In Germany, in connection with the coronavirus, the Ministry of Health advised all older people to be vaccinated against pneumococcal infection (an infection that causes a number of diseases, including pneumonia). This advice has led to a shortage of this vaccine in the country. The Russian Ministry of Health did not give such recommendations.
In any case, it is important to understand: Prevenar 13 and Pneumo 23 protect against diseases caused by pneumococcus
—
they will not help against coronavirus
. Let us remind you that there is no vaccination against covid yet. However, there is an opinion that immunization against pneumococcus will protect against a number of complications. For example, pneumonia that developed against the background of covid19 will not be joined by a bacterial pneumococcal infection, which means there will be fewer complications.
Therefore, the hero of our conversation today is Prevenar.
Description of the drug
The Prevenar vaccine is a drug for the prevention of pneumococcal infection in children starting from 2 months and adults.
Pneumococcal infection is one of the leading causes of child mortality; 800 thousand children under 2 years of age die each year worldwide due to pneumococcal infection. Pneumococcal infection causes a number of dangerous diseases, such as meningitis, pneumonia, bronchitis, otitis media, septicemia, sinusitis, and endocarditis. Often pneumococcal infection occurs in the form of a “regular” ARVI, which complicates diagnosis and increases the risk of developing life-threatening conditions. Vaccination against pneumococcal infection is aimed at preventing the disease, as well as reducing complications from pneumococcal infection and deaths. Indications for use
Prevention of diseases caused by Streptococus pneumoniae (serotypes 1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 18C, 19 A, 19F and 23F), including sepsis, meningitis, pneumonia, bacteremia and otitis.
The vaccine is intended for use from 2 months of age.
Pneumococcus: do we need a vaccine?
Pneumonia is an infection caused by streptococci. Most often, pneumonia occurs in children who go to kindergarten. Western experts have been creating a vaccine for a long time to protect our offspring from this infection. The resulting product was immediately approved by WHO and introduced into national vaccination calendars. However, more and more European doctors began to wonder: is this vaccine really necessary?
Text: Tatyana Lapshina, pharmacist, biochemistry teacher (Moscow)
Main cause of pneumonia
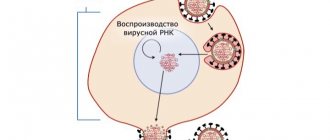
The culprit in the development of the disease is pneumococcus (more precisely, the bacterium Streptococcus Pneumoniae
). Its active life in our body leads not only to the development of pneumonia, but also causes the appearance of bronchitis, sepsis, meningitis, and otitis media.
The bacterium primarily affects children under two years of age (their protective system has not yet formed) and older people (their immunity is weakened due to age).
The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets: when talking, sneezing, coughing. It turns out that one sick person in a room can infect a large number of people. It can be difficult to eliminate pneumococcus with antibiotics - the microorganism is too resistant. This state of affairs prompted the medical world to create a pneumococcal vaccine that can protect us and our children from terrible diseases.
Russia and the pneumococcal vaccine
For a long time, immunization of our children against pneumococcus was carried out only for certain indications: for example, if the child is often sick or goes to camp or kindergarten.
Abroad, the situation was different - in most countries, vaccination was included in national calendars.
The Ministry of Health made a decision in accordance with WHO requirements: in January 2014, the pneumococcal vaccine was included in the vaccination schedule. Starting this year, all children are subject to immunization.
Important: Vaccination, according to recommendations, should be carried out three times: in the first year of life twice (at 7 and 9 months) and in the second - once.
The other side of the coin
In most cases, the vaccine is well tolerated by children. Rarely, but side effects occur - redness at the injection site, swelling or the appearance of irritability and temperature. These symptoms disappear after some time.
Other news causes great concern - Western doctors are skeptical about the effectiveness of such vaccination. Discussions reach the point where the vaccine is considered a dummy, saying that it is useless to do it. A number of experts believe that the need to use the pneumococcal vaccine should be checked again - supposedly previous studies were conducted incorrectly.
