The disease is a common pathology and requires immediate surgical intervention. Surgery to remove the appendix is considered safe and does not affect subsequent health. Surgeons warn that ignoring primary symptoms and prolonged refusal to hospitalize causes the development of complications, including peritonitis. In the latter case, the risk of death increases.
Causes of appendicitis
The exact reasons for the development of the inflammatory process are still unclear. But there are several common options:
- Disturbance in the balance of microflora - bacteria that are safe in a normal environment become toxic and cause inflammation.
- Vasospasm causes deterioration in tissue nutrition. Some areas die and become a source of infection.
- Stagnation in the intestines - feces, foreign bodies, neoplasms or parasites can close the lumen of the appendix. At the site of closure, mucus accumulates, where the microbiome begins to multiply. Narrowing and compression of the appendix disrupts blood circulation and lymph flow, which leads to rapid progression of inflammation and necrosis of appendix tissue.
A predisposing factor will be frequent constipation, which forms fecal stones.
Postoperative period
In cases of uncomplicated forms of appendicitis and a favorable course of the operation, the patient can be immediately taken to the surgical department, in other cases - to the postoperative ward or intensive care unit.
During the rehabilitation period, wound care and early activation of the patient are of great importance, allowing the intestines to “turn on” in time and avoid complications. Dressings are carried out every other day, if there are drainages - daily.
On the first day after the intervention, the patient may experience pain and increased body temperature. Pain is a natural phenomenon, because both the inflammation itself and the need for incisions imply tissue damage. Usually the pain is localized to the site of the surgical wound, it is quite tolerable, and the patient is prescribed analgesics if necessary.
Antibacterial therapy is indicated for complicated forms of appendicitis. Fever may be a consequence of surgery and a natural reaction during the recovery period, but it must be carefully monitored, since an increase in temperature to significant levels is a sign of serious complications. The temperature should not exceed 37.5 degrees during the normal course of the postoperative period.
Many patients prefer to lie in bed, citing weakness and pain. This is wrong, because the sooner the patient gets up and starts moving, the faster intestinal function will be restored and the lower the risk of dangerous complications, in particular thrombosis. In the very first days after the operation, you need to gather your courage and at least walk around the ward.
A very important role in interventions on the abdominal organs is given to diet and nutrition. On the one hand, the patient must get the calories he needs, on the other hand, he must not harm the intestines with an abundance of food, which during this period can cause adverse consequences.
You can start eating after the appearance of intestinal peristalsis, as evidenced by the first independent stool. The patient should be informed what can be eaten after surgery and what is better to avoid.
Patients who have suffered acute appendicitis are assigned to table No. 5. It is safe to consume compotes and tea, lean meats, light soups and cereals, and white bread. Fermented milk products, stewed vegetables, and fruits that do not contribute to gas formation are useful.
During the recovery period, you should not eat fatty meats and fish, legumes, fried and smoked foods; you should exclude spices, alcohol, coffee, baked goods and sweets, and carbonated drinks.
On average, after surgery, the patient remains in the hospital for about a week in uncomplicated forms of the disease, otherwise longer. After laparoscopic appendectomy, discharge is possible already on the third day after the operation. You can return to work after a month with open operations, with laparoscopy - after 10-14 days. A sick leave certificate is issued depending on the treatment performed and the presence or absence of complications for a month or more.
Symptoms of appendicitis
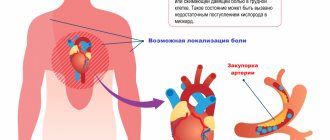
The appendix is located in the lower abdomen. The first symptom is unbearable pain that appears in the navel area and spreads to the lower right side of the abdomen. The pain worsens over a short period of time when moving, taking a deep breath, coughing or sneezing.
Other typical symptoms:
- nausea, even vomiting
- decreased or complete lack of appetite
- constipation or, conversely, diarrhea
- flatulence, painful bloating
- fever, chills, symptoms of intoxication
- urge to defecate
Signs of inflammation of the appendix may differ in men and women. For example, women experience nausea, vomiting and fever. At the beginning of the development of the disease, the pain is pressing, pulling, and not even necessarily on the right side, which can be mistakenly recognized as gynecological problems.
Then the pain may become cramping, such symptoms most often occur in the evening or at night.
In men with acute inflammation, severe pain in the abdominal area and spontaneous tightening of the right testicle occur. When the scrotum is pulled back, discomfort and pain occur in the anal area and a strong urge to have a bowel movement.
In older people, the symptoms of appendicitis may appear less clearly: minor pain, mild nausea. At the same time, appendicitis in older people is often characterized by a severe course and the development of complications.
In children under 5 years of age, the symptoms of appendicitis are not as pronounced as in adults. The pain often has no clear localization. Appendicitis in a small child can be recognized by increased body temperature, diarrhea and the presence of plaque on the tongue.
