July 20, 2021
Burns are one of the most common types of injuries in children and adults. Almost everyone has experienced a burn at some point in their life, particularly a thermal, chemical or solar burn.
Burns are one of the most common types of injuries in children and adults. Almost everyone has experienced a burn at some point in their life, such as a thermal, chemical or solar burn. Often minor burns can be treated with home remedies, but in other cases immediate medical attention is required.
In Russia, about 300 thousand cases of burn injury are registered annually (among those who sought medical help). Physical suffering, long-term disability, possible disability and mortality make this type of traumatic pathology the most relevant. With timely, reasonable, competent provision of first aid, it is possible not only to relieve the patient of pain, but also to prevent the development of complications, to create conditions for subsequent effective treatment and a speedy recovery.
There are several types of burns, including thermal, chemical, and even electrical and radiation. Thermal burns are the most common and account for more than 90% of all types. These are burns from flame, hot steam, hot or burning liquid, boiling water, burns from contact with hot objects, sunburn. The severity of burns is divided depending on the depth of skin damage.
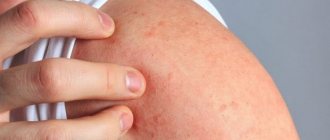
With a 1st degree burn, only the upper layers of the skin are affected. Severe redness and swelling of the skin develop, and pain and a burning sensation are noted in the burned area. Symptoms subside within two days, and after a week complete recovery occurs.
With a 2nd degree burn, the top layer of skin completely dies and peels off, and in its place bubbles filled with a clear liquid form. If the course of the disease is not complicated by wound infection, healing occurs in 10-12 days.
With 3rd degree burns, the skin is affected almost to its entire depth. In this case, massive blisters with a thick shell are formed, filled with bloody contents, tense and very painful.
With a 4th degree burn, the most serious, there is complete death of all layers of the skin, even the deepest ones, including subcutaneous fat, as well as underlying tissues - muscles, tendons, bones. The above burns can affect limited (local) or large areas of the skin.
Classification of burns
The severity of the injury is determined by the depth of damage to the skin. To provide effective assistance, it is necessary to correctly classify the burn:
- I degree. Slight redness of the skin area, swelling, mild pain. The consequences disappear without a trace after 3–7 days.
- II degree. Severe pain associated with the appearance of watery blisters. The deep layers of the skin are not damaged, which eliminates the formation of scars. Characterized by a change in skin color that occurs over time.
- III degree. The symptoms are many times greater than those listed above. Tissue death occurs and scabs and open wounds appear. The skin recovers poorly, forming dense scars.
- IV degree - charring. It is considered the most difficult to cure. In most cases, skin grafting is required. The injury affects the tissues of the muscles, tendons and bones.
In domestic conditions, first and second degree burns more often occur, but it is important to note that incorrectly provided or untimely assistance can lead to infection of the damaged area and serious consequences even with a second degree burn. If you are injured, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Skin restoration after a burn
What helps with burns is careful hygiene and regular wound care.
After injury, a blister immediately forms on the skin, filled with clear plasma, which can seep through the burned tissue. With proper treatment, inflammation and suppuration can be avoided, and regeneration will occur faster.
Within a few days, the blisters from the burns will begin to subside and peel off, and new skin will begin to form under the blister. At this time, the wounds may itch, but you should not touch the affected area - by the end of the first week the itching will go away on its own.
If the wound is neglected, a process of suppuration may develop. It may be accompanied by fever, sudden weakness and chills. With such a history, regeneration of the skin may take weeks. In this case, compacted growths and ridges are likely to appear.
First aid for thermal burns
The basic rule of providing care for burns before being examined by a doctor is to do no harm! What to do:
- Don't panic!
- Provide the victim with a safe place, removing the cause of the injury.
- If the burn is caused by hot liquid, it is important to remove hot, wet clothing as soon as possible. If the fabric is stuck to the skin, carefully cut it with scissors; do not remove the stuck fragments yourself.
- Reduce the temperature of damaged tissues. Immediately after receiving a first or second degree burn, the injured area must be cooled with running water; in more serious cases, a cool bath or a damp sterile bandage can be used.
- If the pain is severe, take a painkiller.
Treatment of scars after burns
If you are interested in how to get rid of the external consequences of a burn, you need to know that in case of serious damage to the skin, the scar will remain in any case. Here you will need the help of a cosmetologist who will help restore the normal appearance of the skin.
