Increased calcium in the blood - what could it be?
Theoretically, there are three most likely clinical problems that could cause elevated blood calcium levels. All possible reasons for calcium levels in the blood being higher than normal are quite serious.
The first cause of high blood calcium
is primary hyperparathyroidism, a disease accompanied by the appearance of a tumor in one or more parathyroid glands (it would be more correct to say “parathyroid glands,” but the term “parathyroid glands” is very widely used). The main task of the parathyroid glands in the body is to maintain normal blood calcium levels. The cells of the parathyroid glands “know how” to sense the concentration of calcium in the blood plasma and, in accordance with the level of calcium, produce parathyroid hormone. The main effect of parathyroid hormone is to increase the level of calcium in the blood (by destroying bone tissue and releasing calcium from it into the blood, as well as by enhancing the absorption of calcium from primary urine in the kidneys and enhancing its absorption from the intestines). When a tumor occurs in the parathyroid gland, its cells stop sensing the concentration of calcium in the blood - it “seems” to them that there is no calcium in the blood, or that it is low. Tumor cells begin to uncontrollably produce parathyroid hormone, which sharply increases the breakdown of bone tissue and the release of calcium from it into the blood. As a result, in the laboratory we determine increased blood calcium and at the same time high levels of parathyroid hormone. Most often, such changes are also accompanied by a decrease in the level of phosphorus in the blood and an increase in the level of calcium in the urine. The danger of the disease lies in a decrease in bone density with a tendency to fractures, bone deformation, and decreased growth. An increased level of calcium in the blood leads to the deposition of calcium salts in the walls of blood vessels and heart valves, which reduces their elasticity and increases the tendency to thrombosis, which means the risk of strokes and myocardial infarction.
The second possible cause of elevated calcium
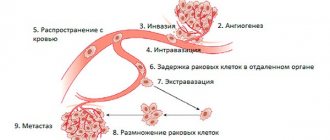
– this is the breakdown of bone tissue due to the occurrence of metastases of a malignant tumor in it. Metastases have a so-called lytic effect, i.e. destroy bone tissue and release calcium salts from it, which enter the blood and lead to increased calcium levels in the blood. In this case, calcium in the blood is increased, but at the same time the level of parathyroid hormone is within the normal range or at the lower limit of normal.
The third possible cause of high calcium levels in the blood
– development of neuroendocrine tumors that produce so-called PTH-like peptides. These tumors are most often located in the lungs, although their location can be very variable. The size of such tumors is usually small - from 4-5 mm to 1-2 cm. They “know how” to produce chains of amino acids, the sequence of which coincides with the active end of parathyroid hormone. Such peptides (they are called PTH-like because they are very similar in action to parathyroid hormone) cause a situation where calcium in the blood is elevated, but laboratory analyzers do not show an increase in parathyroid hormone levels in this case, since PTH-like peptides do not completely copy the parathyroid hormone molecule.
Symptoms
The first signs of hypercalcemia may not be noticeable, and only a random blood test will indicate problems. The appearance of obvious symptoms of increased calcium in the blood depends on the duration of this condition, the rate of development, and the severity of the underlying disease. These symptoms manifest themselves in the main systems of the body: nervous, muscular, digestive, urinary, cardiovascular, eye and skin diseases. The patient's memory deteriorates, lethargy, drowsiness, depression, weakness and muscle pain, restless leg syndrome at night, loss of appetite, constipation, nausea, gag reflex and belching appear. Possible weight loss due to pancreatitis, cholelithiasis, stomach ulcers with high acidity. Arthritis, arthrosis, and gout develop. Hypocalcemia is often combined with a lack of potassium, which leads to excessive excitability of neurons. As a result, muscle spasms occur (shoulders, hands, larynx, facial muscles). Skin sensitivity is also impaired, and a burning sensation or numbness occurs. Hemorrhagic syndrome develops, which is manifested by increased bleeding. Blood clotting decreases. Dystrophic changes in tissues, dental defects, brittle nails, dull hair, dry skin occur, heart rhythm is often disturbed, and cataracts develop.
Blood test for calcium - which one is better?
There are two main types of calcium tests - an ionized calcium blood test and a total calcium blood test. Total calcium includes “free”, ionized calcium not bound to proteins + calcium bound to blood proteins (primarily albumin). The concentration of total blood calcium may change due to changes in protein content in the blood. At the same time, it is not total calcium that has a biological effect, but only that part of it that is not associated with proteins - this part is called ionized calcium. The ionized calcium blood test is more accurate than the total calcium test, but it is also more complex.
