The postpartum period is the period of time during which the female body returns to normal after childbirth. It begins immediately after the birth of the child and ends after 6-8 weeks. Usually this period proceeds normally, but sometimes complications arise that require medical attention.
At MedicCity, qualified obstetricians-gynecologists, gynecologists-endocrinologists and gynecologists-mammologists, who are distinguished by their professionalism and delicacy, receive daily consultations. The latest Voluson 10 ultrasound scanner allows you to identify problems in the female body at the earliest stages. We know how to solve any problems that a patient may encounter during the postpartum period!
1 Observation in the postpartum period
2 Observation in the postpartum period
3 Observation in the postpartum period
How long does the postpartum period last?
The postpartum period for women begins after the birth of the child and lasts 6-8 weeks. This time is considered the final stage of pregnancy. The beginning of the period can be determined accurately, but there are no signs of its end, because the process of reverse restoration of all organs and systems occurs in women at different speeds and depends on a number of factors associated with:
- the constitution of the body;
- external conditions (rest, care, nutrition, sleep, etc.).
Preparing for childbirth
Of course, childbirth is a natural process, but preparation for this important and responsible moment is necessary.
Proper preparation for childbirth will prevent physical and emotional stress, reduce the likelihood of complications, and speed up the mother’s recovery process after childbirth. What should this preparation include, what should it be aimed at?
Knowledge. What scares us most is the unknown. Studying the theoretical foundations of childbirth, a detailed explanation of what will happen and how, and medical answers to questions will help get rid of this fear. Such classes should be conducted by an obstetrician-gynecologist, to whom you can ask any questions, share concerns, and clarify any concerns.
Psychological preparation. Psychoprophylactic preparation for childbirth is carried out starting from the first visit of a pregnant woman to the antenatal clinic. However, special classes are carried out from the 30-week period every 10 days - a total of 5 classes. The main task that is solved during psychoprophylactic preparation is the removal of the feeling of fear during childbirth, which reduces the threshold of pain sensitivity.
School of Fathers. Not only mom, but also dad needs preparation - dad will need skills in caring for the baby, massage techniques that he can use while being present during childbirth, and conversations with a psychologist.
Skills. This includes relaxation exercises between contractions, breathing training, which will later reduce pain during childbirth and ease pushing. Massage and self-massage techniques will allow you to help yourself in the initial stages of labor.
In addition to pain relief during childbirth, classes teach pregnant women the correct behavior during childbirth (following all instructions of medical personnel, the ability to push, understanding the need to examine the birth canal by a doctor after childbirth, etc.). This contributes to the normal course and prevention of complications of labor. Sanitary and hygienic training, which is part of the complex of physical and preventive preparation of pregnant women for childbirth, includes issues of lifestyle, work and rest, balanced nutrition, personal hygiene and the use of natural factors that have a beneficial effect on the body.
In addition, it will be useful for the expectant mother to gain skills in caring for a newborn baby and learn the secrets of breastfeeding.
Gymnastics. Physical preparation for childbirth begins in the early stages and continues throughout pregnancy. Exercises and complexes that are accessible and useful to pregnant women can be found in Pilates, callanetics, yoga, and water aerobics. By combining them, an experienced exercise therapy instructor receives an excellent system that helps improve mood and well-being, cope with back and joint pain, optimize metabolism, prepare the body for childbirth and restore shape after childbirth.
All healthy women can do morning exercises, but during pregnancy it is necessary to avoid jumping, running, and lifting weights. Exercises should be feasible, aimed at strengthening the abdominal and perineal muscles, and not cause overstrain or fatigue.
The best option for conducting effective physical education classes is for a pregnant woman to be taught a set of exercises by a methodologist or a specially trained midwife in a antenatal clinic. To check the correctness of the exercises, you need to contact a methodologist at the antenatal clinic once every 2-3 weeks.
Air baths and hydro procedures (showers, wet rubdowns), which are elements of physical culture, are very useful. Systematic physical education during pregnancy contributes to a more favorable course of labor, reduction of perineal ruptures and a significant reduction in complications in the postpartum period.
Biofeedback (biofeedback) method. We will include it as a separate item, because it is unusual and not known to everyone. This is a non-drug, painless and safe method of teaching the mechanisms of self-regulation of any organs and systems, allowing you to consciously use the enormous functional capabilities of the body. The method works great in preparation for childbirth, helping to cope with fears and psycho-emotional stress, master proper breathing, learn to voluntarily relax muscles and reduce pain.
Physiology of the postpartum period: what happens in the body?
- the nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, urinary, digestive, and immune systems of the body are intensively reconstructed;
- Lung volume is normalized;
- blood flow speed decreases;
- the concentration of hormones in the blood produced by the placenta (estrogens and progesterones) decreases;
- the concentration of prolactin in the blood increases (as the woman begins to feed the child);
- The mammary glands enlarge and swell, colostrum appears, then breast milk;
- the uterus decreases in size (from 500 g on the day of birth to 50-70 g 2 months after birth).
