Every person, regardless of gender, age or other characteristics, receives various injuries, more or less serious. A simple scratch, from a medical point of view, is an injury. As well as a fracture, burn or sprain. No one is safe from bruises or burns, dislocations or cuts, even the most careful people. And in a city environment it is even easier to get one or another injury - transport, slippery sidewalks in winter, modern architecture, and the mechanization of many processes contribute to this.
There are different types of injuries, but, by definition, this is the name for any damage to the integrity of any tissues or organs that occurs due to exposure to external factors. And, regardless of the type, it can have varying degrees of severity. For example, the same cut may be minor, superficial or deep, causing danger to a person's life.
Also, an international classification has been developed based on the cause of damage, division by the number of injured areas, and so on. In each specific case, injuries are classified, based on the results of which a list of necessary diagnostic procedures and a therapeutic regimen are determined.
What types of injuries are there?
The following types of damage are distinguished:
- bruises - soft tissues are damaged without compromising the integrity of the skin;
- sprains - muscles, ligaments, fascia are damaged, with rupture of individual fibers, but maintaining the anatomical integrity of the organ;
- ruptures - the same injury, but with a violation of the anatomical integrity of the muscle, ligament or fascia;
- compression - prolonged compression of a limb by an object or a person’s body, as a result of which the death of muscle cells begins;
- dislocation - a violation of the position of the joint with its exit from the joint capsule;
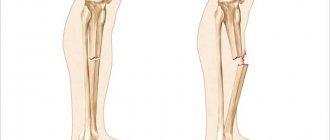
- fracture - violation of the integrity of the bone;
- wounds - types of open injuries received as a result of exposure to mechanical factors;
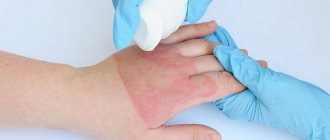
- burn, frostbite - damage caused by thermal effects.
The definition of injury is carried out by its external signs and complaints of the victim; an accurate diagnosis is made based on the results of an X-ray examination or ultrasound.
Street injuries.
Street injuries include injuries received by victims outside of work activities on the streets, in open public places, in fields, in forests, etc., regardless of the reasons that caused them (except for vehicles). They are associated with falling (especially during icy conditions), so their number increases significantly in the autumn-winter period. The dependence of this type of injury on the time of day is revealed. When people fall on the streets, bone fractures occur in 68-70% of cases, bruises and sprains in 20-22%, and soft tissue injuries in 4-6%. Mainly the limbs are damaged (83-85%).
The causes of street injuries are:
- poor traffic management,
- narrow streets with heavy traffic,
- insufficient lighting and alarm;
- violation of traffic rules by pedestrians;
- poor condition of street surfaces, ice, etc.
Prevention of injuries in pedestrian traffic includes:
- rational planning and improvement of streets and pavements, proper care of them (use of sand during icy conditions, filling potholes, etc.), lighting of streets and squares, fencing of buildings under construction and repair;
- rational organization and regulation of street traffic, strict control over compliance with traffic rules;
- ensuring the good technical condition of street transport, its safety (serviceability of automatic doors on buses and trams, etc.);
- supervision of children and their leisure time;
- extensive educational and explanatory work with the population (print, radio, television, cinema, lectures, reports, etc.).
One of the important measures to prevent street injuries is the fight against domestic drunkenness, since street injuries are often caused by people intoxicated.
Classification by type of external influence
Experts identify the following types of damage:
- Household - that is, associated with performing everyday activities at home, at work or at leisure. These types of injuries include dislocations, fractures, sprains and bruises after a fall, frostbite and burns, and so on.
- Mechanical - this type of damage occurs due to the impact of any mechanisms or other objects.
- Electrical - appear when exposed to electric current.
- Thermal.
- Radiation - obtained when exposed to ionizing radiation.
- Explosive - appears when hit by an explosion.
- Chemical - obtained due to exposure to various chemicals.
- Biological - occur when exposed to bacteria, viruses, fungi, poisons of plant or animal origin.
- Mental - obtained under the influence of stress factors.