Advantages of performing an appendectomy at Euromed Clinic:
- Euromed Clinic is a full-service clinic. Before the operation, if necessary, we will arrange for you consultations with a therapist, cardiologist and any other specialist;
- Our own laboratory allows you to take the necessary tests at once and quickly get results;
- all surgeons at Euromed Clinic are experienced and qualified specialists;
- the operating room is equipped with modern medical equipment;
- use of the latest generation of anesthesia;
- own hospital with modern comfortable rooms;
- experienced surgeons at the clinic use the most modern dressing and suture materials and disposable instruments;
- All reusable metal instruments undergo a three-stage sterilization system and are then placed in vacuum packaging to ensure the sterility of the instrument.
You can make an appointment at a convenient time with a surgeon at Euromed Clinic by calling + 7 812 327 03 01 or online.
Types of pathology
Acute appendicitis develops rapidly and manifests itself with pronounced symptoms. With inaction, the pain intensifies and inflammation can lead to serious complications.
By its nature, acute appendicitis can be complicated or uncomplicated. Uncomplicated pathology, in turn, has 2 forms: catarrhal (only the mucous membrane is inflamed), destructive (deeper layers are affected).
Chronic is a fairly rare form. In most cases, it develops as a result of acute appendicitis in the absence of treatment. Has the same symptoms, but they manifest themselves very sluggishly. There are periods of exacerbation and remission, like any chronic disease.
Chronic appendicitis is also divided into subtypes:
- Residual - a consequence of acute appendicitis that ended in self-healing. It manifests itself as a dull aching pain in the right iliac region.
- Recurrent – has a paroxysmal nature: exacerbations occur from time to time, followed by remission.
- Primary chronic – develops independently, without preceding acute appendicitis.
Prices
Price (rub.)In installments* (rub.)Consultation with a surgeon on the operation (SPECIAL)0—Online doctor’s opinion on the operation (SPECIAL)0—Appendectomy Cat. I. complexity 26000—Appendectomy Cat. II. difficulty 36000—* You can read more about the conditions here - Treatment on credit or in installments
The cost is preliminary. The exact cost of the operation can only be determined by a surgeon during a free consultation.
Diagnosis of appendicitis
The first step in examining a patient is an examination and history taking. The doctor asks you to tell us when the symptoms began and how long the discomfort lasts. This is important to understand in order to distinguish the disease from something else.
It is important to consider other factors that could cause the development of appendicitis:
- Surgical operations in the abdominal area in the recent past.
- Taking medications or supplements.
- Bad habits, abuse of alcohol, drugs, etc.
Feeling the abdomen will help determine the location and intensity of pain, its characteristics. A pelvic and rectal examination may be necessary. The final diagnosis is made only after laboratory tests. Blood and urine tests can help detect signs of inflammation or other health problems.
Visual examination methods may also be required - ultrasound of the abdominal organs, CT or MRI. They will allow:
- determine the condition of the appendix and assess its integrity
- detect signs of inflammation
- evaluate blockage inside the appendix
- identify an abscess or other complications
After appendectomy
As a rule, within 2-3 hours after laparoscopy for appendicitis, the patient can get up. Discharge from the hospital usually occurs 1 - 2 days after the operation. The patient can go home once he can eat, drink and move independently without pain. It takes about a week for complete recovery.
You should prepare in advance for postoperative recovery. Most people go home a day after having an appendectomy, but complications may increase the length of your hospital stay. In some cases, the surgeon may have to make an incision in the abdominal wall to remove the appendix. In this case, the patient will have to stay in the hospital for a longer period. It is not always possible to say exactly how the operation will proceed. If you have to stay in the clinic longer, you should immediately take personal items with you, for example, a toothbrush, comfortable clothes, gadgets, books or magazines, so that you don’t get bored.
Arrange for someone to take you home after discharge and look after you. Ask a friend or family member to drive you home and stay with you the first night after surgery.
How quickly a patient can return to normal activities after an appendectomy depends on the surgical procedure and overall health. Patients who have undergone a laparoscopic appendectomy can return to work within a few days. Patients who have open surgery take longer to recover and return to work.
Avoid strenuous physical activity immediately after surgery. If your appendectomy was performed laparoscopically, limit your activity for three to five days. If you have had an open appendectomy, limit your activity for 10 to 14 days. Ask your doctor about your activity restrictions and when you can return to normal activities after surgery.
When coughing, laughing or moving, support your stomach to reduce pain.
Start slowly and increase activity as needed. Start with short walks.
In the first days after surgery, you may feel sleepier than usual. Relax and rest whenever you need.
Talk to your doctor about returning to work or school.
How to treat appendicitis?
