Obstructive jaundice develops when the flow of bile from the gallbladder into the duodenum is impaired. This condition is not an independent disease. Obstructive jaundice is a symptom that is characteristic of many diseases of the abdominal organs. Due to its fairly high prevalence, doctors of different specialties often have to deal with this problem and prescribe different types of treatment to patients.
- Options for the development of obstructive jaundice
- Principles of treatment of obstructive jaundice
- Consequences and prognosis for obstructive jaundice
- Prevention methods
Options for the development of obstructive jaundice
Depending on the reasons for its appearance, the symptom can be of tumor or non-tumor origin. In approximately half of all cases, obstructive jaundice is associated with malignant neoplasms of the pancreas, liver, and intestines. These organs can be affected by the primary tumor process or metastases from distant foci.
In the second half of patients, the development of obstructive jaundice is caused by benign processes, among which the most common are:
- Inflammatory processes of the gallbladder and biliary tract - cholecystitis, cholangitis, papillitis, etc.
- Non-inflammatory diseases of the abdominal organs: cholelithiasis, biliary stenosis, cholangiolithiasis, etc.
- Congenital anomalies: biliary atresia, duodenal diverticula, cysts, etc.
In rare cases, obstructive jaundice can be caused by parasitic diseases. The mechanism of development of the symptom in this case is associated with the entry of helminths into the bile ducts with a violation of their patency.
Screening
Multifactorial analysis of clinical, laboratory and instrumental data allowed us to identify several indicators that allow us to reasonably suspect the presence of choledocholithiasis and continue to search for it using invasive research methods. These include dilation of the extrahepatic bile ducts (more than 8 mm) according to ultrasound, clinical signs of cholangitis, increased levels of aminotransferases and direct fraction of bilirubin in the blood serum, small stones in the gall bladder (less than 5 mm). It is also recommended to evaluate anamnestic data (the presence of episodes of jaundice, exacerbations of chronic cholecystitis or pancreatitis).
Principles of treatment of obstructive jaundice
The main objectives when drawing up a treatment plan are the elimination of cholestasis (stagnation of bile) and the prevention of liver failure. To do this, the doctor draws up a comprehensive program, which can include both conservative and surgical methods.
Diet for obstructive jaundice
It is necessary to follow certain nutritional rules both before the main treatment and after its completion. Patients with obstructive jaundice are advised to maintain a drinking regime, as water accelerates the excretion of bilirubin, thereby reducing its negative effect on the body. It is also very important to completely avoid alcohol, very fatty and fried foods, mayonnaise, sauces, and hot seasonings. Food should be consumed in small portions 5-6 times a day. In this case, it is necessary to monitor the temperature of the dish. It shouldn't be too hot or cold. The best option is warm food, as it helps regulate the secretion of bile, which is especially important for obstructive jaundice.
Other general recommendations regarding diet include limiting the amount of salt in the diet. It is known that excess salt contributes to fluid retention in the body, causes swelling and makes it difficult to remove harmful substances from the body. Patients with obstructive jaundice are recommended to consume no more than 4 grams of salt per day. In general, the exact nutrition plan, calorie content and composition of dishes are selected individually for each patient, taking into account his preferences. There are lists of permitted and prohibited foods, as well as those foods that should be limited. It is these lists that the doctor is guided by when drawing up a nutrition program. For example, permitted products include:
- Vegetables (carrots, cucumbers, cabbage, tomatoes, broccoli).
- Bananas and apples.
- Dried fruits.
- Various porridges (buckwheat, oatmeal, pearl barley).
- Bran bread, pasta, crispbread.
- Jam, honey, marmalade.
- Lean meat (rabbit, beef), poultry (chicken breasts, turkey fillet) and fish (pollock, hake).
- Fruit juices and tea.
