Oncocytology is the study of microflora, the materials of which the doctor takes from the uterus. Such microscopic analysis makes it possible to determine the development of oncological pathologies in the early stages. This is a simple and quick procedure that every woman should go through.
Oncocytological examination during pregnancy is recommended to be carried out at least 3 times. Also, a similar analysis is prescribed if irregularities in the menstrual cycle, pathologies in the uterus and hereditary risks are present. Oncocytological examination during pregnancy is necessary in order to protect the fetus and fully control its development, monitoring the current health of the mother.
Detailed description of the study
Cytology (Greek <cytos> - cell, <logos> - science) - the science of the cell. He studies the structure and functions of cells, their connections and relationships in organs and tissues, and studies the cell as the most important structural unit of living things. The cytologist’s diagnosis may sound like “no atypical cells were detected” - this is the norm. Atypical cells are cells that have changed in shape, size, and nuclear structure. The changes may be caused by a malignant process or inflammation.
The cytological research method is one of the most accurate methods for diagnosing cervical pathology (precancerous and cancerous processes). Smears for cytological examination of cervical scrapings should be taken from all women over 18 years of age, regardless of clinical data. The frequency of cytological examination is determined by a gynecologist (at least 2 times a year). Material for cytological diagnosis is obtained in various ways (by aspiration and scraping of the contents of the posterior vaginal vault, cervix, or obtaining a smear-imprint). In the presence of clinically pronounced pathological changes in the cervix, cellular material is taken specifically. Cells taken from a certain area of the cervix are distributed and fixed on glass.
Cytological screening for cervical cancer is a complex of organizational and medical measures aimed at the early detection of pre-tumor and tumor diseases of this localization.
According to the Clinical Guidelines of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (2017), women aged 21 to 29 years are examined once every 3 years, from 30 to 69 years old - annually, and if a normal smear is obtained three times (3 years in a row), the examination is carried out further once every 3 years. Women over 69 years of age do not need screening if the results of the last two tests were negative. Cervical cancer ranks third in prevalence among all malignant tumors in women (after breast and colon cancer). It occurs in 15-25 out of 100,000 women. Risk factors for the development of cervical cancer include the following: infection with the human papillomavirus (oncogenic serotypes 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, etc.), smoking, chlamydial or herpes infection, chronic inflammatory gynecological diseases, long-term use of contraceptives, cases of cervical cancer in the family, early onset of sexual activity, frequent changes of sexual partners, insufficient dietary intake of vitamins A and C, immunodeficiencies and HIV infection. To prepare a regular smear for cytology and determine atypia, no fixatives are used and simple dyes are used. A scraping obtained using a special cytobrush from the endocervix and exocervix is examined. The smear should contain material from the transformation zone. When performing a smear for oncocytology, signs of infection, pathology of the endocervix and endometrium can also be detected. When the material is collected correctly, both types of epithelium are found in the specimen. A smear containing 8-12 thousand cells of stratified squamous epithelium (including metaplastic epithelial cells) is considered adequate; The number of endocervical epithelial cells and/or metaplastic epithelium (from the transformation zone) should be at least 10 cells (single or in clusters). If more than 75% of the cells of the stratified squamous epithelium are covered with red blood cells, leukocytes, etc., then the quality of the smear is considered unsatisfactory.
Preparation for the procedure
Two days before going to the doctor you need to give up any sexual relations. The use of creams and tampons is also prohibited. The smear itself can be performed on any convenient day of the cycle. Oncocytological examination during pregnancy cannot be carried out in the presence of any kind of inflammation.
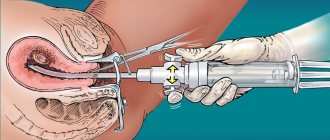
The gynecologist takes a special brush or spatula for a smear. The examination is carried out in a chair. The resulting material is sent to the laboratory. The results of an oncocytological study during pregnancy can be collected 10-14 days after the procedure.
What else is prescribed with this study?
Antigen for squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) (carcinoma of the cervix, nasopharynx, esophagus, ear and other localizations)
8.14. Ven. blood 1 day
2,200 ₽ Add to cart
HPV 16/18/31/33/35/39/45/51/52/56/58/59 type, DNA (HPV, PCR, genotyping) scraping, count.