The information coming to us from the West raises concerns. The “life” of pneumococcus in the United States is burdened by vaccination - the incidence of pneumonia falls every year. In such a situation, other bacteria are not going to sleep and take up the vacant space in the body of children, causing the development of a more serious disease - empyema (accumulation of pus in body cavities). According to one study, hospitalization of children with this diagnosis in the United States increased by 70% (between 1997 and 2006). Scientists believe that the reason lies precisely in the use of the pneumococcal vaccine.
Thus, the question of whether to vaccinate against pneumococcus remains open.
As it turns out, debate about the effectiveness and safety of the vaccine is just beginning to gain momentum. On the one hand, a significant drop in the incidence of pneumonia is observed abroad, noting the high role of vaccination. On the other hand, scientific minds claim that this fact requires further evidence - new research according to a different scheme. But the worst thing is the activation of other bacteria that “decided” to occupy the vacated niche. More time and new research is required.
Photo thinkstockphotos.com
Vaccination scheme
- Children aged 2-6 months: individual immunization: 3 doses with an interval of at least 4 weeks between doses. The first dose can be administered from 2 months. Revaccination is carried out once at the age of 11-15 months. Mass immunization of children: 2 doses with an interval of at least 8 weeks between administrations. Revaccination is carried out once at the age of 11-15 months.
- Children aged 7-11 months: 2 doses of the drug with an interval of 1 month or more. Revaccination is carried out at the age of over 1 year.
- Children aged 12-23 months: 2 doses of the drug with an interval of at least 2 months. Revaccination is not carried out.
- Children over 2 years old: 1 dose of the drug. Revaccination is not carried out.
Disclaimers
- — I do not have a medical education.
Perhaps the article contains factual errors - it does not pretend to be scientific, it is rather an attempt to share information in the form in which I found and understood it. - — I am not an affiliate of
Allegris, the producers of Menactra, etc., this is the independent point of view of an ordinary average mother with a slightly inflated degree of paranoia. - — With this material, I do not call for vaccination
of its opponents, whose opinion I respect just as much as I do not call for vaccination with imported drugs for those who have chosen domestic vaccines. The article is more likely for those who have decided for themselves that vaccinations are necessary, but are still in doubt about Menactra specifically and are studying reviews.
How is vaccination carried out?
Vaccination is carried out in a vaccination room, in compliance with all sanitary requirements. All drugs are certified. A certificate for the drug is provided upon request.
Without reminders, before vaccination, the medical worker must show the drug and the expiration date of the vaccine.
Only sterile and disposable instruments are used. The vaccination must be carried out using disposable medical gloves.
On the day of vaccination, the child is examined by a pediatrician and the temperature is measured. In the absence of contraindications, vaccination is carried out. Information about the vaccination performed is entered into the card, vaccination certificate, and detailed recommendations for caring for the child in the post-vaccination period are given.
Before vaccination, the doctor will answer all your questions. Be sure to bring information about previous vaccinations to your appointment!
Please note that vaccination of a child, Mantoux test, Diaskintest can only be carried out in the presence of parents or legal representatives of the child (guardians), or if the accompanying person has a NOTARIZED power of attorney to carry out the manipulation (indicating the drug planned for administration) . Otherwise, vaccination will be denied. We comply with the laws of the Russian Federation.
Only here!
And now what this article was intended for.
Since the RuNet turned out to be useless, I studied English-language materials - the manufacturer’s website, mom’s forums, even scientific studies I came across. It is these findings that I would like to share in a brief retelling.
- - In 2006, there were reports of Guillain-Barre Syndrome occurring within 6 weeks of Menactra vaccination, but a large 2012 study of more than 2,000,000 people who received the vaccine found NO increased risk of Guillain-Barre Syndrome. .
- - here is an article that cases of fainting have also been reported after vaccination with Gardasil and some other vaccine unknown to me, they do not have a common component, but the age of administration is the same (teenagers), and the opinion is expressed that the reason is not the drug, but in the procedure itself, which causes discomfort in emotional teenagers. The main danger of fainting is injury from a fall.