Types by effect
In addition to the above types, medical classification also implies the division of injuries according to the result of exposure to a damaging factor. The following types are distinguished:
- Isolated - a specific organ or segment is damaged, the surrounding tissues and organs remain intact. Such injuries include a fracture, liver rupture, knife wound to the arm, and so on.
- Multiple - there are several injuries of the same type on the body.
- Combined - in this case, damage to the musculoskeletal system and one of the internal organs is observed.
- Combined - this is the name given to injuries resulting from exposure to several damaging factors (for example, thermal and mechanical, radiation and thermal).
In case of electric shock
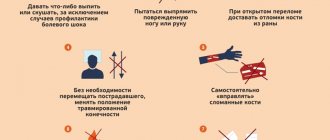
First of all, the victim must be freed from electrical “captivity”. The safest thing is to quickly turn off the power supply or at least move the exposed wire away from the body using available non-conductive materials (a stick or board).
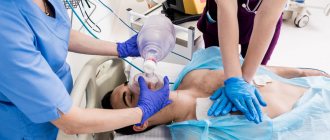
Then the victim needs to be laid down, covered warmly or rubbed with cologne, and given a warm drink. Apply a sterile bandage (clean cloth moistened with water) to the area of the body burned by the electric current. If the victim has lost consciousness, they give him ammonia to sniff and splash cold water on his face. If breathing is lost, immediately begin artificial breathing - “mouth to mouth”. If the heartbeat stops, do an indirect cardiac massage.
Classification by severity
The internationally generally accepted classification distinguishes three degrees of injury severity:
- Heavy. With this degree of damage, serious health problems arise, and even a threat to life. Determination of such an injury is an indication for urgent hospitalization of the victim. In case of a first degree injury, a person loses the ability to work for a period of 1 month.
- Average. In accordance with the classification of the severity of injuries, such injuries also cause loss of ability to work, but for a period of up to 1 month, and are not life-threatening.
- Easy. Injuries of the third degree of severity do not cause serious health problems or disabilities, and the treatment period does not exceed 10 days.
Sources
- Kuršumović K., Hadeed M., Bassett J., Parry JA., Bates P., Acharya MR. Lateral compression type 1 (LC1) pelvic ring injuries: a spectrum of fracture types and treatment algorithms. // Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33860399
- Krutsch W., Memmel C., Alt V., Krutsch V., Tröß T., Aus der Fünten K., Meyer T. Timing return-to-competition: a prospective registration of 45 different types of severe injuries in Germany's highest football league. // Arch Orthop Trauma Surg - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33779832
- Kim JY., Lee SC., Lee S., Lee CA., Ahn KO., Park JO. Characteristics of injuries according to types of personal mobility devices in a multicenter emergency department from 2011 to 2021: A cross-sectional study. // Medicine (Baltimore) - 2021 - Vol100 - N6 - p.e24642; PMID:33578587
- Van Yperen DT., Van Lieshout EMM., Dijkshoorn JN., Van der Vlies CH., Verhofstad MHJ. Injuries, treatment, and impairment caused by different types of fireworks; results of a 10 year multicenter retrospective cohort study. // Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med - 2021 - Vol29 - N1 - p.11; PMID:33413553
- Jacobson L., Sandvall BK., Quistberg DA., Rowhani-Rahbar A., Vavilala MS., Friedrich JB., Keys KA. Severe Fireworks-Related Injuries: Demographic Characteristics, Injury Patterns, and Firework Types in 294 Consecutive Patients. // Pediatr Emerg Care - 2021 - Vol37 - N1 - p.e32-e36; PMID:33394947
- Deng X., Chen W., Shao D., Hu H., Zhu J., Ye Z., Zhang Y. Arthroscopic evaluation for tibial plateau fractures on the incidence and types of cruciate ligamentous injuries following closed reduction and internal fixation. // Int Orthop - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33123747
- Veenman L. Raloxifene as Treatment for Various Types of Brain Injuries and Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Good Start. // Int J Mol Sci - 2021 - Vol21 - N20 - p.; PMID:33066585
- Yamamoto Y., Miyagawa Y., Kitazawa M., Takahata S., Aoyagi S., Hondo N., Koyama M., Nakamura S., Tokumaru S., Muranaka F., Soejima Y. Types and site distributions of intestinal injuries in seat belt syndrome. // Traffic Inj Prev - 2021 - Vol21 - N7 - p.442-446; PMID:32886011
- Wilson CL., Tavender EJ., Phillips NT., Hearps SJ., Foster K., O'Brien SL., Borland ML., Watkins GO., McLeod L., Putland M., Priestley S., Brabyn C., Ballard DW., Craig S., Dalziel SR., Oakley E., Babl FE., Lew J., Teo S., Beattie A., McCaskill M., Rao A., Cole J., Michael A., George S. ., King A., Cassidy C., Ben Lawton FK., Kochar A., Gamage L., Archer P., Mukherjee A., Young R., Mitenko H. Variation in CT use for pediatric head injuries across different types of emergency departments in Australia and New Zealand. // Emerg Med J - 2021 - Vol37 - N11 - p.686-689; PMID:32816840
- Goswami M., Eranhikkal A. Management of Traumatic Dental Injuries Using Different Types of Splints: A Case Series. // Int J Clin Pediatr Dent - 2021 - Vol13 - N2 - p.199-202; PMID:32742103
Why do you need to classify damage?
