The diagnosis of uterine fibroids (fibroma, fibromyoma) is made quite often, and just as often the disease raises questions among patients: what is it, how dangerous is it, how and what to treat, what will happen if left untreated, etc.
You can get answers to all these questions, as well as diagnose the presence of the disease, only at an appointment with a gynecologist
. You can sign up for a consultation and undergo examination at a medical center at a time convenient for you.
What is fibroma and its types
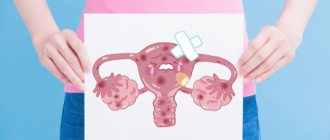
Uterine fibroid is a benign neoplasm that is formed from connective tissue and muscle fibers. Outwardly it looks like a small seal or knot. It can occur both inside and outside the cervix. The size of the tumor can vary - from 1 mm to 20 cm.
This benign tumor is a hormone-dependent neoplasm. This means that its occurrence and growth are associated with hormonal changes. That is why such a diagnosis does not occur in menopause, as well as in girls before puberty.
Depending on the location, the following types are distinguished:
- Submucosal or submucosal. Grows inside the uterine cavity.
- Interstitial - occurs in the thickness of the uterine wall.
- Subserous - forms under the outer lining of the uterus.
- Interligamentous - formed on the ligaments of the uterus or between them.
- Stalked - has a specific leg. Its torsion can lead to severe pain.
All these forms have their own characteristics, which determine the choice of treatment method.
Types, characteristics of fibroids
There are more than 10 different morphological variants. Pathologists give a description of what each form looks like and how it differs after histological examination - elastrophibroma, soft, dense fibroma.
- Dermatofibroma is a single or multiple formation of intradermal localization, mobile and painless when palpated with unchanged color.
- Desmoid fibroma has another name - aggressive fibrosis, refers to mesenchymal tumors originating from excess collagen fibers and differentiated fibroblasts. They often progress and recur, forming in soft tissues, the retroperitoneum or on the abdominal wall.
- Chondriomyxomas are rare tumors that affect bone tissue - the edges of long bones, pelvis, ribs, vertebrae, feet, metatarsus.
- Angiofibriomas in the cheek and nose area, containing small tubercles with connective tissue fibers.
Causes of pathology
The development of fibroids directly depends on the female hormone - estrogen. Therefore, the main reason for its formation is hormonal imbalance. But not every woman has hormonal disorders that lead to such a diagnosis. Why is this happening? This is due to the fact that for compaction to develop there must be fertile soil. Namely, pathological changes in the tissues of the uterine cavity. The following factors can cause them:
- abortion;
- damage to the cervix when installing or removing the IUD;
- childbirth;
- infectious diseases of the pelvic organs;
- miscarriage;
- intrauterine interventions, including diagnostic procedures.
Factors that can lead to hormonal imbalance include:
- endocrine pathologies;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- metabolic diseases;
- obesity;
- frequent stress;
- dissatisfaction with sex life;
- liver diseases;
- low physical activity.
Hereditary factors also play a role.
Why does fibroid develop?
The reasons for the formation of nodes are perhaps obvious; they are also the causes of many gynecological diseases and conditions (dysmenorrhea, endometriosis, early menopause and others):
- Disruption of hormone production for various reasons: chronic stress, exhausting physical work, taking certain hormonal drugs, endocrine diseases; the predominance of estrogen production over progesterone production leads to the growth of the muscular layer of the uterus;
- Late labor, more than 5 births;
- Infections of the genital organs;
- Chronic inflammatory processes of the uterus and its appendages;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Habitual miscarriage.
Symptoms of the disease
Small formations are asymptomatic. The tumor can develop for years before the female body reacts to it with any symptoms.
The following manifestations should alert you:
- Change in the length of the monthly cycle.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Problems with pregnancy or conception.
- Abnormally heavy menstruation.
- Frequent urge to go to the toilet.
- Bleeding during the “dry” period.
As fibroids increase in size, they can put pressure on nearby organs, such as the ureter. In this case, disorders of the urinary system occur. Due to pressure on the blood vessels, a woman may complain of cramps, especially at night.
Large blood loss causes weakness, fatigue, and dizziness. If you have such symptoms, you should definitely contact a gynecologist or gynecologist-endocrinologist.
What complications can there be?
Large formations can lead to compression of the nerve endings of neighboring organs. Other complications of fibroids include:
- Partial or complete necrosis of the neoplasm. Leads to severe intoxication of the body. Characterized by intense pain and fever.
- Pinching or bending of the fibroid leg.
- Inversion of the uterus.
- Suppuration or infection of fibromatous formation.
- Rupture of tumor vessels is rare. Leads to intraperitoneal bleeding.
If a woman does not see a doctor for a long time, the risk of developing severe anemia increases. This condition not only leads to rapid fatigue and loss of performance, but can also be fatal.
General information
Single or multiple fibromas can affect the lungs, mammary glands, liver, skin, oral mucosa, etc. The proliferation of connective tissue occurs under the influence of various factors: unfavorable environmental conditions, severe injuries, bacterial or viral infections. When making a diagnosis and developing a treatment strategy for a patient, dermatologists, oncologists and surgeons take into account laboratory data. Information about the morphology of the tumor allows doctors to assess the risk of its malignant degeneration.
Fibroma and pregnancy
About 35% of women with this pathology have problems conceiving. This is due not only to the fact that there are nodes in the uterine cavity. The main reason is disruption of the ovaries, which are responsible for the ovulatory phase of the cycle.
Small formations do not interfere with pregnancy. But under the influence of hormonal changes, a sharp growth of fibroids is possible. As it increases in size, it will begin to compress the uterus. The embryo will not be able to develop normally, which will lead to miscarriage or premature birth.
