Local therapist
Burnatskaya
Svetlana Nikolaevna
33 years of experience
Local therapist, occupational pathologist. Member of the Russian Scientific Medical Society of Therapists
Make an appointment
Breathing problems and the sensation of a foreign body in the throat can be signs of developing asphyxia. Asphyxia belongs to the category of life-threatening conditions that lead to circulatory and respiratory disorders. Regardless of the causes, asphyxia requires urgent measures, since death is possible as a result of the development of acute oxygen starvation within a few minutes.
The basis for the development of asphyxia can be:
- damage to the respiratory muscles;
- the presence of an obstruction that does not allow air to enter the lungs;
- dysfunction of the respiratory center.
In recent years, doctors have had to deal with such a pathology as autoerotic asphyxia, which occurs as a result of sexual experiments.
Strangulation
Strangulation asphyxia is a mechanical closure of the airways as a result of:
- hanging;
- strangulation with a loop;
- strangulation with body parts;
- strangulation with items of clothing.
When hanging, the airway is closed with a cord, rope, or any long flexible object that can be tied on one side to a stationary support and the other secured around the neck in the form of a loop. As a result of gravity, the neck is pinched and the air flow is blocked. But most often, death occurs not so much from a lack of oxygen, but for a number of reasons such as:
- crushing and fracture of the first and/or second cervical vertebra, which is accompanied by displacement of the spinal cord;
- increased intracranial pressure and, as a result, extensive hemorrhage in the brain.
Very rarely, hanging occurs without the use of elastic objects, such as squeezing the neck with the transfer of a chair or stool, a fork of a tree, or various rigid elements located in such a way that there is a possibility of pinching. Death from asphyxia by hanging occurs very quickly - in the first 10-15 seconds, because squeezing the upper part of the neck is the most traumatic, and the possibility of self-rescue is minimal.
- Removal using a loop. Classic mechanical asphyxia with four stages, which most often accompanies violent suffocation applied from the outside, and the victim can resist.
- Strangulation by body parts is no different from the previous type; it is also violent under the influence of external force: knee, hand, etc.
- Clothes strangulation can be either intentional or the result of an accident.
Strangulation asphyxia is also characterized by spasm of cerebral vessels and their further expansion, a sharp increase in venous pressure, and gas exchange disorders. Blood circulation in the brain is disrupted, diffuse hemorrhages occur, and hypoxic encephalia develops.
Diagnostics
Mechanical asphyxia is diagnosed by external signs. In case of death, the final verdict is made by a pathologist after an autopsy and determination of the cause of death.
External pathomorphological manifestations of asphyxia include:
- facial cyanosis;
- hemorrhages in the conjunctiva;
- cadaveric spots of blue-purple color;
- hemorrhages in internal organs;
- the presence of a groove from a loop or fractures of the cervical vertebrae.
If the patient was saved, the consequences will appear after some time, so it is worth conducting the following studies:
- examination and consultation with a psychiatrist and neurologist;
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- MRI or CT of the vessels of the brain, heart, lungs.
After carrying out complex procedures and clarifying the patient’s condition, rehabilitation therapy is prescribed.
Causes and symptoms of suffocation
Sometimes choking can occur during unconscious states, when the tongue falls into the throat and begins to prevent the normal penetration of air into the person’s lungs. Under the influence of high doses of various drugs, the respiratory muscles may spasm or relax too much.
The same often happens with some diseases, for example, with bronchial asthma, allergic reactions, false croup, and pathologies of the nervous system. A person’s breathing also becomes difficult if there are tumors in the trachea, bronchi, or larynx. If a person experiences prolonged convulsions for one reason or another, this can also contribute to asphyxia. Some work professions also force a person to go through moments when their breathing may become sluggish. This often occurs underground for miners or underwater for divers.
The symptoms of suffocation largely depend on what causes it. The most common symptoms of asphyxia are:
- in case of bronchial or cardiac asthma - the appearance of noise, whistling during breathing, wheezing in the lungs before the onset of suffocation and the release of mucus and sputum after it ends;
- in case of an allergic reaction - frequent gasping for air, redness of the facial skin, swelling of the neck;
- with compression suffocation - bruises, wounds, abrasions in the area of the human respiratory system.
