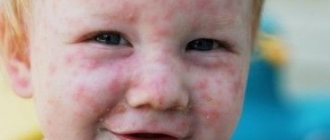
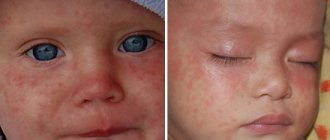
From the time of infection with acute respiratory viral infection (ARVI) to the appearance of symptoms of the disease, a period of time passes, which is called the incubation period. The duration of this time interval depends on the type of infection and the state of the person’s immunity.
- What is the difference between ARVI and ARI
- Incubation period in adults For adenovirus infection
- For respiratory syncytial infection
- For rhinovirus infection
ARVI and acute respiratory infections: what is the difference
First, let's understand the terms. ARVI is an acute respiratory viral infection that can be caused by a large number of different viruses. ARI – acute respiratory diseases. Previously, this was the designation for all respiratory diseases of both a viral and viral-bacterial nature. And ARI (acute respiratory infections) is a term that replaced acute respiratory infections. These infections can also be caused by viruses and bacteria. There is no big difference between the presented groups of diseases. One abbreviation assumes that the causative agents of diseases are only viruses, which is what happens in most cases; another name does not exclude a bacterial component. Clinically, these infections are very similar, which made it possible to combine them into groups.
When do outbreaks of acute respiratory infections occur?
As a rule, an increase in the incidence of ARVI and ARI is observed in the cold season, and the prevalence of infection is widespread - colds and flu are familiar firsthand not only to children, but also to adults in all countries of the world. According to WHO, during periods of peak incidence, these infections are diagnosed in almost 30% of the world's population.
But any cold and flu viruses that have entered the human body do not immediately make themselves felt. There are many varieties of acute respiratory viral infections, the type of which determines the timing of the development of clinical symptoms when a person realizes that he is sick. Runny nose, cough, sore throat and other similar symptoms can be caused by various types of influenza viruses, parainfluenza, adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, reoviruses, ECHO and Coxsackie viruses.
Thromboembolism
Another common phenomenon that is important to consider when talking about symptoms is thromboembolism. It encounters many patients with moderate and severe forms of coronavirus.
Many people know about the serious consequences of thromboembolism. Not everything is about how she manifests herself.
Among the characteristic signs of thromboembolism:
- swelling of veins, often cervical
- blueness (cyanosis) of the face,
- drop in blood pressure.
However, again, these symptoms cannot be considered a direct signal of COVID-19. In addition to coronavirus, thromboembolism can be caused by injuries, varicose veins of the legs, the presence of a catheter, diseases associated with heart rhythm disturbances, malignant tumors, prolonged bed rest, and surgery with large blood loss. Also among the risk factors are old age, taking contraceptives and pregnancy.
In some patients, thromboembolism is not a symptom, but a complication. Most often, this again happens in older people and pregnant women. In addition, people with respiratory and heart failure are vulnerable, as well as those whose coronavirus has damaged the endothelium of blood vessels (a monolayer of vascular epithelial cells).
Incubation period of acute respiratory infections / acute respiratory viral infections in adults
Acute respiratory viral infections share common features, which include an acute onset of the disease with elevated body temperature, signs of intoxication, catarrhal symptoms and an incubation period that lasts on average about a week. But still, different viruses have different “preparatory” periods.
Adenovirus infection
The adenovirus can make itself felt both 2 days after infection and 10-12. In this case, everything will depend on the initial state of the patient’s immunity. The onset of the disease is acute, the temperature immediately rises, profuse nasal discharge, and a wet cough with clear sputum appear. The mucous membrane of the nose, pharynx and tonsils swells, and the lymph nodes become enlarged. Later, signs of bronchitis and laryngitis may appear. Conjunctivitis may also be a concern.
The course of the disease is usually long-term and can be undulating due to the constant proliferation of viruses and the emergence of new foci of infection. In some cases, even after recovery, a person remains a carrier of an adenovirus, which can occupy the tonsils and remain there in a latent state.
Respiratory syncytial infection
The incubation period for this infection ranges from two days to a week. There is a runny nose, pain when swallowing, and the body temperature in adults most often does not increase, but may be low-grade. The onset of the disease is usually gradual, with scanty nasal discharge, a red pharynx, and as the inflammatory process develops, a dry cough appears with the release of viscous sputum.