After the birth of a child, the inner walls of the uterus represent a wound surface, the healing process of which ends approximately 3 weeks after birth. During this period, there is an active release of obsolete tissues, blood clots, blood clots, and lochia from the uterus. In this case, cramping pain in the lower abdomen may be observed, especially during feeding.
There is some reduction in quality of life, including:
- constipation;
- difficulty urinating;
- fainting (especially when getting up from a lying position);
- discomfort in the perineum and lower abdomen;
- depression, mood swings, depressive state (due to the intense rhythm of life, accumulated fatigue, feelings of fear and uncertainty);
- decreased sexual desires.
Physiological amenorrhea
Women who breastfeed have a longer period of amenorrhea. In women who do not breastfeed, the first ovulation usually occurs after 70-75 days; in 60% of women giving birth, the first menstruation occurs 12 weeks after birth.
In women who breastfeed, the duration of anovulation correlates with the frequency of breastfeeding, the duration of each feeding, and the presence of additional nutrition for the newborn.
If a woman exclusively breastfeeds her newborn, on demand, without a night break, ovulation earlier than 6 months after birth is possible only in 1-5% of cases (lactational amenorrhea). To maintain lactational amenorrhea, the interval between feeding a newborn should not be more than 4 hours a day and 6 hours at night, additional nutrition for a newborn should not be more than 5-10% of the total nutrition.
Contraindications to breastfeeding include the following conditions:
- maternal use of alcohol or drugs;
- galactosemia in a newborn;
- HIV infection in the mother;
- active tuberculosis in the mother without treatment;
- treating the mother for breast cancer;
- maternal use of drugs such as bromocriptine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, doxorubicin, ergotamine, lithium, methotrexate, phenycilidine, radioactive iodine, etc.
Suppression of lactation is carried out by using modulators of prolactin receptors antagonists of the action of prolactin bromocriptine (Parlodel) 2.5 mg per day or more until cessation of lactation or carbegoline (Dostinex).
Ovulation suppression occurs due to increased prolactin levels in lactating women. Prolactin levels remain elevated for 6 weeks after birth, whereas in non-lactating women they return to normal within 3 weeks. Estrogen levels, on the contrary, remain low in lactating women, while in those who do not breastfeed, they rise and reach normal levels 2-3 weeks after birth.
Management of the postpartum period
At the first visit, the gynecologist will ask in detail how the birth proceeded, how it ended, how the postpartum period proceeds, and will conduct an examination on the chair.
During examination, the gynecologist:
- assess the condition of the external genitalia (whether there are stitches on them and what happens to them, since failure of the stitches on the vaginal walls can lead to the formation of fistulas);
- Assess the condition of the cervix. If the cervix is not sufficiently formed and has an irregular shape, most often this is due to undetected tears or broken sutures on the cervix, which can lead to an inflammatory process (cervicitis - inflammation of the cervix);
- will take smears for analysis (they will help determine whether there is inflammation, and if there is, prescribe treatment in a timely manner);
- by feeling the ovaries, the doctor will assess their size and consistency: a flabby, enlarged uterus will “tell” about the onset of inflammation of the uterine mucosa - endometritis.
If the birth ended with a cesarean section, you should contact a gynecologist within a few days after discharge from the maternity hospital.
After a cesarean section, the contraction of the uterus is somewhat slower than after a natural birth. And since, as a result of the incision, sutures were placed on the skin and uterus, disrupting the structure of the muscle fibers, you need to be sure that they are healing well and will not cause any trouble in the future.
Proper care of the postoperative suture is very important:
- after a shower, the seam must be lubricated with brilliant green;
- the linen that comes into contact with the seam should be loose, made of cotton fabric;
- The seam must be processed until a crust forms on it.
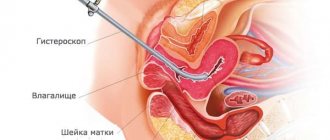
If necessary, the doctor can order an ultrasound examination to determine the shape and size of the uterus, evaluate its contraction function, and determine whether there are any remains of the placenta left in it, whether lochia or blood clots are retained.
How does childbirth go?
Almost every woman is afraid to give birth for the first time. It is difficult for her to imagine how it will be, what will actually happen. She doesn’t know how doctors will and should behave; will they do everything right? It is these questions that torment a woman towards the end of pregnancy before the upcoming birth.
The very first advice that can be given to a future mother is to attend a maternity school, which is located at the antenatal clinic, or choose a private school. It is there that they will explain how childbirth goes, how many hours it lasts, what you need to be wary of and how to behave. If the expectant mother did not think about this school at one time, then this article will be especially useful to her.
Harbingers of the first birth
Before giving birth, a woman should pay special attention to her condition: notice when her stomach hurts, how much the pain in the lower back intensifies, this will help her understand that childbirth is very soon. Perhaps the woman will decide to go to the maternity hospital early in order to be in good hands with doctors from the very beginning.
Many people are skeptical about this and do not want to spend time in the hospital, but it is not as bad as it seems. The mother will be calmer if the child’s life is under the control of doctors, especially if there are any indications for premature hospitalization.