All attacks of suffocation can be diagnosed in advance. Anxiety should be caused by attacks of dizziness, darkening of the eyes, and shortness of breath. In this case, in a person who complains of such symptoms, it is necessary to examine the color of the skin, measure his pulse and pressure, and study the movement of the breathing muscles in the chest. The doctor must listen to the lungs and determine the presence of wheezing in them. Sometimes a test is done to measure the oxygen content of the blood.
Famous people who died from suffocation
History is replete with references to executions by hanging. Such a sentence was passed on robbers, murderers and other criminals who committed serious atrocities. Noble nobles laid their heads on the block, unlike ordinary people. Here will be listed those who, for various reasons, died from strangulation.
Decembrists
The sentence passed by the Supreme Criminal Court to hang five Decembrists was a mitigation of the painful death penalty by quartering. On July 13 (25), 1826, in the crownwork of the Peter and Paul Fortress, the lives of S. I. Muravyov-Apostol, P. G. Kakhovsky, K. F. Ryleev, P. I. Pestel, M. P. Bestuzhev-Ryumin were cut short. The first three fell from the noose and were hanged a second time. The previously existing tradition of pardoning those executed and replacing hanging with hard labor was abolished by Military Article No. 204 under Peter I.
Isadora Duncan
The tragic death of the famous dancer on September 14, 1927 occurred by an absurd accident. During a car ride in Nice, the artist’s fluttering scarf got tangled in the rear wheel of a convertible and literally pulled Isadora out of the car at full speed, breaking her spine.
Jacques Offenbach
The famous composer died of an attack of suffocation on October 5, 1880. His friend Johann Strauss, having learned about the sad event, interrupted his tour and rushed to Paris for the funeral.
Robin Williams
Around noon on August 11, 2014, the wife began knocking on the famous actor’s bedroom, concerned that he had not come out for breakfast. After breaking the door, she found Robin sitting by a chair with a belt fastened around his neck. The other end of the belt was inserted between the frame and the door leading to the wardrobe. Close friend Rob Schneider suggested that Robin was experiencing suicidal thoughts while taking a new drug for Parkinson's disease.
What is asphyxia?
Asphyxia in Latin means absence of pulse or heartbeat. In a broader sense, this term is characterized by the cessation of oxygen supply to organs and tissues. As a result, a large amount of carbon dioxide accumulates in the body, and the body ceases to perform its functions. First of all, functional disorders affect the respiratory organs, brain, cardiovascular system and then the entire body.
Failure to promptly eliminate the cause of asphyxia and provide medical care leads to death.
Is there a difference between asphyxia and hypoxia?
Asphyxia is a process that provokes a state of hypoxia. Hypoxia is a significant decrease in oxygen in the blood and accumulation of carbon dioxide in it. The state of hypoxia also occurs in many other painful conditions of the body, not only in asphyxia. Asphyxia occurs when exposed to certain factors, which will be listed below. The condition entails dangerous changes in the body, including hypoxia.
Main pathogenetic points
The process begins with the closure of the airways or exposure to any factors. The main role is played by the fact that oxygen stops flowing into the lungs, and then into the blood and tissues. At the very beginning, the process can be called a pre-asphyxial state. During this period, the adaptive mechanisms of the human body are activated. The vessels located on the periphery (legs, arms) narrow and most of the blood, which is still saturated with oxygen, rushes to the most important organs - the brain and heart.
After a short time, the level of carbon dioxide in the blood increases critically. During such a period, asphyxia itself occurs. Carbon dioxide affects the respiratory center located in the medulla oblongata (one of the parts of the brain). At first it irritates the center, this is manifested by shortness of breath, increased blood pressure, and possible convulsions. Then carbon dioxide has a paralytic effect on the part of the brain. This manifests itself in the form of a short-term cessation of breathing, terminal breathing (similar to wheezing) and a final cessation of respiratory activity.
More than a hundred years ago, the pathogenesis of asphyxia was not studied. Some volunteer scientists conducted experiments on themselves with self-hanging. The longest experiment time was twenty-six seconds. During the onset of asphyxia, scientists noted unbearable pain in the neck, dry mouth, loss of coordination, dizziness, and severe tinnitus.
Complications
Choking can cause serious complications and unpleasant consequences. The most common consequences of suffocation are:
- neurological and mental pathologies (impaired memory (amnesia) or intelligence, up to dementia);
- disturbances in the activity of the cardiovascular system;
- traumatic shock with manifestations of irritability and indifference;
- vocal cord paresis;
- infection with a risk of developing pneumonia;
- swelling of the brain or lungs;
- death.
Pregnant women should be wary of spontaneous miscarriage.
