be carried out traditionally. When the expulsion of the fetus begins, pushing is delayed; if the doctor allows, you can squat during contractions, since in this position the size of the pelvis increases and the fetal head descends more easily. Between contractions, it is better to lie on your side or take a knee-elbow position. When attempts appear and the birth of the fetus begins, the woman in labor is transferred to another ward, to a special bed designed for childbirth. Here, usually the medical staff themselves manage the mother’s position, facilitating childbirth.
It is very important for a woman to learn to breathe correctly during contractions and completely relax between them. During contractions, due to muscle contraction, the fetus receives less oxygen. Therefore, the lack of it at these moments must be compensated by proper breathing.
In the first stage of labor, when contractions repeat after 8-10 minutes and last for 40-50 seconds, you must use the first type of breathing - slow and deep.
Childbirth is less painful and more gentle for the fetus when the woman in labor alternates walking and lying on her side, that is, an active position alternates with a resting position.
When contractions become more intense, repeat after 5-6 minutes and last about one minute, it is recommended to use shallow breathing (type two). At the beginning of the contraction, it is better to take several deep, slow breaths of the first type, and as the contraction intensifies, you need to switch to shallow breathing, but then, at the end of it, switch to slow and deep breathing again.
At the end of the first stage of labor, when contractions are stronger, repeat after 2-3 minutes and last 60-90 seconds, shallow and rapid breathing should be used. It's reminiscent of a dog breathing with its mouth open on a hot day. So you only need to breathe at the height of the fight. With the onset of a contraction, you can use the first, and then switch to the second and third types of breathing.
During pushing, it is also useful to use the third type of breathing, taking small intervals to inhale air. At this time, there is no need to strain your abdominal muscles. In this case, the fetal head is not squeezed out by pushing, but is pushed, as it were, by exhalations, and the baby is born easier.
During a contraction, it is better to remain in a relaxed state. But this relaxation is not passive, but active - a conscious process that requires concentrated attention. Here the woman in labor should use the relaxation techniques that she learned during pregnancy. During this period, the self-hypnosis formula is used: “I am calm. Contraction is an indicator of labor activity. Gradually the contractions will intensify. My breathing is even and deep. The muscles are relaxed. The fight ends, after which there will be a period of rest.”
There is an idea that childbirth is necessarily accompanied by pain. It is the ingrained fear and expectation of pain that become, especially in impressionable, nervous women, factors that intensify unpleasant sensations and elevate them to the level of pain.
Obstetricians are well aware that the normal course of labor is not necessarily accompanied by pain. Approximately 20% of women experience labor with only minor pain. Moreover, women of some nationalities do not even know what pain during childbirth is.
There is no need to be afraid of pain! Even if it occurs, the doctor will be able to alleviate it; modern obstetrics has great opportunities for this.
Various medicinal painkillers, used in dosages that are absolutely harmless to the mother and fetus, have found widespread use in clinical practice.
The effect of painkillers is short-term; they are used in acute moments. But there are also pain relief techniques that a woman in labor can use herself.
During the period of dilatation of the cervix, the woman in labor takes a deep breath, holding her breath, and then exhales deeply. At the same time, she strokes the lateral surface of the abdomen with her palms and, lying on her side, the lumbosacral region. At the end of the opening period, with more painful sensations, a good effect is obtained by pressing the thumbs on the points on the inner surface of the scallop bones of the pelvis, as well as pressing the “pain points” in the lumbosacral region with hands clenched into fists. Women are usually introduced to this pain relief system at the antenatal clinic.
The use of breathing and relaxation techniques allows you to spend less physical energy, improves the condition of the fetus and contributes to a favorable course of labor.
Conclusion
Childbirth is an individual process. They start and progress differently for everyone. We told you about the symptoms of labor beginning. You can navigate them by comparing them with your feelings. But you won’t necessarily find all of the listed signs. And the order of their occurrence may also differ. And that's okay.
The main thing is to listen carefully to your condition and trust your intuition. If you have even the slightest concern, consult a gynecologist or seek help from a medical facility.
In the end, the most important thing is the health of the baby, as well as the calm emotional state of the expectant mother. And we wish this for you!
Emergency situations in the third trimester
In most cases, pregnancy and childbirth proceed as nature intended. But sometimes emergency situations arise when you immediately need to call an ambulance and rush to the maternity hospital. Below we will talk about such situations.
- If you have a headache, nausea, or painful sensations, urgent medical intervention is necessary;
- Blood on your underwear is a possible sign of placental abruption. This is extremely dangerous for mother and baby;
- An excessive increase in the amount of discharge is a possible sign of water leakage. In this case, the discharge is too liquid. This happens when the integrity of the fetal membrane is violated. This threatens lack of water, and this is very harmful and dangerous for the child;
- If your blood pressure has risen sharply, “spots” flash before your eyes and there is pain in the epigastric region, this is a sign of preeclampsia;
- The uterus has contracted and remains in good shape for half a minute, and at the same time you experience severe pain;
- The baby moves very much - this may indicate hypoxia and other conditions dangerous to the fetus.
All of the listed conditions are assessed as acute and require immediate assistance for mother and child.