Why does tingling occur in the hands?
Physiological factors
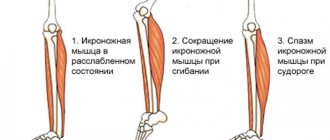
In a healthy person, tingling and numbness in the hand occurs when staying in an uncomfortable position for a long time.
The symptoms are caused by circulatory problems in the limb. As a rule, the symptom manifests itself if the patient sleeps with his hand under his head or under a pillow. A person wakes up and “does not feel” his hand, and when trying to make active movements, unpleasant feelings of tingling and immobility arise. The disorder disappears on its own after 5-10 minutes. The symptom may develop after physical activity (lifting dumbbells, carrying heavy bags). Fatigue of the muscles in the arms causes a slight tingling and heaviness that goes away after a long rest. In people who work physically, similar signs are detected almost every day: the hands get tired in the evening, which is manifested by severe tingling and weakness in the limbs.
Raynaud's syndrome
At the onset of the disease, tingling occurs periodically and is provoked by low temperature, excitement, and smoking. Stitching pains are most pronounced in the fingertips, which suddenly turn white and lose sensation. Gradually, the unpleasant sensations disappear, pallor is replaced by cyanosis or hyperemia. The attacks end with a feeling of heat and burning in the arms, mainly in the hands.
As the pathology progresses, paroxysms of stabbing pain with paresthesia become more common. The tingling sensation lasts more than 1 hour and begins without visible provoking factors. Discomfort often persists even during the interictal period. The skin of the hands is constantly cold and acquires a bluish tint. In the absence of medical care, long-term Raynaud's syndrome ends in trophic ulcers and gangrene.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
When the median nerve is compressed in the wrist area, the patient feels pain and tingling along the palmar surface of 1-4 fingers. The symptoms are most typical for office workers, pianists, packers - people whose hands are subjected to constant monotonous loads (flexion-extension). First, a person experiences periodic shooting and tingling sensations, which are provoked by increased stress on the hands.
The progression of carpal tunnel syndrome leads to constant stabbing pain, disturbing even during rest. The patient complains of difficulty turning and grasping movements with the hand, as if “everything is falling out of his hands.” Symptoms are accompanied by coldness or a feeling of heat in the hands, changes in skin color, and the appearance of marbling. Tingling localized on the back of the hand indicates damage to the radial nerve.
Tingling in hands
Intervertebral hernia
The lesion at the level of the upper thoracic vertebrae is manifested by tingling and paresthesia throughout the skin of the hands. Discomfortable signs are observed periodically and intensify after being in an uncomfortable position or physical stress on the shoulder girdle. Sometimes weakness in the arms develops, and it becomes difficult for a patient with an intervertebral hernia to perform usual housework.
Neurosis
Tingling in the hands is possible with psycho-emotional disorders, such as hysterical neurosis, panic attack, specific phobias. Some patients complain of a crawling sensation, coldness and trembling of the fingers. The tingling sensation lasts throughout the entire attack, after which it disappears without a trace. Sometimes, due to the stabbing sensation, a person begins to scratch the skin, rub their hands together, or make other stereotypical movements.
Avitaminosis
Tingling of the skin of the hands occurs with a lack of vitamin B12, which provokes the development of peripheral neuropathy. Patients feel moderate stabbing pains, which are combined with tickling and a crawling sensation. Unpleasant symptoms first appear in the fingers of the limb, gradually spread to the entire arm, and move to the torso. Sometimes there are hot flashes or, conversely, cold hands.
Rare causes
- Bad habits
: caffeine addiction, alcohol abuse. - Poisoning with toxins
: arsenic, mercury, thallium. - Neurological disorders
: acute cerebrovascular accidents, multiple sclerosis. - Autoimmune pathologies
: scleroderma, dermatomyositis, systemic lupus erythematosus.
What research needs to be done
Because pain in the fingertips is a symptom of diseases that may pose a risk to the patient, a complete baseline examination is necessary. General and biochemical blood tests are prescribed, and an ECG is performed. Even if there is no suspicion that the pain is related to the heart, but problems with the spine cannot be ruled out, the results of the research will be needed to decide on admission to physiotherapy.
Further research depends on what diagnosis the doctor suspects after receiving the results of basic research.
Diagnostics
A neurologist will determine the cause of tingling in the hands. During the initial examination, the patient is asked to perform simple tests (clench the hand into a fist, rotate the thumbs), during which it is easy to detect motor problems and innervation disorders. If neuropathy of the radial or median nerve is suspected, Tinnel's sign is checked. For further examination, the following instrumental methods are used:
- Electroneuromyography.
A comprehensive study of neuromuscular transmission is necessary to identify problems with peripheral nerves and to know the location of the lesion. ENMG helps determine the severity and extent of the process. The technique is effective for the differential diagnosis of neuromuscular and vascular pathologies. - Radiography.
