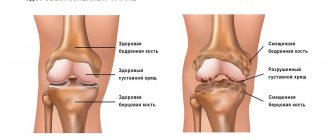
Many urological and gynecological diseases in the initial stage proceed slowly and cause almost no concern to the patient. Among the main signs that are not usually paid attention to, swelling of the limbs and face comes first. This symptom is often not associated with pain, so it is unfairly ignored, but in vain!
What is edema and how does it form?
The content of the article
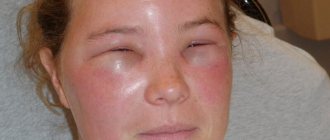
Edema is the swelling of tissue caused by excess fluid, which for various reasons has nowhere to go. Although swelling can occur on any part of the body, the abdominal area is often swollen, but the problem is especially noticeable under the eyes, on the arms, and in the ankles of the feet.
Swelling occurs when small blood vessels become leaky and leak fluid into nearby tissue. Excess fluid accumulates, which leads to swelling of the body area. If the swelling is concentrated in certain areas, it is called peripheral edema. Common signs of peripheral edema include the following:
- The arm or leg begins to get heavier and increase in volume.
- When you press on the swollen area, a dent is formed.
- Clothes and jewelry begin to fit tightly and awkwardly.
- The skin next to the swelling is hard or too warm, and at the site of the swelling it is stretched or shiny.
- It is more difficult to bend limbs in joints that are affected by swelling.
- There may be a feeling of tightness or even pain.
The severity of symptoms depends on the size and cause of the swelling. Swelling from infection or inflammation, such as from an insect bite, may not cause any symptoms. When an allergic reaction occurs, for example to a bee sting, severe swelling of the throat may begin, which can lead to death.
Short-term swelling of the legs can cause fatigue when walking, while regular swelling that impedes circulation leads to skin ulcers.
Pulmonary edema causes shortness of breath, and at the same time the level of oxygen in the blood decreases. Severe pulmonary edema is life-threatening.
Causes of swelling that can be eliminated
The causes of edema can be very diverse.
- One of the most common causes of edema in healthy people is drinking a lot of fluid before bed.
- Swelling on the face can occur if a person slept in an uncomfortable position, with the head lying lower than the feet.
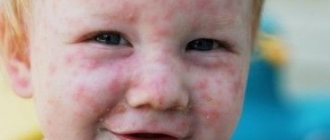
- Often, swelling of the face is the result of an allergic reaction to foods: honey, citrus fruits, strawberries, chocolate, fish and others.
Sometimes even frequently used, well-known medications act as allergens, which, by the way, should be taken into account once again by those who like to take medications without a doctor’s prescription. Finally, swelling can be a manifestation of an allergic reaction to grass and tree pollen, house dust, household chemicals and cosmetics.
Therefore, if swelling on your face has recently appeared, think about what has changed in your environment. A new carpet appeared or the bed was moved next to a bookcase with old books. Or bought another toothpaste, or maybe some other cosmetic product.
Or have you finally decided to read the latest evening newspapers at night? And undried printing ink can also be an allergen.
Causes and forms of peripheral edema
Swelling can occur for various reasons, and they all affect health, so if you notice a problem, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Edema may be associated with:
- With premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
due to changing levels of estrogen hormones. - With complications of pregnancy
. During pregnancy, the body retains more sodium and water than usual due to the fluid demands of the fetus and placenta. This increases the risk of developing edema. - With chronic and severe pathologies,
for example,
lymphedema, liver cirrhosis
. With liver damage, fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity (ascites). - With deep vein thrombosis
. In chronic venous insufficiency, the one-way valves of the veins in the legs are weakened or damaged. Sudden swelling of one leg accompanied by muscle pain may be caused by the formation of a blood clot. - With congestive heart failure
, in which one or both lower chambers of the heart lose their ability to pump blood effectively. Congestive heart failure causes swelling in both the abdomen and lungs (pulmonary edema), leading to shortness of breath. - With the influence of medications taken.
Swelling can be caused by blood pressure medications, non-steroidal and steroidal medications (NSAIDs - ibuprofen, naproxen), hormonal medications containing estrogens, calcium channel blockers, diabetes medications - thiazolidinediones, corticosteroids (prednisolone and methylprednisolone). The side effect is usually mild swelling of the legs. - With an allergic reaction.
Swelling is a manifestation of most allergic reactions. In response to allergens, blood vessels leak fluid into the affected area. - With burns and life-threatening infections
. In this case, the whole body swells. - With pathologies of the lymphatic system
. The lymphatic system helps remove excess fluid from tissues. If the system is damaged, for example due to cancer, the lymph nodes and lymphatic vessels begin to work incorrectly. - With severe, long-term protein deficiency
. Long-term dietary protein deficiency leads to fluid accumulation and swelling.
Very often edema is associated with kidney problems
, in this case, the legs and area around the eyes swell. Damage to the small filtering blood vessels in the kidneys leads to nephrotic syndrome, which is associated with a decrease in the level of albumin protein in the blood. Albumin and other proteins act as a sponge to retain fluid in the blood vessels. Low albumin levels are called hypoalbuminemia.
