One day hospital 3rd KO
Kravchenko
Olga
10 years of experience
Oncologist (CHI)
Make an appointment
Uterine cancer is a serious pathology that manifests itself in the form of a malignant tumor formed from modified endometrial cells - the inner mucous membrane lining the uterine cavity. This is one of the most common cancers developing in women. The most dangerous period for the development of a tumor is the interval between 65 and 70 years; in general, the incidence increases during menopause, i.e. after 50 years.
Kinds
In accordance with histological characteristics, uterine cancer is divided into the following forms:
- adenocarcinoma, which is the most common type;
- squamous cell form - the least aggressive, successfully treatable;
- glandular-squamous, formed from glandular cells of the endometrium;
- leiomyosarcoma, developing from cells of the muscle layer;
- clear cell, a rather rare form, accounting for 1-5% of all cases;
- mucinous, which is characterized by increased mucus formation;
- serous, in which a tumor with a multi-chamber structure and the secretion of serous fluid is formed.
Symptoms
It is important not to miss the first signs of uterine cancer and visit a gynecologist on time. A cause for concern should be copious watery discharge, which is periodically mixed with a small amount of blood. Over time, the discharge intensifies and develops into bleeding. In general, any vaginal discharge during menopause may be a symptom of uterine cancer. Signs of endometrial cancer in women of reproductive age are bleeding between periods and heavier than usual menstruation, often accompanied by pain. In addition, general symptoms of cancer appear:
- feeling of constant fatigue, weakness;
- lack of appetite, sudden weight loss;
- anemia, pale skin;
- nausea, malaise;
- with tumor growth – pain in the pelvis or back.
The appearance of uncharacteristic discharge, especially bloody ones, should be a good reason for a visit to the gynecologist.
Clinical picture
The main symptom of uterine cancer is uterine bleeding (bloody discharge of varying intensity). In young women of reproductive age, symptoms of the disease are manifested by menstrual dysfunction - heavy monthly or intermenstrual bleeding.
In rare cases, pain may occur. Pain indicates the prevalence of the process. It may be due to compression of the nerve trunks by the resulting infiltrate or due to the fact that the contents of the uterine cavity stretch its walls.
It should be noted that the general condition worsens only with advanced disease. Almost all women feel good for a long time. Therefore, in the early diagnosis of uterine cancer, timely contact with an experienced gynecologist is very important.
Causes and risk factors
It is still not known exactly how the malignant process starts, however, the factors that increase the likelihood of uterine cancer have been studied quite well. The most significant of them:
- disturbances in the production of hormones, primarily an increase in estrogen levels;
- obesity, diabetes, hypertension;
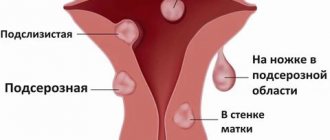
- benign neoplasms of the uterus – endometrial hyperplasia, polyps, fibroids;
- too early or late start and end of menstruation;
- no history of childbirth;
- long-term hormonal therapy;
- hereditary predisposition;
- chemoradiation treatment of tumors in other organs;
- lack of regular sexual intercourse for a long time.
The presence of one or more of the listed signs does not mean that a woman will necessarily develop symptoms of a uterine tumor. However, those who are at risk should visit a gynecologist at least once a year to monitor the condition of the reproductive organs.
Statistics
According to statistical data, the incidence of this type of cancer is decreasing from year to year.
In the European list of common female cancers, cervical cancer is in 7th place, in Russia it is in 5th place. In the world, this disease ranks fourth among female cancers. In 2021, experts estimate that 570,000 new cases will account for 6.6% of all cancer cases among women. Approximately 90% of deaths from cervical cancer occurred in low- and middle-income countries.
In countries with developed economies, due to early screening and vaccination against human papillomavirus, the incidence rate is lower - approximately 3.8%. In the US, it has decreased by 45% since 1980. In Eastern European countries, incidence rates are higher. At the beginning of the 21st century, there was a slight increase in the percentage of patients who were diagnosed with stage IV malignant lesions of the cervix - from 37.1 to 47.3.
At the age of 30–35 years, the disease is quite rare. The risk group is women from 35 to 55 years old. Only in 20% of cases, women over 65 are diagnosed with cervical cancer. Treatment and survival prognosis depend on timely visits to the doctor and early detection of the disease.
If cancer is detected early, 92% of patients live 5 years or more.
Stages
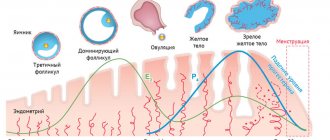
The development of a tumor is preceded by the so-called zero stage, when malignant cells are located on a microscopic area of the mucous membrane. According to the degree of growth of the malignant neoplasm, four stages of endometrial cancer are distinguished.
- The process has spread to the entire endometrium, but has not yet affected other layers of the uterine wall. The lymph nodes are not affected, there are no metastases.
- Malignant cells invade the muscle layer and can spread to the cervix.
- All layers of the uterine wall are affected, the malignant process spreads to the vaginal vault and affects regional lymph nodes.