19.57. Scraping 1 day
1,700 ₽ Add to cart
Gynecological smear for flora
16.1. Scraping 2 days
620 ₽ Add to cart
Oncocytological examination during pregnancy
For pregnant women, the first smear is taken immediately upon registration. This is necessary for the gynecologist to study the condition of the female body in more detail in the early stages. The second study is carried out at week 30, when the patient is issued an exchange card. The third oncocytological study during pregnancy is prescribed at 36-37 weeks. In some cases, the doctor may write more directions.
Reasons for additional tests: • Complaints of burning and itching. • Any change in allocations. • Symptoms of the inflammatory process.
The doctor usually takes 3 swabs for a reliable analysis. There is a separate spatula for each material. Then it is applied to a special glass and sent to the laboratory.
There are several medical technologies that allow you to decipher the results of an oncocytological study during pregnancy. The materials received by the gynecologist are first stained and only then placed under a microscope. A similar technique is used to determine the susceptibility of bacteria to certain types of antibiotics.
An oncocytological study during pregnancy allows you to find out the full composition of a woman’s microflora. It is important to understand that any infections and harmful organisms in the birth canal can lead to serious consequences. Oncocytological examination during pregnancy helps prevent possible infection of the fetus. The doctor must constantly monitor the state of the microflora and, in case of danger, immediately prescribe treatment.
Main indicators of cervical cytology
The cytological smear is subjected to microscopic examination.
This determines:
- The presence of pathogenic microflora.
- The number of red blood cells and leukocytes.
- Condition of the columnar epithelium.
If the number and shape of cells does not cause abnormalities, the study is considered negative, which is the norm.
When the analysis shows that morphological changes have occurred in the cells, with a violation of their structure, this result is considered positive. In this case, a repeat type of analysis is prescribed in combination with additional types of research.
Immunohistochemical determination of p16 protein expression
Immunohistochemical analysis (IHC), or immunohistochemistry, is an analysis that can reliably identify the involvement of the human papillomavirus of high carcinogenic risk as the cause of dysplasia.
The fact is that our immune system prevents the division of atypical cells, and depending on the condition of the cell, it calls an ambulance or destroys it.
To signal a breakdown, cells produce a special protein. But HPV of high carcinogenic risk has learned to bypass the vigilance of the immune system and stimulate the production (expression) of the p16 protein. This protein also acts like an invisibility cloak - it reliably hides the atypical cell from destruction.
This analysis is prescribed only when receiving a questionable cytogram (ASCUS, ASC-H), mild dysplasia (LSIL), moderate and severe dysplasia (HSIL). Since the Ministry of Health does not recommend treating LSIL, in the latter case it is important for me to exclude the risk of its progression to severe dysplasia.
It is considered a serious mistake to conduct an IHC study on p16 protein expression when receiving a normal NILM cytogram analysis.
The presence of 16 indicates a high probability of malignancy of the process - that HPV has taken control of the immune system, that the virus is actively dividing, that the dysplastic process is progressing and treatment is necessary even for a mild form of dysplasia.
How does the procedure work?
A smear for oncocytology is taken during a standard examination or colposcopy. The gynecologist scrapes cells from the cervix with a disposable medical brush. The procedure for taking a smear for oncocytology lasts 30 seconds and is absolutely painless for the patient. The brush has stiff bristles to effectively collect material, so after a smear, scanty spotting may appear. They usually go away within 24 hours and are not a cause for concern. Our doctors will definitely warn you about this minor discomfort and offer the appropriate hygiene product.
Cervical cytology - what is it?
A cytological smear for morphologically changed cells is also called PCR analysis. It increases the chance of detecting atypical cancer cells; they indicate the onset of the oncological process. Also, this type of analysis reliably determines the presence of pathological microflora, human papillomavirus.
Early diagnosis of cancer makes it possible to preserve the health and sometimes even the life of a woman. This is due to the fact that the early stage is asymptomatic, and when the clinical picture of the disease makes itself felt, the disease is difficult to treat even with surgical intervention. Delayed diagnosis sometimes negate the use of radiation or chemotherapy.