Respiratory syncytial infection can invade the airways and lead to respiratory failure, shortness of breath, wheezing, and noisy breathing. It is possible to develop apnea, a pathological process that leads to cessation of breathing during sleep. Mild and moderate forms of the disease usually last 7-10 days, severe ones - up to two weeks or more. Lack of treatment and a weak immune system can lead to recurrence of the infection.
Rhinovirus infection
This disease has one of the shortest incubation periods - it takes only 2-3 days. In rare cases, it lasts up to a week. This disease is not characterized by intoxication and elevated body temperature in adults. The infection is usually accompanied by a profuse runny nose and dry cough. Watery eyes and irritation of the eyelid mucosa may also occur.
Dental problems
Among the symptoms that were not paid attention to at first, but then noticed in a fairly wide number of patients with coronavirus, is exanthema, that is, a rash on the mucous membranes. Typically in the oral cavity.
Just by the presence of a rash in the mouth, one cannot judge that a patient has coronavirus. At the same time, if this sign is present, but there are no other symptoms, it cannot be ruled out that it is not Covid.
Although in many cases, classic enteroviral vesicular stomatitis may be behind the rash in the mouth. This is also an infectious disease, but it requires its own treatment.
A number of coronavirus patients develop ulcers and red bumps in their mouths, which can begin to bleed in spots.
How long is the incubation period of ARVI in children from one to 3 years old?
With ARVI in young children, a more severe course and deeper penetration of viruses are observed. On average, the period after which signs of the disease begin to appear in children when infected with acute respiratory viral infections is shorter than in adults, which is associated with the characteristics of the immune system, as well as with the structure of the organs of the respiratory system: their larynx is shorter than that of adults.
For example, parainfluenza manifests itself after only 2-4 days, and the onset is violent, with a sharp increase in body temperature and obvious signs of intoxication. The voice becomes hoarse, the child complains of a sore throat, and is bothered by a cough. Body temperature rises to 38ºC and above. In children aged one to three years, infection can lead to the development of false croup - acute laryngeal stenosis. Symptoms of this disease include a barking cough, a wheezing voice, and noisy breathing. Also, young children may develop obstructive bronchitis and other complications that require immediate medical attention.
The main difference between parainfluenza and influenza is that parainfluenza does not cause large epidemic outbreaks. The influenza epidemic develops quite acutely, since the incubation period for influenza is even shorter - 12-24 hours.
With adenovirus infection, children under two years of age may experience not only catarrhal symptoms, but also abdominal symptoms - diarrhea and abdominal pain. Also, a sick child may experience decreased appetite, sleep disturbances, pale skin and a bluish discoloration of the nasolabial triangle.
In order to prevent the development of complications, it is necessary to seek help from specialists at the first signs of the disease.
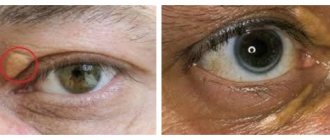
Covid on the skin
In addition to the characteristic symptoms, a number of SARS-CoV-2 carriers who have recovered from COVID also have dermatological symptoms. Most often these are red and purple bumps and redness on the skin.
- Visually, problem areas resemble areas after frostbite. As a rule, these are shapeless asymmetrical spots on the arms and legs. The formations may hurt and sometimes itch.
- Small blisters on the torso, arms and legs.
- Livedo is a red-blue network of vascular nature.
Dermatological problems can make themselves felt both at the first stage of the disease and when the disease has already developed. If we are talking only about redness and rashes, then they disappear within 2 weeks; if bumps have formed, then they can remain on the skin for several months.
In some COVID patients, the skin begins to peel off at the site of the bumps.
Spots are more typical for children, adolescents, young people, blisters - for middle-aged people, and livedo - for the elderly.
Dermatological manifestations of coronavirus infection are most often associated with overexpression of anti-inflammatory cytokines (peptide molecules), which are responsible for transmitting signals between cells. In fact, there is an “imbalance” in the body’s inflammatory response. But some rashes occur due to constant sweating at high temperatures. Infectious and allergic skin lesions are also possible.
