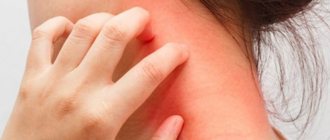
Based on the condition of the skin, you can determine whether there are any disturbances in the functioning of the body. Rashes can be different: small red, dotted, spotty, colorless, watery, pustular, itchy, in the form of tubercles and nodular formations. Skin rashes appear much more often in children compared to adults. As a rule, this is due to the influence of external factors on the skin (sunlight, temperature, humidity, toxic and chemical substances, etc.). Internal processes and diseases also affect the skin.
If a skin rash appears in a child, you should consult a pediatric dermatologist. The First Children's Medical Center offers the services of qualified pediatric dermatologists in Saratov: with us you can not just get a doctor's consultation, but undergo all the necessary examinations and obtain opinions from related specialists. A timely visit to the doctor will allow you to find out the cause of the rash, eliminate it and eliminate the risk of relapse or the development of any complications.
What is urticarial rash?
Urticaria rash is a consequence of a complex inflammatory process that occurs in the thinnest vessels of the human body, capillaries located in the epidermal layer of the skin. This pathological process is commonly called urticarial vasculitis.
Also, this form of rash can be observed with urticaria.
What does the rash look like?
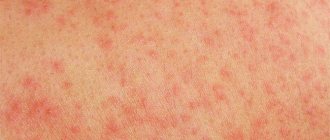
Upon visual examination, a patient with urticaria or urticarial vasculitis can see small nodules that slightly rise above the skin in the form of a papular rash (see photo). With a more severe course of the disease, the bubbles merge into a single whole and blisters appear. They have a reddish color, and are accompanied by a burning sensation and increased itching.
It should be noted that blisters with urticarial vasculitis last longer, and their treatment is sometimes difficult.
Types of rashes
Various childhood diseases manifest themselves as primary symptoms in combination with secondary symptoms. The initial rash varies. Equally important is the quick reaction of the parents and the determination of what formation has formed on the child’s body:
- Tuberous. Any detail of such a rash is located deep in the dermis, in other words, the rash is not superficial. There is no cavity, there is a small protrusion in the form of a tubercle, the color of the skin may change to red or purple.
- Blisters. This is what people call almost any formation on the skin. However, in reality, the blister is a round, pink formation that lacks a cavity and contents. A real blister is short-lived, it can last from a couple of minutes to a couple of hours, then disappears without a trace. As an example, we can recall a nettle burn.
- Papular eruptions. This rash is also called nodular, since the papules are similar in appearance to nodules, which differ in shade from the normal color of the skin. Papular rash can be superficial or deep, and papules can disappear without a trace.
- Vesicular rash. This rash appears as blisters on the skin. There may be a serous, colorless or serous-bloody liquid secretion inside. Vesicles can be single or fused, forming a formation with numerous chambers. Opened vesicles leave erosion on the skin, the size of which is equal to the area of the bottom of the vesicle.
- Bullous. This type of rash also appears in the form of vesicles, but compared to vesicles, the bulla has a more impressive size - at least 5 mm in diameter. Such blisters may, like vesicles, contain serous or serous-bloody liquid contents.
- Pustular. Pustules are a pustular rash. It can be superficial or located deep in the skin. The opening of superficial pustules passes without a trace. If medium and deep pustules (boils, carbuncles) are opened, unsightly scars may occur.
- Spot-like rashes. This type of rash does not appear on the surface of the skin, but is characterized by a change in shade in some areas of the body. Such rashes can be vascular or petechial.
- Roseola. This is the name for rashes that appear in many pathologies of an infectious nature. All elements of the rash are pink or moderately reddish in color. The structure of roseola resembles specks. When the skin is stretched and pressure is applied, the rash turns pale and disappears for a while.
- Hemorrhagic rashes. This type of rash appears as red blood spots that form in the area where the blood vessel burst. When the skin is stretched, hemorrhage does not disappear.
