Removal of the uterus is one of the most common operations in operative gynecology. We resort to it only in cases where other methods of treatment have proven ineffective or when it is necessary to save a woman’s life. Abroad, this operation is very common among women after 40 years of age. It allows you to avoid the formation of malignant tumors and the growth of fibroids.
Having a hysterectomy is a difficult experience for women of any age. Very often they experience depression, vulnerability, and are accompanied by a feeling of inferiority and confusion.
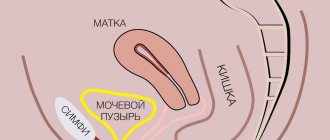
Surgery to remove the uterus: features and types
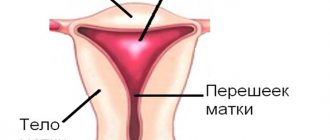
A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the uterus. As a rule, it passes without complications and is used when conservative therapy methods have exhausted themselves and have not yielded positive results.
Depending on the complexity of the disease, the following types of hysterectomy are distinguished:
- subtotal – removal of the uterine body;
- total – removal of the cervix and body of the uterus;
- radical – removal of the uterus, cervix, appendages, lymph nodes.
In each case, the issue of removal is decided individually, taking into account the complexity of the disease. In this case, the doctor tries to preserve as many genital organs as possible without the likelihood of complications in the future.
Indications for removal of the uterus are the following diseases:
- malignant tumors (cervical cancer);
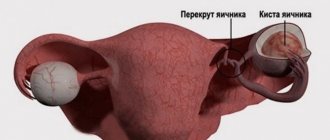
- endometriosis or adenomyosis;
- severe prolapse or prolapse of the uterus;
- pain in the pelvic area caused by diseases of the uterus;
- benign tumors (fibroids) during menopause or perimenopause;
- difficult birth.
What is menopause
Menopause is the decline of ovarian function. They produce less and less sex hormones (estrogen, testosterone, progesterone), and the egg does not mature in them.
Estrogens (female sex hormones) are very important for the condition of bone tissue and blood vessels, so their absence very often leads to problems with the musculoskeletal system and blood circulation.
Decreased production of testosterone (male sex hormone) leads to a lack of sexual desire (libido). Active hormonal changes occur in the body - it is this that can lead to external changes such as excess weight, aging skin, and hair loss. Removal of the uterus cannot cause hormonal changes because the ovaries will continue to function and produce sex hormones.
Clinical studies prove that when the uterus is removed, the ovaries work in the same mode and during the same period, which is planned, “programmed” by the body genetically.
Estrogens are produced regardless of whether the uterus is removed or left, they continue to have a positive effect on bone tissue and the cardiovascular system. Testosterone is also produced, so libido does not decrease and the quality of sexual life does not change in any way.
Moreover, if you are familiar with such a condition as premenstrual syndrome (PMS), then it will persist. Because PMS is caused by the cyclical work of the ovaries.
Preparation for surgery to remove the cervix and methods for performing it
Before the operation, the patient is subject to a comprehensive examination using ultrasound, x-ray methods, and biopsy. The woman will also need to visit an anesthesiologist. Since the operation is performed under general anesthesia, it is necessary to determine whether the patient is allergic to any drugs. The day before the operation, the woman eats healthy, light food. The intestines must be cleansed using an enema.
The method of removing the uterus depends on several factors:
- complexity of the disease;
- surgeon experience;
- general health of the woman.
In operative gynecology, hysterectomy operations can be performed in several ways, namely:
- abdominal - the doctor makes an incision on the anterior abdominal wall;
- through the vagina - after surgery and recovery, practically no traces remain;
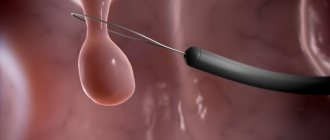
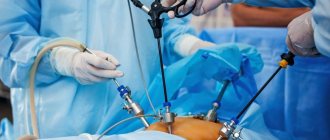
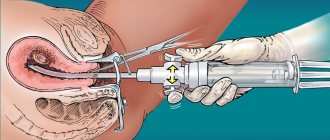
- by laparoscopy - small incisions are made in the lower abdomen through which surgery takes place.
The abdominal operation lasts about an hour and leaves a horizontal or vertical scar about 20 cm long. To help it heal better, you need to wear a post-operative bandage.
