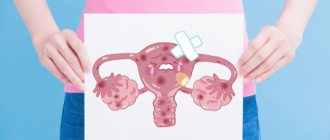
Uterine polyp - This is a rounded growth on a stalk, reminiscent of a mushroom. It is considered a benign formation, that is, it does not pose a threat to a woman’s life. But this does not mean that you can refuse treatment, because over time the polyp can turn into a malignant tumor. But the probability of this is small, only 1-2%.
Polyps appear on the inner lining that lines the uterine cavity (endometrium) or inside the cervical canal. Polyps can form at any age, starting from 11 years. They are especially common in women before menopause at 40-50 years of age.
Signs of the development of uterine polyps:
- menstrual irregularities – periods become irregular;
- heavy bleeding during menstruation;
- white mucous discharge from the vagina between periods (leucorrhoea);
- bleeding after sexual intercourse due to injury to the polyp;
- bleeding from the vagina between periods;
- pain in the lower abdomen with large polyps;
- infertility.
But most often, polyps do not cause any symptoms. They are discovered by chance, during a visit to the gynecologist or during an ultrasound.
What are polyps?
These are small nodules ranging in size from a few millimeters to 3 cm. In most cases, they are no more than 1 cm in diameter. Polyps can be single or multiple. They resemble burgundy-violet or yellowish small cylinders with a porous surface. The vessels are clearly visible through their thin shell.
Where do polyps come from? Scientists have not yet fully elucidated this issue. But many theories have been put forward. The main causes are considered to be hormonal disorders and inflammatory processes.
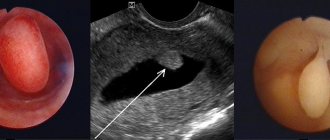
What procedures can detect polyps? The most accessible and painless method is ultrasound.
The most accurate results are obtained by testing using a sensor that is inserted into the vagina. But if a detailed examination is necessary, the doctor may prescribe a hysteroscopy. In this procedure, a thin tube with a camera at the end is inserted into the uterine cavity. Using the same device, you can take pieces of tissue for examination (biopsy). In some cases, special contrast agents are injected into the uterus and an x-ray is taken.
Diagnostics
At the first appointment, the doctor is unlikely to be able to make a diagnosis, since it is impossible to determine the location of the polyp in the internal cavity of the uterus without a thorough examination. There are objective and subjective reasons that may raise suspicions of uterine polyposis.
Subjective signs:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- general malaise.
Objective signs:
- results of general and biochemical blood tests;
- analysis of vaginal smears;
- gynecological ultrasound results;
- hysteroscopy.
If the diagnosis is confirmed by the gynecologist, the doctor gives a referral for a biopsy. Further treatment will depend entirely on the results of histological examination. In most cases, the treatment method for adenomatous and glandular polyps is surgery.
Types of uterine polyps
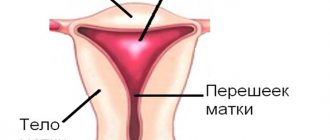
All polyps consist of a body and a stalk. The body is wider and more massive, and with the help of a narrow stalk the outgrowth is attached to the wall of the uterus. If the stalk is long, the polyp may hang into the vagina. It is then visible during a routine gynecological examination.
There are several types of polyps. They are divided by location and structure.
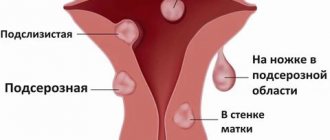
Depending on where the polyp is located:
- Cervical polyps are benign, pedunculated tumors that are located on the surface of the cervical canal.
- Polyps of the uterine body are benign formations in the form of a nodule on the inner surface of the organ. Most often they appear in the upper part of the uterus.
Depending on what cells the polyp consists of, they are divided into:
Glandular polyps are based on glandular cells. More common at a young age. They may look like cysts filled with fluid. Usually occur with endometrial hyperplasia.
- Fibrous polyps are made up of connective tissue cells. They are more dense. They appear after 40 years before menopause and during menopause, when hormonal changes occur.
- Glandular fibrous polyps - consist of cells of the uterine glands and connective tissue.
- Polyps-adenomas (adenomatous) - contain altered atypical cells. More often than others, they degenerate into cancerous tumors.
- Placental polyps occur when a piece of placenta remains in the uterus after childbirth. A polyp can grow from its cells.
Causes of uterine polyps
Doctors cannot give a definite answer to the question of what causes the appearance of polyps. There are several versions.
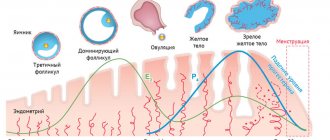
- Hormonal disorders . A high amount of estrogen hormones in a woman’s blood causes the inner layer of the uterus to grow. This may manifest itself in the form of polyps or uniform growth of mucosal areas (endometrial hyperplasia). The lack of another female hormone, progesterone, causes polyps to grow very actively.
- Vessel proliferation . If for some reason a vessel becomes clogged or grows, then epithelial cells begin to multiply around it.