Secondary rashes also vary. It manifests itself in the form of scabs, which are accompanied by the transformation of elements of the primary rash (usually vesicular or pustular) into crusts after opening. The development of cracks, erosions, detachments of epithelial cells, abrasions, scars and ulcers is also often observed as secondary manifestations.
Classification
This type of skin rash is usually distinguished by its etiology. They can be observed when:
- Urticaria . A disease that is caused by exposure to and entry into the human body of an allergen. This may occur due to: Use of medications.
- Use of certain foods, vegetables and fruits.
- Contact with chemical compounds.
- Allergies to mosquito bites, etc. insects
- Genetic predisposition.
- Disorders of the psychoemotional state, psychogenic nature.
- With primary vasculitis, skin rashes occur in large numbers, but they can only affect the upper layer of the epidermis. Most often, the cause of this process is: the appearance of food allergies after wearing tight clothes that contain synthetic fibers.
Causes
Basically, in the etiology of this disease, it is customary to distinguish the following reasons:
- the presence in the human body of an untreated source of chronic infection;
- frequent use of steroid hormones and their analogues;
- individual characteristics of the body that cause food allergies;
- severe diabetes mellitus with high blood sugar;
- severe forms of arterial hypertension;
- any type of hepatitis;
- mononucleosis.
Rash in children. Let's look at the reasons.
Tretyakova Daria Alexandrovna
Pediatrician
April 25, 2021
In the life of every parent, sooner or later there comes a time when, suddenly, some acne appears on the body of their beloved child. It's a rash. A rash is any change on the skin. It occurs in many diseases and conditions, some of them are very dangerous.
Let's try to figure out what the rash is, in what cases it appears, what it is accompanied by, and how mom and dad should behave so that it goes away faster.
Let's start with the simplest thing - insect bites. Primarily mosquitoes. As a rule, this rash causes surprise in early spring and late autumn, when mosquitoes are not yet remembered or are already forgotten. In modern winter conditions, mosquitoes can live indoors (for example, in the basement) almost all year round. Of all family members, small children are the most “tasty” for mosquitoes.
Parents notice changes in the skin in the morning, after the child wakes up. Mosquito bites are characterized by the appearance of pink or reddish spots mainly on open areas of the body: hands, forearms, feet, legs, i.e. those parts of the body that are not covered by pajamas, and there must be elements on the face, or, sometimes, on one half of it (if the child slept on his side). Most often, this rash is accompanied by itching, but not very severe. The child's general condition does not suffer. He behaves as usual - plays, runs, throws things around, watches cartoons and eats with appetite. If the child is not allergic to mosquito bites, then they do not require special treatment. It is enough to turn on the fumigator in the children's room (now there are special ones for children), and the problem will be solved by itself. In case of a severe allergic reaction, accompanied by severe swelling, redness, severe itching, it is necessary to give the child an antiallergic drug (for example, suprastin). You can treat bites with drugs such as Psilobalm or Fenistil-gel, which relieve swelling and irritation.
The next fairly common situation in which a rash occurs is an allergic reaction. Typically this is a food allergy. There are children who have allergies from early childhood. Parents of such children know exactly what food can be given to their child and what not. And they know very well how to care for the skin in this situation. Now I would like to dwell in more detail on the problem of the sudden development of allergies in a previously healthy child. This situation can develop when eating previously unfamiliar foods, exotic fruits, vegetables, and seafood. Or if familiar dishes are prepared in a special way, using a large number of spices and aromatic additives. Or if your child, having lost control, ate a pack of chips, snacked on tangerines, chocolates and washed it all down with a carbonated drink.