Condition before childbirth
- It has become difficult to walk, my lower back hurts
- Insomnia
- Possible loose stools
- The fetus is less mobile
- Poor appetite
- Often there are false contractions - painful, but not regular contractions of the muscles of the uterus
- One or two days before birth, the mucus plug comes off. It looks like stringy and thick mucus
When is it necessary to see a doctor urgently?
- if a woman has an elevated body temperature (it is necessary to exclude the possibility of inflammation of the uterine mucosa and inflammation in the suture area after cesarean section);
- when the nature and quality of discharge from the genital tract changes, especially with an unpleasant odor, more abundant, bloody or purulent (this indicates an inflammatory process);
- if any painful sensations appear in the lower abdomen or in the area of the postoperative suture;
- when discharge appears from the suture or swelling of the suture after cesarean section (signs of an inflammatory process).
Surgical treatment of postpartum hemorrhage
During vaginal birth, after taking conservative measures to stop bleeding, performing manual exploration and curettage of the uterus, if they are ineffective, the patient is transferred to the operating room for laparotomy and surgical stopping of bleeding.
During laparotomy, the presence of hemoperitoneum is assessed, which may indicate uterine rupture. In the absence of coagulopathy and the patient's stable condition, the first stage of surgical treatment is bilateral ligation of the uterine arteries. The second step is to ligate the hypogastric or internal iliac arteries. If the cause of bleeding is uterine atony, hemostatic compression circular sutures are applied to the body of the uterus to achieve hemostasis. If these measures are ineffective, a hysterectomy (postpartum hysterectomy) is performed.
If placenta accreta is found during cesarean section, the first step (after separation of the placenta) is to place hemostatic sutures on the placenta site. If the bleeding does not stop and there are no other causes of bleeding, the second step for an open uterus is to place circular sutures on the body of the uterus. If ineffective, the next step will be suturing the uterus (with or without tamponade) and ligation of the hypogastric arteries. If bleeding continues, a hysterectomy is performed.
If the bleeding is not massive, there is a reserve of time; if the patient’s condition is stable and there is a desire to preserve reproductive function, temporary uterine tamponade and further embolization of the uterine arteries under angiographic control can be performed.
With the development of consumption coagulopathy (DIC syndrome), a hysterectomy is performed with simultaneous rapid restoration of BCC and coagulation factors (fresh frozen plasma, cryoprecipitate, platelets, red blood cells, refortan, albumin, colloidal and isotonic solutions) under the control of hemostasis and coagulogram parameters.
Postpartum hygiene
Childbirth and the postpartum period are times that require compliance with the rules of special intimate hygiene:
- washing should be done several times a day: in the morning, before bed and after visiting the toilet;
- Before washing, you should wash your hands with soap, and perform the procedure from front to back (so that the infection does not enter the vagina). Lastly, you should wash your anus and then wash your hands again;
- The stream of water should also be directed from front to back, avoiding direct contact with the vagina (so as not to affect the vaginal microflora;
- when washing, use only your hands, without using additional sponges or other means;
- To dry the skin after washing, use a separate towel (preferably disposable);
- as a means for washing, use baby soap or a hypoallergenic product with a neutral pH containing antibacterial and anti-inflammatory components.
Possible complications
Most complications arise from bleeding, inflammatory and infectious phenomena. Bleeding occurs due to atony of the uterus, retention of areas of the placenta, and ruptures of soft tissues. The severity is determined by the amount of blood loss. In severe cases, it is 2 or more liters, which requires immediate medical attention. As a rule, bleeding develops in the first days after pregnancy, but the time frame can shift significantly.
Inflammatory complications develop against the background of a cesarean section, manual separation of the placenta, if a long anhydrous period has been noted. The most common symptoms are endometritis and chorioamnionitis. In addition, inflammatory phenomena can be triggered by the addition of an infection. It can be caused by opportunistic microorganisms that inhabit the skin, vagina, intestines, or nosocomial microflora.
Other complications that are often detected in the postpartum period include hemorrhoids, thrombophlebitis, mastitis, pyelonephritis, constipation, etc.
- mommy!
Childbirth guide - childbirth and the postpartum period - frankly and without embellishment How do the heroines of numerous films give birth? Suddenly clutching their stomachs and bending over, they either strainedly scream all the way to the maternity hospital, or courageously say to their spouse: “We won’t make it in time, you’ll have to give birth yourself.” Next is a picture of a happily smiling mother (in the first case) and a new father (in the second), but with hair equally wet from effort. And a newborn baby smacking its lips in anticipation of feeding. Happy end! Reality is VERY far from soap operas. Mother Nature is much kinder to women than movie scriptwriters. In real life, labor lasting less than 4 hours is called rapid and is classified as pathological. The child, flying out of the mother's body like a cork from a champagne bottle, literally tears apart her birth canal . And not only the soft tissues of the perineum: the cervix and even the body of the uterus, the ligaments of the pubic symphysis. It goes to the vertebrae of the sacrum and coccyx, the sphincter of the rectum, and the bladder. And the child is at great risk of getting a brain hemorrhage or a crippling injury, because of which, let alone breastfeeding, he will not want to live. In fact, everything proceeds “without noise and dust”: slowly, according to a reliable scenario proven over centuries, protecting the health of the woman and her baby. After all, a mother must not only give birth, but also feed and raise a child. And be sure to take the baby in your arms for the first time and give him a tired, but such a happy smile: “Everything is fine, baby!” So how does NORMAL childbirth proceed?
