How does a woman feel during each stage of labor?
Thoughts about how childbirth will go and how painful it will be worry, perhaps, every woman throughout her pregnancy. At the same time, the impressions of childbirth and in many ways even the peculiarities of its course depend on the behavior of the expectant mother, her ability not to lose control over herself and listen to the recommendations of doctors. In order to calmly endure the process of bringing a baby into the world, treating all unpleasant sensations as a necessary and natural state, you need to have the most complete information about what happens during each stage of labor and what causes the pain.
Labor begins with the onset of contractions. This process is characterized by tension and compression of the uterus, occurring at regular intervals. At the peak moment of contraction, pain appears in the lower abdomen, sacrum and lower back. These symptoms indicate that under the pressure of the baby's head moving forward along the birth canal, the cervix begins to open. Anesthesia is often used to alleviate the condition of a woman in labor.
At first, contractions last about ten seconds and repeat every 15-20 minutes, so most women tolerate them well and may not even immediately understand what is happening. Sometimes, even before the onset of contractions or in the first hours, the amniotic sac ruptures and water is released. This moment becomes a signal for the expectant mother that she should go to the maternity hospital.
As labor progresses and the pressure of the head on the cervix increases, contractions occur more frequently and more intensely. They may be accompanied by the urge to urinate, as well as spotting. To reduce discomfort, during this period you can walk and even jump on a special ball. It is necessary to ensure that there is no heavy bleeding, which may indicate placental abruption or other serious problems requiring urgent medical attention. The pain reaches its peak at the moment of maximum dilatation of the cervix.
The completion of the first stage of labor is marked by the beginning of pushing: this means that during very long and strong contractions, the expectant mother begins to feel strong pressure in the perineum. After examining her, the doctors will either allow her to push or ask her to wait a little to avoid ruptures. This may be the most unpleasant moment, but remember that there is very little time left until the end of labor. It is very important to breathe correctly: this will relieve pain and relieve you from dizziness and nausea, which often occur during strong contractions.
During the second stage of labor, the baby's head is already in the vagina. The actual process of the birth of a baby begins. The woman goes to the delivery room, where a neonatologist is already waiting to meet with the baby. The doctor and midwife will tell the woman in labor how to push during contractions in order to speed up the birth of the baby and eliminate oxygen starvation, as well as avoid perineal ruptures. If the risk of rupture is still very high, and also in cases where the birth of the baby’s head is difficult, the gynecologist resorts to episiotomy (dissection of the perineum).
At this moment, the woman feels almost no pain, even contractions no longer seem painful, since the woman in labor concentrates on pushing the baby out. First, his head comes out, then his shoulders - and the baby is born, and his mother goes into the postpartum period.
This period is characterized by the cessation of pushing and contractions, a feeling of lightness and relaxation. Almost imperceptibly for the woman, her body gets rid of the membranes and placenta (if this does not happen, the doctor himself will separate them). If the child’s condition does not require urgent medical intervention, at this time he is on his mother’s stomach, adapting to environmental conditions and receiving the first drops of colostrum, which has invaluable properties for him.
If ruptures occur during childbirth or an episiotomy is performed, the woman will need stitches. When the father is present at the birth of the baby, the doctor may suggest that he cut the umbilical cord himself and take the baby in his arms. The woman and her baby remain in the delivery room for two hours. If during this time the condition of the mother and baby does not cause concern, they are transferred to the postpartum ward, where they will remain for several days before discharge. As a rule, all unpleasant sensations are quickly forgotten, giving way to happiness.
Contractions: how to understand that they have begun
When contractions begin, a woman may feel them in different ways.
Sensations can be of three main types, which are often described by women in labor:
- Pain in the lumbar region.
- Pain as during menstruation.
- Cramping pain that spreads throughout the abdomen.
It is impossible to predict how much a woman will be bothered by contractions.
Much depends on the physiology and position of the child in the womb. But, despite the different nature of the sensations, every woman goes through three natural phases of the process: 1. Initial. The pain is mild. The contractions are short, and there are quite long breaks between them. This condition can last up to 8 hours. At this time, the expectant mother can take a warm shower or begin to gradually get ready for the maternity hospital. It is advisable to start marking the time intervals of contractions so as not to miss their transition to the next phase.
2. Active. The duration of contractions increases, the breaks become shorter. A woman may feel discomfort for up to 1 minute, after which a new contraction begins after a short period. The condition lasts from 3 hours. By the time only 5 minutes pass between contractions, it is highly advisable for a woman to already be under the supervision of a doctor.
3. Transitional. This phase is easy to skip on your own - it takes from half an hour to 2 hours and helps the cervix open to a state of full readiness (7-19 cm). At the same time, the woman notices the release of the mucus plug, which at other times “closes” the cervix. The time for the baby's birth is approaching2.
After childbirth
Postpartum department
After childbirth, our patients are placed in the postpartum obstetric physiology department.