Incubation period of acute respiratory infections and influenza in older children
In older children, the incubation period for infection with acute respiratory viral infections is in most cases the same as in adults - from one or two days to a week or more. The duration of the disease in children is usually at least 10-12 days. Sometimes relapses are possible, which especially often happens with the addition of a bacterial infection and the development of otitis media, sinusitis, bronchitis and pneumonia. A runny nose causes damage to the skin around the nasal passages, making it painful for the child to blow his nose. There is also a risk of herpetic rashes in the area of the nasolabial triangle, lacrimation and loss of smell and taste.
In children under 5-6 years of age, acute respiratory viral infections can lead to febrile seizures - convulsive attacks against the background of elevated body temperature. Infections can also cause complications in the form of diseases of the cardiovascular, excretory, nervous systems and exacerbation of existing somatic diseases.
How likely is it to die from coronavirus?
It's important to remember that even if you have a moderate or severe coronavirus infection and require hospitalization, most people are much more than to die from coronavirus.
The model, based on an analysis of coronavirus mortality statistics based on data from 37 countries, states that the mortality rate was about 1.4% for people under 60, 1 in 15 for all people over 60 and 1 in 7 of the sick are over 80 years of age.
Another article reinforces the idea that your risk of dying, even if you end up in hospital, depends largely on your age. Although a significant number of people who require intensive care will not recover, the rate of recovery for people who do not require mechanical ventilation is favorable.
The percentage of people infected with coronavirus who require intensive care is:
- up to 40 years - 5%.
- 40-49 years old - 6.3%.
- 50-59 years old – 12.2%
- 60-69 years old - 27.4%.
- 70-79 years old – 43.2%
- Over 80 years old – 70.9%.
Antiviral drug VIFERON
In children, the level of antiviral protection is significantly lower than in adults. This is primarily determined by the low ability of leukocytes and lymphocytes to induce their own interferons - proteins with similar properties, secreted by body cells in response to virus invasion. This, among other reasons, explains the predisposition of the child’s body to frequent ARVI. Antiviral drugs can compensate for this feature. When treating children, special attention should be paid to antiviral drugs, which cover the entire etiological spectrum of acute respiratory infections, including influenza.
The obvious advantages of drugs containing interferon over other antiviral drugs is their high non-selective antiviral activity. This means that such drugs are able to fight all types of acute respiratory viral infections, without additional tests or specifying the strain of the influenza virus.
To prevent undesirable consequences of acute respiratory viral infections in a child, in consultation with a doctor, you can use the antiviral drug VIFERON Suppositories.
It can be used to treat children from the first days of life and expectant mothers from the 14th week of pregnancy.1
How do VIFERON Candles work?
The drug VIFERON Suppositories (suppositories) contains human recombinant interferon alpha-2b and has antiviral and immunomodulatory properties. It prevents the multiplication of the virus in the human body, which ensures the prevention and treatment of viral and other diseases.
Since the drug VIFERON Suppositories (suppositories) has a wide spectrum of antiviral activity, it is a universal remedy against influenza and ARVI. This drug helps fight infection at any stage of the disease. VIFERON provides a powerful antiviral effect and allows you to shorten the overall duration of the disease, quickly cope with the manifestations of infection (runny nose, cough, weakness, fever, etc.), and also reduces the likelihood of developing complications and subsequent diseases. 2
You can also use the drugs VIFERON Gel and VIFERON Ointment to treat children.
For the treatment of ARVI in children from 1 year to 2 years old, VIFERON Ointment 2500 IU (1 pea with a diameter of 0.5 cm) is used 3 times a day, for children from 2 to 12 years old - ointment 2500 IU (1 pea with a diameter of 0.5 cm) 3 times a day. .5 cm) 4 times a day, for children from 12 to 18 years old - ointment 5000 IU (1 pea with a diameter of 1 cm) 4 times a day. The duration of treatment is 5 days.
VIFERON Gel can be used for the prevention and treatment of children from the first days of life. In order to protect your child from colds and flu, it is necessary to apply a strip of gel approximately 0.5 cm long to the nasal mucosa 2 times a day as a preventive measure. Course duration is 2-4 weeks. For the treatment of ARVI, including influenza, including those complicated by a bacterial infection, the application of VIFERON gel must be repeated 3-5 times a day for 5 days.