A diet for obstructive jaundice involves the complete exclusion of canned vegetables, legumes, grapes, baked goods, white bread, full-fat milk, cream, fatty meats and fish, smoked meats, carbonated drinks, coffee, and animal fats.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy for obstructive jaundice is prescribed to reduce the severity of symptoms, prepare the patient for surgery and reduce the risk of complications. The extent of medical care largely depends on the degree of jaundice. For example, in severe cases, drug treatment is carried out in an intensive care unit and includes:
- Massive infusion therapy.
- Forced diuresis.
- Vitamin therapy.
- Hepatoprotectors.
- Amino acids.
- Metabolism stimulants.
- Hormonal drugs.
To relieve symptoms, in mild forms of obstructive jaundice, antispasmodics, enveloping drugs, antacids and other medications can be prescribed.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is the only effective method that allows you to restore the patency of the bile ducts and thereby eliminate the cause of obstructive jaundice. All known types of operations can be divided into two groups: minimally invasive techniques and direct operations.
Minimally invasive methods of surgical treatment
This group of methods is highly effective and low-traumatic, but it is impossible to apply them to all patients in a row due to certain limitations. Minimally invasive treatment of obstructive jaundice is carried out using endoscopic techniques and percutaneous transhepatic cholangiostomy. Endoscopic operations can be of the following types:
- Endoscopic papillosphincterotomy and lithoextraction.
- Local lithotripsy and lithoextraction.
- Bougienage and stenting of the bile ducts.
In these cases, to treat obstructive jaundice, a gastroduodenoscope with special instruments is used that allow crushing and removing stones, installing stents, and removing tissue. Endoscopic operations in most cases are performed without general anesthesia and do not require long recovery time.
Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiostomy is used in cases where it is impossible to perform decompression of the biliary tract using a gastroduodenoscope. The essence of the operation is to install a drainage tube under ultrasound or x-ray control. In this case, the skin, muscles of the anterior abdominal wall and liver tissue are pierced with a special puncture needle. In the future, the drainage tube can be used not only to drain bile, but also to introduce antibacterial or other drugs directly into the bile ducts.
Direct surgical interventions allow you to create full access to the gallbladder and eliminate obstructive jaundice of any complexity. The surgeon can perform anastomoses, install stents, and perform reconstructive operations. The intervention can be performed using laparoscopic instruments or the classic open cavity method. The latter option is the most traumatic, requires long-term rehabilitation and is accompanied by an increased risk of complications, so it is used only in the treatment of complex cases of obstructive jaundice.
General principles of treatment of obstructive jaundice
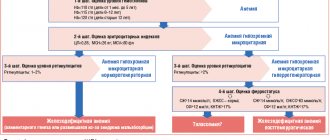
Generally speaking, the treatment tactics for obstructive jaundice include two stages. At the first stage, conservative therapy and minimally invasive methods of surgical treatment are prescribed. It is recommended to carry out such treatment in the first 2-3 days from the moment the patient is admitted to the hospital. If these methods are ineffective, then move on to the second stage of treatment of obstructive jaundice, which involves more radical methods. Treatment at the peak of jaundice is associated with a high risk of developing postoperative complications, so it is carried out only if there are vital indications.
Other treatments
Effective treatment of jaundice involves eliminating the underlying disease that led to the development of this symptom. To do this, it is necessary to use either conservative or surgical methods. Other treatment options for obstructive jaundice, in particular traditional medicine, home treatment and self-medication will not help achieve the desired result. For a certain period of time, they will help hide the symptoms and alleviate the patient’s condition, but the main process will continue to progress and lead to the development of complications. Therefore, when the first signs of obstructive jaundice appear, it is necessary to seek qualified medical help, which will help radically solve the problem.
Why is it necessary to consult a doctor at the first symptoms?
Pain and other signs of illness in the liver area cannot be ignored, especially if there have already been operations in the anamnesis. By self-medicating, we only remove symptoms and waste time. So, in the case of tumors, at an early stage they can be removed and treated. Stones blocking the gap increase in size over time and become more difficult to remove. Timely detection of the cause is 50% of successful treatment.