– not all laboratories are able to perform this analysis, and if they do perform it, not all do it accurately. There is an almost anecdotal situation when one of the largest laboratory networks in St. Petersburg “chronically”, for years, reveals low ionized blood calcium in almost all patients - and for years the laboratory does not want to correct this obvious laboratory error. But the consequence of such an error is tens of thousands of unnecessary additional studies performed on those patients who are “lucky” to receive such an incorrect analysis.
There are situations when ionized calcium is elevated, but total calcium is normal
– in this case, it is the analysis for ionized calcium that should be “trusted” more. At the same time, in most cases, increased blood calcium is manifested in both analyzes at once - increased ionized calcium and at the same time increased total calcium.
Considering the importance of ensuring maximum accuracy of a blood test for calcium and the high “price” of its incorrect determination, the North-Western Endocrinology Center conducts a blood test for calcium using equipment from the Russian representative office of the German laboratory network LADR. To carry out calcium analysis, an automatic biochemical analyzer Olympus AU-680 (Japan) is used, which provides maximum accuracy of the study and is capable of performing up to 680 tests per hour. Daily checks of the analyzer, the consistently high quality of its work and compliance by all center employees with standards for taking blood for calcium allow doctors of the North-Western Endocrinology Center to be confident in the quality of the blood test for calcium performed by the center’s laboratory. If in the blood test performed by our center the calcium is high, it means that the calcium is really elevated
.
| Automatic biochemical analyzer Olympus AU-680 (Japan) in the laboratory of the Endocrinology Center | Olympus AU-680 analyzer - computer station for processing and transmitting results |
Description
Blood calcium has 3 forms: 2 bound - with anions and albumins and 1 free. Only free form is active.
To accurately determine the proportion of free calcium in cases where there are chronic heart and kidney diseases, the content of albumin protein in the blood serum is determined in order to understand how much calcium can be associated with protein. The normal proportion of calcium compounds with protein is up to 38% of the total. The proportion of calcium bound by anions - bicarbonates, lactates, citrates - is about 10%.
Calcium is required for the following processes:
- muscle contraction;
- maintaining heart rhythm;
- transmission of nerve impulses;
- exchange of iron and phosphorus;
- maintaining the strength of bones and teeth;
- construction of the fetal skeleton;
- regulation of cell membrane permeability;
- the formation of thrombin or the main component of a blood clot, without which it is impossible to stop bleeding;
- regulation of enzymatic activity;
- improving sleep quality.
Calcium enters the body with food, is absorbed in the intestines, participates in metabolic processes, and is excreted from the blood by the kidneys. If there is not enough mineral intake from food or its absorption is impaired, then the parathyroid hormone and vitamin D3 extract it from the bones and teeth. If there is too much calcium in the blood, then calcitonin and other hormones reduce its level in the blood, depositing it in the bones and internal organs.
Many biologically active compounds take part in the regulation of calcium levels - hormones of the adrenal cortex, thyroid gland, sex hormones, as well as magnesium and phosphorus.
Both an increase and a decrease in calcium levels in the blood have a bad effect on all types of metabolism and the functioning of the body.
Read completely
Total calcium - 300 rub.
Urgent analysis - 600 rub.
Deadlines
Normal – 1 day.
Urgent – 1.5 – 2 hours.
Taking blood from a vein is paid separately - 300 rubles.
(If several tests are performed simultaneously, the service for collecting biomaterial is paid once)
Indications
- bone loss or osteoporosis, diagnosis of this condition and general population survey or screening;
- decreased muscle tone with normal peripheral nerves;
- a feeling of tingling and crawling, if there is no other reason for this;
- convulsive syndrome or involuntary twitching of the distal muscles, especially the legs;
- chronic diseases of the stomach and intestines, especially gastric and duodenal ulcers;
- passing an abnormally large amount of urine;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- fluctuations in vascular tone;
- comprehensive examination before surgery;
- disruption of the thyroid and parathyroid glands;
- malignant breast tumors in women and lung cancer;
- kidney disease, including nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis with the presence of stones visible on an x-ray;
- bone pain in the absence of metastases of the malignant process;
- pregnancy.
Material for analysis
Blood serum.
Preparing for the study
- You should eat moderately during the day before the test. Blood is taken on an empty stomach in the morning, a break in food is from 8 to 14 hours, water is allowed. For half an hour before taking blood, you need to be at rest for half an hour and not smoke.
If blood calcium is elevated, what should you do?
As we noted earlier, increased calcium is always a reason for additional examination and consultation with an endocrinologist. In order to come to an appointment with an endocrinologist “not empty-handed,” it is better to take some additional tests before meeting the doctor.
