Hysteroscopy
is an operation in the uterine cavity, which can be described 70% in scientific language and 30% in everyday language, but we will try to do the opposite and, hopefully, this will make it easier for you to become familiar with this method.
This is a minimally invasive method, without any incisions. The operation includes: insertion of a hysteroscope (optical instrument) into the uterus through its cervix and careful removal of material for histological examination. Using a fiber light guide, the optical system of the hysteroscope is connected to the illuminator, so the doctor has the opportunity to visually observe the cavity being examined.
The hysteroscope has a video camera. Therefore, even diagnostic hysteroscopies, performed, for example, to determine the location and size of the myomatous node, to assess the structure of the endometrium, the orifices of the fallopian tubes, and to correct the position of intrauterine contraceptives, are carried out using video control. During the operation under visual control, the doctor can perform a number of surgical procedures: removal of polyps, removal of myomatous nodes with a submucous form of growth (when the myomatous node grows into the uterine cavity), removal of foreign bodies from the uterine cavity and cervical canal, dissection of adhesions. An image is displayed on the monitor screen in HD quality, which fully ensures the possibility of careful handling of the uterine cavity, endometrium, and fallopian tubes, which is important when planning a pregnancy in the future.
During hysteroscopy, the specialist’s visual observation area is the isthmic region, the cervical canal - the canal in the cervix and the uterine cavity, which makes it possible to perform all manipulations accurately and absolutely safely for the patient’s health. And most importantly, during the operation all detected pathological areas are removed from the uterine cavity, which is extremely important, since the remaining pathological tissue can subsequently provoke a recurrence of the disease or cause complications. After surgery, if necessary, a histological examination is performed.
For histological examination, under visual control, only suspicious tissue is taken without aggressive curettage, as occurs during conventional separate curettage of the uterine cavity and cervix, when it is carried out without visual control. Thus, hysteroscopy, having a wide range of therapeutic and diagnostic capabilities, also has high information content. This happens because with simple curettage, absolutely everything is taken from the uterine cavity and, if there is a polyp there, it comes off, its leg remains, which has blood vessels, and the polyp grows again. Another advantage of the hysteroscope is that it has a loop, and under visual control you can remove the polyp while simultaneously cauterizing the area where the growth of the polyp stalk begins.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy of the uterus
The operation is performed under general anesthesia (anesthesia), which you should not be afraid of. A little more about anesthesia. As practice has shown, many patients are more worried not about the operation, but about the anesthesia.
How is everything going? A nurse anesthetist installs a catheter (this is comparable to donating blood from a vein) through which drugs for anesthesia are administered. After the administration of the drugs, the patient falls asleep, maintaining spontaneous breathing. A breathing mixture containing 30% oxygen is supplied through a mask. The duration of anesthesia coincides with the duration of the operation itself, namely from 15 to 40 minutes.
Our clinic employs attentive anesthesiologists - professionals in their field. Getting to know the patient begins before the operation. Having learned all the secrets and features of your body, having studied the outpatient card, the anesthesiologist in the operating room, speaking through all his actions, creates a feeling of security, which is so important at this moment. The doctor monitors the patient until she wakes up. After awakening and regaining full consciousness, she is transported to the recovery bed, where she is under the supervision of medical personnel.
The procedure itself is performed on a gynecological chair in a standard position. The cervix is gradually and carefully dilated, and a hysteroscope is inserted into the uterine cavity through it. The cervix, uterine cavity, and fallopian tubes are examined. An endometrial biopsy is taken under visual control. Hysteroscopy does not require a long stay in a medical facility. Patients are admitted at 09.00 in the morning, the entire operation, as already mentioned, lasts 15-40 minutes, an hour after emerging from anesthesia, they are allowed to drink and eat.
After 2-3 hours, the attending physician performs an examination and talks about the progress of the operation. In case of satisfactory health and absence of heavy bleeding, the patient is discharged home under the supervision of a gynecologist at her place of residence. An extract with a detailed individual description of the operation, a list of drugs administered, and recommendations is issued. A certificate of incapacity for work is issued for 1-3 days based on the patient’s well-being. After 2-3 hours you can leave the clinic on your own.
