Almost every person has experienced the unpleasant sensation when, having almost fallen asleep, he suddenly shudders and wakes up. The movements are very sharp, reminiscent of an electric shock, sometimes with a large amplitude. In the medical community, this phenomenon is called hypnagogic twitching or nocturnal myoclonus.
Night shudders when falling asleep
Startling when falling asleep and during sleep is familiar to many. This occurs especially often when falling asleep. Considering the phases of sleep, this phenomenon occurs at the moment when a person feels asleep. With a sharp contraction of the muscles, he wakes up again. Not everyone likes it, but it is not a pathology, except in exceptional cases. If you experience convulsions with sudden, irregular jerking of the limbs or other pain or spasms, you should consult a doctor.
Description of symptoms
A sign of myoclonus is an involuntary startle at the moment of falling asleep or during sleep, which does not have a regular sequence. It does not cause physical pain, but it disturbs sleep. A person wakes up from the fact that his body in one part or another makes an involuntary jerk. Most often, the muscle contraction leading to this movement occurs in the extremities, usually the lower ones. Hands shake much less often.
Sometimes there may be trembling of the whole body. Especially rarely, the action occurs in the area of the tongue or soft palate.
The intensity of movements can vary, from a slight wince to a jerk. The latter can lead to hitting the wall (if the bed is not located in the middle of the room).
Myoclonus syndrome occurs in both adults and children. Even infants can react this way to a sound or color external influence (thunder, flash of light).
Explanation of the syndrome
Why a person shudders in his sleep is not an idle question. A large number of people face this phenomenon. Doctors identify several causes of the syndrome:
- heavy physical exertion on the shuddering muscle group;
- nervous stress that preceded falling asleep;
- emotional outburst;
- stopping taking sedatives or sleeping pills;
- decrease in oxygen content in the air.
In addition to benign myoclonus, there is a malignant variety. In this case, involuntary flinching may be caused by:
- cerebrovascular diseases;
- head or spine injuries;
- suffered micro-strokes;
- disorders of the kidneys or liver.
The type of myoclonus can only be determined by consulting a doctor. Trembling associated with serious illnesses is often accompanied by cramps and other painful sensations, which indicates the need to visit a specialist.
What do the doctor's say
If all the above recommendations do not bring a positive result and the night jerks develop into constant trembling, you need to seek help from a doctor. He will carry out diagnostics using the following methods:
- electroencephalography is used to study brain activity;
- to determine the level of urea, creatinine and blood sugar, a biochemical analysis is indicated, which also helps to identify disorders of the functionality of the pancreas and kidney function;
- To visualize the processes, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging and radiography are prescribed.
When the number of cases of limb twitching increases, the neurologist may decide to admit the patient to the neurology department. The need for this arises when, as a result of a previously conducted examination, it is impossible to determine the cause of the deterioration of a person’s condition.
When medical help is needed
What causes night tremors? Mostly, this condition is mainly associated with people’s lifestyle. It is enough to reconsider your lifestyle, eliminate provoking factors, and therapeutic therapy is not needed, since over time the seizures will completely disappear.
Sometimes people complain of excruciating cramps and severe pain that disrupt their night's rest. Such conditions require multi-stage therapeutic treatment. To stop the occurrence of shudders, the following is recommended:
- Identification and correction of the underlying pathology that provokes myoclonus. As a rule, at the first stage, metabolic disorders caused by failure of biochemical processes are eliminated. In this case, the defect is concomitant with arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus and myocardial ischemia;
- If the body is shaken by epileptic tremors, taking anticonvulsants is recommended;
- General restorative therapy, which includes sedative medications, will be useful. Take them in courses for no more than a month and take a break after each;
- If convulsions are provoked by prolonged drinking, you will need to undergo a therapeutic course to relieve alcohol intoxication;
- For cortical myoclonus, complex therapy will be required, including the use of potent medications such as brain stimulants, corticosteroids, antipsychotics and sedatives.
To obtain positive dynamics of treatment, the correct therapeutic regimen and its strict adherence are important.
Well, we looked at why night tremors are disturbing and how to overcome this condition that causes discomfort. It remains to be noted that reviews from many people indicate that it is the wrong lifestyle that provokes night cramps; by reviewing this, you will get rid of this trouble forever.