Preparing for childbirth
Preparing for childbirth The entire pregnancy is controlled by female sex hormones .
The rapid increase in their level in the first trimester, aimed at preserving the nascent life, causes toxicosis and catastrophic mood swings in the expectant mother. The second trimester is a period of relative hormonal stability. This is a paradise for a growing belly and his blossoming, sexually seductive mommy. The approach of childbirth is reminiscent of the beginning of the movement of a railway freight train: a barely noticeable push, another stronger one, another - the wheels began to rotate, gradually accelerating, and now the clear, characteristic rhythm of the train’s movement can be heard. " Pushes " are:
- - training contractions starting after 28 weeks, increasing in strength, duration and frequency;
- - softening of the cervix with a slow opening of the cervical canal up to 4 cm from 32 weeks to the start of active labor;
- - increased sensitivity of the nipples of the mammary glands, their hardening during irritation, accompanied by a feeling of tightness inside and the protrusion of tiny yellowish-transparent droplets of colostrum;
- - a slight increase in the volume of vaginal discharge (ATTENTION - only quantity, no change in smell or color);
- - constant mild (or not very) nagging pain in the sacrum, pubis, and lower back;
- - cramps in the feet and calf muscles;
- - a change in gait, more and more reminiscent of waddling from paw to paw of a proud duck;
- - a decrease in the height of the fundus of the uterus, externally noticeable as a sudden prolapse of the tummy, and the associated relief of breathing and increased frequency of urination;
- - subsiding sniffing and puffing is replaced by increasingly frequent sighs on the topic “when will I finally give birth.”
All of the above is nothing more than a gradual restructuring of the mother’s body due to a smooth change in hormone levels. This is how the body prepares for the upcoming birth: it relaxes the ligaments of the sacrum and coccyx (and at the same time all the others), “teaches” the uterus to generate contractions, while simultaneously helping the woman get at least a little used to the upcoming pain. Makes the birth canal more elastic and softer so that full dilatation of the cervix occurs without problems and the perineum does not rupture. For most expectant mothers, closer to childbirth, the breasts noticeably increase in size, becoming heavier and firmer. This is how the active growth of the milky lobules, preparing for milk production, is manifested. Therefore, there is no need to buy a lot of nursing bras in advance: suddenly the mammary glands decide to become champions, capable of feeding their own and the neighbor’s triplets.
note
All of the above does not happen in a day or even a week , but throughout the entire third semester. Therefore, most pregnant women take changes in their body and well-being for granted. And that's how it should be!
That's not all. About a week before giving birth, hormonal shocks begin , the manifestations of which are no longer unnoticed. They are called harbingers:
- 1. A pregnant woman suddenly has an obsessive desire to urgently purchase the necessary items to care for the baby, finish arranging the children’s room, scrape the corners until they are sterile and destroy dust even where there was no trace of it.
- 2. Discharge from the vagina of a small lump of white-pink or rusty mucus, called a mucus plug (not necessarily all at once). There is no need to be afraid. Throughout pregnancy, the cervical canal is clogged with thick mucus to protect the membranes from germs that may rise from the genital tract. When the ligaments of the pubic joint and the sacrum relax, the child, under the weight of his weight, sinks lower into the pelvis. The softened neck gives in to increasing pressure and gradually opens. Immediately, amniotic fluid begins to prolapse into this slit. Externally, the picture resembles a rubber ball filled with water if it is placed on a hollow tube: it is still at the top, but a small part of it has sunk inside. There comes a time when the prolapsed part of the amniotic sac pushes the accumulated mucus out. That is, this is a sign that the cervix is already quite flexible and is gradually stretching.
- 3. A small, up to one and a half kilograms, reduction in a woman’s weight due to a decrease in the tendency of tissues to retain fluid. Mommy may notice that the elastic band of the socks leaves a less deep mark on her shins and her fingers have become slightly thinner. By the way, it is better to remove rings, even wedding ones, in the first trimester, at least by the beginning of the second. In the body of the expectant mother, sometimes changes occur at such a tremendous speed that, having fallen asleep with the fingers of a skinny violinist, you can wake up from a throbbing pain in your swollen hands and call rescuers to remove or saw off the ring. Take my word for it: both procedures are extremely unpleasant.