Typically, for such an operation, a scar excision technique is used, after which several cosmetic sutures are applied to the tissue. When the sutures are removed, the damaged area is treated with ointments that prevent the formation of new scars on the skin.
For particularly difficult cases, for example, burns from boiling water, the laser resurfacing technique is used. Modern equipment allows you to completely remove scars and achieve perfect skin. If the severity of the burn is insignificant, chemical peeling with fruit acids is recommended.
Possible consequences
If there are 2-3 degree burns, then deep wounds may appear, and this can cause tissue scarring in the future. If such changes in the skin have formed on open areas of the body, for example, on the face, head, hands, then the person experiences severe psycho-emotional discomfort. In addition to an unstable psychological state, physical health often suffers. Scar tissue from a major burn often interferes with the normal functionality of the limbs.
Infected wounds also pose a high risk, because if treated incorrectly, there is a risk of developing sepsis.
Folk remedies for burns with boiling water: what helps
When treating burns at home, you can combine traditional therapy with traditional methods. Some recipes are very effective (can only be used after consulting a doctor):
- Compress with honey and potatoes: add 1 teaspoon of honey to 100 g of raw grated potatoes, mix. Place the mixture in gauze or a bandage and apply to the burned area. Leave for 2 hours. You can repeat the compress 2-3 times a day.
- Aloe lotion: take a few aloe leaves, chop them and squeeze out the juice. Moisten gauze or bandage and apply to the burn area. You can use the plant without squeezing the juice - simply by cutting the leaf lengthwise and applying it to the wound.
What not to do
- Do not tear off stuck-on clothing if it does not come off after soaking. In this case, it is better to wait for the arrival of doctors who can do this under sterile conditions.
- Do not apply iodine or brilliant green to the burn - these products are too aggressive and dry out already irritated skin. In addition, it will be more difficult for the doctor to determine the extent of the damage if the entire burn site is green or brown.
- Do not treat the skin directly after a burn with fatty products, oils, creams, or sour cream. The oily environment increases the local body temperature, and a film forms on the surface of the skin, which prevents the burn from cooling naturally.
- Do not burst blisters after a burn with boiling water yourself.
- If you doubt whether to apply a bandage and how to do it, it is better not to do it. A bandage that is too tight can cause swelling.
A 1st degree burn does not require any action and will heal in a couple of days. You can speed up recovery by taking care of your skin, moisturizing and nourishing it.
Immediately after first aid, you can apply a medicated bandage to the skin. There are special napkins for sale after burns with an analgesic effect - use them or make a bandage yourself by soaking the gauze or bandage with anti-burn agent. Use La Cree cream to soothe irritated skin. It contains panthenol, so the cream is perfect for treating burns with boiling water.
A 2nd and 3rd degree burn with minor damage still requires contacting a medical facility. It is necessary to carry out some procedures to disinfect the burn surface, which are performed by a doctor.
The skin at the burn site is anesthetized, treated with an antiseptic, exfoliated epidermis, dirt and remnants of clothing are removed, the doctor carefully pierces the blisters after the burn, removing the liquid and leaving a thin skin to protect the wound. A bandage with bactericidal ointment is applied to the burn. Further treatment is carried out independently or under the supervision of a doctor, if it is necessary to replace the bandage every 2-3 days until the burn is completely healed.
Serious 3rd and 4th degree burns and burns of more than 30% of the body are treated exclusively in a hospital. The first actions of doctors are aimed at removing dead tissue. If necessary, this is done surgically. The patient is under the supervision of doctors, they eliminate the consequences of burn shock, which causes intoxication of the body and damage to internal organs.
After the damaged skin is rejected, the formation of a scab begins. At this stage, it is important to prevent the development of inflammation. Depending on the location of the burn and the degree of skin damage, treatment is carried out in an open or closed manner; the affected areas of the body are lubricated with an antiseptic ointment 3-4 times a day.
How to avoid complications and improve wound healing?
The main complication may be burn disease. It develops when more than 5–10% of the total skin area is affected. The complication arises due to a complex malfunction of organs and systems. We are talking about tachycardia, poor circulation, intoxication and other pathological conditions. It is important to contact the burn department in time, where specialists will eliminate pain, normalize breathing, and prevent kidney and cardiovascular failure.
Another complication of burn injuries is sepsis. To avoid infection, you need to use only specialized plasters on burns and only as prescribed by a doctor when it comes to serious injuries. Regular treatment, monitoring the condition of the wound and the healing process is what is required during treatment to avoid complications.
To reduce the risk of general burns
At home, you can quite simply reduce the risk of burns; you just need to follow a few recommendations:
- Do not leave cooking or already cooked food on the stove unattended;
- frying pans are placed on the stove with handles towards its back;
- any hot liquid must be placed out of the reach of children and animals - boiling water is a common cause of thermal burns;
- Do not store electrical appliances near water;
- Do not cook in flammable clothing;
- You should block your child’s access to electrical and gas appliances;
- Protective caps must be put on sockets that are not in use;
- you should not smoke at home;
- smoke detectors require regular maintenance and battery replacement;
- the house or apartment must be equipped with a fire extinguisher;
- Chemical burns are caused by chemicals - they must be stored in a place inaccessible to children and animals.
Clinical researches
The effectiveness, safety and tolerability of the product for children and adults has been proven by a clinical study. The product is also suitable for daily skin care of children with mild to moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
La-Cri cosmetics, according to research results, are recommended by the Russian Union of Pediatricians.
Effect of antiseptic patch against burns
The classic adhesive plaster is not suitable for burns; its purpose is to protect the skin from minor cuts, calluses and other non-dangerous injuries. There are specialized products for 1st-2nd degree burns. Their difference from the classic ones is the presence of a breathable base, since air access is necessary for the healing of burned skin.
When using a patch for burn wounds, a moist environment is created on the injured area, which helps the epidermis to recover. Special impregnation turns into a gel upon contact with exudate. If a standard adhesive plaster slows down healing, then a burn plaster maximizes regeneration. Additionally - reducing itching, cooling, pain relief, protection against bacteria, prevention of blisters. Regardless of the manufacturer, such products are hypoallergenic and suitable for the most sensitive skin. Easy to apply and remove.
Using a patch to heal burns provides a cleansing, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect, accelerates the healing of minor injuries, and reduces the risk of the formation of unsightly scars and cicatrices.
BURN DISEASE. CLINICAL SYNDROMES
In burn disease, four clinical syndromes can be distinguished: Burn shock, Intoxication, Infection, Convalescence. There are no sharp boundaries between these syndromes.
BURN SHOCK. It occurs as a result of a neuro-reflex and neuro-endocrine reaction of the body. As a result of a strong inflammatory process in a burn victim, the central and peripheral blood supply is disrupted, the permeability of vascular and cellular membranes increases, the volume of circulating blood decreases with a violation of the ratio of its formed elements and plasma (hypovolemia), plasma escapes from the vascular bed and plasma loss through burn wounds. Plasma loss during burn shock depends on the depth and area of the burn.
Thus, with superficial burns, predominantly external loss of plasma is observed, and with deep burns, plasma enters the surrounding tissues and swelling occurs.
During a burn, the evaporation of fluid through damaged skin increases significantly, leading to a large loss of fluid from the victim’s body. Loss of fluid reduces the mass of circulating blood, resulting in a sharp deterioration in glomerular filtration of urine. Burn shock usually occurs within 2-3 days. Signs of burn shock include: an excited or inhibited state, in severe cases, consciousness is confused or absent; decreased pulse blood pressure, decreased amount of urine excreted by the kidneys (oliguria), vomiting, thirst, chills, muscle tremors.
INTOXICATION. As a result of the appearance in the victim’s body of toxic products, under-oxidized compounds, and bacterial tissue, a period of acute burn toxemia begins. Body temperature rises, loss of appetite occurs with the development of signs of toxic damage to internal organs (toxic myocarditis, hepatitis). During this period, it is necessary to carry out active detoxification measures (forced diuresis, plasmaphoresis, hemosorption).
INFECTION. At the third stage of burn disease, infection begins to progress. Metabolic disorders and weakened immunity give rise to infection of the body. Infection significantly complicates the course of the wound process - it maintains intoxication, suppresses restoration processes in tissues, and can affect various organs.
RECONVALESCENCE (recovery). It occurs from the moment of complete closure of granulating wounds. An important factor in recovery is prompt closure of burn wounds.