The standard examination of patients with elevated blood calcium includes the following blood tests:
- parathyroid hormone;
- calcitonin;
- phosphorus.
This is the minimum with which you can already come to a consultation with a doctor. It is clear that the doctor can then order additional tests, but the three blood tests listed above will help him figure out in which direction he should conduct a diagnostic search.
When consulting patients with endocrinologists at the North-Western Endocrinology Center, we almost insist on performing blood tests in the laboratory of our center
- this is the only way we can be sure that there are no laboratory errors and that our reasoning about the possible causes of elevated calcium levels in the blood is correct. The ion composition of the blood in the laboratory of our center is studied using the Olympus AU-680 analyzer (Japan) already mentioned above, and the blood test for such important indicators as parathyroid hormone and calcitonin is performed by an automatic chemiluminescent immunoassay analyzer of the 3rd generation DiaSorin Liaison XL (Italy) - some of the best machines in the world for analyzing blood for hormones and tumor markers.
| Automatic immunochemiluminescent analyzer 3rd generation DiaSorin Liaison XL (Italy) | The 3rd generation chemiluminescent immunoassay analyzer allows you to identify situations where high calcium is combined with high parathyroid hormone |
Endocrinologists and endocrinologist surgeons at the North-Western Endocrinology Center independently perform
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and neck is important for searching for possible tumors of the parathyroid glands, which we simply have to suspect in the patient if there is an elevated level of calcium in the blood.
The second important instrumental study that needs to be done in patients with elevated blood calcium levels is determination of bone density, densitometry
. Calcium in the blood does not increase on its own - it is “taken” from bone tissue, which releases calcium into the blood and, as a result, reduces its density, which can lead to fractures. Densitometry, as well as ultrasound of the thyroid gland, is performed independently by endocrinologists at the North-Western Endocrinology Center. This is also an important argument in favor of examination and treatment in a specialized center.
The third important argument to contact a specialized center in any case if your blood calcium is elevated is the opportunity to undergo any medical procedures within the walls of the same institution
. Even during the examination, not only will you have high blood calcium, but it will also become clear that parathyroid hormone is elevated, and a parathyroid adenoma will be detected in your neck - its removal can also be effectively performed at the North-Western Endocrinology Center. At the moment, our center is the undisputed leader in the treatment of patients with high blood calcium in Russia - every year the center's endocrinologist surgeons remove parathyroid adenomas from more than 300 patients. In terms of the number of operations on the parathyroid glands, our center is now in third place in Europe.
Treatment
The initial stage of hypercalcemia, which is caused by excessive consumption of foods and medications containing calcium, can help solve the problem of a slight increase in the amount of calcium in the human body: changing the diet towards reducing the amount of foods containing large amounts of calcium. Dose adjustment, replacement or refusal of medications containing calcium. For healthy kidneys, sufficient consumption of water, preferably distilled (no more than 2 months). If hypercalcemia develops against the background of serious illnesses, then treatment is aimed at the underlying disease and cleansing the body of excess calcium. When the kidneys are functioning normally, calcium is usually washed out with the help of diuretics and intravenous saline. In severe conditions, hemodialysis is performed (cleansing the blood of waste products). If the process of increased removal of calcium from the bones cannot be stopped, then hormonal drugs are used. The main task of hypocalcemia is to compensate for calcium deficiency in the body. In addition, treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease. So, for hypoparathyroidism (lack of parathyroid hormone), hormonal therapy is prescribed. Chronic hypocalcemia is treated by regularly taking calcium tablets and vitamin D. In addition, measures are taken to normalize the levels of magnesium, potassium and protein in the blood.
Blood calcium is elevated, other tests have been taken - how to decipher them?
Of course, deciphering a blood test is the prerogative of the attending endocrinologist, and independent study of one’s blood test can lead the patient to diagnostic errors, however, within the framework of this article, we will give some information about the possible results of a laboratory examination for elevated blood calcium. Use the information obtained with caution and remember that it is not a substitute for consultation with a medical specialist.
So, possible options for laboratory results and their interpretation.
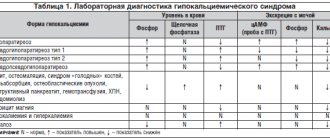
Blood calcium is increased, parathyroid hormone is increased, phosphorus is decreased, calcitonin is normal, calcium in daily urine is increased
– most likely, we are talking about primary hyperparathyroidism and the presence of a parathyroid adenoma. Additional examination is necessary using ultrasound of the thyroid gland and neck, scintigraphy of the parathyroid glands with technetril, and in some cases, computed tomography of the neck. It is treated surgically (endoscopic surgery through an incision about 2 cm long is possible in a specialized center).