Help for asphyxia should be provided as soon as possible.
Treatment
Treatment of mechanical asphyxia begins with measures to restore airway patency:
- eliminating tongue retraction;
- loosening the loop squeezing the neck;
- removal of foreign bodies from the respiratory tract using bronchoscopy;
- tracheal aspiration of water, blood, accumulated mucus.
If the patient is in a state of clinical death, that is, there is no cardiac activity and spontaneous breathing, then after restoration of airway patency, cardiopulmonary resuscitation immediately begins.
Rotokan is important during pregnancy and breastfeeding, reviews
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation for asphyxia
If indicated, tracheal intubation or tracheostomy is performed, after which the patient is connected to a ventilator.
The occurrence of ventricular fibrillation is the basis for electrical defibrillation.
In some cases, treatment of asphyxia begins with thoracentesis. If venous pressure is high, phlebotomy may be performed. Treatment of toxic forms of asphyxia is based on antidote therapy.
After restoration of cardiac activity and breathing, correction of the acid-base balance and water-electrolyte disorders, dehydration therapy (to prevent pulmonary or cerebral edema) are carried out.
Electrical defibrillation for asphyxia
If asphyxia is caused by an infectious disease or pathology of the nervous system, active pathogenetic therapy is carried out.
How to sign up
To make an appointment with a doctor at our clinic, you can use any of the following methods:
- online form on the website;
- by phone +7 (495) 775-73-60;
- through your Personal Account or Mobile Application.
If necessary, you can get emergency help by phone.
JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) is located in the center of Moscow at the address 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, building 10. The clinic is located near the metro stations "Mayakovskaya", "Tverskaya", "Chekhovskaya", "Belorusskaya".
How to determine the presence of mechanical asphyxia
Diagnosing this type of suffocation is simple. Particles of a foreign body will be located on the larynx, in the stomach. It is difficult to know whether death occurred due to reflex cardiac arrest or due to lack of oxygen. Changes in internal organs are the same in both cases; clinical examination is required.
Blockage of the respiratory tract with a powdery mass, liquid or semi-liquid substance (except water) is an obstructive type of suffocation. If a person chokes on vomit or drowns, this is referred to as aspiration.
Now let’s look at what mechanical obstructive asphyxia is confused with.
Obturation
Obstructive asphyxia is a mechanical blockage of the air path and disruption of its patency. Suffocation can have the following types:
- random (for example, food);
- violent (suffocation with any object, for example, a pillow);
- unconscious (stomach contents)
Oxygen deficiency can also occur due to fluid entering the lungs, and drowning also refers to this type of asphyxia, divided into two types:
- Filling of the lungs with water due to inhalation: death occurs within one to three minutes as a result of dilution of the blood with water, decreased pressure and cardiac arrest.
- A reflex spasm of the respiratory tract, which prevents water from entering the lungs: they do not straighten, inhalation is impossible, the remaining fluid enters, and death occurs due to paralysis of the respiratory center and hypoxia. Individual heart beats are monitored for 10-20 minutes.
Classification and features of types of asphyxia
Asphyxia is suffocation, in which the level of oxygen in the blood and tissues sharply drops and the content of carbon dioxide increases. Depending on the reasons that caused the condition, it is divided into three types.
Mechanical asphyxia
Impaired external respiration due to mechanical reasons that prevent the flow of air into the respiratory organs. This type of asphyxia is also divided into several varieties.
- Strangulation.
Strangulation occurs due to compression of the neck with hands or a noose made of rope, wire or other materials. The collar of the victim’s own clothing may also be the cause.
- Compression.
The pressure is placed on the chest and abdomen, as a result of which the contractility of the lungs and the general blood supply are affected. Because of this, oxygen circulation is disrupted. We are talking about asphyxia if the victim does not have fractures or serious injuries. Examples include tightly swaddling babies, pressing a child with the mother's body in a dream, and prolonged squeezing in a crowd. Compression asphyxia can occur as a result of a transport accident or being under collapsed structures.
- Obstructive.
It involves closing the openings of the mouth and nose with hands or soft objects. This also includes blockage of the airways by foreign bodies:
- liquid (water, blood);
- semi-liquid (food, vomit);
- bulk (sand, earth, cereals);
- dense (small toys, fallen teeth, buttons, etc.)
Obstructive asphyxia
- Staying in a tight confined space.