The newborn in our maternity hospital is together with the mother in the postpartum department. Pediatric neonatologists and nurses explain and help young mothers learn the rules of caring for a newborn.
The department has single wards with improved living conditions, as well as “Lux” wards, consisting of two rooms, one of which contains a mother and child, the other is intended for guests.
Every day, postpartum women receive training on caring for a newborn, hygiene of the postpartum period, and, if necessary, qualified psychological and legal assistance can be provided.
Vaccination is carried out only with written consent and in the presence of the mother. Children are vaccinated against hepatitis B (in the first 24 hours of a child’s life) and tuberculosis (weakened by the BCG-M vaccine on the 3rd day of life).
Before discharge, all women undergo an ultrasound of the uterus and a clinical blood test. Upon discharge from the maternity hospital, recommendations are given on possible methods of contraception, taking into account the nature of concomitant extragenital diseases and the method of delivery.
With a favorable course of the postpartum period in the mother and the period of early adaptation in the newborn, discharge home occurs on the 3rd day after birth, on the 5th day after cesarean section.
All children are examined according to the program during the 1st month in the pediatric center. In the maternity hospital, it is possible to observe the child under various programs in the pediatric center.
The department has experienced, caring staff who help women easily adapt to their new condition and make caring for their newborn easier.
The team of the postpartum department is a team of like-minded people, in which the exceptional friendliness and respectful attitude of the employees create a particularly warm atmosphere.
Breast-feeding
Our maternity hospital implements a program to “support and encourage breastfeeding”, “technologies” for proper feeding, and provides information about the benefits of natural breastfeeding. The baby is placed on the mother's breast immediately after birth, directly in the delivery room.
A mother's milk is ideal for her baby. It contains a large number of immunoglobulins that protect the child from infections and allergies until his own immune system begins to work at full strength.
Our maternity hospital does not provide supplemental feeding to the baby. It is prescribed only by a neonatologist if the child’s weight loss is greater than is physiologically acceptable, i.e. more than 10% per day.
Milk usually comes in 2-4 days after birth. In the first days after birth, to establish and maintain lactation, you need to drink plenty of fluids (up to 2 liters of fluid per day).
Technology of proper feeding
- The mouth is wide open and the lips are pulled back.
- The nipple is located deep in the newborn's mouth, with its tip in the very back of the mouth.
- The baby's lips and gums are pressed against the areola.
- The lower lip should be turned out. The child should take not only the nipple, but also the isola, more from below than from above.
This technique promotes better emptying of the mammary gland, eliminates injury to the nipples, and also prevents the child from swallowing air.
When breastfeeding, you can eat: meat (lean beef or pork), chicken, turkey, fish (cod or flounder), eggs (2 times a week), porridge (buckwheat, oatmeal, rice), wholemeal bread, butter or vegetable oils, milk, dairy products, vegetables, fruits (bananas, green apples).
When breastfeeding, it is not recommended to eat: red vegetables and fruits (tomatoes, red apples, strawberries, etc.), citrus fruits, sweets, candies, chocolate, seafood, spicy seasonings, garlic, onions, celery. Alcoholic drinks, carbonated drinks, coffee, cocoa.
Epidural anesthesia
Advantages
Epidural anesthesia is absolutely safe for the child; its use completely anesthetizes and relieves sensitivity, which is why it is often used during a cesarean section. The patient remains conscious, but feels absolutely nothing, however, with the introduction of small doses of anesthetics, some women feel uterine contractions.
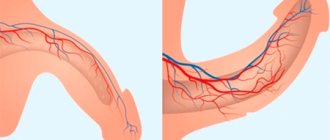
An epidural anesthesia procedure is performed under local anesthesia in the lumbar region, then the doctor uses a thin long needle to insert a catheter into the spine, more precisely into its epidural space, through which a dose of anesthetic is administered, if necessary. After the procedure, you need to lie down for fifteen minutes, during which time the medicine will begin to act. The catheter is not removed until labor is over; patients are usually not recommended to get out of bed and lie down, but there is also a mobile version of epidural anesthesia.
According to reviews of patients who have undergone childbirth with this type of anesthesia, pain is practically not felt, especially if an additional dose of medication is administered in a timely manner. However, there are strict contraindications for this procedure:
- Various neurological diseases;
- placental bleeding or any other origin;
- use of anticoagulants or bleeding disorders.
And finally, refusal of such a procedure is also a categorical contraindication.
Side effects
Typically, when a woman thinks about the side effects of this type of pain relief, she thinks about paraplegia, spinal nerve damage, or respiratory arrest. However, these complications are rather exceptions. The main danger is the long-term consequences: headaches, severe back pain that can last for months. Drug therapy for such pain usually does not produce results and it only goes away over time. While the medication is in effect, the patient may experience chills, trembling, decreased blood pressure, and difficulty breathing. You must tell your doctor about all the symptoms so that, if necessary, he can prescribe symptomatic treatment. Difficulty breathing occurs quite often during epidural anesthesia. This is a consequence of too large a dose of the administered drug and requires the use of an oxygen mask.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
According to the latest data from medical studies, the use of epidural anesthesia in almost half of the cases led to various difficulties during childbirth. Since the woman in labor cannot control the birth process and does not understand when to push. In forty percent of cases, this led to protracted labor, forceps on the baby's head and traumatic brain injuries to the child. The high probability of ruptures of the perineum and vagina during such childbirth also does not add advantages to such anesthesia.