But that's not all! A day before the development of labor, the level of sex hormones is so high that it causes the woman to relax her stool. And the belly, squeezed by a trained, “muscle-pumped” uterus, due to a slight decrease in the volume of amniotic fluid, rotates more slowly, less often, or even calms down, unsuccessfully trying to win at least a little more space with rare strong pushes. Moreover, almost every movement he makes triggers a cycle of training contractions. This is especially noticeable during CTG recording (cardiotocography): on the uterine tone graph there is no longer a straight line, but constant low sinusoids.
What should a pregnant woman do if warning signs appear?
- 1. Have fun by doing some major shopping in children's stores together with your spouse and general cleaning of the house - by the future dad.
- 2. Check whether everything is prepared for hospitalization in the maternity hospital (an “alarm suitcase” with things for the baby and for yourself).
- 3. Place your credit card, insurance policy (if any) and identification document in a visible place.
- 4. After the mucus plug comes out, do not take a bath , wash in the shower and pay special attention to the hygiene of the genital organs.
- 5. Monitor the discharge: if the panty liner gets wet suspiciously quickly, immediately consult a doctor to prevent leakage of amniotic fluid: the “ball” of the amniotic sac inside the cervical canal may burst. The water will leak out little by little through this crack, but the microbes are not asleep! More than 6 hours are enough to infect a baby.
- 6. Eat “finally” (but not to the point of nausea or heartburn) of those favorite foods and dishes that you will almost have to give up during breastfeeding. Chocolate, for example.
- 7. Listen to training contractions so as not to miss when they become rhythmic, constant and gradually intensifying. By the way, lovers of thrills can arrange a dress rehearsal for a trip to the maternity hospital by waking up their spouse at dawn. Nothing will happen for this: encephalopathy in pregnant women reaches its maximum. The so-called protective inhibition is activated in the brain, thanks to which mothers perceive pain impulses much weaker, endure the hardships of childbirth more easily and forget them very quickly. But the main thing is that oddities in behavior are very noticeable to others, so we repeat: “Seize the moment - they won’t even scold you.”
What not to do when pregnant:
Provoke intensification of training contractions by jumping, walking up stairs or squats. If the level of hormones has not yet reached the optimal level, then it is possible to achieve premature, that is, before the onset of labor, the discharge of amniotic fluid or, which is very life-threatening, placental abruption. Lifting weights is for the same reason. Be nervous: stress causes hormonal disruption, which only in the movies causes people to give birth quickly. In fact, the restless behavior of the mother before and during childbirth slows down the dilation of the cervix and can cause weakness in pushing or incoordination of labor. The latter is very dangerous, and an emergency caesarean section cannot be avoided.
The first stage of labor - who invented these contractions!
The first stage of labor - who invented these contractions!
It’s time for the training contractions to subside, but they are becoming more rhythmic and stronger? Do you want to arch your back and rub your sacrum? Is it difficult to sit down due to a very hard tummy and a feeling of pressure from the inside in the perineum? Congratulations on the start of labor! Being nervous now is like trying to stop a speeding freight train at full speed. Therefore, we take the prepared bags and go to the maternity hospital to pick up the heir. The main difference between real contractions and training ones is their rhythm, the longer duration of the period of tonic tension of the uterus and their effectiveness . Each contraction presses the fetal body harder and harder against the entrance to the pelvis and stretches the cervix. Please note: with a whole amniotic sac, when a small part of the amniotic fluid flows into the cervical canal in front of the hard head, the mother DOES NOT HURT. It doesn’t hurt so much that you can “not give up” for a long time, postponing a trip to the maternity ward. And, like in the movies, start giving birth in the car. This is why gynecologists recommend not waiting for pain, but counting how much time passes between contractions and how long they last. As soon as the stomach hardens more than once every 10 minutes, or for longer than 1 minute, immediately head towards the nearest obstetric hospital!
Who hurts:
- 1. Primipara. The cervix gives in more slowly and not immediately along its entire length, but gradually, from top to bottom (it resembles a carrot in shape: from the side of the uterus the fetal head has already entered, but at the bottom it is still almost closed). The ligaments of the pubic and sacral joints should stretch, the tailbone should straighten to form a straight birth canal through which the child will pass. Therefore, the first birth is usually longer and more painful. But by the third, everything goes as if on a well-trodden track - quickly and easily.
- 2. After the discharge of amniotic fluid. It doesn’t matter whether they came out on their own, or whether the amniotic sac was opened by a doctor. It is not without reason that this manipulation is carried out for labor stimulation if contractions cannot gain the required strength. Just imagine: the neck is stretched not by a small pliable ball, but by a hard head with a circumference of 30 cm! In response, the muscles of the cervical canal, like a spring, sharply tense, trying to protect the soft tissue from rupture. At this moment, the woman feels pain comparable to a burn with boiling water or a stab with a knife. The main difference is that as soon as the contraction weakens, the pain completely disappears. It doesn’t matter what kind of birth there will be.