An allergic reaction appears quite quickly. Red spots of irregular shape, prone to merging and accompanied by severe itching, appear on the skin of the entire body or individual areas (cheeks, buttocks, behind the ears). The child's general condition may change: he may be lethargic or, conversely, too excited. Sometimes there is vomiting or loose stools. But more often the child feels well, but is very itchy. How can you help your child in this situation? First of all, it is necessary to exclude from his diet foods that cause an allergic reaction, even if they are very tasty and he loves them very much. Then you need to give the child sorbents - drugs that will remove the allergen from the child’s body. These include activated carbon, smecta, zosterin-ultra, filtrum. It is mandatory to take antiallergic drugs (the same suprastin or other drugs from this group). Fenistil-gel and moisturizer are applied to the skin. It would be a good idea to see a pediatrician or dermatologist.
An allergic reaction can also occur when the skin comes into contact with some substances, such as washing powder, fabric softener, etc. In this case, the rash appears only in those areas that were in direct contact with the allergen. The tactics of parental behavior in this case are similar to those for food allergies. Additionally, the substance that caused the reaction should be removed from the skin - rinse off under running water.
Now it is necessary to dwell on a large group of infectious diseases accompanied by a rash.
Varicella (chickenpox).
The appearance of a rash is usually preceded by a slight malaise, and symptoms of a mild acute respiratory infection may be observed. Then a rash appears. At first there is not much of it - a few red spots. Every day more and more new spots appear, and the old ones turn first into a papule - a “bump” that protrudes slightly above the skin, then into a blister with transparent contents, and finally, the blister dries out and a crust forms, which after a while disappears. From the moment the first spot appears until the last crust falls off, about 10-15 days pass, during which the sick child is contagious. The chickenpox rash is spread throughout the body, including the scalp and mucous membranes (mouth, eyes, genitals). The appearance of a rash with chickenpox is accompanied by itching, sometimes quite severe. Therefore, you can use suprastin, fenistil gel or psilobalm that you already know.
Rubella.
With rubella, the rash appears almost simultaneously throughout the body, but is more pronounced on the face, chest and back. It looks like small pale pink spots, almost the same size. The rash is profuse. Disappears without a trace within 4 days. A characteristic sign of rubella is enlargement of the occipital lymph nodes. All this is accompanied by mild symptoms of acute respiratory infections. There is usually no special treatment for rubella. But all children aged 1 year are recommended to be vaccinated against rubella.
Scarlet fever.
The disease begins acutely with high fever, sore throat when swallowing, and sore throat. At the beginning of the disease, the tongue is thickly covered with a white coating, then becomes bright red and shiny. The rash appears a few hours after the onset of the disease on the torso, limbs, with thickening in the natural folds of the skin (armpits, groin area). The rash is pink, pinpointed. In this case, the area around the mouth remains pale. After the rash disappears at the end of the first - at the beginning of the second week of the disease, peeling appears on the palms and soles. The disease is quite serious, because... leaves behind complications in the form of damage to the heart and kidneys. Requires mandatory prescription of antibiotics and a period of clinical observation with mandatory monitoring of blood and urine tests.
Measles.
A measles rash appears on the 4-5th day of illness against the background of severe signs of acute respiratory infections (cough, runny nose, conjunctivitis, high fever) and rashes within 3-4 days. The first elements of the rash appear on the face and upper chest. On the second day they spread to the torso, and on the third day to the upper and lower extremities. It looks like small red spots that tend to merge. Nowadays it is rare due to immunization of children at the age of 1 year.
“Sudden exanthema”, “roseola” or “sixth disease”.
It manifests itself as a high temperature, up to 39C, for 4-5 days with relatively good health. Then the temperature returns to normal, and a soft pink rash appears all over the body. Once the rash appears, the child is not contagious. Very often this rash is mistaken for an allergic reaction to antipyretic drugs.
Meningococcal infection and meningococcal sepsis are a deadly disease.
It is manifested by a very high temperature, a severe general condition of the child, which worsens every hour, vomiting, and impaired consciousness. Against the background of a high temperature, the child develops a rash (there may be only a few elements), which does not disappear with pressure. If you see such a picture in a child, you should immediately call an ambulance.