What are the types of hysteroscopic surgeries?
If intrauterine pathology is detected, the following surgical interventions are performed:
- removal of myomatous nodes;
- lysis of intrauterine synechiae (adhesions);
- dissection of the intrauterine septum;
- polypectomy;
- targeted endometrial biopsy;
- myomectomy;
- removal of remnants of the intrauterine contraceptive device;
- removal of foreign bodies;
- preparation for the IVF program.
Indications for diagnostic hysteroscopy
- submucosal myomatous node, which causes deformation of the uterine cavity;
- suspicion of internal endometriosis of the uterine body;
- endometrial hyperplasia (a disease in which a woman is bothered by heavy, prolonged menstruation with clots);
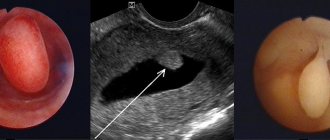
- endometrial polyp (grows due to inflammation, hormonal imbalance);
- any types of menstrual irregularities;
- pathological uterine bleeding (in the absence of pathology according to ultrasound data, since only hysteroscopy with visualization of the process will give a complete picture of the process in the uterine cavity);
- remnants of the fertilized egg (after an unsuccessful medical abortion, without visual control, tissue elements that cause inflammation often remain in the uterine cavity);
- synechiae (adhesions) in the uterine cavity (a consequence of inflammatory processes that make conception difficult);
- infertility (you can evaluate the nature of the endometrium and carefully take a biopsy for histological examination of the condition of the endometrium, and also examine the uterine cavity for the presence of adhesions and patency of the fallopian tubes);
- preparation for IVF and not carrying a pregnancy (you can assess the nature of the endometrium, carefully take a biopsy for histological examination of the condition of the endometrium and exclude intrauterine pathology);
- perforation (puncture with an instrument) of the walls of the uterus during abortion or diagnostic curettage without visual control;
- complicated course of the postpartum period (examination of the uterine cavity for the presence of a placental polyp - remnants of placental tissue in the uterine cavity after spontaneous childbirth, as well as cesarean section. In the presence of placental tissue, the uterus cannot contract, and an inflammatory process develops;
- abnormalities of the uterus (diagnosis of intrauterine septa, duplication of organs);
- the presence of a foreign body in the uterine cavity (parts of the intrauterine device, parts of instruments after normal curettage of the uterine cavity);
- control examination of the uterine cavity after operations on the uterus (for abnormal development of the uterus, conservative myomectomy - removal of myomatous nodes).
The hysteroscope has a loop in its design for targeted removal of pathological formations (polyps, fibroids, synechiae, etc.). When a snare is used for surgery, the device is called a hysteroresectoscope and the procedure is called hysteroresectoscopy.
Is menstruation a contraindication or not?
During menstruation, routine hysteroscopy is not performed. It is usually prescribed on days 5-7 of the cycle to identify neoplasms, fibroids, and polyps (in the first phase of the cycle, the endometrium is thinner, which allows you to see even tiny defects). But foci of inflammation are easier to detect when the endometrial layer is thicker (in the second half of the menstrual cycle, on days 20-24). Hysteroscopy of the uterus with biopsy before IVF is prescribed immediately after the end of menstruation. Two or three weeks are often enough to restore and renew the endometrium, which allows the patient to enter the protocol already in the next cycle.
However, if emergency hysteroscopy is indicated (in case of intense bleeding, suspicion of the presence of a dead fertilized egg or foreign objects in the uterus), it can be performed on any day of the cycle. It doesn’t matter whether you’re menstruating or not.