- Inflammatory processes in the genital organs (endometriosis, cervicitis). When inflammation occurs in the uterus, many immune cells - leukocytes - appear in its tissues. They destroy the infection, but at the same time cause the growth of endometrial cells.
- Abortions or unsuccessful curettages . Poorly performed medical procedures can cause erosions and increased cell growth in certain areas of the uterine mucosa.
- Diseases of the endocrine glands . The work of all glands in the body is interconnected. Therefore, disorders in the thyroid gland, liver or adrenal glands cause a malfunction of the ovaries and excessive production of sex hormones.
- Diabetes mellitus and high blood pressure . These diseases disrupt blood circulation in small capillaries. And where cells do not receive oxygen and nutrients, they begin to change and can begin to divide intensively.
- Excess weight . It has been proven that adipose tissue is not just deposited under the skin and in organ cells. It can also produce estrogen hormones, which provoke the growth of polyps.
- Heredity . The tendency to grow polyps in the uterus is inherited. Therefore, if the mother had polyps, then her daughters should be especially attentive to their health.
- A sedentary lifestyle leads to stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs. Less oxygen reaches the uterus and ovaries and this disrupts the production of hormones and cell reproduction.
- Taking tamoxifen . This drug is used to treat tumors. It blocks receptors that are responsible for sensitivity to sex hormones. This medicine may cause polyps to grow in some women.
Preparing for polypectomy
Women undergoing polypectomy require careful preparation. At the Yusupov Hospital, patients can undergo all the necessary examinations and undergo the appropriate tests. Preparation for removal of a polyp in the uterus includes:
- Consultation with a gynecologist, therapist, anesthesiologist;
- General blood and urine analysis;
- Vaginal smears for flora and cytology;
- Electrocardiogram and fluorography.
In the presence of an active inflammatory process, surgery is performed only after a course of appropriate therapy.
Make an appointment
Mechanism of development of uterine polyp
It all starts with the fact that the ovaries are disrupted and they release too much estrogen into the blood. If normally this hormone controls the female body only the first two weeks of the menstrual cycle, now it is produced without stopping. As a result, the endometrium grows. Its individual sections do not peel off during menstruation, but remain in the uterus. This continues for several cycles. A small growth appears at this place. Gradually, vessels and connective tissue fibers grow into it - this is how a polyp is formed.
Symptoms
The severity of external manifestations of polyposis depends on the following factors:
- woman's age;
- the presence of regular ovulation;
- normal functioning of the ovaries;
- gynecological pathology (uterine leiomyoma, endometrioid disease, adnexitis).
The main complaint with endometrial polyposis will be pathological changes in the menstrual cycle:
- a significant increase in the abundance of critical days;
- intermenstrual bleeding;
- premenstrual bleeding;
- uterine bleeding;
- the appearance of bleeding during menopause.
Rarely occurring pain in the lower abdomen is caused by the following reasons:
- cessation of blood flow in the endometrial polyp;
- prolapse of a large polyp through the cervix (“birth”).
How can a polyp be removed?
Surgical treatment methods are the most reliable. They quickly rid a woman of polyps. Modern techniques make it possible to do without bloody operations, large incisions and scars. If there is only one polyp, then it is cut out. And if many small growths have formed, then it is necessary to scrape out the top layer of the mucous membrane.
When should you have surgery to remove polyps?
You cannot do without surgery in the following cases:
- if treatment with hormones does not produce results;
- if the woman is over 40 years old;
- polyp size more than 1 cm;
- when altered cells were discovered that could become the basis of a malignant tumor.
If the doctor has prescribed an operation to remove polyps - a polypectomy, you should not be afraid. Many women have gone through this procedure. Modern medicine offers gentle techniques that make the intervention almost bloodless, avoid postoperative complications and quickly return to normal life.
The hysteroscopic method is the treatment of polyps using a low-traumatic procedure. It is prescribed when it is necessary to clarify the location of polyps and remove them. This procedure is done under “light” anesthesia and lasts only 15-20 minutes. The woman can return home the same day.
The best period for this procedure is 2-3 days after the end of menstruation. On such days, the uterine mucosa is at its thinnest and the polyp rises above it. This makes it possible to remove the growth “at the root”.
The operation is performed under regional or general anesthesia. The doctor opens the cervical canal with a special instrument. A tubular apparatus called a hysteroscope is inserted through the vagina into the uterus. In the first step, the surgeon examines the uterine cavity using a small camera at the end of the tube. It determines the number of polyps and their size. After this, the polyp is cut off from the wall of the uterus using an electric surgical loop. The place where it was attached is cauterized with liquid nitrogen or 5% tincture of iodine.
A large single polyp can be removed with forceps. It is unscrewed by rotating around its axis. This method allows you to remove all tumor cells as much as possible. After this procedure, the vessels that fed the polyp also twist and do not bleed. Then the polyp bed (the place where it was attached) is scraped out with a curette and treated with an antiseptic. If this is not done, the polyp may grow back from the remaining cells.