Laparoscopy is a gentle method of removing the uterus, which avoids large incisions in the abdominal cavity. This operation will require special equipment. The essence of the operation is as follows: small incisions are made on the abdomen through which tubes are inserted, then a video camera and surgical instruments are inserted through the tubes into the abdominal cavity, with the help of which the uterus is removed.
All operations are performed under general anesthesia. Also on the day of surgery, the woman may be given a sedative injection to reduce anxiety. A trusting relationship between doctor and patient is very important. When a doctor treats a woman with understanding, tells her about the operation, its consequences and future lifestyle, then the woman can correctly assess the current situation, avoid stress or, worse, nervous disorders.
Recovery after hysterectomy
Recovery after surgery is divided into the following stages:
| Recovery stage | Signs and timing |
| First stage of recovery | the period of the first 24 hours after surgery when any movement is prohibited |
| Second stage of recovery | inpatient treatment, usually 9 to 12 days with minimal movement |
| The third stage of recovery | follow-up treatment at home |
All women who have undergone surgery have the right to sick leave. Its duration depends on the reason for the operation, the result, and the healing process.
For a month after the operation, you should not swim in the bath or swimming pools so that water does not enter the wound through the vagina or sutures on the body. Light showers are allowed. Lifting heavy objects should be avoided for six to ten weeks.
This surgery does not remove the vagina, so after abstaining from sexual intercourse for the first 6-10 weeks, you can start having sex.
Three months after the operation, the woman usually completely returns to normal life.
Early rehabilitation after hysterectomy surgery
The patient is under the supervision of a doctor for the first time (at least 3-4 days). Immediately after removal of the uterus, treatment is aimed at eliminating pain, restoring body functions, preventing bleeding, inflammatory processes, and anemia. The doctor also monitors how the suture “behaves,” whether there is any discharge from the genitals, and how the intestines work.
Immediately after the operation, the patient is placed on a drip for intravenous administration of antibiotics, detoxification drugs, painkillers, vitamins and other solutions. If necessary, the patient is injected intramuscularly with proserin, which helps to start the intestines. In the first two days, the woman is fitted with a urinary catheter to remove fluid.
At first, a woman’s diet should be balanced and aimed at restoring intestinal motility. On the first day, the woman is given nothing but ordinary water without gas. Starting from the second day, you can eat low-fat broths and yoghurts. Every day two new products are added, gradually making the diet more varied. In the first stages, it should be easily digestible, low-fat food (baked apples, chicken breast, pomegranates, honey, porridge). It is necessary to exclude foods that can cause constipation (cabbage, corn, legumes, chocolate, coffee). You need to eat often (4-5 times a day) and in small portions. Every day you need to drink about 1.5-2 liters of water, although depending on the individual characteristics of the body, the doctor may recommend drinking 3-4 liters.
Why do many gynecologists advise removing the uterus for fibroids?
The main reason for such a long dominance of therapeutic radicalism in the treatment of uterine fibroids is that for too long uterine fibroids have been considered, although benign, to be a tumor process, and the tumor, as the canons of surgery say, must be removed. Indeed, there is a list of organs without which a person can more or less exist. And from the point of view of many gynecologists, the uterus is almost in first place on this list.
For some reason, it is believed that having realized her reproductive function, a woman can part with the uterus completely painlessly, that is, a unique monofunctional relationship has been developed towards this organ. Wrong attitude. At the same time, it is quite obvious that there are no unnecessary organs in the body, and the uterus, in addition to the reproductive function, also has others, some of which are clear to us, and some of which are still not fully understood. To simplify, we can say that, being integrated into the whole organism, the uterus maintains a natural physiological balance.
A person can exist without one kidney, a lung, or part of the intestines, but everyone understands that this existence is no longer a completely full-fledged person, so why is a woman without a uterus considered healthy in the minds of a number of doctors? Indeed, it has been known for many years that removal of the uterus entails the development of the so-called posthysterectomy syndrome - a symptom complex of disorders of the endocrine, nervous, cardiovascular and other systems that occurs after removal of the uterus and is associated with this removal through a direct cause-and-effect relationship.
A special place is occupied by psychological consequences - the presence of a uterus is a subconscious element of femininity, involvement in the female gender. The presence of a uterus gives a woman constant inner confidence that she can give birth to a child. And even if she definitely does not want to have more children, permanent deprivation of this function may be emotionally unacceptable for her.