General swelling or swelling caused by water retention
Signs of this type of edema include swelling of the arms, legs and/or face. This type of swelling is temporary and goes away without treatment. The causes of general swelling are prolonged periods of inactivity, drinking alcohol or eating too salty foods.
SELF-MASSAGE AND LYMPH DRAINAGE
Massage is used to move the lymph flow from the original (non-contracting) lymphatic vessels to the deeper muscular (contracting) lymphatic vessels. Most patients with lymphedema after mastectomy have some degree of swelling extending from the beginning of the arm to the upper torso. If signs of swelling are observed in the armpit, then it can be assumed that the process has already affected the upper part of the body. Edema of the trunk may also be seen in patients with lymphedema of the legs.
Massage is the only way to deal with swelling of the torso (as a result, lymph can drain more freely from the swollen limb). It is necessary to train the patient and/or caregiver in massage techniques and provide them with instructions with pictures. A massage of the torso and limbs usually takes about 20 minutes.
Manual drainage of lymph is based on a special technique (more complex than massage), so this is usually done by specially trained therapists, but their services are quite expensive, and therefore they are usually not consulted unless absolutely necessary.
Diagnosis of edema, which doctor to contact
If you notice swelling, you need to visit a doctor. Women should see a gynecologist, and men should see a urologist, since the main causes of this condition often lie in these areas of medicine.
To understand what may be causing the swelling, your doctor will perform a physical examination and order tests. You must submit:
- Analysis of urine;
- blood chemistry;
- hormone tests.
Also held:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands;
- comprehensive pelvic ultrasound.
Further, based on the test results, a comprehensive ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, ultrasound of the thyroid gland and other studies may be prescribed.
Swelling due to kidney disease
Proteins (proteins) retain water in the body. Proteins are an important building element; they restore muscle tissue, heal wounds, maintain water-salt balance, and promote the production of antibodies. When protein breaks down, it forms an amino acid, which enters the bloodstream. The unused amino acids are then broken down into water, ammonia and carbon dioxide. Ammonia is toxic, so it is sent for processing to the liver, where it is “neutralized” and becomes urea. It enters the kidneys and from there enters the bladder along with urine.
Sick kidneys cannot completely remove protein breakdown products from the body, so the protein ends up directly in the urine. A disease called proteinuria develops. It is characterized by the fact that large protein particles pass through damaged or dilated kidney tubules.
Dilation of the tubules indicates a disease such as a spongy kidney with small cysts inside the tubules. Calcified grains of sand and small stones form in the cystic cavities, which are washed further into the renal pelvis. Often the disease develops unnoticed because the kidney is functioning normally. However, any inflammation or passage of large stones leads to severe pain or the development of inflammation - pyelonephritis.
It is the protein in the urine that indicates the development of a spongy kidney. Normally, there should be no protein in the urine. The exception is a protein diet, in which a slight loss of protein in the urine may occur. But severe swelling coupled with protein in urine indicates pathology of the renal tubules.
Edema in renal failure
Kidney failure is characterized by a decrease in the level of albumin, a protein found in the blood. It maintains the level of fluid in the blood vessels, and in case of kidney failure, fluid enters the soft tissues of the body. They swell, especially loose tissues - eyelids, ankles, feet - are affected. From edema, characteristic of heart disease, renal edema is characterized by a distribution from the face downwards and appears in the morning hours. They are especially visible under the eyes; the skin on the eyelids becomes dry and pale.
Swelling due to infectious infection of the urogenital tract
Pyelonephritis is a bilateral infection of the kidney, leading to inflammation and structural changes in the organ. The infection enters the kidney through the urethra. Women are more often susceptible to the disease because, due to their physiological characteristics, their canal is shorter than that of men. Pathogenic microbes penetrate from it faster. With pyelonephritis, the kidney tissue becomes inflamed, leading to kidney failure. The organ cannot filter urine, and toxins are retained in the body.
With pyelonephritis, swelling is especially noticeable in the morning. After waking up, swelling is noticeable in the upper half of the body - on the face, neck, under the eyelids. By the evening they go away on their own, but in the morning the problem returns again.
Edema in cancer
Swelling in oncological diseases is very pronounced. With cancer, a lot of transudate is formed in the body under the skin, causing swelling of the legs, face, and peritoneum. The formation of swelling also contributes to:
- Metastases in the liver. They prevent the organ from functioning normally. Toxins accumulate, disrupting water-salt metabolism.
- Cytostatic drugs , which slow down the process of cell division and renewal, weaken the immune system, which also results in fluid stagnation.
- Steroid and non-steroidal hormonal drugs fight inflammation, but also cause allergies. Often taking anti-inflammatory drugs is accompanied by urticaria, in special cases there is angioedema.
- Hormonal treatment leads to the development of hypertension, even if the patient has not previously suffered from this disease. The patient's blood pressure increases due to the narrowing of the lumen of the arteries and vessels, the walls of the vessels thicken. The heart has to pump more blood and contracts more often. as a result - swelling of the face and body;
A tumor of a certain organ is accompanied by swelling in the corresponding part of the body.