Approximately forty-five percent of women who undergo it experience this reaction to epidural anesthesia. This is quite a lot and before agreeing to such a procedure, you need to carefully weigh and think it over.
Suffering scale
There is a common phrase “birth pangs”. This is exactly how most people imagine the process of bringing a new life into the world - through terrible physical suffering, on the verge of life and death. And recently, scientists even measured the level of labor pain and found that it exceeds the maximum pain a person can withstand by as much as 12 units - 57 versus 45 del (del is a unit for measuring pain). After such research, even the bravest first-time mothers will involuntarily feel a chill run down their spine. What if the expectant mother never had her sights set on being a heroine? How can she stop panicking?
The parents turned away, the husband left. Stories of mothers who changed their minds about having an abortion Read more
What to do when contractions start
When the interval between contractions becomes less than 5 minutes, the woman needs to be under the supervision of a doctor as soon as possible. Until this time, if the mother is not bothered by severe pain, it is enough to simply relax and calm down, count down the time intervals and get ready for the hospital. Calmness and proper breathing play a big role in how easily discomfort will be tolerated. Fear of pain can only intensify spasms - this has long been a known fact.
But you don’t need to take painkillers yourself. The very first advice to a woman giving birth is to “breathe deeply.” Proper breathing and focusing on exhalation not only prevents stress, but also relaxes the pelvic floor muscles. A light massage of the lower back also helps. And most importantly, don’t overexert yourself. It is important to use the time between contractions to rest before the most important thing - childbirth3.
Drug pain relief
For drug pain relief during childbirth, analgesia and anesthesia methods are used. They differ in that during analgesia they use drugs that only partially reduce pain, while during anesthesia the patient is completely anesthetized, often with the loss of motor functions and consciousness.
Analgesia is provided both during contractions and during childbirth, and anesthesia is most often used during a cesarean section, that is, during childbirth. Epidural anesthesia occupies a special place in this classification - it is used both to relieve pain during contractions and for anesthesia during childbirth or during surgery.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Help yourself
There are many ways, both physical and psychological, that help you adapt to the pain of childbirth.
Some people feel better just from the presence of a loved one nearby: mother, husband, girlfriend. In addition, the mother in labor will benefit from:
- Listen to the doctor in everything. If you strictly follow his commands, it will be easier to survive the pain.
- Try not to scream. At least not too much. This will take a lot of energy, but will be of little use. In addition, screaming causes vasospasm - and the baby may not receive enough oxygen at this time.
- Rest as much as possible between contractions. Maybe even sleep. You will still need strength, and very soon.
- During contractions, change your position, taking the one your body tells you. You can squat, kneel with your legs spread wide, lean on the bed, hang on the door frame.
- Master proper breathing and the basics of self-massage (this is taught in courses, but you can learn all this yourself on the Internet). The main thing is not to forget to apply knowledge in practice at the most crucial moments.
How to Reduce Pain When Contractions Start
Today, there are relatively safe ways to relieve a woman in labor from severe pain during childbirth. However, many doctors are wary of these activities. The point is not only in the risk of side effects (which, although not great, still exists), but also in the fact that the drugs can lead to a weakening of labor functions.
If the doctor nevertheless decides on the need for pain relief, the choice is given to one of the groups of drugs:
1. Drug pain relief. This includes various analgesics, taken mainly orally (with water).
2. Epidural anesthesia. An anesthetic substance (lidocaine, ropelocaine, etc.) is delivered under the membrane of the spinal cord using a thin needle, which the doctor inserts between the vertebrae. The method is effective (after administration, sensitivity below the back disappears completely), but due to a number of nuances it is used only in exceptional cases. For example, as a result of such anesthesia, a woman can no longer push effectively, so instrumental intervention may be required.
It is preferable when childbirth occurs naturally, without drug intervention3.
False contractions
Above we gave an example of how prenatal contractions begin. However, in obstetrics there is also the concept of false contractions.
False contractions are exactly the same process of contraction of the uterus. However, they do not lead to dilatation of the cervix, therefore they are considered “training”. False contractions can cause the expectant mother to rush to the maternity hospital, although in fact it is not difficult to bring them to light. Firstly, a woman, as a rule, does not experience pain. Secondly, the intervals between “training” contractions are not shortened, and they do not intensify.
Usually, starting from the end of the second trimester, a woman begins to feel uterine contractions, which become stronger and longer as the baby grows. If such contractions do not cause pain or increased discomfort, then this is the absolute norm. Shortly before childbirth, such uterine contractions intensify, gradually developing into real contractions.