Some studies that examine the functions of the uterus show interesting results. For example, in 2021, scientists from Arizona State University (USA) conducted an experiment on rats: some animals had their ovaries removed, others had their uterus, others were not operated on, and their uterus and ovaries continued to function. Animals whose uterus were removed were less able to navigate mazes.
However, other studies show that women who have a hysterectomy have an increased risk of developing dementia. The uterus somehow influences the functioning of the nervous system, and these relationships remain to be studied.
In addition, during the experiment it turned out that the hormonal levels in the body changed in rats that had undergone hysterectomy. And this, as we know, can potentially create a number of health risks. This suggests that the uterus is needed not only during pregnancy. When a woman is not pregnant, the uterus does not “sleep” and is not at rest. It performs some functions that have yet to be understood in more detail.
The results of such studies provide a strong argument against hysterectomy in cases where there is no truly justified indication for it.
Late rehabilitation after hysterectomy
If the operation was performed by laparoscopy, then sick leave is provided for 30 days, and for a normal uncomplicated operation - 45 days. Although there are cases where women felt good after 3 weeks and went to work.
This period begins immediately after discharge and is considered no less important than the period of early rehabilitation. You need to be no less responsible about your health and direct all efforts towards restoring the normal functioning of all organs.
During the postoperative rehabilitation period, the woman also takes medications, including enzyme, hormonal and restorative agents. While at home, you need to limit physical activity and not put stress on the muscles of the pelvic floor and abdominal cavity. If medicinal exercise has been recommended, it should not be neglected to avoid complications.
You need to abstain from sex for a month. If there is pain or suspicious discharge, you should consult a doctor. Most likely, he will prescribe additional medications and extend the period of sexual rest.
After leaving the hospital, nutrition should also not be left unattended. You need to eat only healthy foods, while limiting confectionery, alcohol, spicy, smoked and fatty foods. You need to drink as much fluid as possible, as it helps detoxify the body.
In most cases, after rehabilitation, a woman’s quality of life remains unchanged, namely:
- the menstrual cycle is restored;
- hormonal levels return to normal;
- libido remains the same;
- the opportunity to lead an active sex life returns.
Naturally, a woman loses her reproductive function, but life does not end there.
Experience and consequences of hysterectomy
- Most women decide to undergo surgery for one of the benign reasons listed above, which creates serious problems in their life, such as heavy and frequent bleeding, pain, etc. The disappearance of unpleasant symptoms improves the quality of their life.
- Without a uterus there is no way to get pregnant.
- If the ovaries were removed along with the uterus, menopause will occur. The patient may require hormone replacement therapy. Women who do not have their ovaries removed go through menopause several years earlier than expected.
- A woman without a uterus does not lose her femininity. But awareness of the absence of a reproductive organ can lead to psychological problems. They manifest themselves as a feeling of constant loss and a decrease in the desire for sexual intercourse.
Complications after hysterectomy
As mentioned above, hysterectomy surgery is quick and without complications. Very rarely, in severe forms of the disease, bleeding may occur during surgery. After it, as a rule, the patient’s condition improves. Rarely there are complications such as:
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen;
- urinary incontinence;
- discharge from the genitals;
- formation of a fistula tract;
- prolapse of the vaginal walls;
- menopause symptoms;
- nervous disorders.
Headaches, dry mucous membranes, sleep disturbances, palpitations, and decreased libido may also occur. All these complications can be treated conservatively, but in some cases repeated surgery may be necessary.
If bleeding occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor. He will be able to determine their cause and prescribe treatment. The fistulous tract can only be eliminated with the help of an additional operation, since the sutures during the removal of the uterus were applied incorrectly. Prolapse of the vaginal walls and urinary incontinence are associated with weakening of the muscles. In this situation, the doctor will recommend a special set of exercises aimed at restoring the tone of the pelvic floor muscles, or a set of hormonal medications. Painful sensations are most often associated with incompetent sutures. If enzyme preparations do not produce results, additional diagnostics and surgery will be required. The symptoms of menopause can be easily eliminated by taking a complex of estrogen and progesterone. Physical exercises and herbal treatments will also give positive results.