If the doctor discovers many small polyps in the uterine cavity or in its cervix, then separate curettage is performed under the control of a hysteroscope. An instrument similar to a spoon with a pointed edge is attached to the equipment - a curette. With its help, the entire functional (upper) layer of the uterine mucosa is removed.
After the procedure, the tissue that is removed from the uterus is sent to the laboratory for examination. The hysteroscopic method of treating uterine polyps allows you to effectively and safely get rid of any benign polyps and minimize the risk of their reappearance.
Advantages of the hysteroscopic method:
- absolute safety;
- painlessness;
- the camera allows you to control the quality of the operation and not miss even the smallest polyps;
- There are no incisions to be made and there will be no postoperative stitches.
The laparoscopic method is an operation performed through small holes in the lower abdomen. The uterus is removed using the laparoscopic method if atypical cells are found in the polyp and there is a high risk of developing uterine cancer.
- Through a hole in the abdomen with a diameter of 0.5-1.5 cm, the abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide. This is done in order to raise the abdominal wall, which is in the way of the surgeon. Then a laparoscope with a camera at the end is inserted. The doctor examines the condition of the uterus and determines what needs to be done. Then he uses special equipment to excise the diseased organ and remove it. After this, stitches are applied. A few hours later, the woman is transferred from surgery to the gynecological ward. There she remains under observation for 5-7 days. The method is very effective in cases where the risk of a malignant tumor is high. It has many advantages: the woman does not experience postoperative pain; There are practically no complications;
- no scars remain on the body;
- rapid recovery (after 2 weeks the woman can return to work).
How does a polyp inside the uterus affect pregnancy?
A woman can become pregnant if there is a small polyp in the uterus or cervix. But in this case complications often arise. The fact is that a polyp can cause placental abruption. This organ is responsible for ensuring that the child constantly receives oxygen and nutrition. Through the placenta and the umbilical cord, maternal blood brings everything the baby needs. If the placenta is not tightly adjacent to the wall of the uterus, then not enough blood enters it. As a result, the child goes hungry. This can cause developmental delay, fetal hypoxia, or threatened miscarriage. In addition, if the polyp is injured, bleeding, spotting or bloody discharge occurs. In this case, the woman should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Polyps are not usually treated during pregnancy. All efforts of doctors are aimed at improving the baby’s condition. In addition, during pregnancy, many women's polyps resolve on their own. This happens because estrogen levels have dropped and these hormones no longer cause polyps to grow. If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with a polyp, she can carry and give birth to a healthy child. But she needs to take special care of her health.
Pregnancy with endometrial polyposis
Patients with endometrial polyposis may develop infertility. This is due to changes in hormonal levels and difficulties that arise during the implantation of a fertilized egg into the wall of the uterus. According to statistics, removal of polyps significantly increases the chances of both a natural pregnancy and IVF success.
If you have any questions related to polyposis, you can ask them to the doctors at Nova Clinic. You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling the number listed on the website or using the booking button.
Is it possible to cure a uterine polyp without surgery?
Today, medicine can cure uterine polyps without surgery.
But this cannot be done in all cases. If a woman has one small polyp, then with the help of special medications it can be made to decrease in size and disappear completely. Doctors try to do without surgery if the patient is still very young. Sometimes polyps appear in girls during adolescence, and in women who have not given birth, the operation can cause problems with conception.
Hormonal drugs reduce estrogen levels and increase the amount of progesterone. They eliminate the cause of the disease, and the polyps gradually dry out and come out of the uterus during menstruation.
Women over 35 years of age are prescribed gestagens : Duphaston, Norkolut, Utrozhestan. They are taken 2 weeks after the first day of menstruation for six months.
Treatment of uterine polyps is supplemented with folk remedies.
This comprehensive approach helps to quickly cope with the disease. After treatment of polyps, a woman needs to be observed by a gynecologist. The fact is that these growths sometimes appear again after treatment.
Recovery after the procedure
To avoid infection or injury, the following precautions are recommended to the patient after the procedure:
- Sexual rest for two weeks;
- Prohibition on the use of tampons and/or douching for a month after surgery;
- Refusal to visit the sauna or steam bath for a month;
- Refrain from significant physical activity during the recovery period.
If your temperature rises or excessive bleeding from the genital tract appears, you should contact your operating doctor.
If there are indications, the patient is prescribed drug therapy: anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal agents, possibly local sanitation with suppositories.
Prevention of polyps
The appearance of polyps is associated with disruption of the ovaries and excess estrogen.
Prevention of this disease includes many factors. Find out what you need to do to avoid polyps
- Do not eat foods contaminated with dioxide and meat containing hormones.
- Live in an area with good ecology.
- Avoid hypothermia, dress appropriately for the weather and do not sit on cold surfaces.
- Do not be promiscuous.
- To live an active lifestyle. Physical exercise does not allow blood to stagnate in the genitals.
- When choosing hormonal birth control pills, be sure to consult your doctor.
- Visit your gynecologist regularly.
Women's health is an essential component of a happy life. Take care of yourself and be healthy!