- 3. With improper breathing and restless behavior during contractions. Trying to squeeze, holding your breath, screaming or throwing around the bed only intensifies the protective spasm of the cervix. And that means pain. How to breathe correctly during contractions : take a deep breath through your nose and exhale 1.5 times slower through your mouth and lips with a tube. It's not easy without a habit. Great: you’ll have to concentrate, which means take your mind off thoughts about your poor tummy. Some find it easier to take very frequent, shallow, noisy inhalations and exhalations with a half-open mouth. The main thing is to try to relax as much as possible.
- 4. In case of incoordination of labor. Thousands of muscle fibers of the body of the uterus suddenly begin to contract chaotically, each in its own rhythm. The result is an endlessly long, very painful and completely useless fight. This is an extremely dangerous condition: the child may die due to the complete blockage of oxygen supply to him through the vessels of the placenta, and the mother’s uterus will rupture at any moment. In such cases, labor is immediately stopped with the help of special medications and anesthesia and an emergency caesarean section is performed.
- 5. With a scar or large myomatous nodes on the uterus. These areas stretch more heavily, which means they react more strongly to the pressure of the head. Hence the pain and the threat of rupture at the peak of the fight. With such a pathology, even before birth, the obstetrician determines how high the risk to the mother’s health is. If ultrasound and examination reveals scar incompetence or very large nodes, surgical delivery is required.
- 6. If you set yourself up for pain. He who seeks will find, including trouble. Be patient a little, and your huge belly will no longer interfere with tying your shoes, walking in high heels, sleeping in any position, and breathing deeply. You can scare your spouse with a ton of makeup on your face and put 2 rings on each finger, throw away a huge jumpsuit and put on a sexy slip. Isn't this a reason to smile? Yes, just to stop sniffling, you can endure two births at once. What are a few hours versus a whole 9 months of waiting mixed with toxicosis and heartburn? And I really want to know who the child will be like.
How long is left to suffer in guessing? The classic is when the cervix dilates 1 cm every hour, up to 10-12 cm in total. That is, the most reliable folk sign is that a woman in labor never sees more than one dawn. But our accelerated children are in a hurry before they are even born. Now even first-time mothers give birth in an average of 7-10 hours. And the third and subsequent births go much faster.
The second stage of labor is a miracle of birth!
The second stage of labor is a miracle of birth! The strength of the circular muscles of the cervix is enormous! No weightlifter can resist them. But as soon as they stretch so much that they finally let the baby’s head through, nothing can stop him from being born. If the beginning of the first stage of labor is difficult to pinpoint, then no woman in labor will confuse the very first push with a contraction : they are so different. Instead of the expected pain, mommy suddenly feels an irresistible desire to push something unpleasantly large out of the perineum. This is very reminiscent of trying to get rid of many days of constipation, because the fetal head puts a lot of pressure on the rectum. Just a minute ago, the midwife’s advice to push a little during a painful contraction seemed like a mockery, but now - try, stop! It seems that the mother, exhausted by waiting, is getting her second wind. And what! Taking a deep breath, she growls from the effort, stopping herself with difficulty only when she hears the doctor shout: “Don’t push!” This is the moment when the baby's head passes the soft tissue of the perineum with its largest diameter. The doctor quickly removes the skin from the baby's hairs, another push - and then the delivery room is filled with the indignant loud cry of the baby. But he will quickly calm down when he is first put to the breast. It’s a miracle, but he will suck as if he had been starving and training for the previous 9 months. So, healthy! In the meantime, he smacks his lips, you can count his fingers, stroke his forelock and check whether the doctor guessed the gender on the ultrasound.
Third stage of labor – end of pregnancy
The third stage of childbirth is the end of pregnancy. No matter how the birth takes place, at the moment the baby’s body is born, the woman’s strength leaves.
But, closing her eyes from weakness and happiness, she hears a firm: “The birth is not over yet.” What, really twins?! The midwife asks the new mother to massage her nipples, as if she were winding a watch. This is necessary so that an additional portion of the hormone oxytocin enters the blood. It will quickly contract the still very large uterus and push the placenta out. You will have to push half-heartedly again, and then wait a little while the doctor carefully examines and treats the perineum. The ruptures may have to be sutured, then local anesthesia or anesthesia will be offered.
During this time the child will be washed, weighed and measured. Afterwards, mother and baby will rest.
"Pleasures" of the postpartum period
“The delights” of the postpartum period And now about those small problems that very quickly make childbirth no longer seem like the most terrible event in life. Don't worry: everything will pass quickly and be easily forgotten. Ready? - begin.
- 1. Severe weakness .
No wonder: several hours of continuous contractions and powerful efforts consume so much energy that it would be enough to heat the palace of an Arab sheikh in winter. With sweat and noisy breathing, the woman in labor gives up a lot of fluid, which, coupled with even slight blood loss, reduces blood pressure. Therefore, in the first two days, when you try to get out of bed, blackness in the eyes and noise in the ears are guaranteed. What to do: drink more water in the form of sweet tea and dried fruit compote, rise slowly, do not make sudden body movements or turn your head. Do not tolerate even mild hunger! At the first request of the stomach, without hesitation, gobble up crackers, candies, marmalade, boiled meat, yoghurts with cereals and non-allergenic fruits. Don’t think about your figure for now: it’s healthier to have regular bowel movements. For long distances (that is, beyond the threshold of the room), walk slowly, next to the wall, in order to lean on it during an attack of dizziness. If weakness persists, be sure to tell your midwife or doctor about it. So it’s not far from fainting! - 2. Drowsiness .