Contraindications to hysteroscopy and hysteroresectoscopy
- infectious diseases (flu, sore throat, pneumonia, etc.);
- acute inflammatory diseases of the genital organs (vaginitis, cervicitis, endometritis, salpingoophoritis);
- recent or existing inflammatory process of the genital organs at the time of the study;
- progressive pregnancy;
- advanced cervical cancer;
- general infectious diseases in the acute stage (influenza, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, thrombophlebitis);
- the patient’s serious condition with diseases of the cardiovascular system, liver, and kidneys.
How does the postoperative period proceed? After hysteroscopy.
- After hysteroscopy, the patient requires observation for 2 hours. Most patients experience nagging pain in the lower abdomen, which decreases 1-2 hours after surgery. Analgesics are prescribed to relieve pain.
- Bloody discharge from the genital tract after surgery is usually small and stops within 24 hours, followed by bloody discharge that can last for several weeks.
- In the case of surgical hysteroscopy, antibiotic therapy is necessary. Antibacterial therapy can be supplemented with metronidazole drugs (Trichopolum 1 tablet x 2 times a day, Metrogyl 100 ml x 2 times a day IV). For patients at risk of developing infectious complications, it is advisable to prescribe antibiotics even after diagnostic hysteroscopy.
How long is the patient in the hospital?
If the condition is satisfactory and there are no complaints, patients can be discharged either on the same day, a few hours later, or the next day in the morning. Patients are warned not to use vaginal tampons. Sexual life is possible through
2 weeks.
When is the next inspection?
A repeat examination is scheduled after 10 days. By this time, the histology result is ready. Histology is the examination of removed tissue under a microscope to establish a definitive diagnosis.
Preparation for hysteroscopy surgery
It is necessary to make an appointment with a gynecologist for examination. Select with your doctor the most optimal day for the operation and prescribe a preoperative examination, which includes the following:
- ECG;
- fluorography;
- smear for vaginal microbiocenosis, oncocytology;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- clinical blood test with leukocyte formula;
- general urine analysis;
- biochemical blood test (total protein, ALT, AST, total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, glucose, cholesterol, creatinine, urea, sodium, blood potassium);
- coagulogram;
- HIV, HBsAg, HCV, Treponema pallidum;
- final consultation with a therapist;
- BLOOD GROUP and RH FACTOR (must be taken EXCLUSIVELY at our institution).
Despite the fact that hysteroscopy is a fairly safe diagnostic and surgical procedure, complications sometimes occur in 1% of cases.
Most common complications
- injury (perforation, puncture) of the uterus or cervical canal,
- the occurrence of severe bleeding,
- allergic reactions associated with the administration of anesthesia drugs.
If such complications arise, the patient is provided with qualified assistance and, if necessary, transferred to a hospital.
Since prolonged local pressure on the calves of the legs due to the position in the gynecological chair can lead to inflammation or thrombosis of the deep veins of the legs, to prevent this complication, all patients are operated on in compression stockings. And if there are varicose veins, the patient is recommended to consult a phlebologist before surgery.
Methodology of the procedure
Hysteroscopy can be gas or liquid. The type of procedure depends on the goals pursued, indications, contraindications, scope of intervention and other factors.
With gas, carbon dioxide is used to expand the uterine cavity. It is delivered into the uterus using a hysteroflator. The device supplies gas in a controlled manner, in the amount required by the doctor for normal visualization of the uterine cavity. This method cannot be used for menstrual and uterine bleeding.
The liquid type involves the use of low-molecular and high-molecular solutions. Most often, low molecular weight saline solutions are used in gynecological practice. They do not cause allergic reactions, are quickly absorbed from the abdominal cavity and have low viscosity. Moreover, they are quite cheap.
The examination is carried out in a specially equipped room, with strict adherence to the rules of asepsis and antiseptics. The prepared patient is placed in a gynecological chair. After the onset of anesthesia, the gynecologist expands the cervical canal to the desired size using special instruments. Then a hysteroscope is inserted into the uterine cavity and the examination begins. By sequentially examining different areas of the endometrium, the doctor draws conclusions about the patient’s health status. After completing the examination, the instruments are removed - the hysteroscopy can be considered completed.