Complications of hysterectomy
No surgical procedure is without risk, even with the most advanced equipment and the most experienced physician. The patient has the right to ask the doctor about the procedures and risks of surgery.
According to statistics, this operation has a small number of complications, but they are possible both during and after it.
The following complications were noted in some patients:
- formation of adhesions;
- bleeding requiring blood transfusion;
- injuries to neighboring organs;
- infection;
- constipation;
- bladder dysfunction (urinary incontinence);
- blood clots (thrombosis);
- painful scar;
- sexual dysfunction;
- formation of fistulas (an abnormally formed channel, most often between the vagina and bladder);
- chronic pain.
These complications can occur at any time during recovery. They must be reported to your doctor.
Vaginal removal cost
You can see the cost of individual procedures on the website. When choosing a treatment method, doctors take into account indications, contraindications, as well as the client’s financial capabilities.
Our employee calculates the final price for all necessary procedures after examining and consulting the patient. Treatment with drugs takes precedence over surgery. If the patient is of reproductive age, the doctor does everything possible to preserve her ability to conceive. Vaginal hysterectomy is indicated only as a last resort.
You can make an appointment at our clinic through the website or by phone. Our consultants will answer all your questions in detail and tell you about the procedures and treatments that interest you.
Author of materials
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the first category
Bychkov Alexey Alexandrovich
Other articles:
Hysteroscopy Hysterectomy Hysteroscopic removal of uterine polyp Vacuum removal
Prices for vaginal hysterectomy
| G-1 | Initial appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist | 1200 rub. |
| G-2 | Repeated appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist | 1000 rub. |
| G-3 | Taking a smear | 420 rub. |
| G-5 | Insertion of an intrauterine device | 2600 rub. |
| G-6 | Removal of the intrauterine device with treatment | 2100 rub. |
| G-7 | Colposcopy | 1700 rub. |
| G-8 | Cauterization of cervical erosion | 5500 rub. |
| G-9 | Conization of the cervix with histological examination | 9000 rub. |
| G-10 | Removal of condylomas | 2000 rub. |
| G-11 | Cervical biopsy (without the cost of histological analysis) | 3500 rub. |
| G-13 | Opening a Bartholin gland abscess | 7000 rub. |
| G-14 | Separate diagnostic curettage (without the cost of histology and anesthesia) | 8000 rub. |
| G-15 | Taking an aspirate from the uterine cavity | 2600 rub. |
| G-18 | Diagnostic hysteroscopy | 12000 rub. |
| G-21 | Hymenoplasty (hymen restoration) | 22000 rub. |
| G-21.1 | Hymen incision | 7000 rub. |
| G-22 | Hysteroscopy | 15,000 rub. |
| G-23 | Diagnostic laparoscopy | 22000 rub. |
| G-24 | Laparoscopy planned | 27,000 rub. |
| G-25 | Emergency laparoscopy - ectopic pregnancy (with intra-abdominal bleeding), rupture of an ovarian cyst | 35,000 rub. |
| G-26 | Complicated laparoscopy - pelvic adhesions | 39,000 rub. |
| G-27 | Plastic surgery of the anterior (posterior) vaginal wall | 28,000 rub. |
| G-28.1 | Laparotomy 1st category of complexity | 30,000 rub. |
| G-28.2 | Laparotomy 2nd category of complexity | 35,000 rub. |
| G-28.3 | Laparotomy 3rd category of complexity | 40,000 rub. |
| G-29 | Emergency laparotomy | 40,000 rub. |
| G-30 | Hysteroresectoscopy | 18,000 rub. |
| G-31 | Intimate plastic surgery | 27,000 rub. |
| G-32 | Sling surgery for urinary incontinence | 27,000 rub. |
| G-33 | Surgery for prolapse of the vaginal walls using mesh prostheses | 30,000 rub. |
| G-34 | Vaginal hysterectomy | 32,000 rub. |
| G-35 | Removal of Bartholin's gland cyst | 20,000 rub. |
| G-36 | Screening examination for detection of ovarian cancer of the uterus (appointment, examination, colposcopy, oncocytology) | 3000 rub. |
| G-39 | PNVL (perineovaginal lift) | 45,000 rub. |
| G-40 | Echohysterosalpingoscopy of the fallopian tubes with contrast injection | 1000 rub. |
Go to the full list of paid gynecology services
What are the advantages of modern diagnostics?