- The tumor has spread to neighboring organs - intestines, bladder, etc. Lymph nodes are affected, metastases have spread to distant organs - lungs, liver, bone structures.
Organ structure
To make the process of pathology more understandable, let’s say a few words about the structure of the female reproductive organ. Visually, the uterus looks like an inverted pear (see photo). At the top there is a wide “pear-shaped” base - the fundus of the uterus, to the bottom (towards the vagina) there are:
- body;
- isthmus;
- Cervix.
The tissue that makes up the organ is formed by 3 layers:
- endometrium - a mucous layer facing inward (on top the endometrium is lined with epithelial cells);
- myometrium - muscle (middle) layer;
- perimetry - the outer shell.
Diagnostics
For uterine endometrial cancer, the symptoms and signs of the disease are not specific. Therefore, instrumental and laboratory studies are of utmost importance for diagnosing a tumor.
- Transvaginal ultrasound. Allows you to describe the structure of the endometrium and control its thickness.
- Hysteroscopy. The procedure for examining the internal cavity of the uterus using a special optical system. During the examination, a biopsy of pathologically altered tissues may be performed.
- Biopsy. An aspiration biopsy is a procedure to remove a sample of the endometrium using a thin, hollow needle.
- Histological analysis of the biopsy specimen. Microscopic examination of the prepared sample is necessary to confirm the diagnosis and to determine the type of malignant cells.
- MRI of the uterus. As a rule, it is carried out at the third or fourth stage of tumor growth to identify the extent of spread, affected lymph nodes and neighboring organs.
Attention!
You can receive free medical care at JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) under the program of State guarantees of compulsory medical insurance (Compulsory health insurance) and high-tech medical care.
To find out more, please call +7, or you can read more details here...
Treatment
To successfully treat endometrial cancer, different methods are used, which are selected based on the prevalence of the cancer process, the type of tumor, its location and structure.
- Extirpation of the uterus. During the operation, as a rule, the uterus and fallopian tubes are completely removed, especially if we are talking about a woman who already has at least one child. If the tumor size is small, the cervix is preserved to reduce the risk of complications during the recovery period. At the fourth stage, surgical treatment is not performed.
- Radiation therapy. Treatment is carried out before surgery to reduce the size of the malignant tumor, and also after surgery to prevent relapse due to remaining tumor cells. At the inoperable stage, radiation is used to prolong the patient's life.
- Chemotherapy. Often, cytostatic drugs are prescribed in combination with radiation treatment before or after surgery, as a palliative in inoperable cases and in case of relapse of the disease.
- Hormonal method. Effective for the treatment of hormone-dependent tumors, it is used mainly for the treatment of young patients with a highly differentiated type of cancer.
Prevention programs
In some regions of the country, education and cancer screening programs are in place. To prevent this disease, cultivate healthy habits, manage your weight, and remain physically active. It is very important to visit your gynecologist regularly, since chemotherapy and radiation therapy are usually not required for timely detection of the disease; surgical intervention that successfully treats the disease.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Diagnosis and treatment of uterine cancer in Moscow
If you have discovered signs of uterine cancer, contact the Medicina clinic to be examined using modern high-precision diagnostic equipment. Consultations regarding diagnosis, and if the diagnosis is confirmed, qualified treatment is carried out by oncologists-gynecologists of the highest category according to protocols used by leading clinics in the world. Our patients have our own laboratory, which performs all types of tests, and a comfortable hospital with attentive, professionally trained staff.
Questions and answers
How long do they live with uterine cancer?
The lifespan of a woman after detection of a uterine tumor directly depends on what stage of development the disease is at. After surgery performed at an early stage, the patient can live safely for decades. Patients with stage 4 without medical care can die within a few months, and with quality treatment they can live for more than five years.
What does uterine cancer look like?
It is impossible to independently detect a cancerous tumor of the uterus. A full diagnosis is required in a specialized medical institution to confirm or refute the suspicion of uterine cancer.
How does uterine cancer manifest?
The main symptom of a uterine tumor is bleeding from the vagina, which appears between periods and even during menopause. If any bleeding occurs during these periods, you should immediately consult a gynecologist. The earlier a tumor is detected, the higher the chances of a complete cure.
Attention! You can cure this disease for free and receive medical care at JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) under the State Guarantees program of Compulsory Medical Insurance (Compulsory Medical Insurance) and High-Tech Medical Care. To find out more details, please call or visit the VMP page for compulsory medical insurance
Forecast
The prognosis for survival from uterine cancer, as well as complete recovery and relapses, depends on many factors. First of all, this is the time of cancer detection; the earlier the tumor is diagnosed, the more favorable the prognosis. The type of malignancy, the patient’s age, the presence of concomitant diagnoses, the chosen treatment tactics and the body’s response to therapy also influence.
Average prognosis for five-year survival if cancer is detected at the appropriate stage:
- in situ – 90%;
- I – 75%;
- II – 69%;
- III (A, B, C) – 58%, 50%, 47%;
- IV (A, B) – 17%; 15%.
Recurrence of uterine cancer is possible, most often it occurs within 2 years after treatment. The relapse rate is on average about 10%, it depends on the type of tumor and the degree of differentiation.