Edema in lung cancer
Fluid from the blood penetrates through the permeable walls of blood vessels into nearby tissues. At the initial stage of the disease, swelling is not expressed, there is a decrease in the volume of urine excreted and slight weight loss. Then the patient’s legs swell, the skin on the feet dries out and peels off. When pressed for a few seconds, fingerprints remain.
Swelling in breast cancer
It is characterized by lymphostasis - stagnation of lymphoid fluid caused by an increase in the soft tissue of the chest and impaired lymph microcirculation. Lymphostasis provokes the formation of trophic ulcers and sepsis in case of inflammation of the skin at the site of the tumor. If the tumor rises higher, the entire face swells. The patient's vision is impaired and it is difficult for him to turn his head.
Edema in liver cancer
The disease is accompanied by blockage of the inferior vena cava by a thrombus and destruction of the lymph nodes. For this reason, the lumbar region swells, and later the swelling moves down to the legs.
Abdominal cancer. It is characterized by ascites, an accumulation of lymphatic fluid in the abdominal cavity. The abdomen increases significantly in volume, the navel protrudes. Ascites is accompanied by severe shortness of breath, flatulence, respiratory and cardiac dysfunction.
Edema due to endocrine disorders
With hyperglycemia, blood vessels and arteries are especially affected. They become more permeable and less elastic. Due to the high concentration of glucose, nerve endings die, especially the vessels of the lower extremities, which bear a heavy load, suffer. The most terrible consequence of poor circulation in the extremities is diabetic foot. In advanced cases, gangrene develops, and the patient's leg is amputated.
Swelling is promoted by disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys (in diabetes, water-salt metabolism is disrupted, protein is excreted along with the urine). With type 2 diabetes, obesity develops; excess weight increases the load on the legs.
Myxedema, a significant decrease in the production of thyroid hormones, causes severe swelling. it is different from the characteristic signs of heart or kidney failure. The swelling with myxedema is dense and elastic, affecting not only the skin, but also the trachea and vocal cords. The skin is hot and dry to the touch, the voice changes, and breathing becomes difficult.
PHYSICAL EXERCISE FOR LYMPHOEDEMA
Special exercises will help improve lymphatic drainage, prevent fibrosis, increase the tightening effect, expand the range of motion of swollen limbs, and help prevent stiffness of the joints. Patients should be encouraged to move the swollen limb as often as possible because muscle contraction stimulates both lymph flow and blood circulation. Walking is an excellent exercise. If it is impossible to perform active movements, then the patient should perform passive physical exercises at least twice a day.
It must be remembered that too vigorous, strenuous exercise can sometimes be harmful, as it causes dilation of blood vessels and increases lymph flow. Patients with swollen feet should not sit or stand for long periods of time. Activities such as moving heavy objects should be avoided as they reduce blood and lymph flow.
The arms should not be raised at an angle of more than 90 degrees, as this position reduces the space between the collarbone and the first rib and impairs blood circulation, which can lead to increased swelling.
Continuous use of arm support wraps should be avoided as this may cause stiffening of the shoulder and elbow joints. A wide arm support bandage can be used while the patient is walking, but should be removed when the patient is resting (the arm can be placed on a pillow). The sling can also be used to support a paralyzed arm, to prevent subluxation or dislocation of the shoulder joint, or when the back muscles are severely weakened.
Treatment of edema
By taking medications to remove excess fluid and reducing the amount of salt in food, swelling can be relieved, but if the underlying condition is not treated, it will immediately return. Therefore, the first task of the doctor is to identify the cause and prescribe treatment to eliminate it. Over time, the symptom - swelling will go away on its own.
If edema significantly worsens the patient’s condition, in parallel with the treatment of the underlying disease, measures are taken to remove excess fluid from the body. The doctor prescribes diuretics - diuretics, herbal decoctions, physiotherapeutic procedures that stimulate the outflow of fluid from tissues.
You cannot take diuretic medications on your own. The outflow of fluid carries away substances that are very important for the body, so by getting rid of edema, you can develop metabolic disorders, problems with the heart, skin, and other pathologies.
PSYCHOLOGICAL SUPPORT
A patient with lymphedema may experience problems associated with changes in body shape, for example, difficulties in choosing clothes and shoes, when moving, problems with personal hygiene, sexual problems, difficulties in preparing food, and in spending leisure time.
Since lymphedema is chronic, the patient needs constant support, counseling and training, since in order to achieve a positive result, the patient’s desire to improve his condition and carry out daily self-care is very important.
Where to get tested, undergo an ultrasound and recover from edema in St. Petersburg
If you find swelling on any part of your body, we invite you to undergo examination at the Diana specialized clinic. Here you can take all the tests, undergo a comprehensive expert ultrasound (costs only 1000 rubles) and consult with a gynecologist, urologist, endocrinologist or oncologist. The cost of seeing these doctors in St. Petersburg is 1000 rubles.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter