Diphtheria
Whooping cough
Colpitis
Thrush
Fungus
28603 03 November
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable; the information below is for reference only.
: indications for use, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and normal indicators.
Why do you need a flora smear?
A gynecological smear is what the doctor should first recommend at the initial appointment, regardless of the symptoms. This study, along with colposcopy, is included in the gold standard for annual preventive examinations in women. Smear microscopy allows you to assess the condition of the vagina and the presence/absence of an inflammatory process in the organs of the reproductive system. The laboratory technician will see the number of leukocytes, epithelial cells and the ratio of bacteria on the slide. If cocci predominate over beneficial bacilli in the results or fungi are visualized, this means dysbiosis, inflammation or candidiasis. If the number of leukocytes in the smear is increased, the gynecologist may prescribe additional tests for STIs.
When is a smear prescribed?
Bacterioscopic examination in gynecological practice is prescribed for the following symptoms:
- pain during urination;
- discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen;
- pathological vaginal discharge;
- itching or irritation of the genitals.
This test is also performed after long courses of antibiotics, even if there are no symptoms. This is done for preventive purposes to prevent disturbances in the bacterial balance on the mucous membranes of the genital organs.
Bacterioscopy must be performed during pregnancy to exclude inflammatory processes and sexually transmitted infections, which is necessary for normal pregnancy and the birth of a healthy child.
A smear should be performed on every woman once a year during a routine gynecological examination.
Preparing for a smear test
The optimal time for a smear on the flora is the middle of the cycle. During menstruation, biomaterial is not collected. This is due to the fact that the presence of blood cells can significantly distort its results. Material for analysis can be taken from the urethra, from the vaginal walls or from the cervical canal. The preparatory measures for all three studies do not have any fundamental differences. At the consultation, the obstetrician-gynecologist will clarify whether antibiotics have been taken in the last two weeks before the appointment. If the answer is positive, the smear will be rescheduled for another time. The most reliable results can be obtained only by observing a number of conditions. On the eve of the smear you should:
- Eliminate the use of any vaginal suppositories for two to three days.
- Limit sexual intercourse in two to three days
- The day before the test, do not take a bath (shower only)
- Avoid vaginal douching for two days
- On the day of visiting the doctor, perform a standard toilet of the genitals with water
- Reschedule other gynecological examinations to another time (for example, colposcopy, ultrasound scanning with an intravaginal probe)
How does the procedure work?
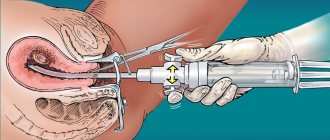
Taking biomaterial for smear examination takes several minutes and takes place in a gynecological chair. The doctor, using a mirror and a sterile disposable instrument, takes samples and then places them on a glass slide with the symbols U, C or V. The letters indicate the location of the biomaterial - the urethra, cervix or vagina. Tools for smearing can be a cotton swab, cervical brush or spatula. The manipulation is completely painless and does not cause discomfort.
How is the research conducted and what do its results show?
The fence material is distributed on a special glass and the preparation is colored using a dye in order to more clearly display the bacteria under a microscope. The assessment is carried out according to the following indicators:
- number of erythrocytes, leukocytes;
- presence of lactobacilli;
- the presence of trichomonas, gonococci, fungus;
- general composition of the flora.
Subsequently, based on the results obtained, the doctor prescribes treatment with suitable drugs.
Smear standards for flora
Normally, among the microorganisms that make up the vaginal biocenosis there are lactobacilli, gram-positive bacilli, bifidobacteria, opportunistic microorganisms and fungi.
In a healthy woman, about 90% of the microflora is made up of beneficial bacteria. These microorganisms prevent the proliferation of conditional pathogens and fungi, releasing special substances that have an antibacterial effect. When the number of beneficial bacteria decreases, conditional pathogens begin to grow. This condition is called flora dysbiosis and requires therapy. Treatment consists of strengthening the immune system with probiotics. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. Among other microorganisms, the smear may contain staphylococci, streptococci and other bacteroids. Their number should not exceed 5% of the total bacterial mass.
The norm of leukocytes in a vaginal smear is from 0 to 15 units. In the urethra and cervix - up to 10 units. Leukocytosis is considered a condition in which their number in the analysis exceeds 15 or more units. As a rule, during pregnancy and during the recovery period after childbirth, this figure increases slightly. Such leukocytosis does not have any accompanying symptoms and does not cause discomfort in the woman.
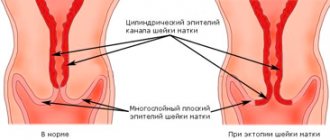
The smear results contain small numbers of squamous epithelial cells. Their level in women correlates depending on the day of the menstrual cycle. If there are many such cells in the analysis, and they are visualized in layers, this may be the result of an inflammatory process in the vagina.
Another indicator of the study is the mucus secreted by the glands of the cervical canal. If such mucus is found in excess, this may be a sign of acute or chronic cervicitis.
Are bacteria good neighbors or irreconcilable enemies?
After reviewing the results of the study, the doctor can obtain information about the composition of the vaginal microflora, the total number of microbes, the presence and severity of inflammation, and, finally, the condition of the vaginal epithelium.
The microflora of the vagina is the microbes that inhabit it. In the vagina of a healthy woman, beneficial microorganisms predominate. The leading place among them is occupied by lactobacilli, which form a kind of barrier to the spread of pathogenic (disease-causing) microbes. In addition, lactic acid, which is formed during their vital activity, largely determines the acidity (pH) of the vaginal environment. With a sufficient number of lactobacilli, the acidic environment of the vagina suppresses the growth of pathogenic microbes. Under conditions where lactobacilli die, the acidity of the environment decreases and the number of pathogenic bacteria increases.
Side by side with beneficial bacteria live bacteria that have pathogenic properties, but these properties do not have the opportunity to manifest themselves while their beneficial neighbors interfere with this. With normal immunity, as a rule, the various microorganisms that populate the vagina are in a state of truce. When immunity is weakened, favorable conditions are created for expanding the sphere of influence of pathogenic microbes. The vaginal microflora reacts sensitively to both external and internal changes occurring in a woman’s body. The use of antibiotics, hormonal fluctuations, chemotherapy or hormonal therapy, radiation therapy, surgery, stressful situations and other factors can have a negative impact on the normal flora of the vagina. Pregnancy also affects the vaginal microflora, since during this period hormonal levels and immunity change significantly. These changes reach their peak in the third trimester. Therefore, it is during this period that women are very often concerned about the symptoms of inflammation discussed above. Most often, the cause of this condition during pregnancy is the yeast-like fungus Candida albicans, and the disease itself is called candidiasis, candidomycosis, or simply thrush.
The fungus Candida albicans lives on the skin and mucous membranes of any person, but it is activated only when the immune system is weakened or the bacteria that inhibit its proliferation, including lactobacilli, die. Thrush manifests itself as signs of inflammation and a milky-white coating on the mucous membrane; this coating resembles grains of cottage cheese or the remains of dairy food.
Flora smear during pregnancy
In order for pregnancy to proceed favorably, a woman’s body must be as prepared as possible for it.
Therefore, as soon as the doctor establishes on a gynecological ultrasound the fact that the fertilized egg is in the uterus, it is recommended to immediately take a smear for STIs and biocenosis. Untreated and chronic infections can subsequently provoke spontaneous abortion and cause miscarriage. Sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia can cause infection of the child during his passage through the birth canal. In the test results of a pregnant woman, leukocytes are often elevated. Their number during this period can range from 15 to 30 units in the vagina and up to 5 in a smear from the urethra. This is due to the body’s natural reaction to physiological stress, since during pregnancy the woman’s immune system is activated. This condition is considered normal and is regulated by estrogen.