- — vaccination is mandatory and free for all 7th grade schoolchildren; without it, they may not be accepted into summer camp. Then, after three years (at 16-18 years), a repeat (booster) dose is administered to consolidate the effect. Students living in New Jersey residence halls are required to be vaccinated against Meningococcus.
- — I was unable to find negative reviews about vaccination besides official reports about fainting, Guillain-Barre Syndrome and others.
The English-language Internet, if not completely reassured me, at least reduced my doubts.
However, I, of course, again dashed off a list of questions, among which were such as “What drugs to relieve the rash” (“Give Suprastin”), “What to give if there is vomiting” (“Can you give Motilium”), what -more, after which Alexander Petrovich advised me to drink valerian and went with me to read the instructions in search of the adverse reactions I mentioned (“Where did you even read about all these horrors?” - “On the official website But they don’t have a website” - “ Yes, in English”) while the nurse took out and prepared the vaccine. The instructions indicate the frequency of side effects, after studying which Alexander Petrovich commented: “Their frequency is comparable to the frequency of side effects of Placebo. During the period of observation of patients after vaccination during clinical trials, vomiting or rash may have occurred due to the person being poisoned, for example, however, this should also be recorded in the report. Don’t worry, the vaccine is very well tolerated, it’s lighter than Pentaxim.”
Update from January 16, 2017
Immediately after the publication of the article, I sent a link to it to the Allegris MC in order to receive comments from competent medical professionals in case I got something wrong and was misleading readers. To my pride, I received a review that did not contain corrections, but there was a comment on the merits, I quote it in its entirety:
«I value the opinion of a thinking mother, especially one so erudite and inquisitive. The only thing I’ll explain is the price of the drug, which depends on the delivery batch. The shorter the residual shelf life, the lower the retail price. That's why we even have Promotions at more attractive prices. Perhaps the pharmacy offers a time-limited vaccine. I usually don’t bully parents about our price list. If there is an opportunity to get vaccinated yourself at a more comfortable price, I always welcome it.
» DMN, Cherdantsev A.P., MC Allegris.
Possible side effects
In children 6 weeks to 17 years of age, the most common side effects are irritation, redness or swelling at the injection site, irritability, decreased appetite, decreased or increased sleep, and fever.
Serious but very rare side effects in infants and toddlers include pneumonia, bronchiolitis and gastroenteritis (inflammation of the stomach and small intestine) (0.9% of all vaccine recipients). A temporary pause in breathing after vaccination occurs in some babies born prematurely.
The high safety of vaccination has been confirmed by 230 million years of experience in administering Prevenar over the past 10 years. The vaccine is registered in 88 countries and is included in the national vaccination calendars of 30 countries.
Come get vaccinated at MAMARADA. A full range of vaccines for children and adults, family vaccinations - at a special price!
Contraindications
Only a doctor can decide whether Prevenar is suitable for a child to be vaccinated
Prevenar vaccination is contraindicated if there is a history of an allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine, as well as in the following cases:
- Hypersensitivity reactions to previous administration of Prevenar drugs (including anaphylactic shock, severe generalized allergic reactions);
- Hypersensitivity to diphtheria toxoid and/or excipients;
- Acute infectious or non-infectious diseases, exacerbation of chronic diseases (vaccination is carried out after recovery or during remission).
- If an acute or exacerbation of a chronic disease occurs, the child receives a deferment until complete recovery or a period of remission. The pediatrician determines the required duration of delay from vaccinations, guided primarily by the risk of complications. In most cases, the delay is about 1 month. In case of meningococcal meningitis and other severe diseases of the nervous system, vaccinations are postponed for a longer period - up to six months from the onset of the disease.
- The main contraindications to vaccination, which provide grounds for medical withdrawal from vaccinations, are strong reactions and post-vaccination complications after the administration of the previous dose of the vaccine. A strong reaction is understood as an increase in body temperature above 40 °C with the occurrence of swelling and redness at the site of vaccine administration over 8 cm in diameter, severe allergic reactions, anaphylactic shock, the development of infectious diseases and damage to individual body systems.