Previously, atypical hyperplasia had only one treatment option - removal of the uterus. This method was used for any age and regardless of whether the patient had given birth or planned to do so in the future.
This was explained by the difficulty of controlling the disease in the absence of normal diagnostic methods. The older generation remembers how traumatic curettage procedures were. Now it is possible to easily, quickly and on an outpatient basis, that is, without going to the hospital, to do all the tests. In just an hour and a half, a general blood test is taken, an ultrasound examination, or ultrasound, is performed - and it immediately becomes clear whether the epithelium is outside the normal range. If the doctor sees the excessive thickness of this layer, the patient is offered an aspiration biopsy - a technique that is convenient in that it does not require expansion of the cervical canal, without which it was previously impossible to identify the danger of cells inside the organ.
Precautionary measures
Regardless of whether the formation of a stump or complete excision is planned, the preparation algorithm remains identical. First, the patient needs to find an experienced surgeon who will agree to perform the manipulation. It is best to base your choice on the reviews of women who have already experienced such a difficult period in life. You can find their responses on thematic websites or you will need to visit a specialized medical city forum.
Many people are concerned about the price, but all clinics adhere to their own strategy for setting costs, taking into account the qualifications of the medical staff, the instruments used, and medications. Before making a final decision in favor of a radical measure, a woman needs to sign up for a routine gynecological examination. During the appointment, the doctor will write out directions for a number of tests, the standard package of which includes:
- clinical examination of blood, urine;
- analysis for blood group and Rh factor;
- a smear from the vagina and cervix, which characterizes microscopy, PCR and oncocytology;
- colposcopy;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- X-ray of the lungs;
- electrocardiogram.
A mandatory point of the plan is blood biochemistry, which allows you to determine the level of hormonal content of the body, as well as identify markers of the inflammatory process. Along the way, testing detects antibodies to infections.
Those representatives of the fairer sex who have not passed a coagulogram, liver and kidney tests, and a test for electrolytes will not be allowed to undergo surgery.
Sometimes the victim’s condition is very advanced, which requires auxiliary consultation with related specialists of a narrow profile. This could be a cardiologist, who should help find out whether the body can cope with the load of general anesthesia, or a pulmonologist with a vascular surgeon. The risk group includes victims with a high probability of developing thrombosis.
They will have to sign up for a Doppler ultrasound so that the doctor can evaluate the condition of the veins of the lower extremities. Additionally, antispasmodics and other medicinal pharmacological products may be prescribed. When, during preparation, it turns out that the body is infected with an infectious disease, you will first have to get rid of the source of the disease with the help of antimicrobial drugs.
Only such a thorough approach will guarantee final success, and the consequences of what is done will not hit women’s health too hard.
Preparation
A planned operation with vaginal access is preceded by a diagnostic stage:
- general clinical studies;
- colposcopy;
- smears from the cervical canal for cytology;
- PCR, ELISA and other methods for detecting sexually transmitted diseases.
The day before surgical procedures, it is recommended to adjust the diet, the basis of which should be only food in liquid form. You should avoid eating vegetables, fruits, breads, etc. Your doctor will give you more detailed recommendations at a preliminary consultation.
The day before, all hair is removed from the pubic area; if necessary, and on the advice of an anesthesiologist, sedatives can be used. Immediately 1 hour before surgery, premedication is administered.
How is the operation performed and how long do you need to stay in the clinic?
Operations also differ in the method of incision. Laparotomy is a traditional method performed through a wide incision in the abdomen. Its advantage is that the doctor clearly sees the entire surgical area and can successfully work with the surrounding tissues without affecting the tumor. In some clinics, this option is performed using robotic technology: the surgeon controls the process using a remote control and screen. There is also laparoscopy, in which several punctures are made in the abdominal wall and removal is performed through them. The advantages include a minimum of trauma and accelerated healing, and the disadvantages –
lack of visibility for the doctor.
There is also a vaginal removal method - it is carried out without any external tissue damage at all, but in case of malignant disorders it increases the risk of relapse, due to the fact that during the operation dangerous cells can enter healthy tissue.
The period from the start of hospitalization to discharge will take approximately 7-8 days for benign pathology and 10 days for malignant pathology, sometimes a little more.