Degrees of vaginal cleanliness
When deciphering a smear for flora, much attention should be paid to indicators of cleanliness, which reflect the general condition of the genital organs.
I. _ Acidic reaction (pH 3.8–4.5). This means that a large proportion of microorganisms are lactobacilli (or Doderlein bacilli). Leukocytes and epithelial cells may be present in small quantities. This result indicates excellent reproductive system health.
II . Acidic reaction (pH 4.5–5.0). In this case, the microflora is represented mainly by lactobacilli, but gram-negative bacteria are also found.
III . Alkaline or slightly acidic reaction (pH 5.0–7.0). The smear reveals only a small amount of lactobacilli; bacterial flora and a large number of epithelial cells predominate.
IV . Alkaline reaction (pH 7.0–7.5). There are no Doderlein bacilli in the smear, the microflora is represented by pathogenic microorganisms, and there is a large number of leukocytes. This degree of cleanliness indicates inflammation of the vaginal mucosa.
How long to wait for research results
In general, the time frame for a smear test for women is from one to four days.
In this case, the day of the visit to the obstetrician-gynecologist is not taken into account. The duration of obtaining analysis results is determined by the specifics of the laboratory research method. The condition of the vagina, cervix and urethra is assessed within 24 hours. If the test results are unsatisfactory, the doctor may prescribe a PCR test*. Advantages of the PCR method:
- Reliability thanks to high sensitivity
- Speed of execution
- Specificity for STIs in any form
- Ability to diagnose most urogenital tract infections
- Accuracy of identifying the type of infectious agent
Balance control
Why is vaginal microflora examination necessary for every pregnant woman? The fact is that an infectious process affecting the birth canal (cervix, vagina, external genitalia) is fraught with infection of the child during childbirth. The microflora of the mother's vagina has a significant impact on the formation of the microbiocenosis of the intestines and skin of the newborn. In addition, in some situations, intrauterine infection of the fetus is possible. Sometimes altered microflora has an adverse effect on the course of the postpartum period: the recovery process may slow down, and the development of infectious complications in a woman is possible. A control smear after a course of therapy will help evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. A decrease in the percentage of lactic acid bacteria and an increase in the number of pathogenic microbes is one of the signs of inflammation. The presence of inflammation is also confirmed by a large number of leukocytes - protective cells that fight for health. To assess the state of the vaginal microflora, doctors use the concept of “degree of purity.” There are four such degrees. The first characterizes the optimal state: lactobacilli predominate in the microbial “landscape”, the acidity of the environment is normal, there are no signs of inflammation. In the fourth degree, there are no lactobacilli, many pathogenic microbes, signs of inflammation are expressed, and the environment turns from acidic to alkaline. The second and third degrees are intermediate between the first and fourth. When choosing treatment, the doctor will focus on the general condition of the pregnant woman and the results of the examination. Of course, he will choose the treatment method that in a particular situation will be safer for the fetus.
In situations where signs of inflammation are present, but the cause is not clear from the results of conventional smears, doctors can resort to additional research methods, for example, PCR diagnostics using a smear. The PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method is based on repeatedly increasing the number of DNA of pathogenic microbes to such an amount that it is possible to determine the type of causative agent of the disease, even if the smear contained a very small amount of pathogenic bacteria. This analysis requires special equipment, so it can only be done in well-equipped laboratories. The results of vaginal smears are given great importance when hospitalized in a maternity hospital: if the results are absent or a large number of leukocytes or pathogenic microflora are detected in them, and also if the results were received more than 40 days ago, the pregnant woman is hospitalized in the II maternity ward, intended for women with infectious diseases and pathology of pregnancy, which exists in all maternity hospitals. Of course, a pregnant woman has every right to refuse to take a vaginal smear: this test, like all others, is carried out voluntarily. But practice shows: all expectant mothers are well aware that the examination is carried out in their interests and determines their health, the outcome of childbirth and the health of the newborn.