A rare situation. It can occur as a result of imprisonment in the compartments of sunken ships or a long stay in a closed box. Violent actions can also cause asphyxia. For example, pulling a bag over your head and securing it tightly around your neck.
Toxic asphyxia
Occurs as a result of toxic chemicals entering the body. Some of them depress the respiratory center, for example, morphine. Others paralyze the muscles of the respiratory organs. These substances include muscle relaxants. Cyanide compounds destroy respiratory enzymes. Nitrites and carbon monoxide interfere with the respiratory function of the blood. The inability to breathe leads to a critical oxygen deficiency.
Traumatic asphyxia
Occurs due to internal damage to the chest. These may include bruises and ruptures of the lungs, damage to the respiratory system due to broken ribs, gunshot and knife wounds.
Diagnosis confirmation
The diagnosis of asphyxia is confirmed by the absence of pulse, cardiac activity, or their weakening. There may be an increase in blood pressure at the very beginning of the process, an increase in the intensity of breathing (frequent breathing, but not deep). Terminal breathing that sounds like wheezing. The act of spontaneous urination, defecation, ejaculation - due to the weakening of all muscle sphincters in the body, as a rule, occurs in the last stages of the asphyxial state. Blood gas studies reveal a significant increase in carbon dioxide in the blood and a lack of oxygen.
Characteristic symptoms
The symptoms of strangulation asphyxia are obvious: complete loss of consciousness of a person, bruises and abrasions on his neck. Non-violent suffocation can develop rapidly or slowly, gradually increasing. In any case, the symptoms of asphyxia are accompanied by acute shortness of breath and “go through” 4 stages.
Stage 1:
- Strong excitement, fear;
- Increased breathing rate and heart rate;
- Dizziness;
- Darkening in the eyes;
- During breathing, inhalation is emphasized;
- Blood pressure levels increase;
- The patient's face changes its natural color: it turns red or pale;
- A cough begins, with the help of which a person tries instinctively to eliminate the object that is interfering with breathing;
- The patient stretches his neck and, opening his mouth slightly, reflexively sticks out his tongue.
Stage 2:
- Breathing and heart rate decrease;
- The emphasis in the breathing process shifts to exhalation;
- Blood pressure levels decrease;
- The skin becomes blue or gray.
Stage 3:
- Complete cessation of breathing (period duration – from 3-4 seconds to 2-3 minutes);
- Critical decrease in blood pressure;
- Fading reflexes;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Hypoxic coma.
Stage 4:
Characterized by rare “agonal” breathing, reminiscent of convulsive sobs. Lasts for 3-4 minutes. Ends in death.
A severe consequence of stages 3 and 4 of asphyxia is edema of the lungs and brain.
The duration of suffocation varies, it depends on the pathology that caused it. Most often, no more than 10 minutes pass from the onset of an attack to death.
If asphyxia is caused by diseases, it will always be accompanied by symptoms of this pathology. For example, if suffocation is caused by an asthma attack, then the above signs will be supplemented by noisy and wheezing breathing. And when listening to the patient’s lungs, wheezing is clearly audible. After the attack ends, the cough is accompanied by mucus and phlegm.
During an attack of suffocation caused by an allergic reaction, the patient grabs his throat, swallowing air with his open mouth. The neck swells greatly, becomes much larger than usual, and the skin on the face turns red.
Symptoms of asphyxia
| Symptom | Manifestation | Photo |
| Cough | If a foreign object enters the larynx, a person will reflexively begin to cough. At the same time, the cough is convulsive, painful, and does not bring relief. | |
| Excitation | A person instinctively grabs his throat, coughs, screams and tries to call for help. Small children are characterized by strangled crying, frightened eyes, wheezing and wheezing breathing (stridor). Less often, the crying is strangled and muffled. | |
| Forced pose | Tilt of the head and torso forward allows you to increase the depth of inhalation. | |
| Blue complexion | As a result of oxygen starvation, a large amount of blood containing carbon dioxide is concentrated in the tissues. A protein that is bound to carbon dioxide and gives the skin a bluish tint. | |
| Loss of consciousness | The blood flowing to the brain does not contain enough oxygen. With hypoxia, the nerve cells in the brain cannot function normally, which leads to fainting. | |
| Stopping breathing | Breathing stops within a few minutes. If the cause of asphyxia is not eliminated and the foreign body is not removed from the lumen of the respiratory tract, then after 4–6 minutes the person will die. | |
| Adynamia | Reduced physical activity up to its complete cessation. Adynamia occurs due to loss of consciousness. | |
| Involuntary urination and defecation | Oxygen starvation leads to increased excitability of the soft muscles of the walls of the intestines and bladder, while the sphincters relax. |
Classification
The classification of mechanical asphyxia depends on the cause of suffocation.