This is the body's persistent attempt to cope with physical and emotional exhaustion. Sleep, better than any medicine, will help you forget about the worries, pain and fears you have experienced, and will increase milk production. In the first week after giving birth, you need to sleep as often as possible, every minute free from feeding and procedures. To prevent your phone from becoming an annoying alarm clock, it is better to turn it off and call yourself at a convenient time. The only but most important condition is that the baby be in his own cradle, and not in bed with his mother. No matter how hard it is to get up to him, and no matter how wide the mattress seems. Falling into deep sleep, you can fatally crush your precious little bag. And not necessarily with the whole body - it is enough that the breast presses the nose during feeding. - 3. Pain in the perineum .
Stretched during labor to 35-38 cm in diameter, it is simply bound to hurt. Even if there is not a single microscopic crack. And even more so with fresh stitches. Therefore, you will have to endure tingling when urinating, pain during bowel movements (especially the first), tears from the eyes during constipation. And a feeling of fullness when sitting. In order for pain to bother you less and go away faster, you need to wash yourself often, preferably after each visit to the toilet, without soap, and do not sit down abruptly. Rectal suppositories with an anesthetic and a timely cleansing enema with warm water will help relieve painful spasms of the rectum. To prevent the stitches from becoming infected, use sterile fabric pads provided by the midwife on the first day, and then use soft pads and mesh panties. Healing scars after tears or episiotomy will bother you for about 3 weeks. - 4. Lochia .
During a full-term pregnancy, the thickness of the placenta is from 2.5 to 4.5 cm, even more in case of gestational diabetes. After the birth of the child, the afterbirth is rejected, leaving a deep gaping wound with a diameter of 12 to 15 cm in the wall of the uterus. No matter how quickly the uterus contracts, it is not able to immediately completely compress the torn blood vessels. Therefore, small, gradually decreasing bleeding from the genital slit is normal. Within 3-7 days, the discharge becomes clearer, lighter, and by the end of the first week resembles menstrual discharge. The appearance of dark clots adds to the resemblance to them. This is due to a sharp drop in the level of pregnancy hormones, the remaining part of the overgrown uterine mucosa is rejected. This is how the woman’s body prepares to resume the cyclical changes of the endometrium again in order to accept and grow a new fertilized egg. - 5. Stomach ache.
Compressive pain above the pubis, which sometimes feels very reminiscent of contractions, occurs every time the midwife or doctor strongly squeezes the stomach, during breastfeeding and after an injection of oxytocin. At the same time, the secretion of lochia increases: the less time has passed after birth, the more abundant it is. We’ll have to be patient: how else will the uterus quickly shrink to the size of a non-pregnant one? Sluggish contractions are a sign of a possible problem: a piece of placenta remaining in the uterus, infection (endometriosis), myomatous nodes. The result is subinvolution of the uterus and the threat of atonic bleeding, due to which you will have to additionally go for an ultrasound and tests, receive “shortening” injections, antibiotics, and even agree to remove the remnants of the placenta, popularly known as “cleansing”. In any case, this will cause a delay in discharge from the hospital.What to do? Lie on your stomach more, or even better - placing a diaper roll over your pubis. Turn over in bed more often and get up and start walking around as early as possible. Do not stop breastfeeding out of self-pity: at the moment of active sucking, a large amount of the hormone oxytocin is released - the main stimulator of contractions and contractions of the uterus.
- 6. Beginning of lactation.
Only an infant can free the milk ducts from thick, viscous (and so healthy!) colostrum. But even for him, who has suffered the stress of childbirth, it is not easy: the baby gets tired. Therefore, after birth, the baby will sleep a little, and then begin to frequently and persistently ask for the breast, quickly abandoning it and looking for it again literally in a few minutes. At the same time, he has many reasons to get angry and shout: he still doesn’t know how to grasp the nipple correctly, he has to try very hard to get enough, but he’s lazy. There was no need to work in the mother's womb. Hot, unusually tight mammary glands become painfully sensitive to any touch. Even just thinking about a baby causes the milk ducts to contract, causing milk to separate and increase its production. If you do not express in time, it accumulates and compresses the excretory ducts. As a result, lactostasis often occurs, especially in primigravidas: a sharp difficulty in milk secretion. Inept breastfeeding or pumping only aggravates the problem: the production, and therefore the accumulation of milk, increases like a snowball. Severe throbbing stabbing pain quickly appears, and body temperature may rise. So it’s not far from mastitis.What to do? It is correct to place the nipple in the baby’s mouth so that he does not “chew” it and can actively suck. During feeding and pumping, do a soft stroking massage of the tight areas in the breast in the direction strictly from the periphery to the nipple (do not knead!). If you cannot cope with the onset of lactostasis on your own, ask for help from a midwife or a lactation consultant as soon as possible. Patiently and with calm(!) understanding put the baby to the breast as often as he asks. Almost impossible, BUT: rest more and don’t be nervous. Transitional milk, which appears by the third day after birth, is no longer so thick, but mature - and even more so. Surely in a couple of weeks another problem will appear: remember to change the absorbent pad in your bra in time so that your clothes don’t get wet. And one more thing: isn’t it possible to earn an increase in benefits by selling surplus milk?