Types of spasms and twitching
At the moment of falling asleep, the body relaxes, and the brain classifies this fact as dangerous. A sharp muscle twitching becomes a triggering mechanism, a reaction to danger. Excessive muscle tension can also lead to involuntary winces. Convulsions during sleep are of various types:
- synchronous and asynchronous;
- rhythmic and arrhythmic;
- spontaneous;
- reflex.
Experts classify involuntary muscle spasms as
- myoclonic jerks;
- hypnogogic convulsions;
- restless legs syndrome;
- sleep paralysis
Let's figure out what is unique about each type. Is the “shudder and wake up” state dangerous for the body?
Myoclonic jerks
Irregular twitching that does not have a constant location is characteristic of people suffering from epilepsy. It often occurs in older people and is associated
- with neuroses;
- decreased amount of oxygen in muscle tissues;
- age-related degenerative changes occurring in cells.
Muscle contractions can occur in individual parts of the body (legs or arms, facial muscle contractions are possible) or cover it completely. The location of seizures often changes. The danger of myoclonic twitches lies in their ability to progress.
Involuntary muscle contractions (myoclonus) can occur not only at rest, but also during movement.
Hypnogic seizures
This type of involuntary movement, when the legs move when falling asleep, is still being studied. Experts have not come to a definite conclusion about the cause of their occurrence. According to the results of recent studies, it was discovered that involuntary spasms occur when the cervical vertebrae relax at the moment of falling asleep. The nerve fibers leading to the muscles simultaneously become excited, and the person feels a sharp spasm, leading to awakening.
Restless legs syndrome
The phenomenon is typical for middle-aged and elderly people and has a precise location. Unlike previous varieties, the cause of the movements produced is an unpleasant sensation that occurs in the lower extremities: burning, pain. To relieve the feeling of discomfort, a person begins to make involuntary movements with his legs. The disease can progress, and as a result, movements begin to be made with the hands. The syndrome occurs either as a result of acquired health problems or at the genetic level.
Sleep paralysis
This disease phenomenon is distinguished by the fact that the body does not produce sudden shudders, but on the contrary, the person does not have the ability to make them. The brain realizes the need to perform certain movements when waking up, but the body refuses to obey the ongoing impulses. Sleep paralysis does not cause a sudden awakening. Attacks occur only upon normal awakening after sleeping on your back. Doctors believe that stress and an inactive lifestyle are prerequisites for the appearance of sudden numbness.
Did you know that in medieval Europe people were subjected to the Inquisition due to sleep paralysis?
Restoration of motor function will occur when the brain is fully involved in work and is aware of what is happening. At this stage, you can begin to slowly move your tongue, eyes, limbs, starting with your fingers. Having managed to raise your head, you can try more active movements.
Differential diagnosis
The cause of involuntary shuddering when falling asleep can only be determined by differential diagnosis. Modern equipment makes it possible to identify diseases with similar symptoms at an early stage. Only after a full examination, in some cases:
- CT or MRI;
- electroencephalography;
- radiography;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the cervical spine and head;
- ECHO.
Treatment is prescribed individually.
Physiological factors of night twitching
The occurrence of attacks of nocturnal myoclonus, according to scientists, is influenced by various physiological factors.
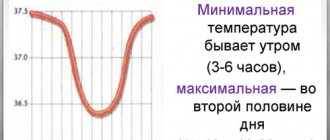
- Sleep phases - during the transition from shallow to deep sleep, the brain receives a motor impulse, to which it reacts with a sharp start.
- Neurophysiology - twitching is caused by the incompatibility of a completely relaxed body and rapid eye movements. The brain gives an impulse that returns the body to activity. Further falling asleep occurs more calmly and evenly.
- Circulatory problems - lead to a decrease in the amount of oxygen in the blood and poor blood supply to the limbs and their numbness. The sharp impulse sent helps to wake up, restore activity and improve blood circulation.
- Physical fatigue after hard work or sports.
- Nervous stress to which a person has been exposed during the day does not allow the body to completely relax when going to sleep.
- Myoclonus associated with a sharp noise or a bright flash of light provokes fear, which ends with a shudder.
- Myoclonus caused by apnea (stopping breathing) - the brain turns on and provokes a wince.
Learn more about the stages of sleep, how much sleep you need to get enough sleep and other interesting facts about your sleep.