Important Antibiotics for bronchitis in children: a list of names of the most effective drugs, drugs in the form of suspensions, a review of reviews of some medications
Compression of the respiratory organs has the following types:
- strangulation suffocation - causes hanging, strangulation with a noose or hands;
- compression suffocation - determined as a result of compression of the abdominal and thoracic cavity organs.
Closing the breath occurs:
- obstructive, when the access of air to the mouth and nose is blocked due to the ingress of foreign objects or liquid;
- aspiration, when the inhalation of oxygen is prevented by interference in the form of vomit or blood.
Mechanical asphyxia (hanging) is divided into a complete form (when the legs do not touch the support and the noose is tightened under the influence of the weight of the whole body) and an incomplete form (asphyxia occurs in a lying, sitting or standing position). This variety has the lowest survival rate. Hanging is established after the fact, when the person is dead.
Due to hanging, the neurovascular tissues of the neck are compressed, the access of arterial blood to the brain is stopped, causing acute hypoxia and inhibition of the cerebral hemispheres and the brainstem area in the head. A person often loses consciousness and is unable to independently interrupt the pathological process.
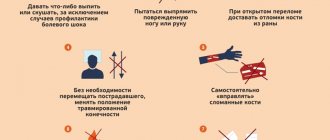
First aid. A reminder for those around you
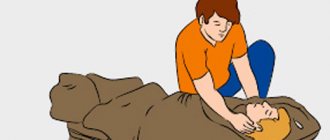
First of all, call an ambulance! Next, free the airways from mechanical stress (remove the noose from the neck, remove heavy objects from the body, try to at least partially remove foreign objects from the airways). Assess the pulsation of the arteries in all possible places familiar to you (wrist, neck, thigh). Pay attention to the chest - whether it moves, whether it makes breathing movements. Assessing the situation should take a few seconds!
Start cardiopulmonary resuscitation until the doctor arrives. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is performed according to the principle of two mouth-to-mouth breaths, thirty chest compressions (pressures) in adults, two breaths and fifteen compressions in children. It is advisable to inhale using a mask or any thin fabric that allows air to pass through (for example, a clean handkerchief). People who have any diseases that can provoke asphyxia may have medications in the form of ampoules, inhalers, nebulizers in their pockets or near them.
If you are still in doubt and you do not have certain knowledge in the field of first aid, just call a doctor!
Specifics of urgent actions
Before you begin emergency care for asphyxia, quickly become familiar with its symptomatic manifestations. Remember that in this case, first aid depends on the cause of suffocation. Call an ambulance, and then, according to the symptoms, provide the necessary assistance until the doctors arrive.
Foreign body in the respiratory tract
A dangerous condition arises against a background of relative prosperity. In infants, as in adults, asphyxia most often occurs due to pieces of food stuck in the respiratory tract. The following extraction methods are used for newborns:
- Place the baby in your hand so that his chest is in your palm and his head is lower than his body;
- Wrap two fingers around his lower jaw;
- With your free hand, apply 5 sharp blows to the shoulder blade area;
- Turn the baby over so that his face is facing up;
- Make sure that the head is also lowered below body level;
- Lean the hand on which the baby is lying on your knee;
- With 2 fingers of your free hand, apply intense pressure in the center of the chest;
- The intensity of movements is checked by lowering the chest;
- The total number of pressures is 55-60 times in 1 minute.
Such resuscitation actions are carried out until doctors arrive to help.
If asphyxia occurs in a child over 1 year of age or an adult, check the victim’s mouth for the presence of a foreign object. If it is located deep and it is not possible to get it out, do the following:
- Stand behind the patient;
- Grasp it with both hands so that your hands are located at the place where the victim’s ribs end;
- Clench the palm of one hand into a fist, and clasp it with the other;
- Quickly make 6 movements, pressing on the stomach from top to bottom, “squeezing out” the object;
- When pressing, take into account the pressure of your hands: it should be strong and sharp.
If a foreign object comes into view, carefully remove it. If this does not happen, continue until the doctors arrive.