- 7. Back pain .
Childbirth is a serious test for the flexibility of the spine. In the third trimester of pregnancy, he, like a spring, bent forward under the pressure of a heavy, large uterus. And then she disappeared in a few minutes! But for a reason: first, the baby’s head drove along the inner surface of the sacrum like a tank, mercilessly pressing and stretching the intervertebral ligaments, and at the same time the sensory and motor nerve fibers passing nearby. It is not surprising that many postpartum women complain of aching pain in the rapidly straightening spinal column, especially in the sacrum, lumbago in the back, burning on the back of the thighs, numbness in the legs and in the tailbone area. You will have to be patient a little, protecting the spine from overload in the form of sudden movements, lifting weights of more than 4 kg and staying in an uncomfortable position for a long time. How many? From 2 weeks to 3 months: your back will tell you. - 8. Pain in the feet .
Remember about relaxing the ligaments before childbirth? The foot is made up of more than 30 bones, flexibly connected to each other so that two movable arches are formed. These shock-absorbing arches are extremely necessary in order to absorb the impact of the foot on the ground when walking. During the third trimester and several weeks after childbirth, the arches of the feet flatten. Therefore, after a long period of standing or walking, the overworked bases of the fingers can seriously ache. And in the morning you will have to walk around, waiting for the cutting pain in the heel that appears with every step to subside. Another manifestation of such temporary flat feet is greater fullness of shoes. What to do? Do not rush to stand on high heels, do not carry heavy objects, do without jumping. Try to keep your foot at a right angle to your shin while you sleep: this way, nodules are formed at the base of the ligaments that form the shock-absorbing arches, which are extremely painful to step on. - 9. What to do with the baby?!
Why is he crying - read above. Also, the baby just has to LEARN not to scream when it is necessary to strain to pass gas or stool. It is advisable to master the swaddling technique before birth, and not on a doll, but on a child. The difference is enormous: children’s arms are constantly trying to free themselves, their legs are bent, and when they touch their chin, their mouth hides behind their neck, opening in search of food. After all, if a baby is not sleeping, it means he wants to eat. How to feed - they told. At least for the first few days, pick up the baby only to feed it or move it to the changing table. Postpartum weakness can strike at any moment; a sore back must be taken care of. And the family will help the baby quickly get used to motion sickness after being discharged from the hospital. Many newborns are afraid of loud noises, being touched, and even their own sudden movements. There is no need to scare them: speak quietly, swaddle them slowly, stroke them with light touches. And don't be nervous under any circumstances. The umbilical cord has already been cut, but the baby remains in a strong connection with the mother for a long time. It is enough just to press it to the chest, and the baby will immediately guess from the rhythm of the woman’s heartbeat that mommy is worried. And since he is used to empathizing with her in his tummy, he will cry and refuse to eat. And then you will have to start reading from the beginning: “Why is he crying?...”/li> - 10. Tearfulness and anxious thoughts .
In the first days after childbirth, due to a sharp drop in hormone levels and physical and emotional stress experienced, a new mother may feel devastated. It would seem: here it is, the long-awaited happiness - snoring and smiling in your sleep! But instead of joy, tears roll into your eyes, sad thoughts swarm in your head, and bad forebodings creep into your soul. Your mood will improve if you try to get enough sleep, allow yourself a little forbidden (for nursing) favorite delicacy, and share your experiences with more experienced roommates or a midwife. But it is important to remember that at home you cannot immediately shoulder all the household chores and control over the household. Overload can cause postpartum depression, which is much more difficult to cope with.
note
The menstrual cycle is restored regardless of whether the mother is breastfeeding or not. Lactation in some cases postpones this moment if the hormonally active corpus luteum remains in the ovary, suppressing the maturation of new eggs. But often after 1.5-2 months a new conception and pregnancy is possible. Don't believe me? Take a closer look at how many brothers and sisters the same age with an age difference of less than 1.5 years are playing on the playground. Surely these are babies who were conceived without preconception preparation and became a surprise for their mother, who had not yet recovered from childbirth.
Upon discharge from the maternity hospital, the doctor will recommend sexual rest to the woman. How long? Minimum 3 weeks. Depends on how deep the perineal tears were sutured, how the scars heal, whether there is inflammation or thrush. The desire for intimacy with a spouse is suppressed by fatigue from sleepless nights, depression, and temporary difficulties in “starting” lactation. If in doubt, it is best to visit a gynecologist on the 20-25th day after birth and get the go-ahead to start sexual activity. And at the same time – choose a method of contraception.