Also, low-lying nodes will interfere with natural delivery. In this case, there is a need for a caesarean section. During childbirth, fibroids may be damaged. This can lead to postpartum complications such as inflammation of the node, uterine bleeding.
General signs of hormonal disorders
There are a number of symptoms that do not indicate the development of uterine fibroids, but precede the onset of the disease. Some of them are individual and depend on the woman’s health status and the characteristics of her body. Some are typical for all patients with hormonal imbalance, for example:
- increased irritability, emotional instability, depression and apathy;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle, expressed in frequent, painful, too abundant or, conversely, rare and scanty bleeding;
- uterine bleeding;
- decreased libido;
- problems with the mammary glands;
- alopecia or hypertrichosis in various parts of the body;
- weight gain;
- frequent headaches;
- dizziness, loss of orientation, fainting;
- noticeable swelling;
- disturbances of appetite and eating behavior;
- insomnia;
- blood pressure surges;
- increased fatigue.
Uterine fibroids: diagram
If a patient is diagnosed with uterine fibroids, symptoms may intensify. In this case, it is necessary to begin comprehensive treatment of the disease as quickly as possible, paying special attention to hygiene and restoration of hormonal levels. To improve the condition of the reproductive system, experts recommend using Gynocomfort restoring and moisturizing intimate gels. They carefully care for the intimate area, provide the necessary level of humidity and prevent bacterial infections.
Diagnosis and treatment methods for the disease
A tumor can only be detected during a gynecological examination. An accurate diagnostic method is ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may order the following additional studies:
- Metrography (x-ray of the uterine cavity).
- Diagnostic curettage.
- Bimanual (manual) examination of the uterus.
An important point in making a diagnosis is the woman’s age. In 80% of cases, fibroids are diagnosed after 35-40 years.
Small formations that do not cause discomfort to the woman are subject to dynamic monitoring. Treatment in this case is not required. An independent decrease in the node is observed during menopause, when the ovarian function fades.
Conservative therapy
For minor pain, as well as problems with conception, the doctor may prescribe hormonal treatment (progesterone injections intramuscularly for 7-10 days).
It is possible to take a course of androgen medications. They reduce estrogen production in the ovaries, which leads to tumor shrinkage. An effective method is to install a special intrauterine hormonal system. However, such methods are used only for small nodes.
In exceptional cases, it is possible to perform radiotherapy on the area of both ovaries. This type of treatment leads to a stop of the menstrual cycle, so its use is undesirable for women planning a pregnancy.
Surgical treatment
The operation is indicated in the following cases:
- rapid growth of fibroids;
- prolonged and heavy uterine bleeding;
- severe anemia;
- node necrosis;
- infertility;
- suspicion of transformation of fibroma into sarcoma (malignant tumor);
- large tumor size, which negatively affects other organs.
In most cases, organ-preserving surgery is performed using a gentle laparoscopic method. It allows you to remove formations while preserving the uterus. Manipulations are carried out through small punctures in the lower abdomen. The rehabilitation period is short, since there is no classic peritoneal incision.
It is also possible to perform a procedure such as embolization of the uterine arteries. The purpose of the operation is to introduce a special substance into the arteries, which disrupts blood circulation in this area. This leads to obstruction of the vessels that feed the fibroma.
A modern method is also ultrasound ablation (USA). With its help, the formation is “evaporated” without injuring the uterus. The operation is performed under MRI guidance.
Removal of myomatous nodes
If the node is small in size and does not manifest any symptoms, then the woman is advised to undergo dynamic observation by a gynecologist with mandatory ultrasound examination once a year. Patients are prescribed drugs that stop further progression of the myomatous node and correct the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian relationship. Excess fats and carbohydrates should be excluded from the diet, as well as spicy and salty foods. Patients are not recommended to take thermal procedures, sunbathe in the sun or in a solarium. They need to limit massage. Vitamins and hormones are prescribed. Homeopathic and herbal remedies, as well as alternative medicine methods, are effective.
In some cases, after drug treatment, positive dynamics are observed. However, surgical methods for treating uterine fibroids remain leading. In eighty percent of cases, radical operations are performed. Surgeries for uterine fibroids account for forty-five percent of abdominal interventions performed in gynecology.
Prevention of uterine fibroids
To maintain women's health, it is enough to visit a gynecologist annually. You should also follow these simple recommendations:
- Do not take hormonal medications without consulting your doctor.
- Installation of intrauterine devices should only be performed by an experienced doctor. The structure must be removed strictly within the prescribed period.
- Use protection if you are not planning a pregnancy.
- Treat all infectious diseases.
- After childbirth, do not ignore preventive examinations with a doctor.
- Don't give up breastfeeding. This is a natural method of preventing mastopathy.
Try to maintain peace of mind. The female reproductive system is sensitive to emotional experiences and stress.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of fibroids is performed by doctors of various specializations - dermatologists, oncologists, surgeons, gynecologists, etc. Methods for confirming the primary diagnosis are determined by the location of the benign neoplasm. At the first stage of the examination, patients receive a referral for radiography. Computed tomography allows you to determine the exact size of the tumor and identify signs of its invasion into adjacent organs.
Fibrous formations in bone and cartilage tissue are detected during scintigraphy. If necessary, the doctor can take a biopsy sample for laboratory tests. Microscopy of the obtained biomaterials will allow doctors to assess the morphological structure of tumor cells and the likelihood of their malignant degeneration.
Benign neoplasms of the female reproductive system are often detected during ultrasound examinations. The focus of the pathological process has less echogenicity compared to adjacent tissues.