Parathyroid hormone is elevated, calcium is normal, phosphorus is normal, calcitonin is normal
– with a high degree of probability we are talking about secondary hyperparathyroidism due to a banal deficiency of vitamin D in the blood. It is treated by taking vitamin D and calcium. It is important to exclude a laboratory error associated with an underestimation of the level of ionized calcium in the blood (it is better to retake the test for ionized calcium in a specialized laboratory of the endocrinology center).
Calcium in the blood is increased, parathyroid hormone is normal, phosphorus is normal, calcitonin is normal
– a neuroendocrine tumor that produces PTH-like peptides or forms lytic metastases in the bone should be suspected. Examination and treatment depend on the type of tumor detected.
High calcium in the blood (usually slightly increased calcium is observed), parathyroid hormone is moderately increased, phosphorus is normal, calcitonin is normal, calcium concentration in daily urine is reduced
– we can talk about a rare familial disease, the so-called familial benign hypocalciuric hypercalcemia. This disease is accompanied by a change in the sensitivity of cellular receptors to parathyroid hormone and impaired calcium excretion in the urine. Does not require treatment and is not dangerous. Often, inexperienced doctors diagnose primary hyperparathyroidism in such cases and refer the patient to unnecessary surgery to remove a non-existent parathyroid adenoma.
Ionized calcium is increased, total calcium is normal, parathyroid hormone is increased
– we are usually talking about parathyroid adenoma.
Ionized calcium is elevated, total calcium is below normal
– laboratory error must be excluded. The analysis should be re-taken in a specialized laboratory.
Ionized calcium in the blood is increased, parathyroid hormone is increased, calcitonin is increased
– the patient should be suspected of having both a parathyroid adenoma and medullary thyroid cancer. Together, these two diseases indicate a high probability that the patient has type IIA multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome - a rare hereditary pathology transmitted in the family and leading to the development of three dangerous tumors: medullary thyroid cancer, parathyroid adenomas (usually multiple), pheochromocytoma (tumor adrenal gland, which produces adrenaline or norepinephrine). Urgent consultation with an endocrinologist or endocrinologist surgeon is required!
Calcium in the blood is elevated during the first test, I want to retake the test - what is the best way to do this?
If you want to check whether your blood calcium is really elevated and are going to take a second blood test, follow some important rules that will help the second test be as accurate as possible:
1. a blood test should be taken only in a specialized laboratory using high-quality equipment;
2. a blood test must be taken only on an empty stomach;
3. if you are taking vitamin D or calcium supplements (or combination medications with vitamin D and calcium), stop them at least 2-3 days before your blood test; the entry of calcium from the drug into the blood can lead to an increased calcium level in the blood - of course, in this case a falsely elevated calcium is detected.
4.What are the risks and what could interfere with the analysis?
What are the risks of a calcium blood test?
If you are taking a blood test for calcium, then possible risks may only be associated with taking blood from a vein. In particular, the appearance of bruises at the puncture site and inflammation of a vein or artery (phlebitis). Warm compresses several times a day will relieve phlebitis. If you are taking blood thinning medications, you may bleed at the puncture site.
What can affect the results of the analysis?
A calcium blood test may give inaccurate results if:
- You took calcium or vitamin D in any form (not only specially prepared preparations, but also, for example, dairy products) immediately before the test;
- You have had dialysis;
- You recently had a large blood transfusion.
How does deficiency manifest itself?
Calcium is necessary for healthy teeth and bone tissue, growth and beautiful appearance of nails and hair. The mineral also participates in metabolic processes. In the case of prolonged calcium deficiency, various diseases occur: osteoporosis, rickets (together with a lack of vitamin D), hypertension, cataracts, growth retardation in children, scoliosis.
The main signs of mineral deficiency in the blood:
- fatigue, constant weakness, drowsiness, loss of strength;
- depressed mood, depression, irritability;
- fragility and weakness of nails, their separation;
- leg cramps (especially at night);
- hair loss;
- unhealthy complexion, pallor;
- dryness and flaking of the skin;
- tooth decay, frequent caries;
- decreased immunity;
- spontaneous formation of bruises on the body;
- weak tooth enamel;
- bleeding gums;
- fragility of bones (especially in childhood and old age);
- frequent colds;
- severe form of PMS in women.
To find out for sure whether there is a lack of calcium in the bones of the skeleton, you need to conduct a biochemical blood test. The following mineral content is considered normal:
- 2.10–2.55 mmol/l – in adults;
- 2.20–2.70 mmol/l – in children.