The pathology requires immediate treatment, since the appendage may burst and its contents will spill into the abdominal cavity and peritonitis will begin. Therefore, the only solution is to remove the appendix surgically.
Appendectomy is a surgical operation to remove the appendix. It can be carried out in two ways:
- classic – abdominal surgery
- laparoscopic, when there are no large incisions
Abdominal surgery is performed if the appendix ruptures and if its contents spill into the abdominal cavity, as well as if the rupture causes an abscess.
Laparoscopy is considered the most modern method of removing the appendix for various reasons: less invasiveness, quick recovery, and fewer complications.
The operation is carried out as follows:
- the surgeon makes small incisions through which access to the appendix appears
- a camera with illumination is introduced
- other instruments are used to remove the process
- areas are treated to disinfect infectious material
- the operated area is examined and sutures are placed
Recovery
Appendectomy
Emergency and planned surgical removal of the appendix in medical. Professional doctors will perform the operation quickly and painlessly.
After the operation is completed, the patient is transferred to a hospital, where he will spend 2-5 days, depending on the chosen surgical technique and the presence of complications. To relieve temporary pain and prevent the development of postoperative infection, painkillers and antibiotics are prescribed. The patient can have a drainage system installed to avoid a purulent inflammatory process. Rehabilitation continues until the stitches are removed (7-9 days).
Pain syndrome with appendicitis in pregnant women and children
During pregnancy, appendicitis can occur at any stage. The pain syndrome can be mistaken for a threatened miscarriage. In the second half, the growth of the uterus causes the dome of the cecum to shift upward. The localization of pain moves higher, to the right hypochondrium. Difficulties arise during palpation.
Signs of appendicitis during pregnancy
Hidden signs of pain should be looked for when the appendix is located behind the uterus. Then the abdominal pain is insignificant.
The risk of misdiagnosis is growing. In children, pain is rarely localized, quickly spreads along the abdominal wall, and manifests itself as contractions.
The disease occurs as infectious gastroenteritis, dysentery. Stomach damage is suspected. Behind the rapid flow, it is difficult to identify signs of peritoneal irritation. In old age, on the contrary, abdominal pain is less intense. Tension of the abdominal wall muscles may be absent even in destructive forms.
Bibliography
- Barsukova, I.M. Acute appendicitis: history and modern organization of medical care// I.M. Barsukova, M.V. Gavshchuk, A.P. Krivov. - text: direct // Scientific notes of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. I. P. Pavlova, 2021.- No. 3 – P. 43-49, DOI: 10.24884/1607-4181-2018-25-3-43-49.
- Clinical guidelines “Acute appendicitis in adults”, 2021, Developers: All-Russian public association “Russian Society of Surgeons”, All-Russian public organization “Russian Society of Endoscopic Surgeons”. - Text: electronic. - URL: (access date: 09/29/2021).
- Draft clinical guidelines “Acute appendicitis in children”, 2016. Developer: Russian Association of Pediatric Surgeons, -Text: electronic.- URL: (access date: 09.29.2021).
Author:
Pugonina Tatyana Alekseevna, Therapist
Pain syndrome in atypical forms of the disease
Features of the anatomical variants of the location of the appendicular process determine why in a significant number of patients the pain syndrome is atypical in localization and manifestation.
The red arrow shows the pelvic localization and the possibility of fusion with the genital organs
Retrocecal location (behind the cecum) is the most common (32% of cases) after descending (63%). Since the process is adjacent to the liver, lumbar muscles, and right kidney, the disease takes on the mask of other pathologies. Usually the pain begins in the epigastrium, then moves to the right side or lower back.
Difficulties arise in identifying even destructive forms of inflammation. There are no symptoms of peritoneal irritation. Sometimes tension in the lower back muscles is detected. The positive Obraztsov symptom helps in diagnosis—increased pain when lifting the right leg.
With pelvic localization, the appendage comes into contact with the intestines (sigmoid and rectum), bladder, and uterine appendages in women. Painful manifestations become similar to colitic ones - cramping.
If it hurts in the left iliac zone, it occurs due to inflammation and spasm of the lower parts of the large intestine. Initially, the attack is localized in the epigastrium, then moves to the groin or to the area above the pubis. Tension of the peritoneal muscles is often absent. In such cases, appendicitis can be suspected only through a rectal examination; women are examined by a gynecologist.
Subhepatic localization is rare, but has significant diagnostic difficulties. It is difficult to distinguish which pains are caused by the atypical location of the appendix and which are caused by inflammation of the gallbladder.
The center of pain when the appendix is located subhepatically is in the hypochondrium on the right; pain on palpation of the abdomen is also determined here
In order not to endanger the patient’s health in surgery, it is customary to treat appendicitis or cholecystitis conservatively for 24 hours. If the pain does not disappear, operate; the diagnosis will be made only during the operation.