Tips on how to normalize sleep
If you experience periodic startling, here are a few tips to help you sleep better:
- Get examined and rule out the cause that is causing the seizures. Get therapy if necessary;
- in some cases, a course of sedatives prescribed by your doctor will be required;
- in the cold season, protect the body from hypothermia;
- often night cramps are a sign of a lack of magnesium, potassium and calcium. To replenish these healthy components, include greens, vegetables and dairy products in your menu;
- You can get rid of this unpleasant condition by limiting your consumption of caffeine drinks. Excessive intake of caffeine increases the heart rate and has a stimulating effect on the nervous system, which leads to tremor;
- Proper preparation for bed will help relax the body and eliminate spasms. To do this, take a bath with herbal infusions;
- do not watch horror films and other similar programs that frighten you at night. Such transmissions cause fear, which in turn provokes night twitching;
- exercise and maintain muscle tone. Light exercise will reduce the contraction that causes cramps. A walk in the fresh air will help you get a good night's sleep;
- Often the culprits of night twitching are loud noises or bright lighting. These factors are especially negative for infants. As a rule, the newborn immediately reacts to them with a wince. A similar reaction occurs in the adult body;
- Develop an optimal rest regime for yourself. Try to go to bed no later than 23:00, otherwise the nervous system will be overexcited, which provokes frequent and severe shudders;
- the sleeping place should be comfortable. Sometimes, on a subconscious level, we jerk our arms or legs to warm up stiff muscle mass.
In most cases, nighttime jerking is not a dangerous sign. Thus, the nervous system reacts to daytime stressful situations and neuroses. However, if twitching occurs regularly, it is necessary to visit a neurologist. Since such a symptom may signal the development of a dangerous pathology.
Pathological factors of myoclonus
In addition to natural physiological causes, shuddering can result from various diseases:
- epilepsy;
- hereditary degenerative problems in the brain stem and cerebellum;
- inflammatory processes in the brain caused by viruses;
- brain pathologies associated with human motor function;
- nervous and mental disorders;
- essential myoclonus (a disease of hereditary origin);
- restless legs syndrome;
- lack of microelements.
For tremors caused by the listed diseases, consultation with a doctor and individually selected treatment is necessary.
Nervous tic
A nervous tic is a muscle contraction that is arrhythmic and involuntary. It can be temporary or permanent. The temporary effect can be caused by strong feelings, fear or a pinched nerve. And a permanent tic is formed due to a lack of microelements after illnesses. Types of nervous tics and hyperkinesis: – Teeth grinding. - Twitching of the wings of the nose. – Brief twitching of the muscles of the limbs. - Shaking head. – Nervous tic from hyperkinesis in sleep.
Ticks are also divided depending on their location: – Local tics manifest themselves in the contraction of one muscle group. – A generalized tic combines the simultaneous contraction of several groups at once, and at the same time they begin and stop simultaneously.
Startles during sleep in children
Involuntary movements in children due to abnormal electrical activity of the brain. It gives signals to muscle tissue. This leads to sudden twitching of the baby. They usually go away with growing up, but sometimes seizures are triggered by diseases:
- meningitis;
- head injuries associated with brain damage;
- intoxications (during treatment);
- brain tumors.
An external stimulus (light or sound) can cause such a reaction.
To find out the reasons, you need to consult a doctor and examine the child. If pathology is detected, urgent treatment is required.
Twitching in children can be caused by high fever. It is easy to identify this reason yourself and take measures to eliminate it.
Why does my nose twitch?
Twitching of the nose and involuntary sniffing are quite often caused by psychological experiences. This type of twitching requires a mandatory visit to a neurologist. If such a tic is one-time in nature, it would be advisable to take sedatives and perform calming breathing exercises. Facial massage will also help eliminate nervous tics if they are associated with overstrain of facial muscles.
Is treatment necessary?
To determine whether treatment for myoclonus is required, it is recommended to consult a doctor if signs of it appear (if the twitching is frequent and causes discomfort). They decide on the need for treatment. In most cases, the problem is solved by eliminating the causes of twitching:
- taking sedatives;
- weakening of physical activity;
- creating comfortable conditions for sleep.
Trembling, unless caused by serious pathologies, is not dangerous. It goes away after eliminating the causes that cause them. When a pathology is identified, it is necessary to treat the disease that is causing the seizures.