In addition to these diseases, a rash on the body occurs with a herpetic infection - in the form of blisters, with infectious mononucleosis - with the prescription of antibiotics from the amoxicillin group, with pseudotuberculosis and yersiniosis - in the form of “socks” and “gloves” and many others.
As a rule, the rash associated with various infections is quite typical and additional laboratory examination is not required to make a diagnosis.
In almost all infectious diseases, in addition to the rash, there is a high (or not so high) temperature, general malaise, loss of appetite, and chills. Your head, throat, or stomach may hurt. Have a runny nose, or cough, or diarrhea.
In addition to infections, the rash occurs with diseases of the blood or blood vessels. In these cases, the appearance of a rash is provoked by injuries, sometimes very minor. The rash looks like large or small hemorrhages (bruises) and requires additional examination to make an accurate diagnosis.
In conclusion, I would like to once again draw the attention of parents to the fact that they should not try to understand on their own what kind of rash the child has developed. Call a doctor. And most importantly, do not paint on this rash with fucorcin, iodine or brilliant green. Once you have satisfied your drawing needs, no doctor will ever guess what was really there.
Symptoms
This pathological process begins with the appearance of small pink nodules and blisters , which at first are sporadic. As the disease progresses, they merge and their number increases. Very often they are located:
- on the back of the forearm;
- on the hands;
- in the lower abdomen;
- on the knees and inner thighs.
Their contents may have a slightly reddish liquid as they are formed from small capillaries.
Pain syndrome may appear . Dyspeptic disorders in the form of nausea and vomiting, and diarrhea, which can last for several days, are also observed. These symptoms are accompanied by a feeling of thirst, which occurs due to dehydration.
In more severe cases, changes occur in the central nervous system, the following appears:
- severe temporal or occipital pain;
- blood pressure rises;
- Delusional states may occur.
It is very important to differentiate urticarial rash from the consequences of urticaria. With vasculitis, blisters have clear boundaries and are hard on palpation. In the case of urticaria, the skin always remains soft and elastic, despite multiple rashes.
Purulent rashes
Pustular purulent rashes are characteristic of bacterial infections. Most often, such diseases develop under the influence of Staphylococcus aureus. Sometimes the reason may lie in the influence of epidermal staphylococcus and streptococcus, as well as some other microbes, on the body.
A similar rash can appear due to microtraumas on the skin, scratches and wounds that allow microbes to penetrate inside. If the rashes are itchy and itchy at first, and the baby begins to scratch them, a bacterial infection occurs and pustules appear.
The formation of pustules in the area of the knees and elbows in childhood is possible with frequent trauma to the skin due to numerous falls. The formation of deep abscesses is called furunculosis.
Diagnostics
After examining and interviewing the patient, the doctor, based on the clinical picture, necessarily prescribes a histological examination of fragments of the affected skin taken for analysis. This is done to exclude the development of oncological pathologies, such as skin cancer (this disease begins with similar symptoms).
In parallel, the following is assigned:
- general blood test, where the main indicator is the level of red blood cells and ESR;
- general urine analysis;
- blood for bacterial, fungal and viral infections;
- Sometimes an ultrasound of the affected areas is prescribed.
It is very important to establish the correct diagnosis, since the removal of the urticarial rash will depend on this. Because it is a consequence of the disease, and to eliminate it it is necessary to cure urticarial vasculitis.
Treatment of urticaria rash
To cure this disease, therapy must be comprehensive. The patient is prescribed:
- Antihistamines to relieve swelling and hyperemia.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (if their use does not produce positive dynamics, corticosteroid hormones are prescribed).
- Plasmapheresis may be used.
In very severe cases, therapy using immunosuppressive drugs . This helps to weaken the immune system, as it negatively affects the body’s own tissues. The big disadvantage of this treatment is a decrease in immunity, as a result of which the patient can easily become infected.