X-ray imaging of the bones of the shoulder, forearm, and hand makes it easier to identify the location of nerve damage. In the pictures you can see bone deformations, degenerative changes or narrowing of bone canals, which could cause tingling and paresthesia in the hands. - Angiography.
Examination of the peripheral vascular bed using contrast is necessary to verify Raynaud's syndrome. The doctor pays attention to the unevenness of the lumen of the vessels, the absence of collateral branches and a decrease in the number of capillaries. Additionally, capillaroscopy of the nail bed is indicated. - MRI of the spine.
This is the most accurate method that allows neurologists to diagnose herniated discs. MRI shows not only the presence of a hernial protrusion, but also its size and the degree of compression of the spinal cord. The study is informative for excluding tumors, hematomas and other space-occupying neoplasms. - Additional methods
. To clarify the degree of spinal compression in intervertebral hernias, computed tomography with myelography is used. Peripheral microcirculation is assessed using Doppler flowmetry. Gastroscopy, gastric intubation, and blood tests help identify the causes of B12 deficiency.
Electromyography
Tingling during pregnancy
In the early stages, the cause of autonomic disorders, manifested by tingling in the arms, legs or other parts of the body, is usually pregnancy neurosis, which occurs as a reaction to a sharp change in hormonal levels.
Other symptoms of neurosis will be:
- depression;
- the appearance of phobias;
- apathy.
Later, when the developing child’s body needs an increased amount of calcium to build the skeleton, the expectant mother may feel tingling in her legs, accompanied by cramps in her legs - a sign of a deficiency of this mineral.
Around the middle of the pregnancy, a pregnant woman may notice that her hands are numb and there is a tingling sensation in her fingers - this is caused by carpal tunnel syndrome. Its development is determined by the action of hormones that support pregnancy.
They provoke swelling of the tendons located next to the carpal tunnel, a large nerve that provides mobility to the fingers. The tissue puts pressure on the nerve and interferes with its normal functioning.
In late pregnancy, the most common cause of tingling in the legs is the pressure of the enlarged uterus on nearby vessels and nerve fibers, which leads to disturbances in their functioning. Paresthesia is usually intense in the feet and is accompanied by swelling.
Most of the causes that cause paresthesia during gestation are not dangerous and will disappear after childbirth. However, it is necessary to consult a doctor, since a tingling sensation may also indicate diseases that previously did not manifest themselves in any way, but began to develop intensively during pregnancy.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To prevent episodes of tingling in the hands, the patient is advised not to overload the hands and take breaks from monotonous work. For those who have to work at a computer all day, there are special palm rests and computer armrests that relieve some of the stress. It is necessary to avoid sudden overheating or hypothermia of the hands, so as not to provoke vascular spasm.
Conservative therapy
Tingling is generally mild or moderate, so symptomatic treatment with analgesics is usually not necessary. For sharp stabbing pains, it may be necessary to take systemic painkillers or administer local anesthetics (therapeutic blockades). Complex therapy is selected taking into account the etiology of the disease. The following groups of drugs are used:
- Calcium antagonists
. Recommended for expanding the lumen of blood vessels, which plays a decisive role in the treatment of Raynaud's disease. If they are ineffective, treatment is enhanced with ACE inhibitors and selective serotonin receptor blockers. - Antiplatelet agents
. They improve blood flow in peripheral arteries and capillaries, reduce the phenomena of vasospasm and ischemia of the hands. Medicines help reduce the frequency of attacks in those suffering from Raynaud's syndrome and prevent complications of the disease. - Anti-inflammatory drugs
. Exacerbations of neuropathies require the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which eliminate pain and swelling and eliminate discomfort. In severe cases, therapy is supplemented with systemic corticosteroids. - Sedatives
. For neurotic disorders, herbal and synthetic sedatives are effective, they stabilize the patient’s emotional background. Occasionally tranquilizers and antidepressants are used. - Vitamins
. For vitamin B12 deficiency, cyanocobalamin is administered parenterally, which quickly eliminates tingling in the hands and paresthesia. For neuropathies and intervertebral hernia, other B vitamins (thiamine, pyridoxine) have a good effect.
In the treatment of neuropathies, targeted administration of drugs into the affected area is effective, which is carried out through electrophoresis and phonophoresis. After clinical improvement and disappearance of stabbing pain, mud therapy, electrical myostimulation, and myofascial massage of the hand are prescribed. Physical therapy is needed to restore nerve function and improve muscle strength.
Psychological reasons
This group of causes includes factors that are not associated with mechanical effects on nerve fibers, but cause excessive stress on the nervous system. This leads to malfunctions in its functioning, which can manifest itself as a persistent tingling feeling.
These include:
- depression, severe stress, anxiety;
- obsessive-compulsive disorder, in which the patient is haunted by obsessive thoughts or ideas of doing something;
- psychosis is a serious mental illness characterized by the presence of hallucinations, including tactile ones.