Cervical biopsy is one of the most informative and effective methods for diagnosing pathologies of the reproductive system. In most cases, the study is prescribed to confirm or refute the progression of cancer processes. The technique involves surgical intervention, during which samples of the affected tissue are removed for further histological examination. Proper preparation for a cervical biopsy will help prevent postoperative complications and recover faster. The results of the study are as informative as possible, therefore they allow us to determine the most correct management tactics and effective treatment for the patient. Our multidisciplinary medical center has all the necessary and high-precision diagnostic equipment that allows you to safely, painlessly perform a biopsy and obtain reliable results in the shortest possible time.
What is a cervical biopsy?
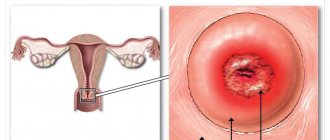
A cervical biopsy is a diagnostic surgical procedure during which the doctor removes a sample of pathologically altered tissue for further examination under a microscope. In gynecology, the technique is carried out with the aim of making a final diagnosis, when there is the slightest suspicion of oncological degeneration of the tissues of the uterine cavity. A biopsy of the cervix is performed after receiving poor results from colposcopy and PAP test, which are necessarily carried out before the procedure.
Indications for the procedure are:
- abnormal changes in the cervical mucosa;
- suspicious formations on tissues;
- endometriosis;
- leukoplakia;
- cervical polyposis;
- dysplasia;
- pre-cancer conditions.
Biopsy for erosion
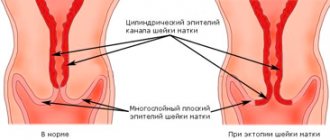
Erosion is a very common pathology of the cervix. Its detection requires caution and the exclusion of oncological pathology. Every patient must know that examination of the cervix is not carried out “by eye”, in mirrors, but only during colposcopy. If a specialist has prescribed a biopsy, you should definitely agree, since an incorrect or unspecified diagnosis can lead to ineffective treatment and the development of cancer.
A biopsy allows one to differentiate erosion from simple cell metaplasia and dysplasia. After the procedure, spotting is possible for several days, but it should not be too profuse and should not be accompanied by fever or severe abdominal pain. Such symptoms require consultation with a specialist. In most cases, the biopsy is well tolerated by patients.
Purpose of cervical biopsy
The main goal of the procedure is the collection and detailed histological examination of the biopath for the presence of atypical cells. Histology is the study, using diagnostic optics, of a previously prepared and stained section of a biopath extracted from the cervix. The study of the material helps to determine the causes of pathological changes in organ cells, identify exophytic condylomas, and oncological processes. The results of the biopsy will help make a final diagnosis and select the most effective treatment regimen.
Types of cervical biopsy
Taking into account the method of collecting material for research, there are several types of biopsy. The doctor determines which method is advisable to resort to in a particular case, based on the results of a preliminary diagnostic examination, which necessarily precedes a biopsy.
Colposcopy and cervical biopsy
A biopsy of any type is carried out under visual control, which is provided by the colposcopy procedure. This is a minimally invasive method of examining the vaginal surface and cervix using an optical device - a colposcope, which magnifies the image 15-40 times, providing the most voluminous and detailed picture. Colposcopy allows you to detect the most significant anomalies, as well as conduct the most accurate targeted biopsy. Colposcopic devices of the new generation are convenient, mobile, and allow the doctor to carry out all the necessary manipulations for the most detailed examination of the affected areas.
Targeted cervical biopsy
This type of diagnostic biopsy is performed under local anesthesia. Samples for histology are collected using a special surgical needle. Before taking the tissue, the doctor examines the surface of the cervix, determines the pathological foci from which the material will be collected. The cervical walls are treated with the drug, after which the doctor cuts off the tissue.
Targeted biopsy is a low-traumatic, safe, effective diagnostic procedure that is often prescribed to nulliparous women. The technique does not deform the cervix, does not provoke complications and does not have negative consequences for the successful conception and bearing of a child.
Circular biopsy of the cervix
Taking a biopath for histology is painful and is therefore performed under general anesthesia. Includes sampling of atypical and healthy tissues and can be used not only for diagnostic, but also for therapeutic purposes. The biopsy sample is excised with a surgical scalpel. This is the most traumatic diagnostic method, involving the application of a surgical suture to the wound surface. Therefore, a circular biopsy is not prescribed to young and nulliparous women. It can lead to serious deformation of the cervix and negatively affect conception and subsequent pregnancy.
Extended excisional biopsy of the cervix
Extended excisional biopsy of the cervix is an improved type of circular biopsy. The technique is used when the pathological area is large, when it is necessary to obtain the most informative material for histological examination.
The following instruments are used to collect samples:
- LEEP biopsy. It is a standard electrode loop of the appropriate size.
- CONE biopsy. This is a sail electrode of the appropriate size.
Tissue collection for histology is carried out using a non-contact radio wave method. Thermal damage and destruction of healthy tissue is excluded. Coagulation of blood vessels and nerve fibers ensures a bloodless, painless incision. In addition, radio waves have an antiseptic effect, which minimizes the risk of tissue infection. An extended biopsy of the cervix can be performed on young women who have never given birth, since the risk of postoperative complications is almost completely absent.
Cervical biopsy by curettage - endocervical curettage
Endocervical curettage is recommended for all patients to exclude processes that precede cancer, as well as adenocarcinoma inside the cervical canal. During the procedure, using a special surgical instrument, the doctor removes the mucous tissue of the cervical canal, after which he sends the material for histology. For some pathologies of the uterus, endocervical curettage can be performed for therapeutic purposes. For example, with polyposis, dysplasia, etc.