Classification is necessary for a number of reasons. Firstly, the urgency of hospitalization of the victim depends on the severity of any injury. Secondly, the treatment tactics depend on the result of the damaging factor and its type, because it is impossible to treat a fracture and rupture of the liver, or a thermal and chemical burn in the same way.
There is another type of international classification - ICECI. In accordance with it, when determining the nature of damage, such points as the mechanism of receipt, the type of object or substance that caused the damage, the place of its occurrence, the effect of the damaging factor, the time of injury, the intention of the person, his use of alcohol or psychoactive substances at the time of injury are taken into account. These are the main points, but there are additional ones. Thus, the type of impact (violent or non-violent), the specific location of the injury (in transport or not), the type of activity (sports, industrial accident, and so on) are taken into account.
But such a division is needed more for statistics and the development of preventive measures regarding injuries.
Other methods of distinguishing injuries are necessary directly for their effective treatment and provision of first aid to victims.
Sports injuries.
Sports injuries are accidents that occur during sports (scheduled, group or individual, at a stadium, in a sports section, on a sports ground) under the supervision of a teacher or coach. Accidents involving schoolchildren during physical education classes according to the school curriculum are not included in this group of injuries. Sports injuries account for 2-3% of all injuries. Most often they occur during boxing, football, hockey, wrestling, motorsports, and gymnastics. Every sport has common injuries. Thus, football and hockey players are more likely to experience damage to the menisci of the knee joint; in skiers and figure skaters - helical fractures of the diaphysis of the tibia, ankles and sprains of the ligamentous apparatus of the ankle joint. The most common injuries are soft tissue, with a predominance of abrasions and abrasions; bone fractures do not exceed 3% of the total number of injuries, dislocations account for 3-5%. By location, the largest number of injuries occur on the extremities, followed by injuries to the head and torso. An objective indicator of the severity of the injury is the duration and persistence of loss of athletic performance.
The main causes of sports injuries:
- violations in the organization of training sessions and competitions;
- unsatisfactory condition of training places and unfavorable conditions for conducting them;
- unsatisfactory condition of sports equipment and equipment, clothing, shoes;
- insufficient medical supervision;
- poor physical fitness of the athlete (long breaks in classes, lack of systematic training, overwork, etc.);
- violations of discipline by athletes during training and competitions.
Basic preventive measures:
- control over the organization and methodology of educational training sessions and competitions (especially for beginner athletes). The so-called insurance and assistance in classes are very important;
- technical and sanitary-hygienic supervision of the condition of places of training and competitions, sports equipment, clothing, shoes and equipment of the athlete. Use of special protective devices (shields, elbow pads, knee pads, wrist pads, etc.);
- protection from adverse weather conditions (heat and sunstroke, frostbite, etc.);
- medical control over those involved in sports. Primary and secondary medical examinations before participation in competitions, before resuming activities after a break;
- instilling discipline and camaraderie among athletes, as well as suppressing any manifestations of indiscipline;
- mandatory analysis of sports injuries together with the instructor, coaches, and athletes.