The victim is unconscious
If, after a foreign body enters the larynx, a person loses consciousness, resuscitation measures must be immediately initiated. The same algorithm of urgent actions is taken in case of strangulation asphyxia, after first freeing the person’s neck from the suffocating object.
Quickly detect the presence of a heartbeat. Then follow these steps sequentially:
- Lay the victim on his back;
- Throw your head back;
- Push out the lower jaw with your fingers;
- Use a spoon to open the patient's mouth;
- If the airway is blocked by the tongue, use your fingers to pull it out.
In all other cases, if there is no heartbeat, proceed to cardiac massage and artificial respiration.
Laryngospasm
Laryngospasm is a disease as a result of which the muscle tissue of the larynx sharply contracts, and the glottis closes almost completely. Because of this, oxygen cannot flow in the required quantity to the patient’s organs and tissues. Occurs more often in children.
There are many reasons why a dangerous attack occurs:
- Taking medications;
- Severe stress or fear;
- Rickets;
- Complications of respiratory diseases.
The main symptom of laryngospasm is sudden difficulty breathing, accompanied by profuse sweating and shortness of breath.
Actions before the doctor arrives:
- Calm and distract the baby;
- Provide fresh air to the victim;
- Prepare a solution for local inhalation: dilute baking soda in hot water and let the child breathe;
- Lay the victim down, loosen the pressing elements of clothing;
- If the baby loses consciousness, there is no heartbeat and breathing, proceed to resuscitation measures.
Asthma
The symptoms of an attack in asthmatics are pronounced: strong whistling and noise accompany heavy breathing. At the first manifestations of bronchial asthma, take the following actions:
- Provide a flow of fresh air into the room;
- Use a bronchodilator medicine inhaler;
- As an emergency, administer adrenaline diluted in isotonic sodium chloride solution.
In the complete absence of vital processes, the victim’s life is supported using artificial respiration.
Recovery period
The recovery period after asphyxia is characterized by such signs as lack of consciousness, motor agitation, and tension of all muscles. In some cases, non-stop convulsions develop, the skin turns pale, hemorrhages occur in the sclera and ocular conjunctiva, and rapid, intermittent breathing is observed. The initial examination reveals arrhythmia, tachycardia and increased arterial and venous pressure.
In the traditional understanding, all types of asphyxia are mechanical, that is, formed as a result of physical blockage of air movement. But today the boundaries of use of this concept have been expanded.
Questions to ask a specialist examining asphyxia
- Is mechanical asphyxia a cause of death?
- As a result of what impact did mechanical asphyxia occur?
- What are the features of the strangulation groove?
- Is the strangulation groove intravital or postmortem?
- Are there signs of struggle or self-defense?
- What object was used to compress the neck?
- Was the cause of death compression asphyxia?
- What signs indicate compression (any other) asphyxia?
- What is the victim's blood alcohol content?
- Are there marks on the neck of the corpse consistent with squeezing by hand (noose)?
- What was the relative position of the victim and the attacker?
- What are the features of the loop?
Causes of asphyxia
Causes of asphyxia:
- diseases of the nervous system;
- diseases of the respiratory system;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- aspiration of food or vomit in children;
- weakened infants;
- psycho-emotional states;
- alcohol intoxication;
- talking while eating;
- haste in eating;
- lack of teeth;
- dentures;
- entry of small objects into the respiratory tract.
Nervous system diseases
apnea, cessation of respiratory movements, neuritis, weakening of voluntary movements, swallowing, coughing or gag reflexes are impossible when the pharynx is irritated
Respiratory system diseases
The following diseases can cause asphyxia:
- Abscess of the epiglottis. This pathology leads to swelling of the epiglottic cartilage, an increase in its size and a decrease in its mobility. During food intake, the epiglottis is not able to perform its functions as a valve that closes the lumen of the larynx during the act of swallowing. This inevitably leads to food entering the respiratory tract.
- Quinsy. Phlegmonous tonsillitis or acute paratonsillitis is a purulent-inflammatory disease of the tonsils. It occurs as a complication of lacunar tonsillitis. This pathology leads to swelling of the soft palate and the formation of a cavity containing pus. Depending on the location of the purulent cavity, blockage of the respiratory tract is possible.
- Diphtheria. Diphtheria is an infectious disease that usually affects the oral part of the pharynx. In this case, the occurrence of croup, a condition in which the airways are blocked by diphtheria film, poses a particular danger. The airway can also be blocked if there is extensive swelling of the pharynx.