Popular questions
What kind of discharge can there be after hysteroscopy?
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure, after which atypical vaginal discharge may occur. Within a few days or even 2-3 weeks after the intervention, bloody or spotting discharge appears, which is accompanied by a slight nagging pain in the lower abdomen. Don’t worry, scanty discharge as a result of hysteroscopy is normal and will go away on its own without the help of doctors or taking medications. In some cases, the treating doctor may prescribe painkillers to relieve pain. However, if the discharge becomes profuse and has a strong odor, large blood clots appear in it, and if the temperature rises and there is severe pain, you should definitely consult your doctor.
On what day of the cycle is it done?
The optimal period for hysteroscopy is the first phase of the menstrual cycle, that is, approximately 9-11 days after the start of menstruation. During this period, the uterine mucosa has the thinnest structure, and any pathologies or changes on it during a hysteroscopic examination become most noticeable. It is not recommended to carry out the procedure on days 15-28 of the cycle, during the secretory phase, since during this period the structure of the endometrium is difficult to distinguish from intrauterine pathologies. However, the doctor may change the timing depending on the goals of the intervention, the patient’s test results and the overall clinical picture. If the patient takes hormonal contraceptives, as well as in emergency cases, hysteroscopy is performed on any day of the menstrual cycle.
When is pregnancy possible after hysteroscopy?
After the procedure, the permissible time for pregnancy planning depends on the goals of the study and its results. If hysteroscopy was prescribed to identify the disease, it is necessary to carry out competent treatment and discuss the prognosis with the attending physician. If no pathologies are found during the procedure and re-examination is not required, the uterus will recover quite quickly after minimally invasive intervention. In this case, pregnancy is allowed three months after hysteroscopy. In any case, you should consult your doctor before conceiving. Only a gynecologist will be able to evaluate the results of the examination and determine the time required for the body to recover.
Is it possible to delay menstruation after hysteroscopy?
Often, after a diagnostic examination, the menstrual cycle is not disrupted. However, in some cases, it will take some time for the cycle to return after hysteroscopy. The delay can range from 4 to 15 days. The first period often lasts longer than usual, and this is normal. If the procedure was therapeutic in nature, the delay period depends on the purpose of hysteroscopy and its complexity. For example, after removal of tumors or curettage, menstruation may not occur during the entire next cycle. As a rule, the maximum delay period does not exceed one month, but recovery in each case depends on the individual characteristics of the body. After the procedure, the doctor will definitely give recommendations and advise on the norms for restoring the cycle.
Author of the article
Khokhlova Maria Viktorovna
Specialty: Gynecologist
Experience: 15 years
4 out of 5 (ratings: 12)
Thank you for your mark.
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price, rub.) | In installments* |
| Hysteroscopy (diagnostic) | 9 000 | — |
* You can read more about the conditions here - Treatment on credit or in installments.
What to expect after the procedure
After the operation is completed, the patient will wake up in the operating room and will be transferred to the hospital ward, where for two to three hours she will be under the supervision of medical staff, talk with the attending physician, and receive information on the results of the operation. She will be offered lunch or dinner, depending on the time of day. After this, the patient returns to normal life and can leave the clinic.
After receiving the results of the histological examination, the doctor, together with the patient, will select the most effective treatment regimen, medicinal or surgical. If a subsequent operation is necessary, the doctor will carry out all the necessary preoperative measures and set a date for the intervention and subsequent hospitalization. The results of histological examination are reported and discussed during the face-to-face consultation.
OFFICE (OUTPATIENT) HYSTEROSCOPE STORZ
An office hysteroscope from the recognized world leader in the production of endoscopic stands Storz allows you to identify and eliminate intrauterine pathologies in an outpatient setting. Advantages of a flexible hysteroscope:
- atraumatic;
- flexible shape allows you to easily adapt to the shape of the uterus;
- easy insertion into the cervical canal;
- the movable distal end provides a large viewing angle and better orientation in the intrauterine space.