Radiosurgical biopsy is the most modern method of cervical biopsy
Radio wave biopsy is the most gentle, fast, informative, painless procedure. Using the Surgiton apparatus, the doctor, without touching the tissues, evaporates pathological cells, while simultaneously sealing the blood vessels, preventing internal bleeding. The technique ensures the integrity of tissues removed for histology, and also does not damage healthy tissue, providing the patient with rapid rehabilitation and the absence of negative consequences. Radiosurgical biopsy is more often prescribed to young girls and nulliparous women, since it does not leave scars or other deformations that impede normal conception and childbearing.
Contraindications to the procedure
The list of restrictions on performing a cervical biopsy is relatively small:
- poor blood clotting;
- acute inflammatory processes localized in the vagina, on the cervix or in the body of the uterus itself;
- infections that are sexually transmitted.
If an STD is detected, the procedure is postponed until the patient has completed the course of treatment prescribed by the doctor and has fully recovered. These rules apply to inflammatory processes in the organs of the reproductive system. Such strict measures are due to the fact that during the biopsy the cervical mucosa is injured, and the risk of wound infection increases significantly.
What can and cannot be done after the procedure?
After the procedure, the woman can travel home or to work on her own. No hospital or bed rest required
. There are no complications; mild discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen goes away on the second day. Infection is excluded because a sterile, disposable instrument is used.
Are you looking for a clinic in Moscow in the Konkovo area to quickly and inexpensively undergo a pipel endometrial biopsy? Residents of the Yasenevo, Belyaevo, Mosrentgen, and Tikhy Stan districts often contact us.
Preparing for cervical biopsy surgery
To prevent serious complications, careful preparation for the cervical biopsy procedure is required. The optimal time frame for diagnosis is days 7–11 of the cycle, starting from the first day of the onset of menstruation.
Before giving a referral for a cervical biopsy, the doctor performs a gynecological examination, which usually includes the following procedures:
- biomanual examination;
- vaginal smear for microflora;
- PAP analysis;
- colposcopy;
- ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system.
If the results of the smear for microflora are positive, additional PAP testing for infections is prescribed. After this, the patient is prescribed appropriate drug therapy, after which a biopsy can be performed.
A woman must also undergo general clinical tests before a cervical biopsy:
- general blood test, urine;
- biochemistry;
- coagulogram;
- blood test for hidden infections, HIV, hepatitis.
Electrocardiography, fluorography, and consultation with specialized specialists are required if there are concomitant diseases.
5–7 days before the procedure, stop taking medications that affect blood viscosity. For 2-3 days, exclude sexual activity, douching, and the use of vaginal suppositories, tampons and other means.
It is also important to follow the rules of hygienic preparation:
- The evening before the biopsy, shave your intimate area.
- In the morning, on the day of the procedure, take a refreshing shower and put on clean underwear.
- After the biopsy, you will need sanitary pads, since after the biopsy is taken, the wound will bleed for some time.
When is it carried out?
Before prescribing the study, the doctor determines the most favorable days of the menstrual cycle; they differ for different pathologies:
- in case of infertility due to insufficiency of the corpus luteum or the presence of a large number of anovulatory cycles, a biopsy is done before menstruation or at the very beginning;
- in case of heavy menstrual bleeding due to slow rejection of the uterine mucosa, the material is taken on the 5-10th day of the cycle, depending on the duration of menstruation;
- if there are no menstruation and there is no pregnancy, patients are prescribed repeat biopsies within 3-4 weeks with breaks of 1 week;
- in case of acyclic bleeding, scraping is done immediately after the start of bleeding or spotting;
- To determine the day of the menstrual cycle, the study is carried out between the 17th and 24th day;
- if endometrial cancer is suspected, the material is taken on any day of the cycle.
How is a cervical biopsy done? Progress of the operation
A cervical biopsy is performed in the treatment room. The patient sits comfortably in a gynecological chair, after which the doctor resorts to an anesthesia procedure. A speculum is inserted into the vaginal cavity and the cervix is exposed. Next, using a colposcope, the doctor determines the exact boundaries of the pathological focus.
Under the control of colposcopy, the specialist carries out all the necessary manipulations, after which the biopath is removed and given to a laboratory assistant for histological examination. The procedure takes 15, maximum 20 minutes. After the biopsy, rehabilitation is required, during which you must strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Diagnostic results are usually available within a few days. Based on the data obtained, the specialist will determine the further treatment plan for the patient and select the most effective treatment.
Cost of cervical biopsy
If you or your loved ones need high-quality, professional medical care, contact the Healthy Family multidisciplinary clinic, where experienced specialists with many years of experience work. Our doctors will quickly establish the correct diagnosis and select the most effective treatment regimen that will help restore women’s health and prevent the development of serious complications.
To find out the cost of a cervical biopsy and make an appointment with a medical specialist, call the number or fill out the feedback form. As soon as the administrators see your request, they will immediately contact you and answer all your questions.
To avoid the risk of complications after a biopsy, the patient is prohibited from:
- take a bath (only showers are allowed);
- go to the bathhouse and sauna;
- swim in pools and open water;
- use vaginal tampons;
- exercise and lift weights weighing more than 3 kg;
- douche for a month after surgery;
- be sexually active for two weeks after the procedure.
Most often, the restrictions continue until the end of the next menstruation, but sometimes they can be extended, about which the doctor warns the patient in advance.
In multidisciplinary medicine, much attention is paid to women's health. Before the procedure, the gynecologist must conduct an examination, talk with the patient and identify the individual characteristics of the woman.