- Tumor of the larynx. A malignant tumor of the larynx leads to the destruction of surrounding tissues. The degree of destruction determines the size of food that can penetrate from the pharynx into the larynx. Also, the tumor itself can cause asphyxia if it partially or completely blocks the lumen of the larynx.
- Tracheal tumor. Depending on the shape, the tumor can protrude into the lumen of the trachea itself. In this case, stenosis (narrowing) of the lumen of the larynx is observed. This will significantly complicate breathing and subsequently lead to mechanical asphyxia.
Important White sputum: foamy and viscous, as evidenced by the lack of color in the cough discharge (transparent), if coughing in adults without fever
Digestive system diseases
burns The following diseases can cause asphyxia:
- Cancer of the upper esophagus. A tumor of the esophagus, growing, can exert significant pressure on adjacent organs - the larynx and trachea. Increasing in size, it can partially or completely compress the respiratory organs and, thereby, lead to mechanical asphyxia.
- Gastroesophageal reflux. This pathology is characterized by the entry of stomach contents into the esophagus. In some cases, the contents of the stomach can penetrate into the oral cavity and, when inhaled, enter the respiratory tract (the process of aspiration).
- Tongue abscess. An abscess is a purulent-inflammatory disease with the formation of a cavity containing pus. The following picture is typical for a tongue abscess: the tongue is enlarged in volume, inactive and does not fit in the mouth. The voice is hoarse, breathing is difficult, and there is profuse salivation. With a tongue abscess, a purulent cavity may be located in the root zone and prevent air from entering the larynx. Also, increased size of the tongue can cause asphyxia.
Aspiration of food or vomit in children
mammary glandvomitesatresia of the esophagus, esophageal-tracheal fistulatoxicosispregnancycomplication of pregnancy, manifested by edema, high blood pressure and loss of protein in the urine
Prevention
The best ways to prevent choking:
- Compliance with safety rules. When near a body of water, it is not recommended to swim while intoxicated. Children must be supervised wearing a vest, a circle or armbands. If the water is cold, you need to follow the rules of thermoregulation and not dive suddenly.
- Do not give small children small toys or sucking candies.
- The child should not have bulky soft toys or blankets in the playpen. After feeding, you should wait until the baby releases air (burps).
- If you are going on vacation to the mountains, you should consult with a specialist so as not to get caught in a landslide. Maintain daily contact with relatives or friends via telephone.
- It is worth following the rules of the road and undergoing an annual vehicle inspection for serviceability.
Closely monitor your child's condition, especially during hormonal changes in adolescence, to avoid the emergence of suicidal tendencies.
Is everything in the article correct from a medical point of view? Answer only if you have proven medical knowledge
Not really
Diseases with similar symptoms:
Types of asthma attack
Symptoms, causes and signs of asphyxia depend on the influence of certain factors. Based on them, there are 3 types of suffocation:
- Mechanical. Occurs as a result of a foreign object entering the respiratory tract or being compressed by swelling. Drowning can also cause mechanical suffocation.
- Toxic. The development of pathology is associated with the effects of toxic substances on the human body. As a result of their toxic effect, the functioning of the respiratory organs is disrupted and the respiratory muscles are weakened. The blood flow cannot deliver sufficient oxygen to organs and tissues. Occurs as a result of insect bites, animal poisons, medications and narcotics.
- Traumatic. Appears due to injury. This group includes strangulation asphyxia, which occurs during mechanical forced strangulation.
We list no less common causes of asphyxia:
- As a result of loss of consciousness, as well as in a state of coma, the victim’s tongue sinks, which interferes with full breathing;
- Due to improper treatment and selection of the dosage of potent drugs based on narcotic drugs, the natural functioning of the respiratory muscles is disrupted;
- Diseases of the nervous system, respiratory system and allergic reaction cause swelling in the larynx and respiratory distress;
- Prolonged convulsive muscle contractions.
All of the above reasons lead to rapid disruption of respiratory and circulatory functions and require emergency first aid measures.
Treatment tactics after eliminating the causes
After eliminating the causes of suffocation, the patient is hospitalized, since the condition entails many functional disorders of the body. Monitor vital signs (respiration, pulse, blood pressure, etc.). If you are unable to breathe on your own, you will be connected to a ventilator. Cardiac disorders are corrected with various medications according to indications. Treat the underlying disease (bronchial asthma, infections, allergies, toxic poisoning). For violent types of asphyxia, consultation with a psychiatrist is possible in the future.