Another advantage of early diagnosis of cancer is the ability to preserve the integrity of the genital organs and the possibility of the reproductive function of the body.
To prevent the development of undesirable consequences, it is necessary to undergo an annual examination by a gynecologist and undergo this type of analysis.
Sometimes this type of test may be called a PAP test.
Unscheduled cervical cytology
During colposcopy, two smears are usually taken:
- The material is collected directly from the cervical canal.
- A vaginal smear allows you to determine the presence of pathogenic microflora.
In some cases, an unscheduled appointment of this type of study occurs. It occurs in the following cases:
- If there is a suspicion of the presence of papillomavirus, or genital herpes.
- Vaginal discharge of unknown etiology.
- Disorder of menstruation, prolongation or delay.
- Heavy uterine bleeding.
- Suspicion of HIV infection.
- If a woman wishes to have an intrauterine device installed.
Doctors' recommendations
All experts in the field of medicine (gynecology and oncology) argue that this type of analysis should be done once a year.
This will make it possible to identify cancer pathology at an early stage of development. Only timely detection of this disease will allow for a complete recovery.
Cervical cytology allows you to identify women who are at risk. Register them and carry out monitoring to monitor the progression of the oncological process.
What does cytology show?
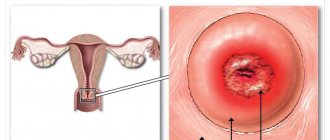
The result of cervical cytology can be divided into positive and negative:
- A positive analysis indicates that atypically altered cellular inclusions were found in the cervical tissue. They have a changed morphological structure, shape, and can be observed in different quantities.
- If the result is negative , no cellular changes are detected; this is a normal indicator.
Changes in cell structure are divided into 5 stages:
- Stage 1 . The study picture is not alarming and is within normal limits.
- Stage 2 . The inflammatory process is within relative normal limits. The number of modified cells is relatively small. This serves as a reason for prescribing additional diagnostic measures.
- Stage 3 . The study may reveal cells with changes in the nucleus or cytoplasm. This result is not a deviation from the norm. Most often, it is a risk factor that a woman may develop cancer. In this case, a histological examination is mandatory.
- Stage 4 . Indicates the initial degeneration into an atypical form of a small number of cells. There is a pronounced change in the nucleus, chromosome, and cellular contents. Re-appointment of cytological and histological analysis is required.
- Stage 5 . It is characterized by a high level of modified cells, this is the reason for conducting a comprehensive examination and prescribing appropriate therapy.
Material for cervical cytology
Oncological diseases of the cervix (90% of all cases) affect the stratified epithelium; much less often, the glandular layer is involved in the pathological process.
In this regard, the following material is collected:
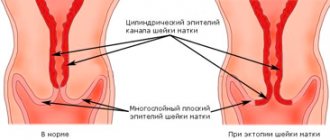
- Columnar epithelial cells in the area of the cervical canal (endocervical cells) are taken.
- Flat epithelial cells are collected from the vaginal side of the cervix (ectocervical cells).
- Cells that are formed at the junction of columnar and squamous epithelium will be taken and subjected to cytological examination.
Integration of various laboratory methods
In the diagnosis of cervical diseases, clinical data and microflora test results (classical microbiological (culture), ANC methods (PCR, RT-PCR, Hybrid Capture, NASBA, etc.) are important).
If it is necessary to clarify the pathological process (ASC-US, ASC-H), cytological examination is, if possible, supplemented with molecular biological ones (p16, oncogenes, methylated DNA, etc.).
HPV detection tests have low prognostic significance, especially in young women (under 30 years of age), due to the fact that in most patients in this age group, HPV infection is transient. However, despite the low specificity of the test for intraepithelial tumors and cancer, it can be used as a screening test in women under 30 years of age, followed by cytological examination. Sensitivity and specificity increase significantly with the combined use of the cytological method and research to detect HPV, especially in patients with questionable cytological data. This test is important in the management of patients with ASC-US, during follow-up to determine the risk of relapse or progression of the disease (CIN II, CIN III, carcinoma in situ, invasive cancer).