If the skin and sclera turn yellow, emergency medical attention is needed. Failure to see a doctor promptly can lead to death.
Consequences and prognosis for obstructive jaundice
The prognosis will be favorable in cases where the treatment of jaundice was timely and correct. The behavior of the patient himself is also of great importance. If you adhere to the principles of proper nutrition and strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions, the risk of relapse or complications will be minimal. Otherwise, the likelihood of recurrent obstructive jaundice will be very high. In addition, the risk of developing concomitant diseases, for example, liver failure, liver cirrhosis, encephalopathy, sepsis, etc., will increase.
Possible complications
If you seek medical help in a timely manner, the prognosis for recovery is favorable. However, with prolonged poisoning of the body with bilirubin, damage to the liver, kidneys, heart, blood vessels, central nervous system, and blood coagulation system is possible. If medical recommendations are not followed, complications can arise in any of the listed organ systems.
In the area of the outbreak itself, irreversible processes in the tissue of the liver and pancreas can occur. Gallstone disease tends to recur, so it is especially important to follow the diet prescribed by your doctor.
What is hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammatory process in the liver under the influence of a provoking (in most cases viral) agent, causing damage to its tissues.
Today, hepatitis is considered one of the most common infectious diseases after ARVI, influenza and chickenpox. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in young people aged 15-30 years (especially those prone to unprotected sex and drug use), another “risk group” is usually represented by medical specialists who have direct contact with blood (including infected people).
Differential diagnosis
It is not difficult even for a person far from medicine to suspect jaundice. But only a qualified specialist can determine the type of cholestasis and identify the causes of its occurrence. The diagnosis is made based on the results of a detailed examination of the patient.
Traditional laboratory tests will not give an accurate result, since research indicators for obstructive jaundice may not differ in any way in the presence of viral liver lesions. To clarify the diagnosis, laparoscopy, ultrasound, CT, RCP and much more may be required.
First, let's compare obstructive jaundice with parenchymal jaundice. Let's consider the differences between pathologies from the angle of clinical manifestations:
- coloring. With cholestasis, the skin becomes yellow with a green tint. The parenchymal form is characterized by an orange-red color;
- skin itching. Absent in the parenchymal form;
- pain in the right hypochondrium. When obturation is pronounced. The second pathology is characterized by mild pain that rarely occurs;
- liver size. The organ is not enlarged with cholestasis. With parenchymal jaundice, hepatomegaly is noted.
Important! With obstructive jaundice, the level of bilirubin in the blood increases.
If we talk about the anamnesis, or medical history, of the patient, then in case of obstruction of the biliary tract there are operations on the biliary tract and cholelithiasis. There is a decrease in body weight. In the parenchymal form, contact with a patient with jaundice, infectious pathologies or toxic effects are recorded.
Now let's talk in more detail about the hemolytic form, which is also often confused with cholestasis. The history of patients with this diagnosis records the presence of jaundice in childhood. Often similar diseases are diagnosed in close relatives. With parenchymal jaundice, the skin becomes lemon-yellow in color. There is no itching or pain in the right side. The size of the liver is also unchanged.
What is liver cirrhosis
Liver cirrhosis is a pathological and chronic process in the liver, as a result of which its parenchymal tissue is replaced by fibrous connective tissue (stroma). There is also a structural restructuring of the vascular bed and a decrease in the number of normally functioning hepatocytes (liver cells).
According to statistics, the global annual mortality rate from cirrhosis is about 300 thousand people, with a progressive upward trend. The disease most often affects men over 40 years of age, those prone to alcoholism, as well as patients with:
- chronic hepatitis B, C and D;
- pathologies complicated by fatty hepatosis;
- some hereditary diseases (for example, hemochromatosis);
- some autoimmune diseases;
- toxic liver damage from chemicals.