Reference and information material
Author of the article
Belyaev Dmitry Alexandrovich
General doctor
- VIFERON Suppositories are approved for use by children from the first days of life and pregnant women from the 14th week of pregnancy, VIFERON Gel - by children from the first days of life, there are no restrictions for use during pregnancy, VIFERON Ointment - from 1 year, there are no restrictions for use during pregnancy.
- Nesterova I.V. “Interferon drugs in clinical practice: when and how,” “Attending Physician,” September 2021.
Loading...
Take other surveys
Tunnel consciousness, panic attacks
Among the signs of coronavirus in people with severe forms of the disease is tunnel consciousness. A person cannot concentrate on anything. He focuses only on the disease and the fears around it. He does not focus on recovery, “here and now,” but obsessively searches for the reason why he got sick, suicidal thoughts are possible.
Among the mental manifestations of coronavirus are panic attacks . Women suffer from panic attacks twice as often as men.
A panic attack is not just a feeling of anxiety, but pronounced fear, which is accompanied by a number of physically unpleasant sensations. Among them are increased sweating, trembling of fingers (tremor), nausea, upset stool, and chest pain.
The most informative evidence that this is a symptom of Covid or a classic panic attack is obtained by a test (smear), but there are also a number of other signs. The role is played by whether such signs are observed for the first time and how long the panic attack lasts. If this is a true panic attack, and not a symptom of COVID, then 15 minutes after the onset of the attack the person begins to “let go,” especially if you take deep breaths.
With COVID, this exercise most often does not help. After all, the reason is a lack of air, depression of respiratory function, and in this case only saturation of the lungs with oxygen helps to cope with the attack.
Headache
8% of COVID-19 patients have headaches. Their intensity is quite strong even if there is no high temperature at the same time.
As a rule, ordinary antispasmodics, painkillers such as nemisulide, analgin for pain arising from COVID do not help much.
With such pain there are no other typical signs for other pathologies (for example, dizziness, as with hypertension, vegetative-vascular dystonia). However, the nature of headaches with Covid is also of a vascular nature. The virus negatively affects vascular endothelial cells. There are problems with blood flow. The lumen of blood vessels narrows significantly. A headache in this case is a signal of a lack of oxygen. And if this deficiency is replenished, then the headache problem is solved.
By the way, when pathologists autopsy the bodies of those who died from coronavirus and micrograph the brain, sharply narrowed blood vessels and signs of inflammation are visible. The vessel becomes unable to properly supply the brain with blood.
And also, as practice shows, about 1% of headaches during a pandemic are completely false. Suspicious people experience headaches when reading news about coronavirus, hearing news that one of their friends has contracted coronavirus (even if there was no contact with him).
How to influence COVID symptoms with breathing exercises?
Exercises that are aimed at optimizing air exchange in the alveoli of the lungs also help to reduce a number of symptoms (if the disease is not severe) or increase the speed of treatment in severe forms of the disease.
Exercises based on quick short breaths of air through the nose and passive exhalation give good results.
In addition to the fact that exercise saturates the body with oxygen, blood circulation improves and lymphatic drainage is put in order. Breathing exercises are also useful for combating inflammatory processes. The optimal option is about 30-40 breaths, 3-6 seconds of rest and cyclic repetition of the exercises 3-4 times. It is best to do exercises in a well-ventilated area on an empty stomach, or if you feel very weak, 1.5-2 hours after eating.
Hypertension is a contraindication for performing breathing exercises. Exercise can further raise your blood pressure.
What to do first when symptoms appear
The first and most important thing is self-isolation. If symptoms of Covid are detected, it is necessary to limit contact as much as possible and inform your family doctor about the symptoms. He will order a COVID-19 test to ensure the presence or absence of infection. If Covid is confirmed, the doctor will select treatment tactics, and the carrier will need to remain in quarantine for the prescribed time. Self-isolation ends when you take the test again with a negative result.
Other important recommendations for those exposed to coronavirus:
- try to get plenty of rest so that your body has the strength to fight the disease;
- eat a healthy diet and drink enough fluids;
- follow the correct daily routine;
- Monitor the humidity in the room so that it always remains at the optimal level.
And be sure to follow all doctor's instructions.